EVIDENCE BASED FINAL
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
false
T/F most epidemiologist would conclude that case-control study reliably estimates the odds of disease risk when properly designed
all free from cancer
all participant in cohort study in smoking and oral cancer have the following characteristic at base line:
false
T/F patients are randomly selected from a population in most randomized controlled trials
residual confounding
bias which is caused by imperfect adjustment
false
T/F it is simple to account for confounding bias
overdiagnosis
increase of disease with increased screening but mortality rate remains the same
better control over confounding
why does mendelian randomization hold great promise for the future in providing more reliable evidence
a business man
Claude hopkins had significant impact on the hypothesis that plaque removal prevents carie. claude hopkins was:
a person with interproximal dental caries
in a case control study on interproximal dental caries and dental floss habits, a case is
identifying changeable causes of ill health
clinical practice and public health is mostly focused on
false
T/F George Davey Smith in the YouTube movie on Mendelian randomization talks about how a disease and the identification of a disease (e.g., high blood pressure) can lead to a change in behaviors (e.g., reduced alcohol drinking). George Davey Smith subsequently states that such biases can be controlled for in an observational study by careful history taking of the participating subjects
false
T/F George Davey Smith reports that genotyping study participants is expensive making Mendelian randomization studies very expensive when compared to randomly assigning study participants to treatments (i.e., randomized controlled trials).
true
True or false: George Davey Smith reports that mothers who drink during pregnancy in the studies had a higher education than those who did not.
genetic variant are unrelated to confounders
What is the reason Mendelian randomization is superior to observational studies according to George Davey Smith
confounding
George Davey Smith describes which bias when pointing to the lack of trustworthiness of epidemiological findings (which fall within the zone of bias)
false
True or False: George Davey Smith states that cohort studies provide the best way of getting the most reliable evidence that a changeable risk factor suspected of being beneficial might influence disease.
true
True or false: George Davey Smith states that there are genetic variants which relate to drinking more or less alcohol.
true
T/F George Davey Smith reports that Mendelian randomization shows that for "mothers who drink more alcohol during pregnancy, their offspring actually do worse on IQ tests and in school performance rather than do better as the observational studies suggested".
retrospective
registering trial AFTER data collection has begun
2000
When approximately did clinical trial registration become required
time
what variable does the x-axis represent
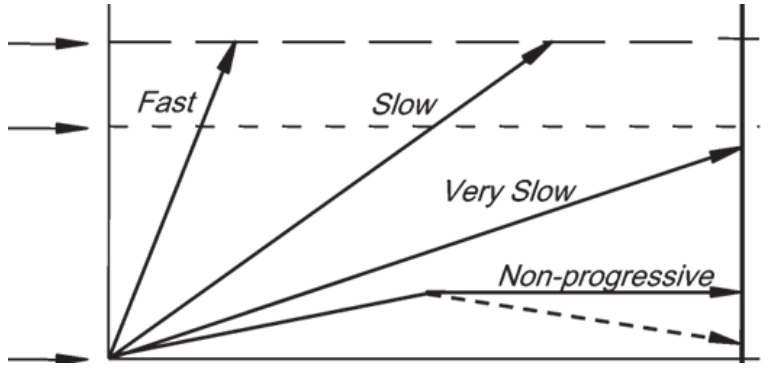
size (extent) of disease
what variable does the y axis represent
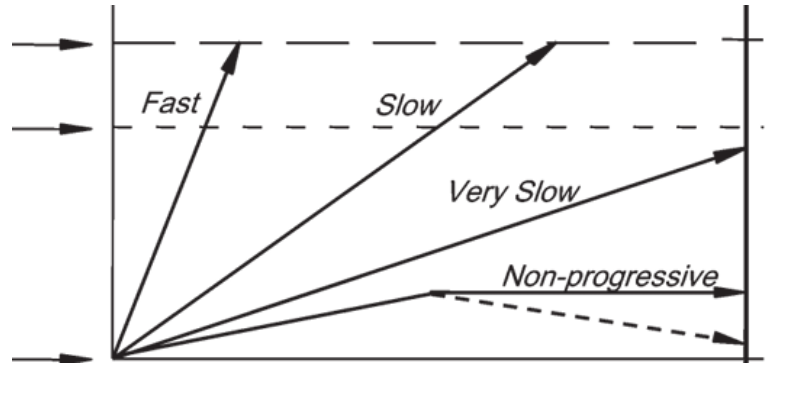
size at which disease causes death
what does the red circle indicate?
