ko's review
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
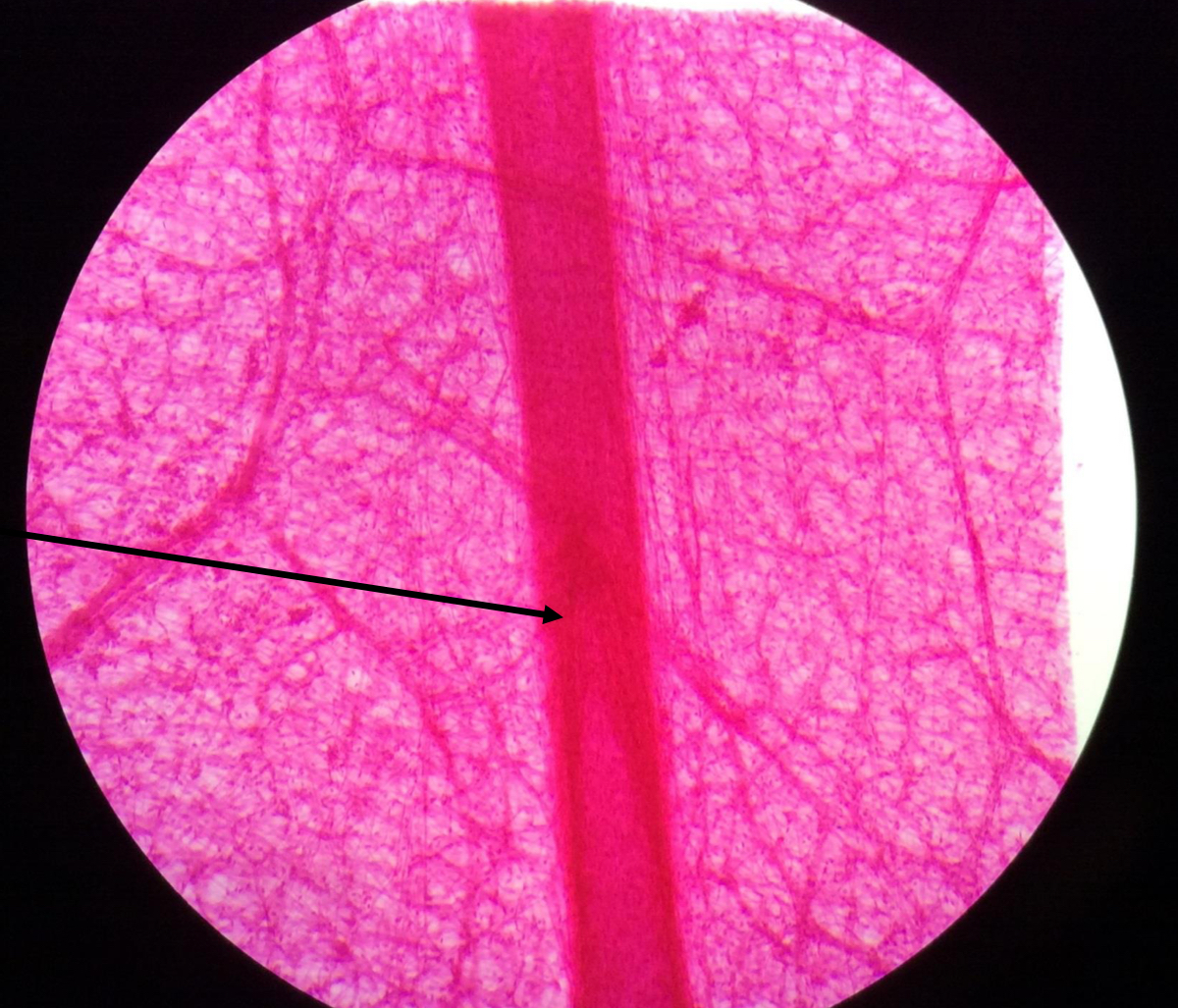
what is this?
lymph vessel
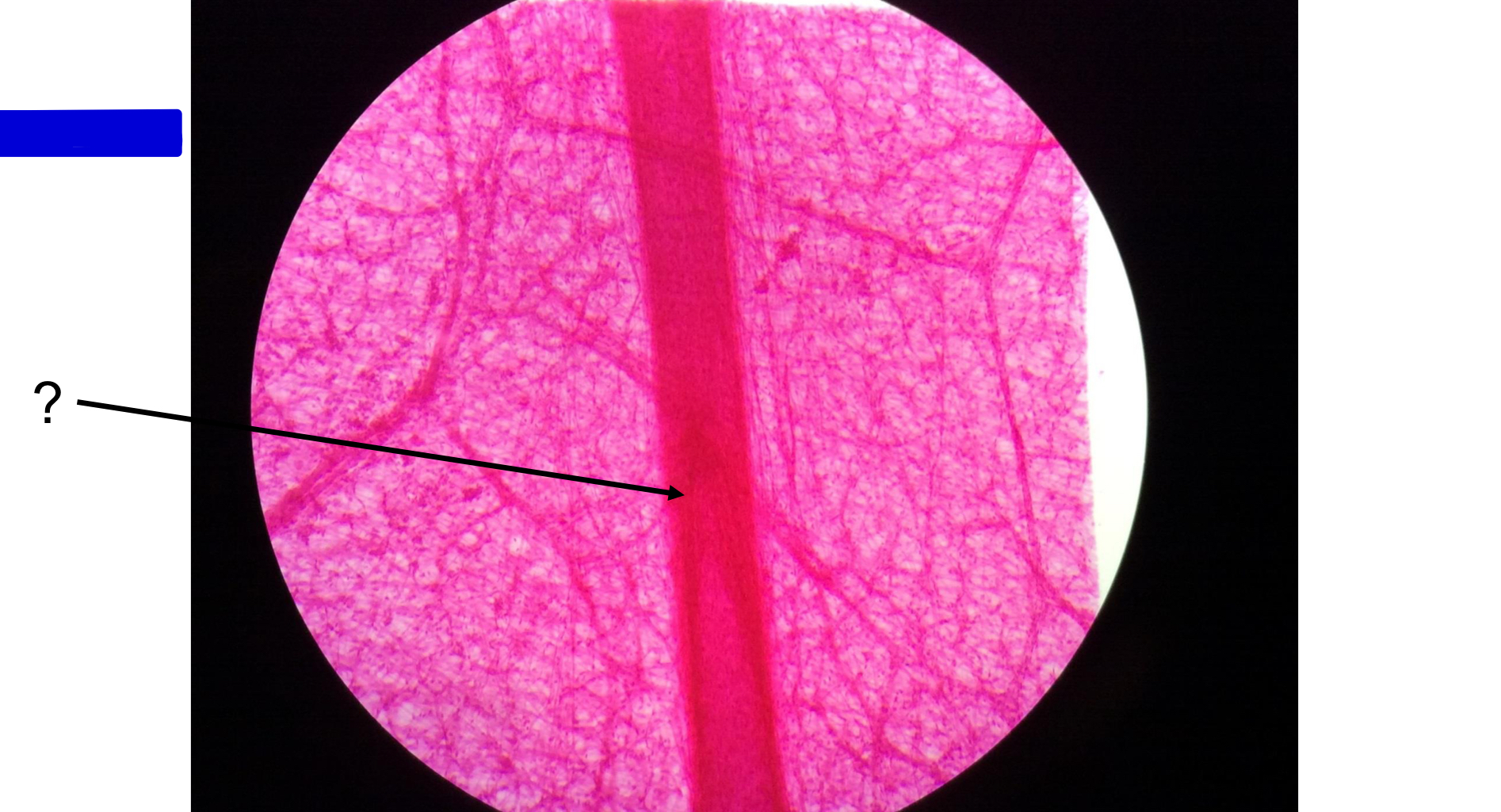
?
valve (lymph goes from the bottom up!)
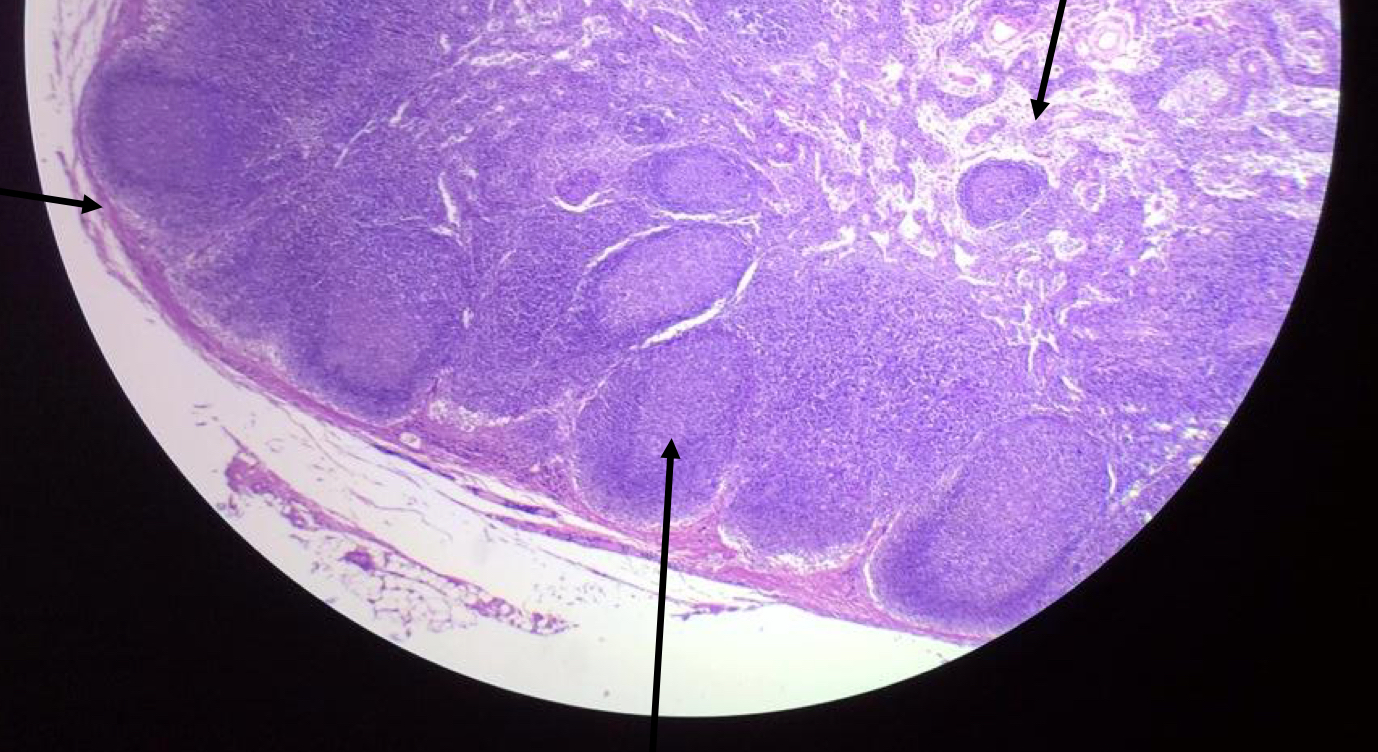
what is this?