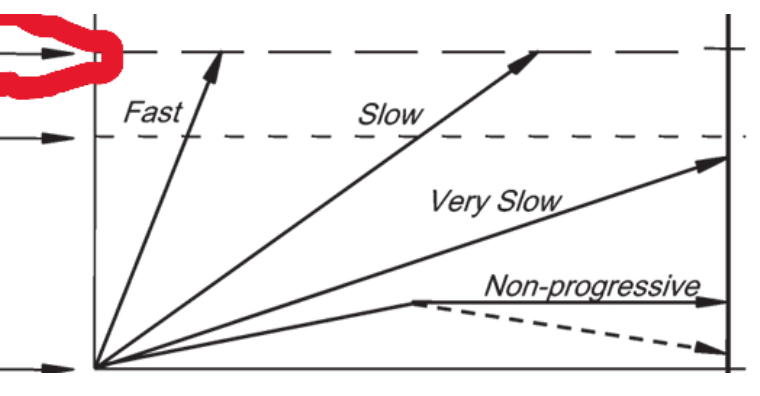
size at which disease of interest causes morbidity
what does the red circle indicate?
start of disease progression
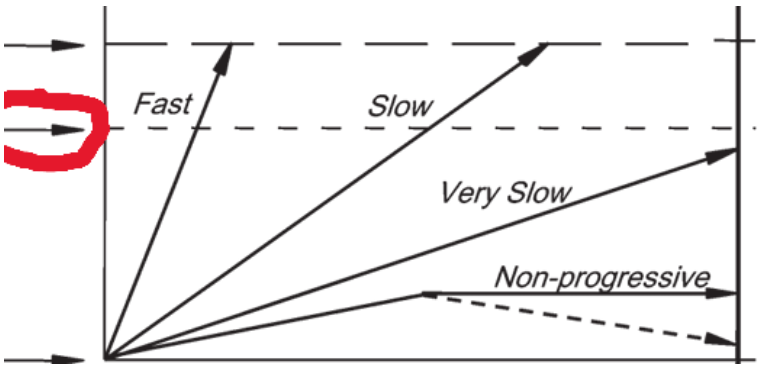
what does the red circle indicate?
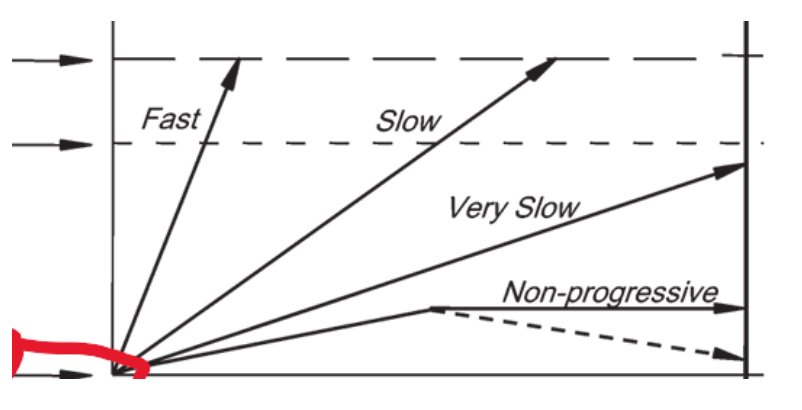
death from other causes
what does the red circle indicate?
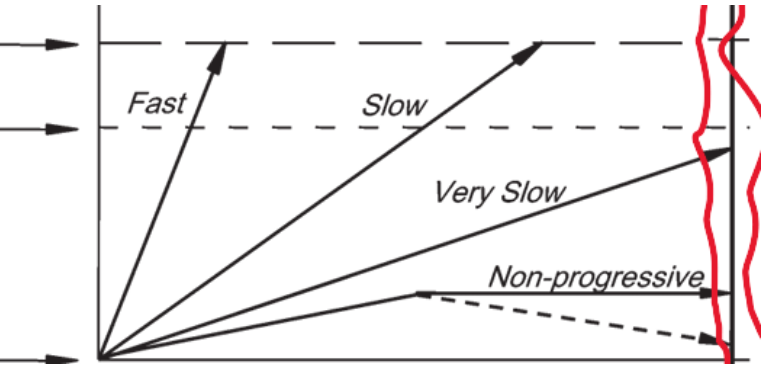
fast and slow
which arrow leads to morbidity during a person’s lifetime?