lymph node
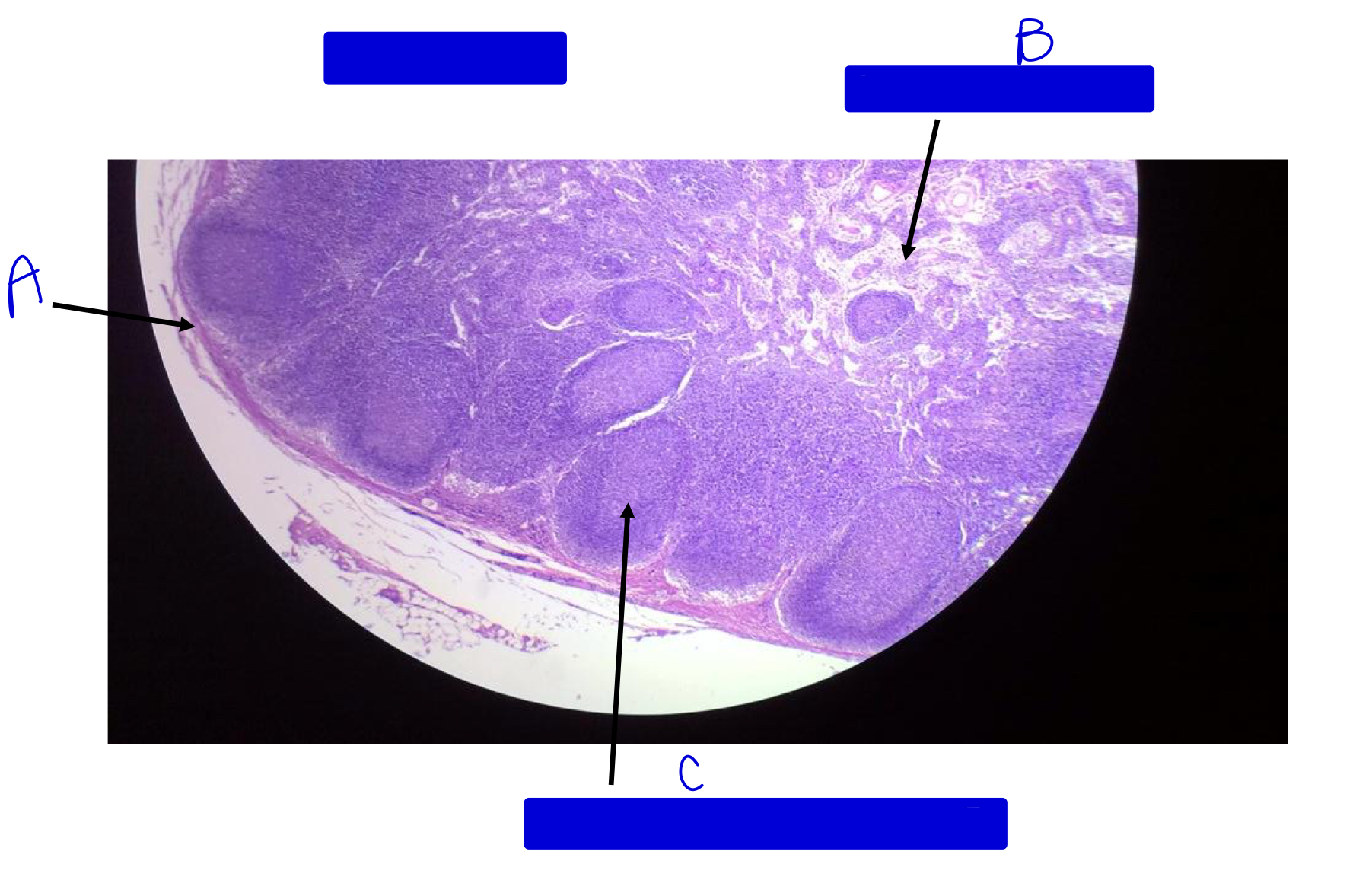
A
outer covering (capsule)
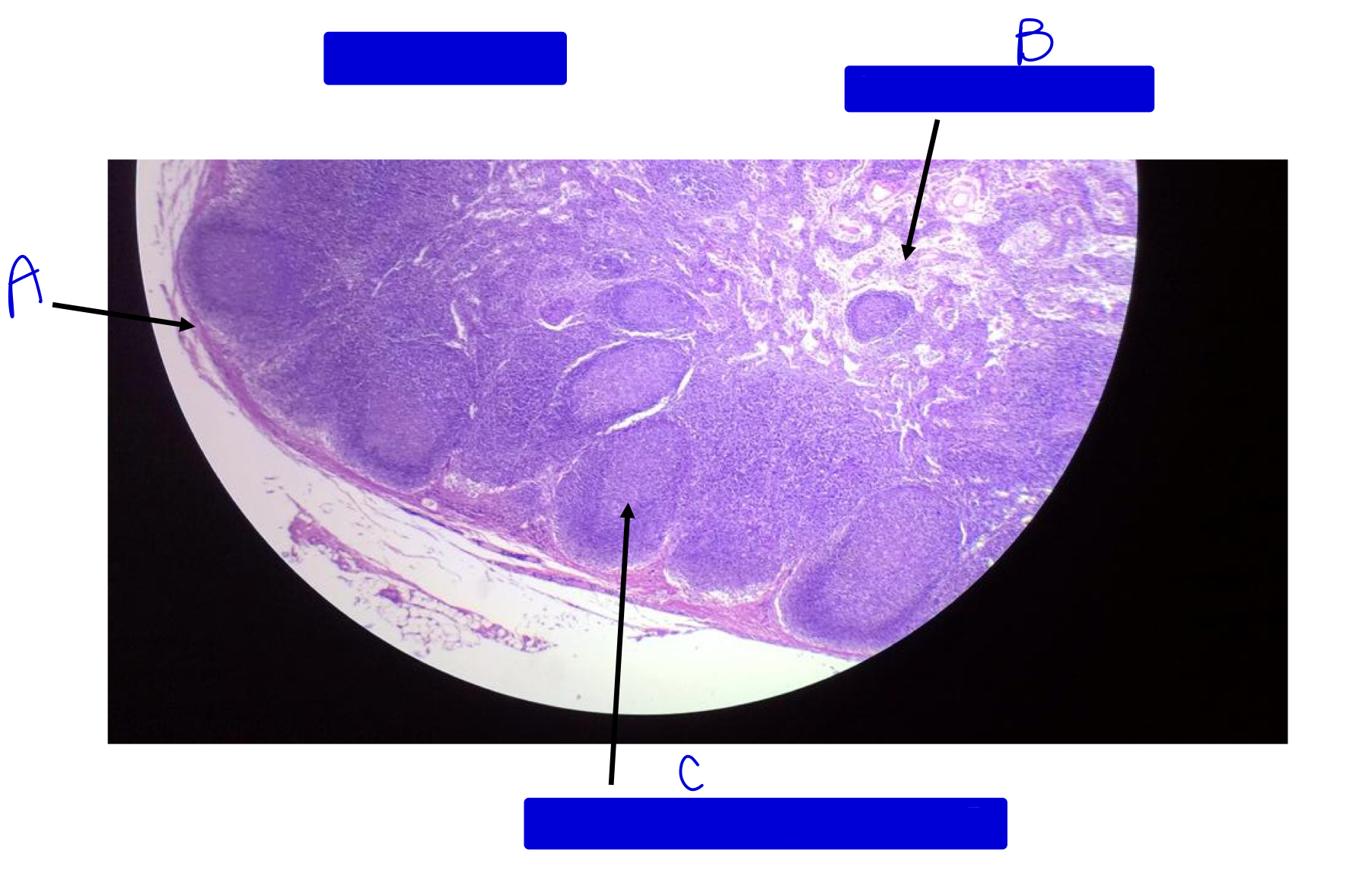
B
medullary sinus (no nodules in the middle)
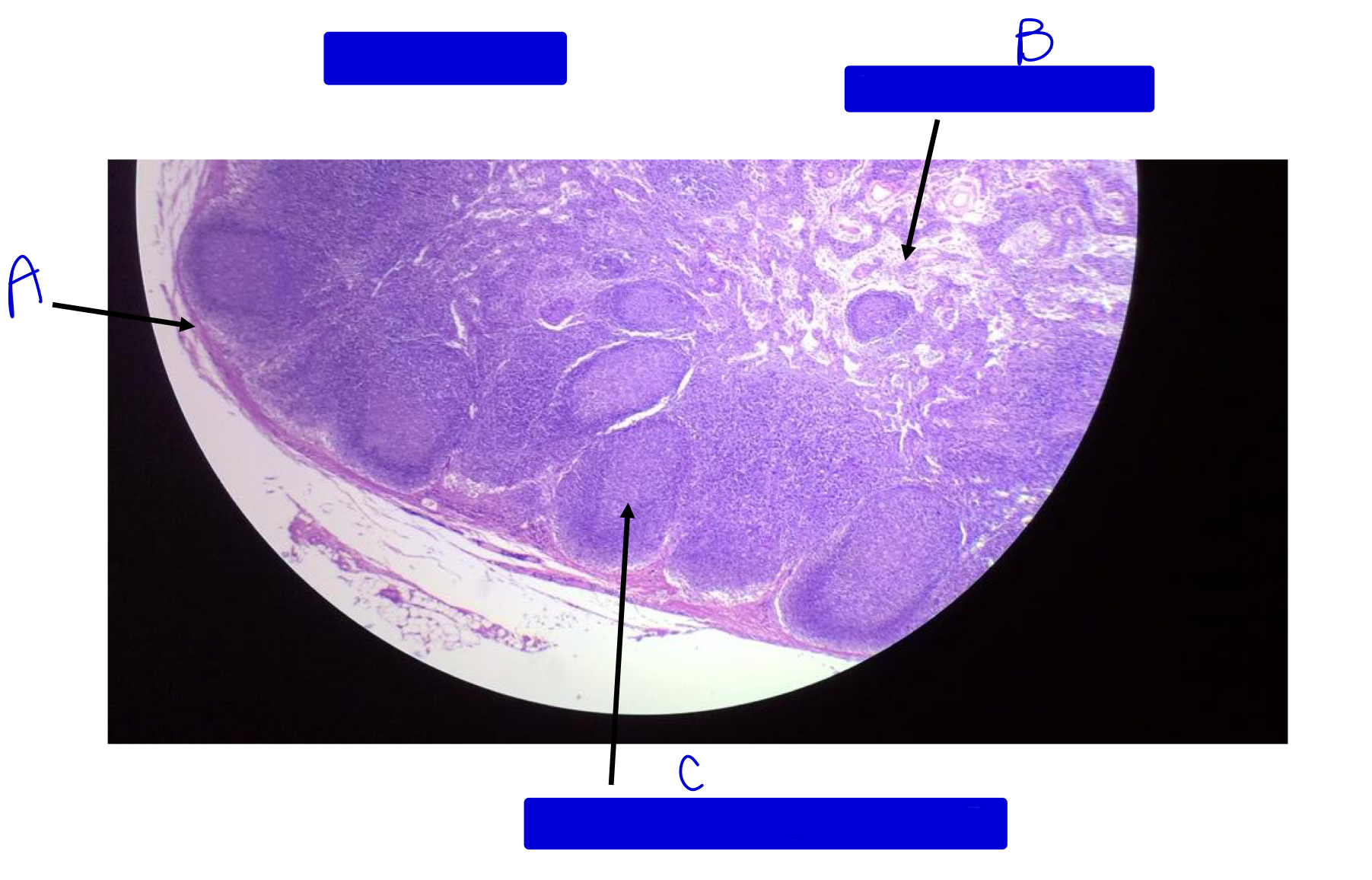
C
germinal center of nodule (notice nodules are touching)
what tissue is this?
spleen
A
white pulp (macrophages in nodules)
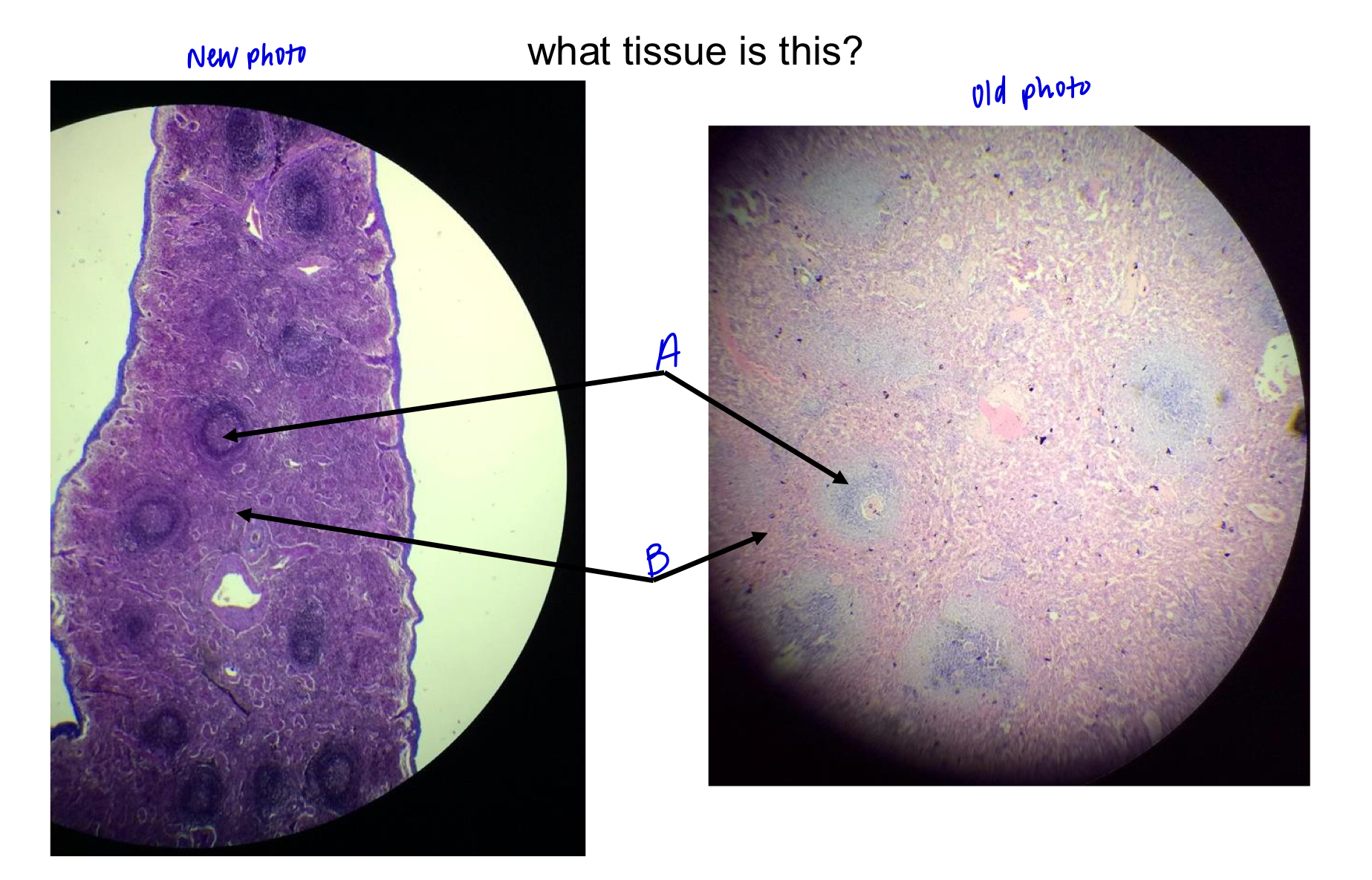
B
red pulp
A
cortex of nodule
B
medulla of nodule
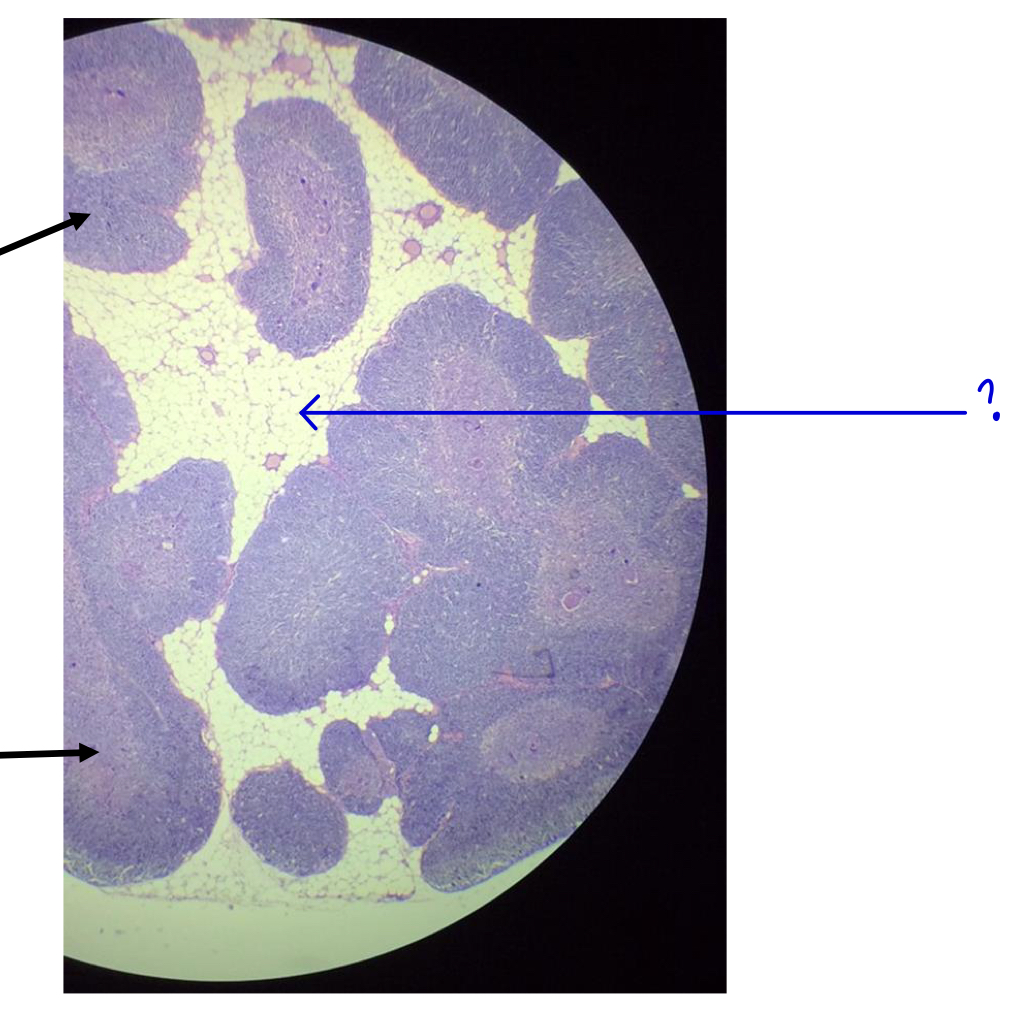
?