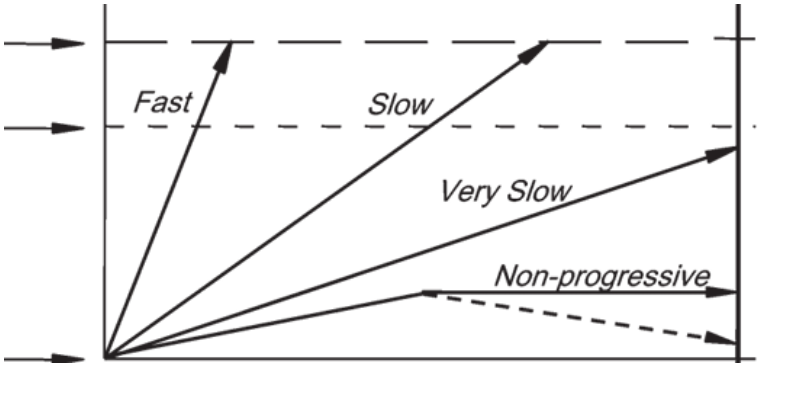
very slow and non-progressive
For which of the arrows can screening only cause harm.
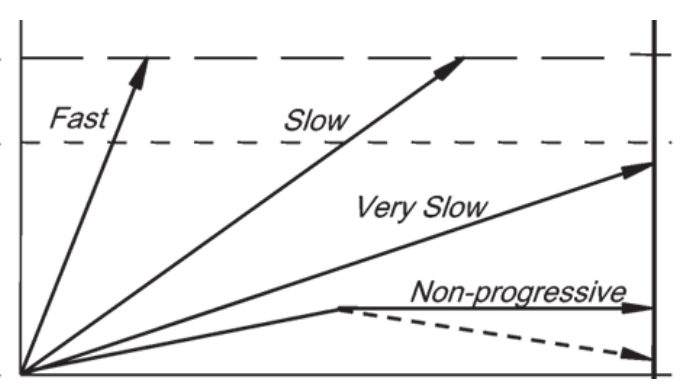
fast
Which of the arrows is the least likely to be captured with regular screening programs
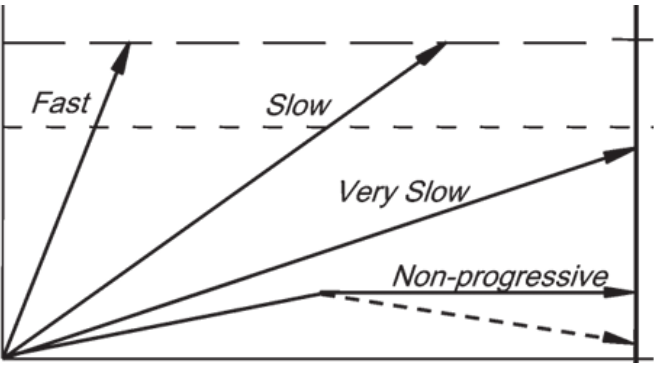
non-progreessive and very slow
which arrows lead to overdiagnosis
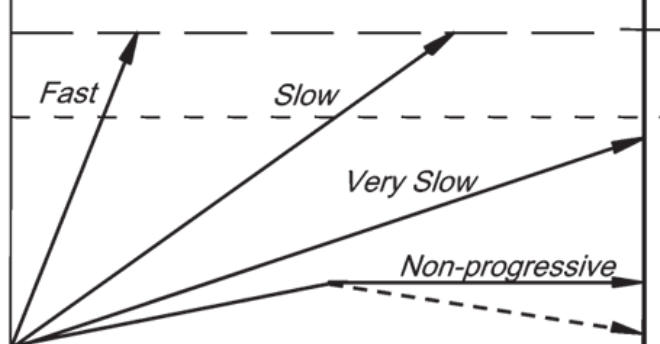
overdiagnosis
the identification of a disease that will not cause symptoms or death during a patient's lifetime, often leading to unnecessary treatment
true
T/F As a general rule, randomized controlled trials can be used to reliably test small risks or benefits, epidemiology cannot.