adipose tissue (fat cells)
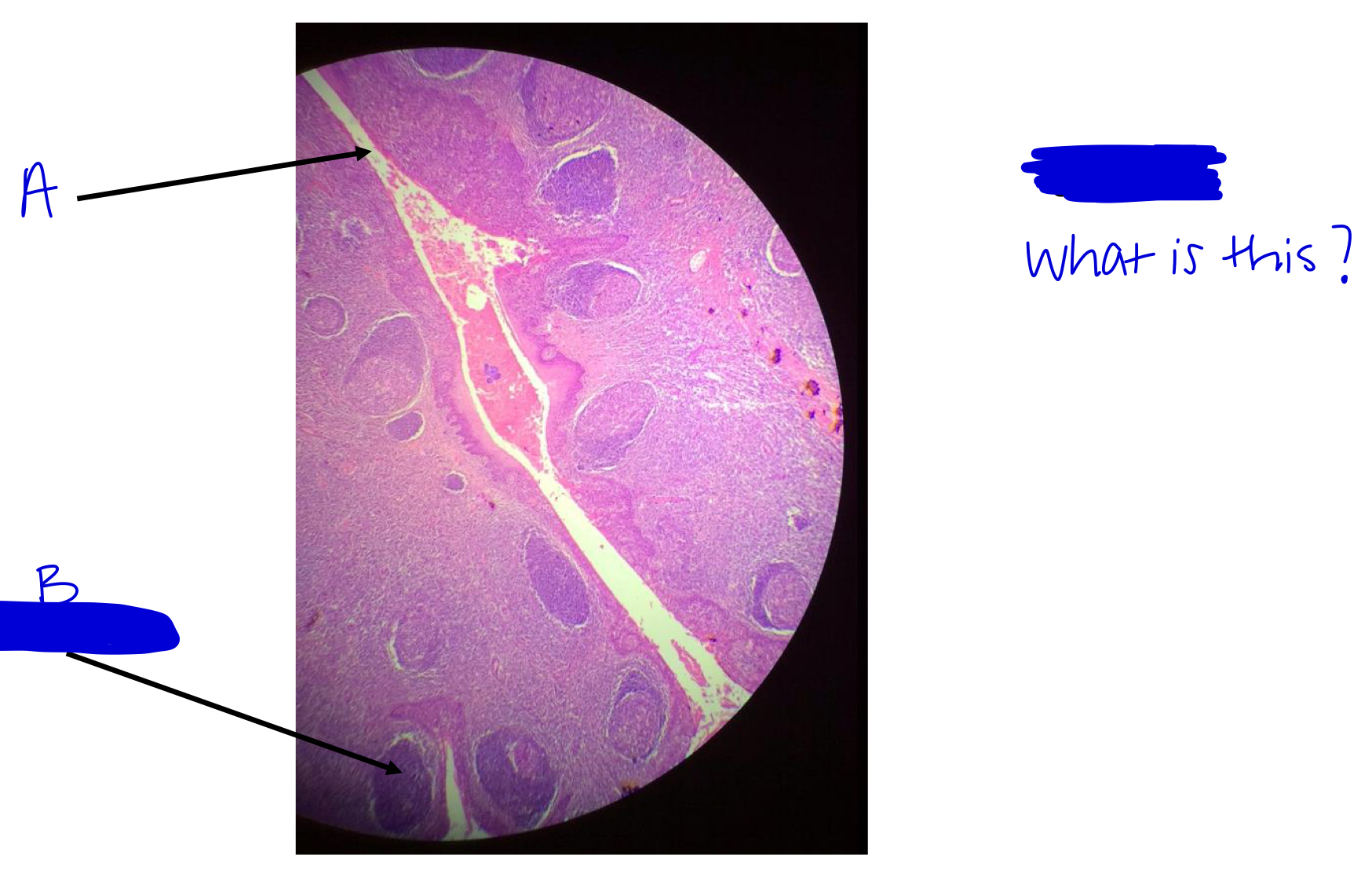
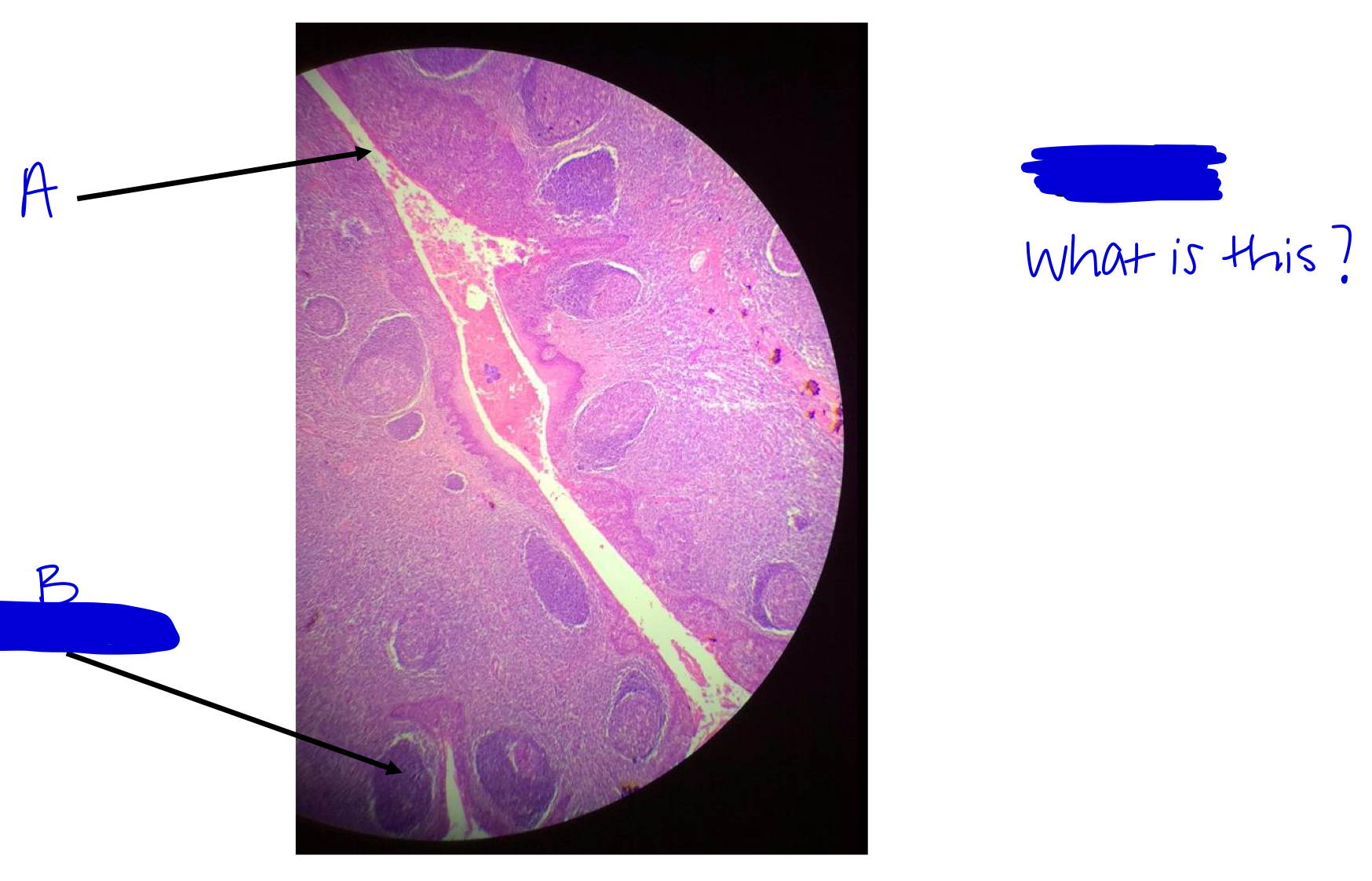
A
tonsilar crypt
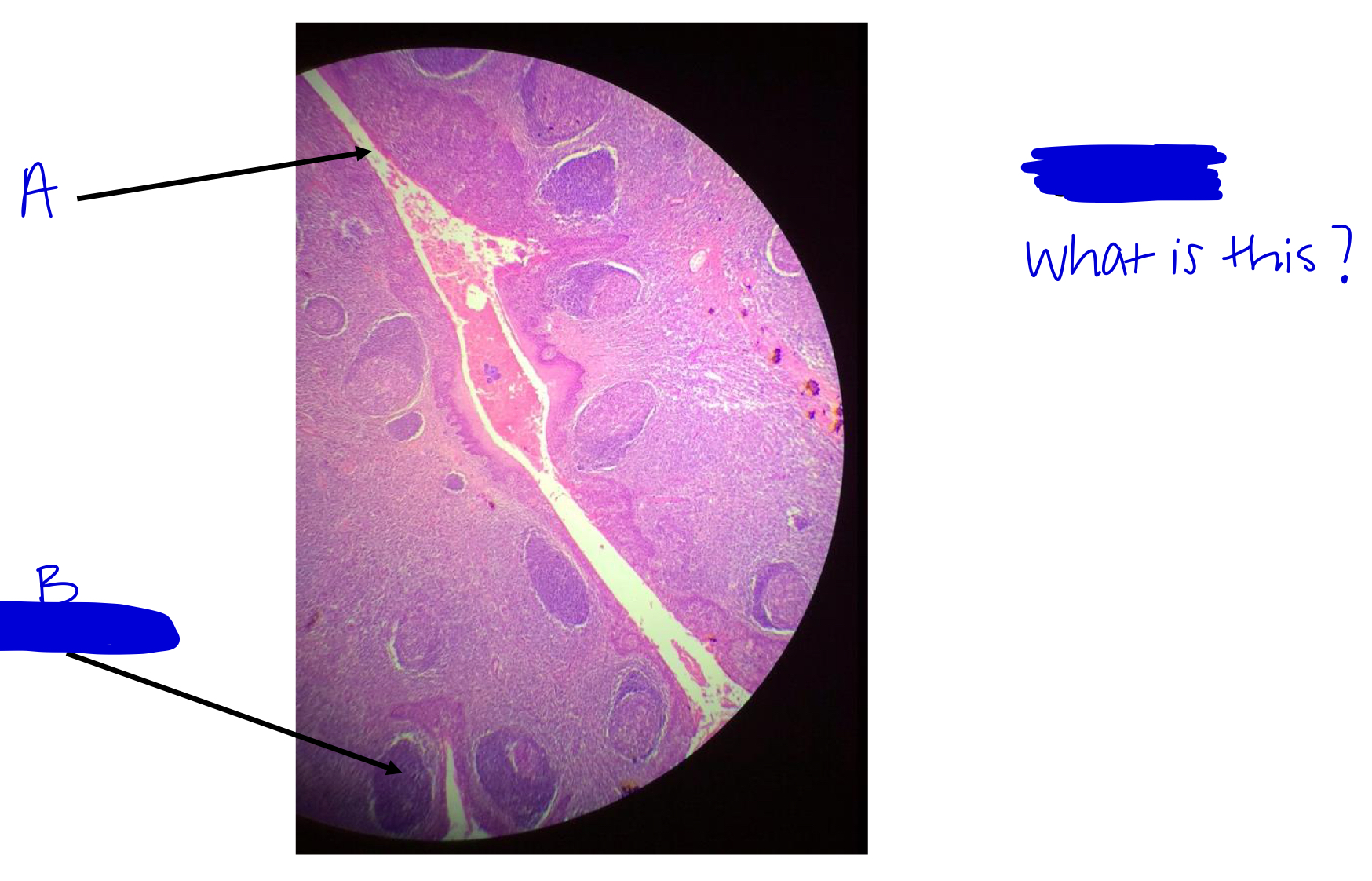
B
lymphatic nodule
what is this?
tonsil (remember a long, straight white road)
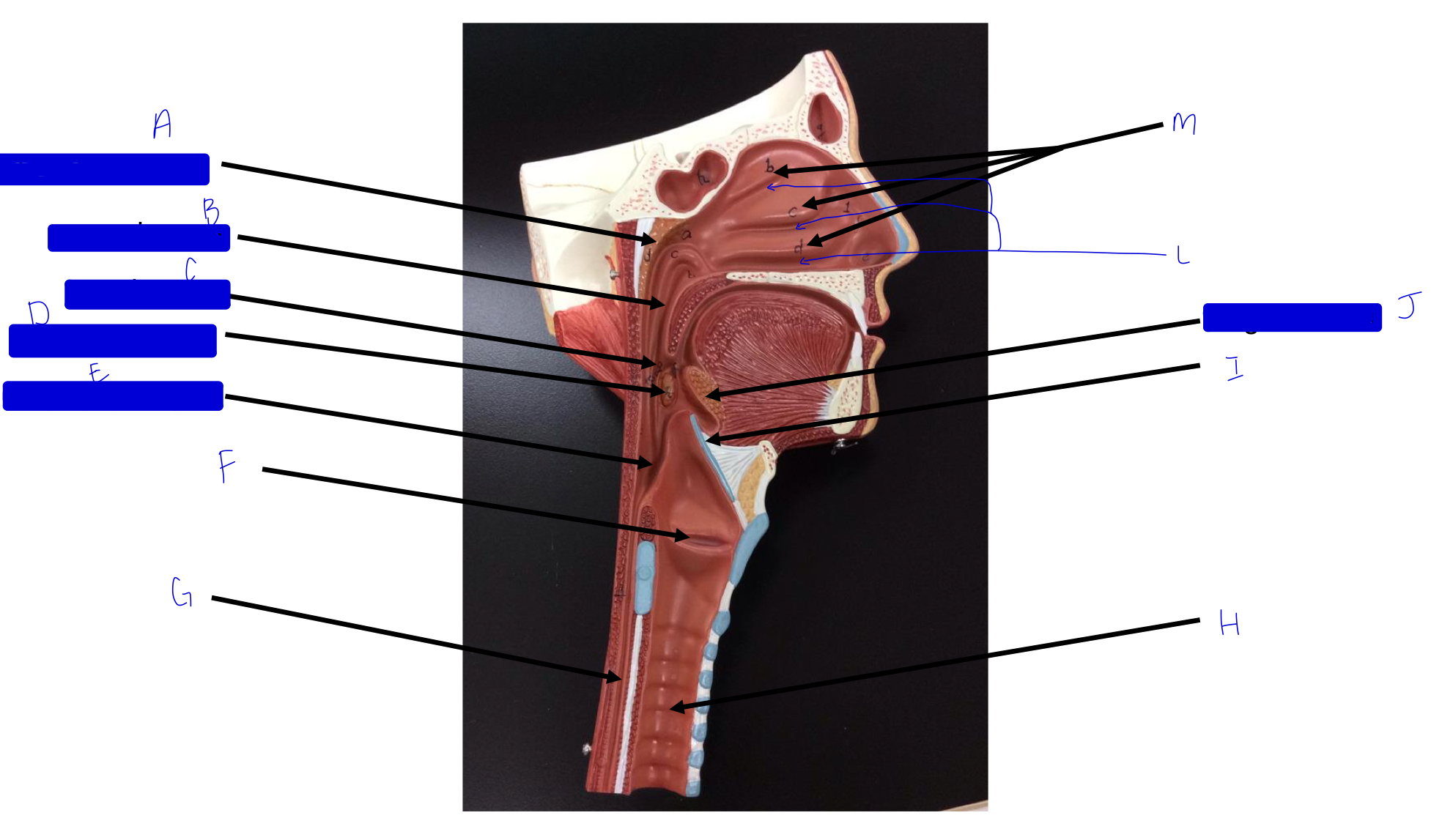
A
pharyngeal tonsil
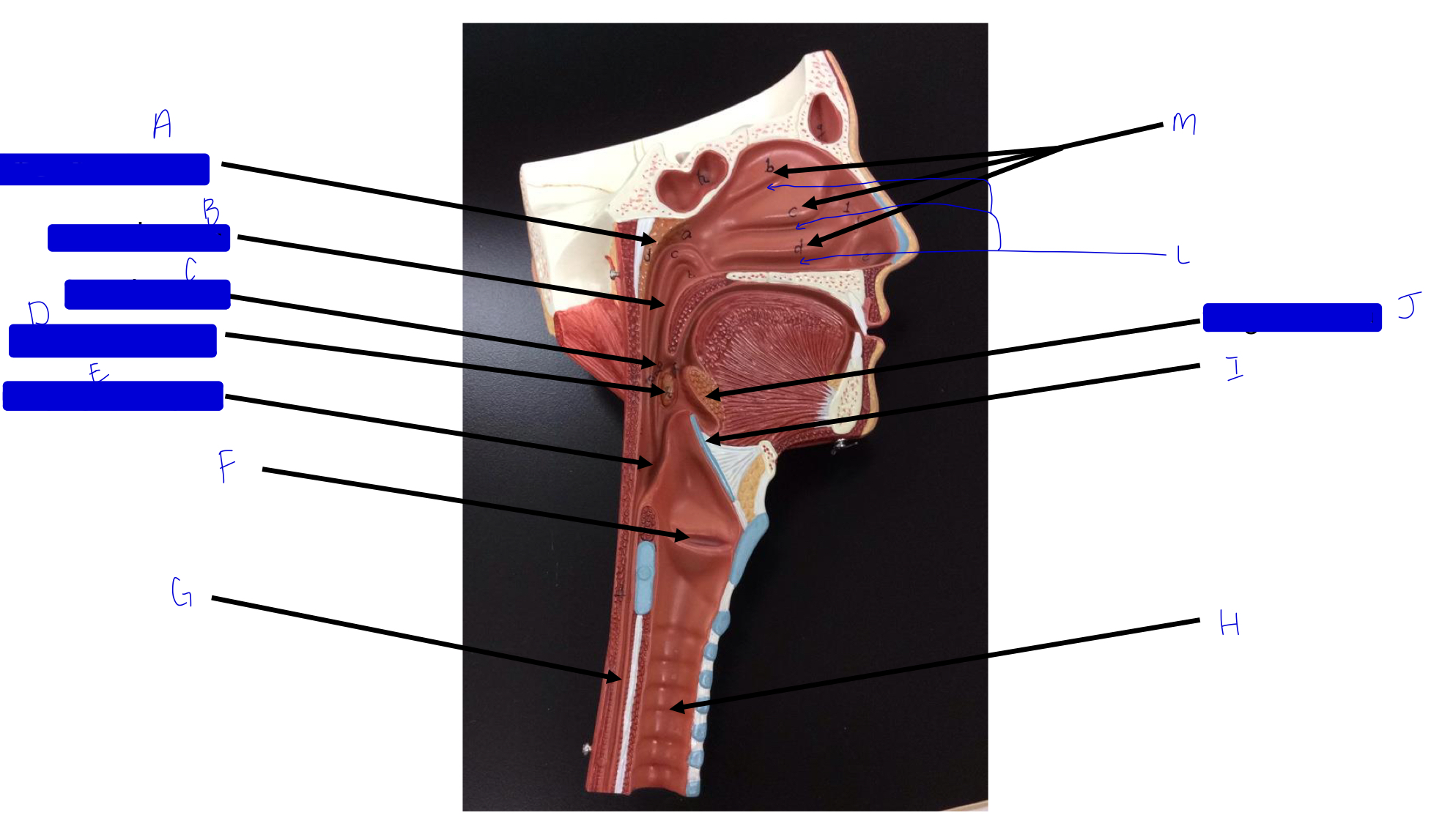
B
nasopharynx
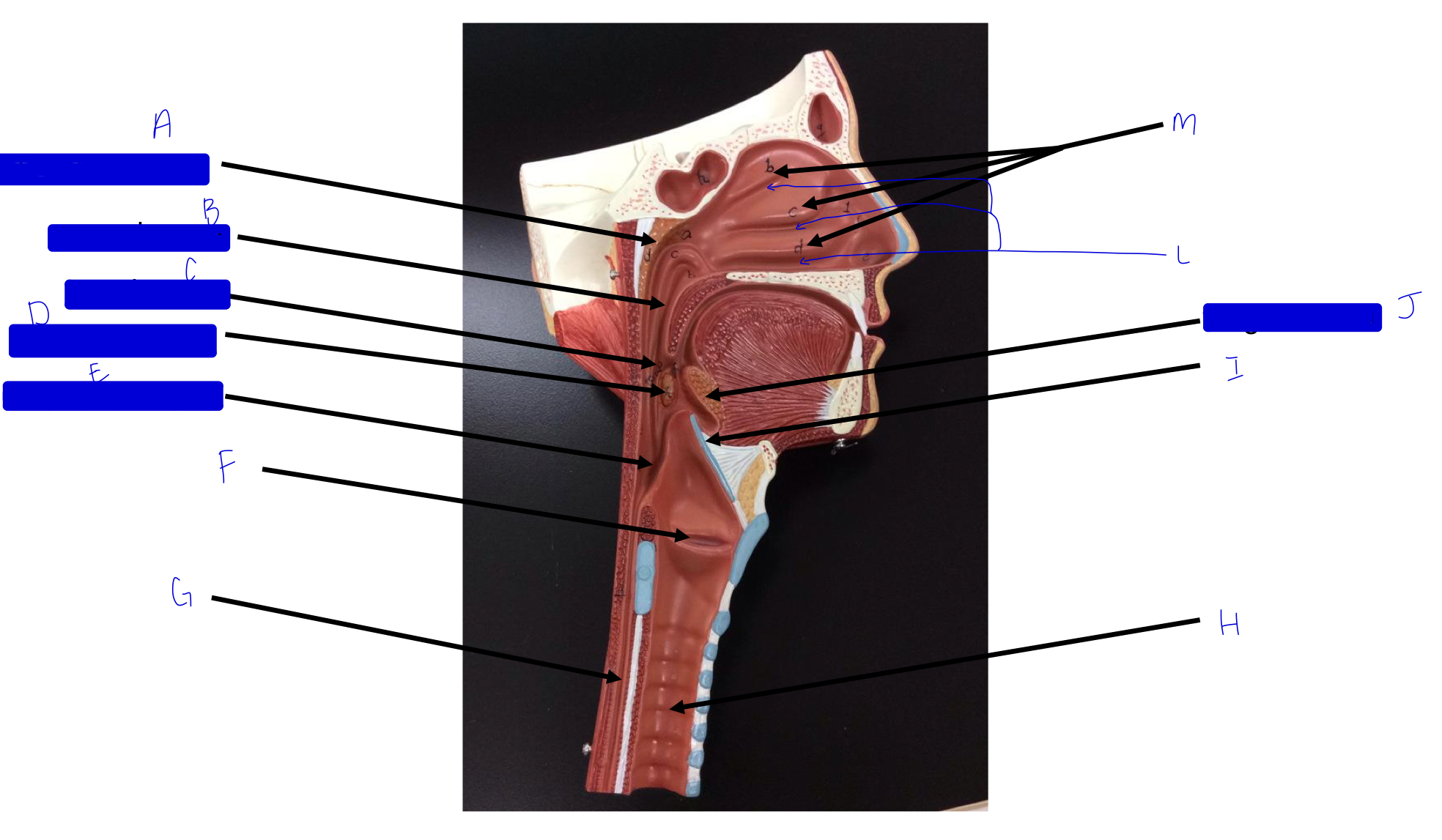