turkey shoots
the consistent identification of large risk increases for diseases (i.e., large relative risks for smoking and lung cancer, huge relative risk for hep B and liver cancer)
true
True or false: Success stories in epidemiology are often the result of "turkey shoots"
true
True or false: Compliance with the dentist recommendation to use dental floss is one of the many markers for healthy user bias.
unexpected harm
which result of epidemiological study is most reliable
hard measures (ex:bone biopsy)
most reliable exposures to measure in epidemiological studies
towards null (ie. 1)
The crude odds ratio between periodontitis and a marker of infection is 3.3. When the odds ratio is adjusted for BMI it equals 2.2.
The change in direction from the crude to the adjusted odds ratio is ...
true
True or False: Randomized controlled trials typically do not adjust for confounding variables (magic!), epidemiological studies typically have to adjust for confounding variables and the ability to do so is not perfect
prescriber bias
the influence of a prescriber's personal beliefs or preferences on their prescribing practices, potentially leading to inappropriate treatment choices.
false
True or false: Case-control studies are associated with a smaller zone of bias than cohort studies
decreases odds of outcome
a odds ratio below 1 indicates that the exposure:
statistically insignificant
a confidence interval that includes 1 is:
zone of bias
The range in which results are not clearly conclusive and are more likely to be affected by bias, confounding, or random error.
true
T/F a statistically insignificant finding fall within the zone of bias
false
T/F An odds ratio moving from 0.61 to 0.66 is a move away from the null hypothesis
true
T/F when a model has more confounders, trustworthiness increases as the odds ratio moves away from the null hypothesis
confounding
Which bias has been referred to as the Achilles heal of epidemiology?
selection bia
distortion in measure of association to to sample selection that doesn’t reflect target population
14%
percent of clincical trials that are fabricated
surrogate dont always relate to real world health benfits
importance of true endpoints
cohort study
Follows a group over time to assess exposure-outcome relationships
case-control study
Starts with outcome (cases) and compares past exposures to controls
.5 - 2.0
zone of bias for cohort studies ?
Statistical significance
confidence interval does not include 1.0
Harm (increased risk)
relative risk > 1
Benefit (decreased risk)
relative risk < 1
200% risk increase
what does a relative risk of 3 mean
endpoint switching
Changing primary outcomes after a trial has started or ended — can mislead results and inflate findings
confounding
major source of bias in observational studies
associated with exposure and independently affects outcome
what two criteria need to be satisfied for a variable to be a confounder
reverse causality
The situation in which the outcome influences the exposure, rather than the other way around, leading to misleading conclusions in studies.
evenly distributes confounders
Why is randomization is magic?
Null hypothesis
relative risk and odds ratio = 1
confounding inflated original result
if an odds ratio move towards null (closer to 1) after adjusting for confounding variable what does that suggest?
stronger real association
If a value moves away null (farther from 1) after controlling for confounders what that suggest?
placebo
positive effects from inert treatment due to expectation of benefit
nocebo
negative effect from inert treatment due to expectation of harm
overdiagnosis
detecting disease that would not cause symptoms or harm in a person's lifetime
reduce frequency of screening, limit screening to high risk, raise diagnostic threshold, RCTs
What actions did the National Cancer Institute suggest to minimize overdiagnosis?
earlier detection of condition that will cause death and early treatment more beneficial
Two criteria needed for screening to provide tangible patient benefits.
lead time bias
refers to the perceived increase in survival time due to earlier detection of a disease, despite no actual increase in lifespan.
length time bias
occurs when slower-growing diseases are more likely to be detected by screening, giving an illusion of improved survival rates.
incidentalomas
Accidental findings that may not be clinically significant but can lead to unnecessary treatment
backed by high-quality randomized evidence
what is a requirement of preventative interventions for healthy individuals
linear-no-threshold
Radiation doses greater than zero will increase risk of excess cancer or herritable disease in proportionate manner in low dose range
zombie trial
Clinical trials that continue to be cited or used in practice despite being outdated, flawed, or refuted
.33 - 3.0
zone of bias for case control study