C
oropharynx
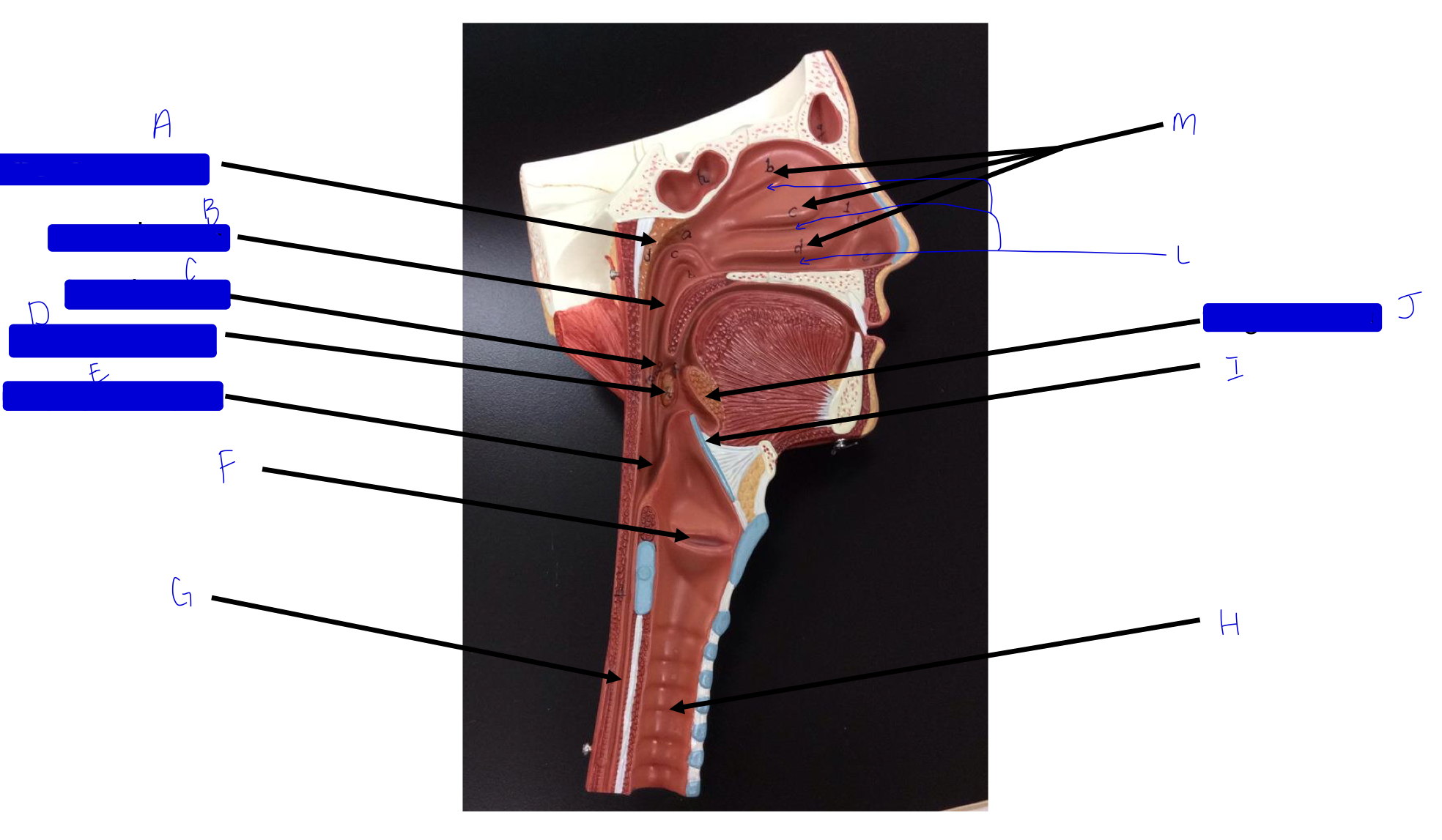
D
palatine tonsil
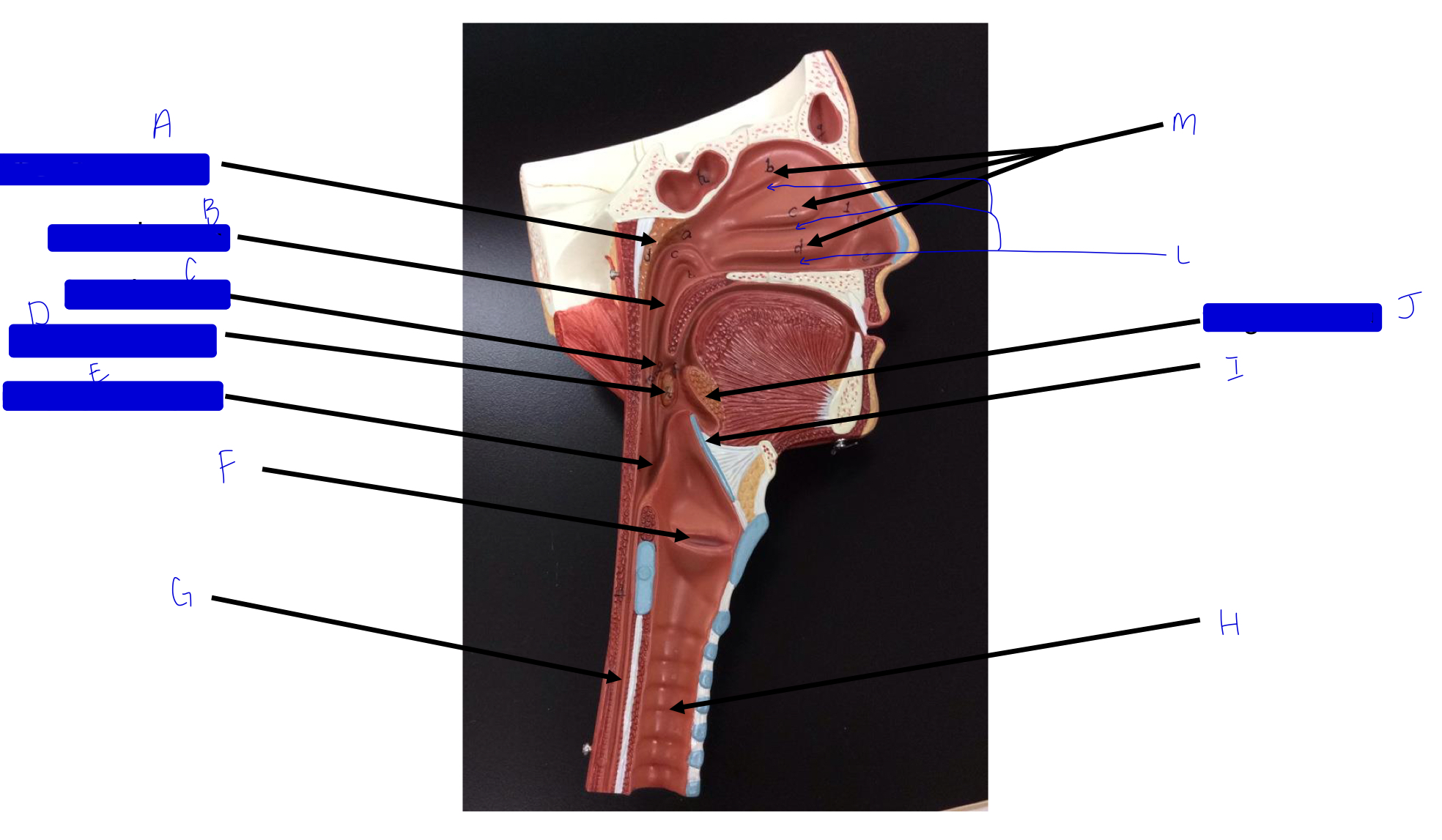
E
laryngopharynx
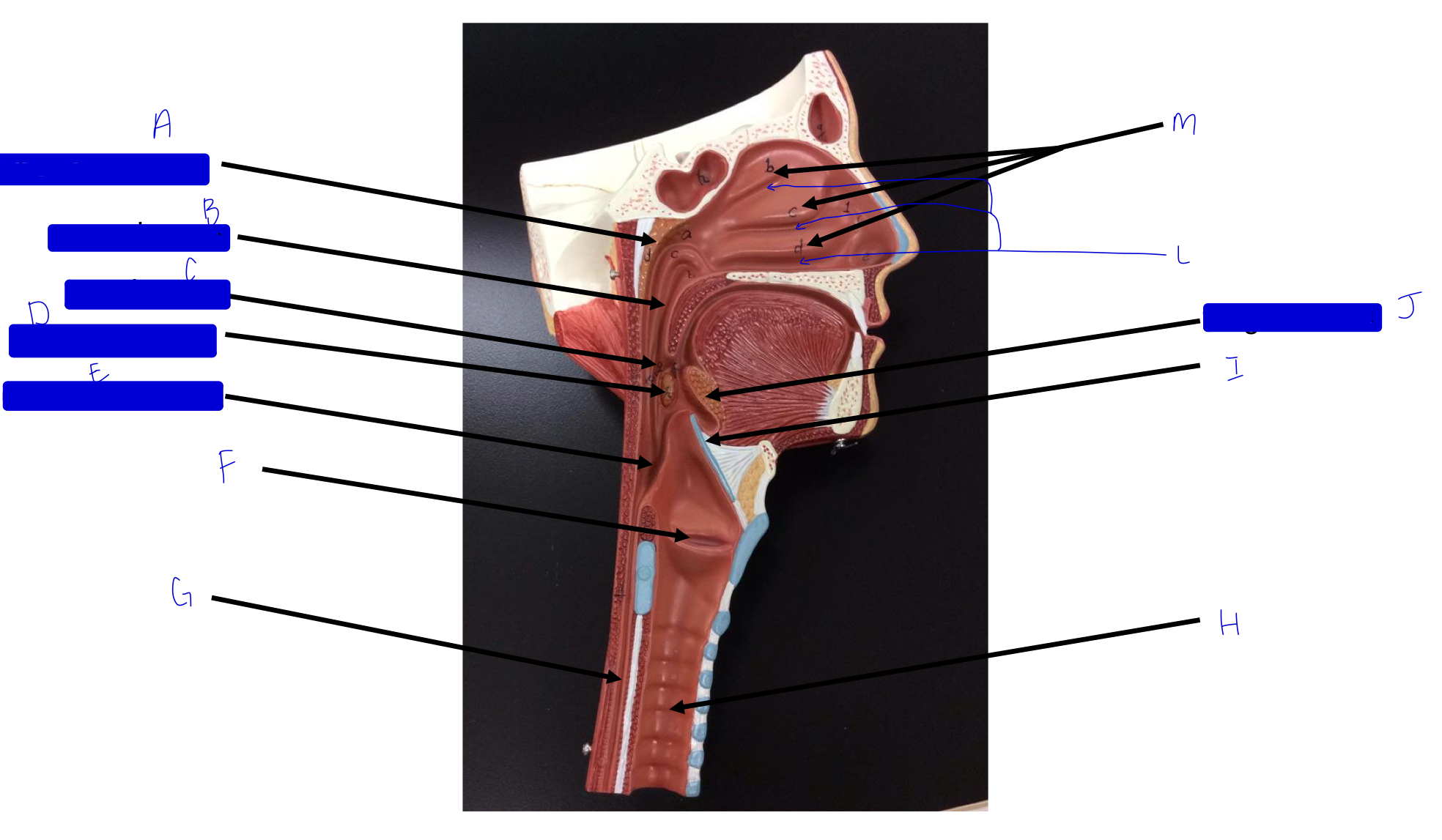
F
larynx (voice box/vocal cords)
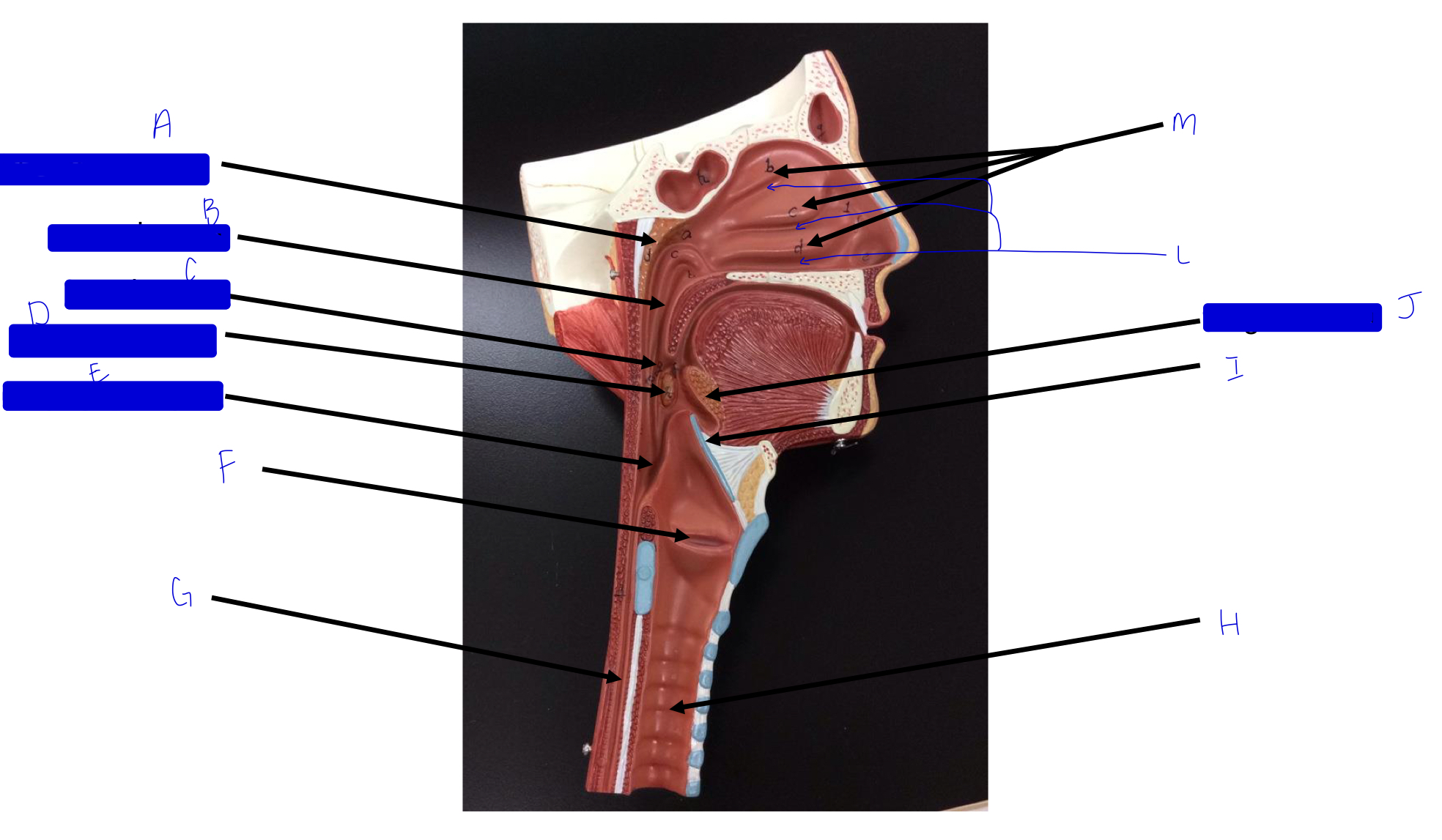
G
esophagus
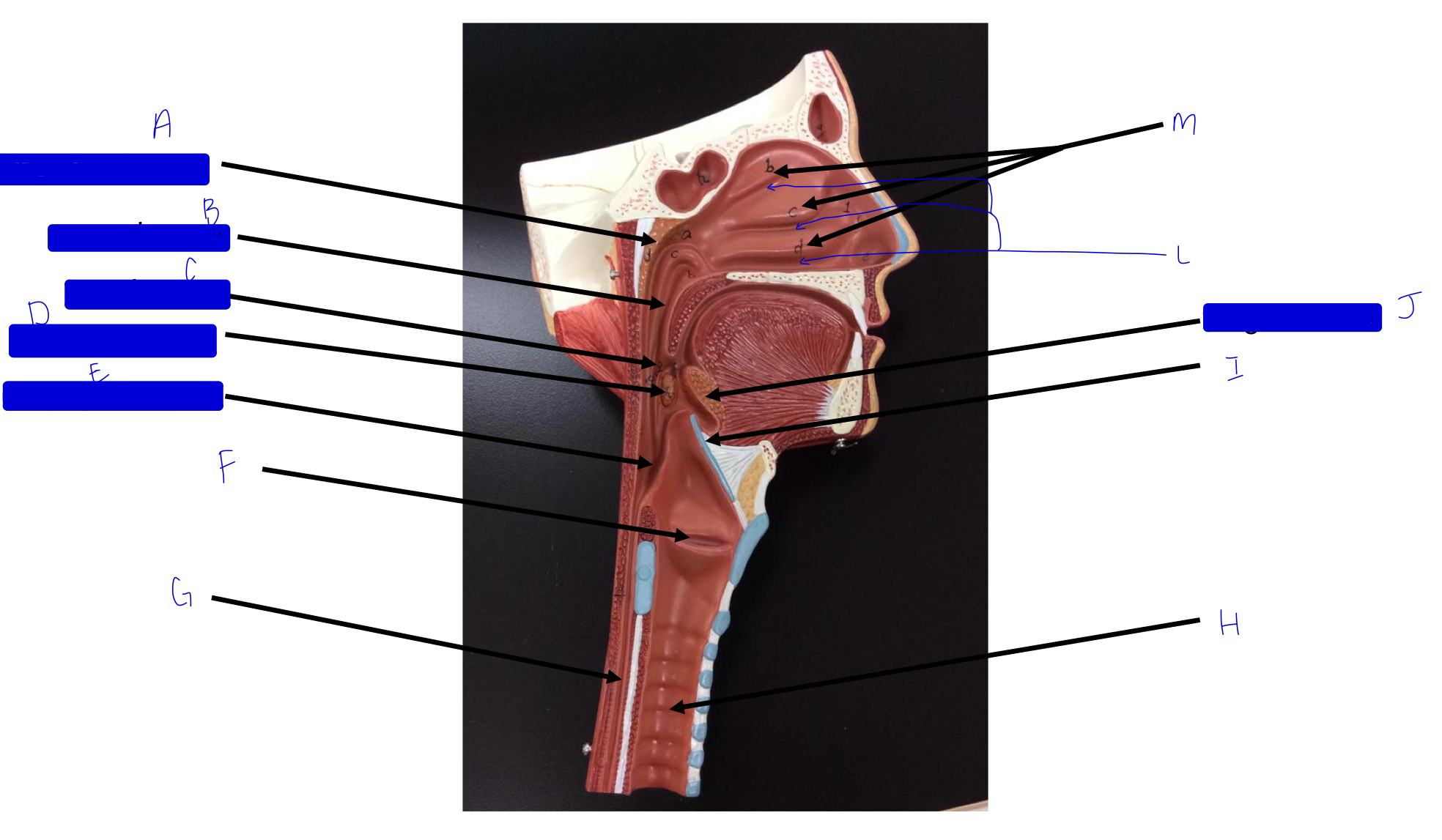
H
trachea
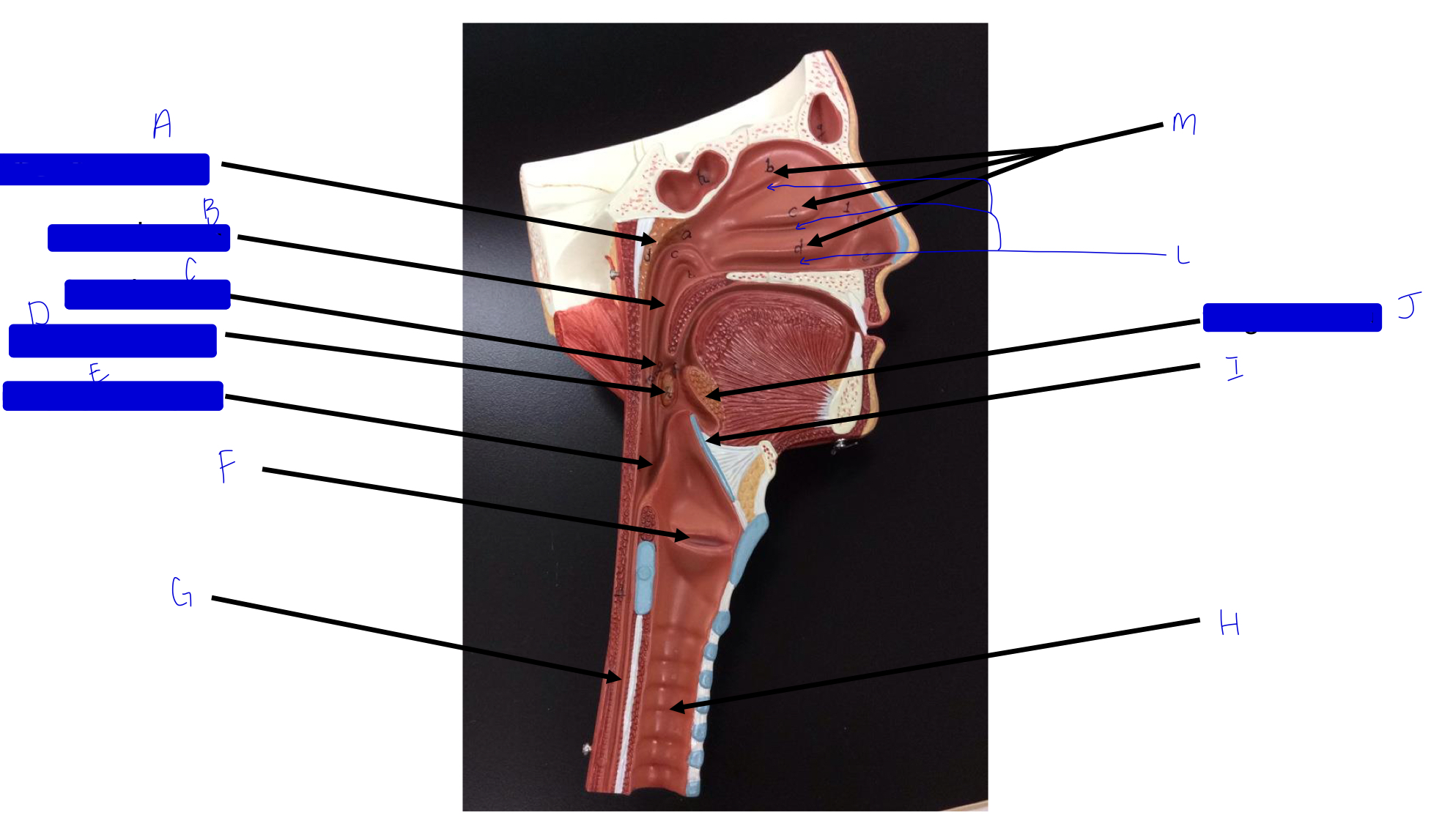
I
epiglottis
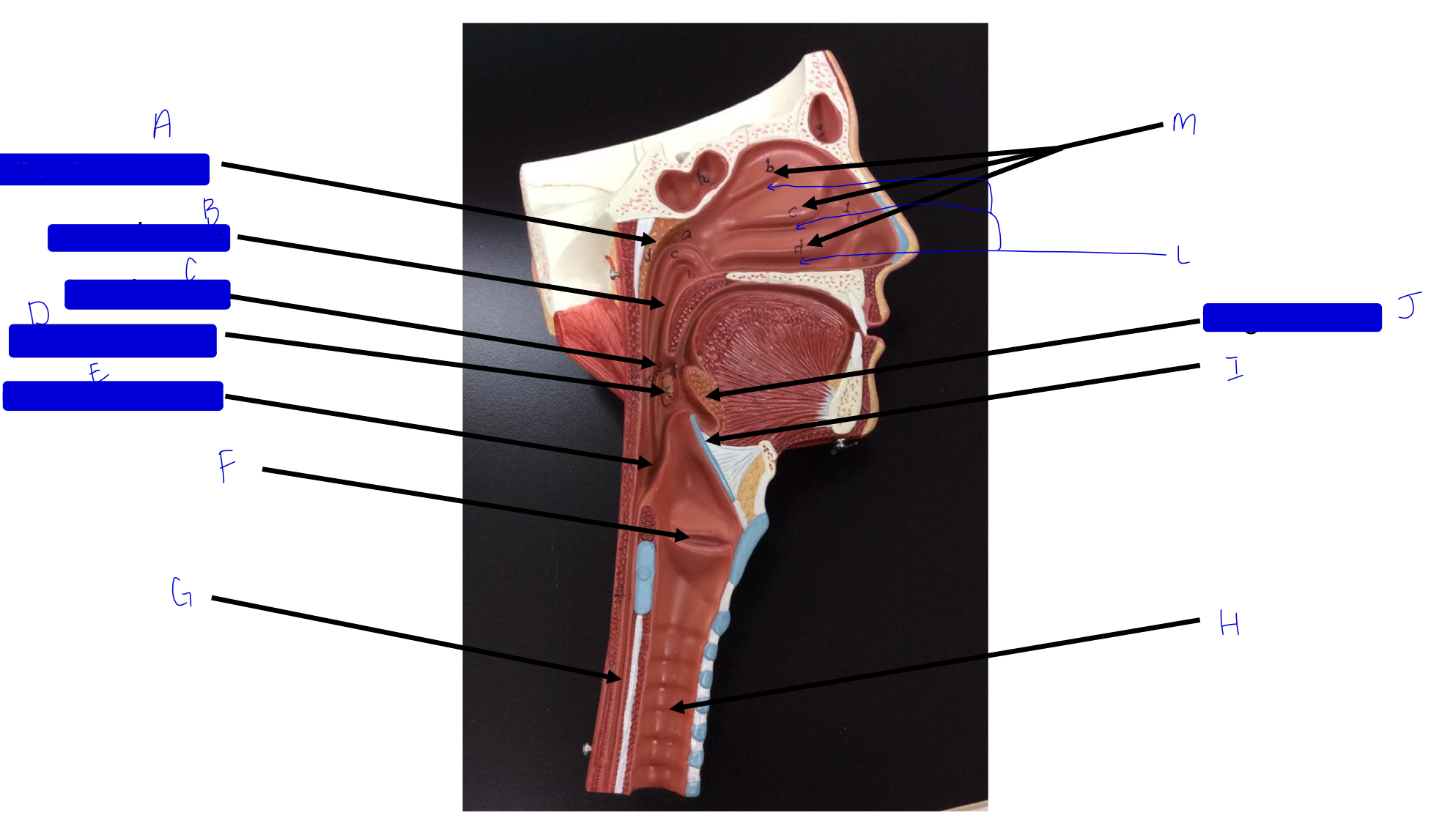
J
lingual tonsil
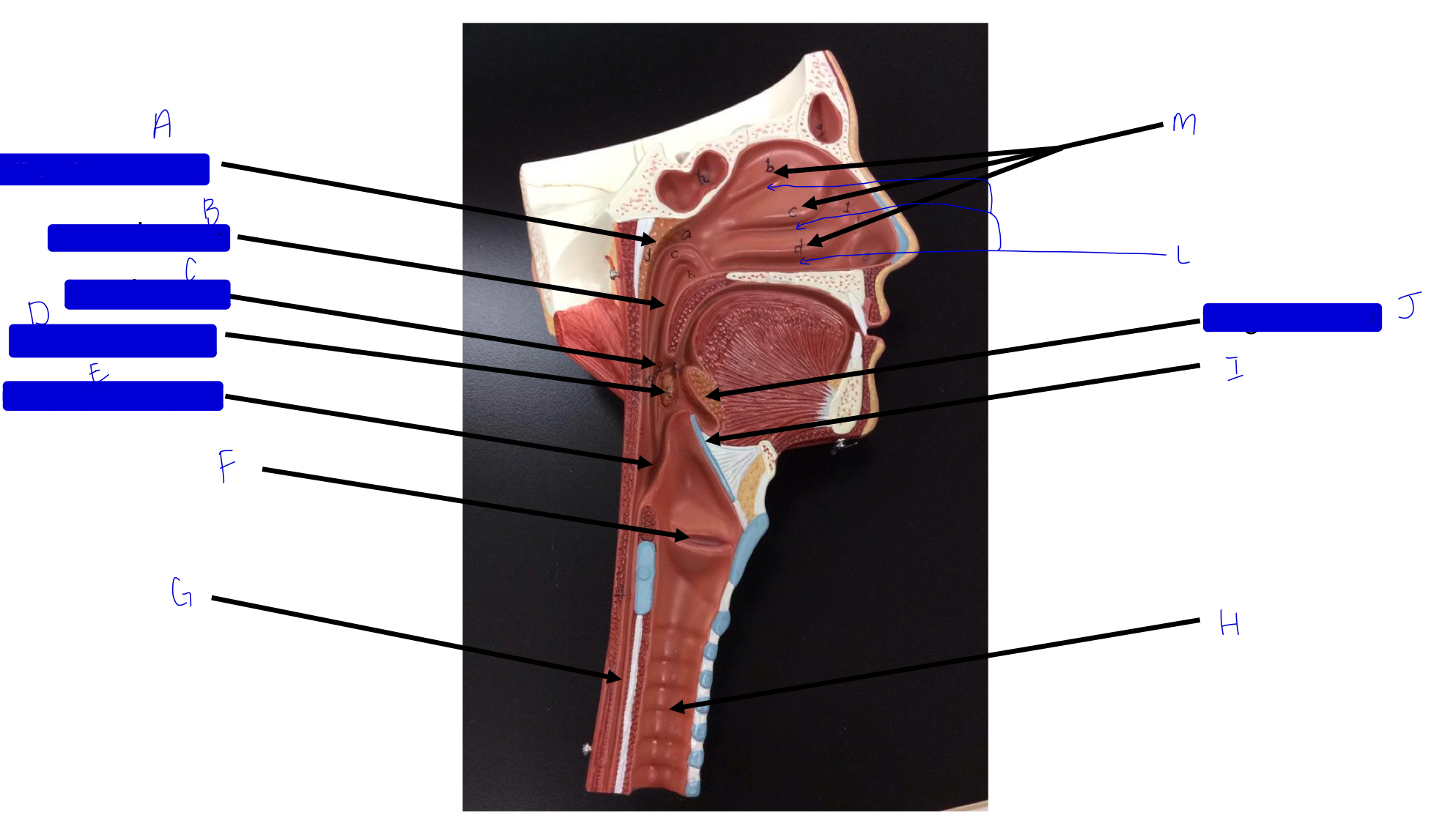
L
meatuses (valleys)
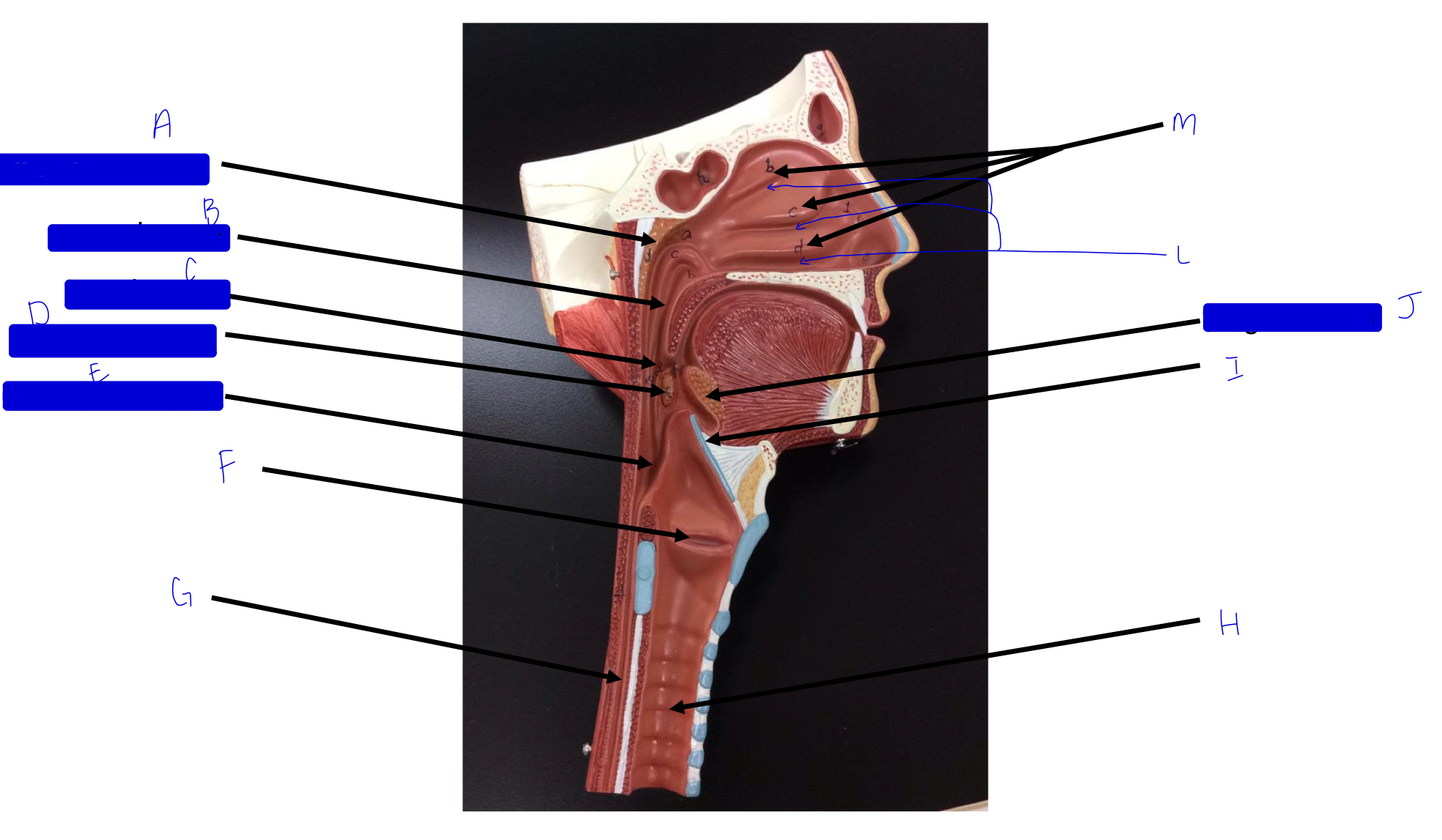
M
nasal conchae (superior, middle, inferior)
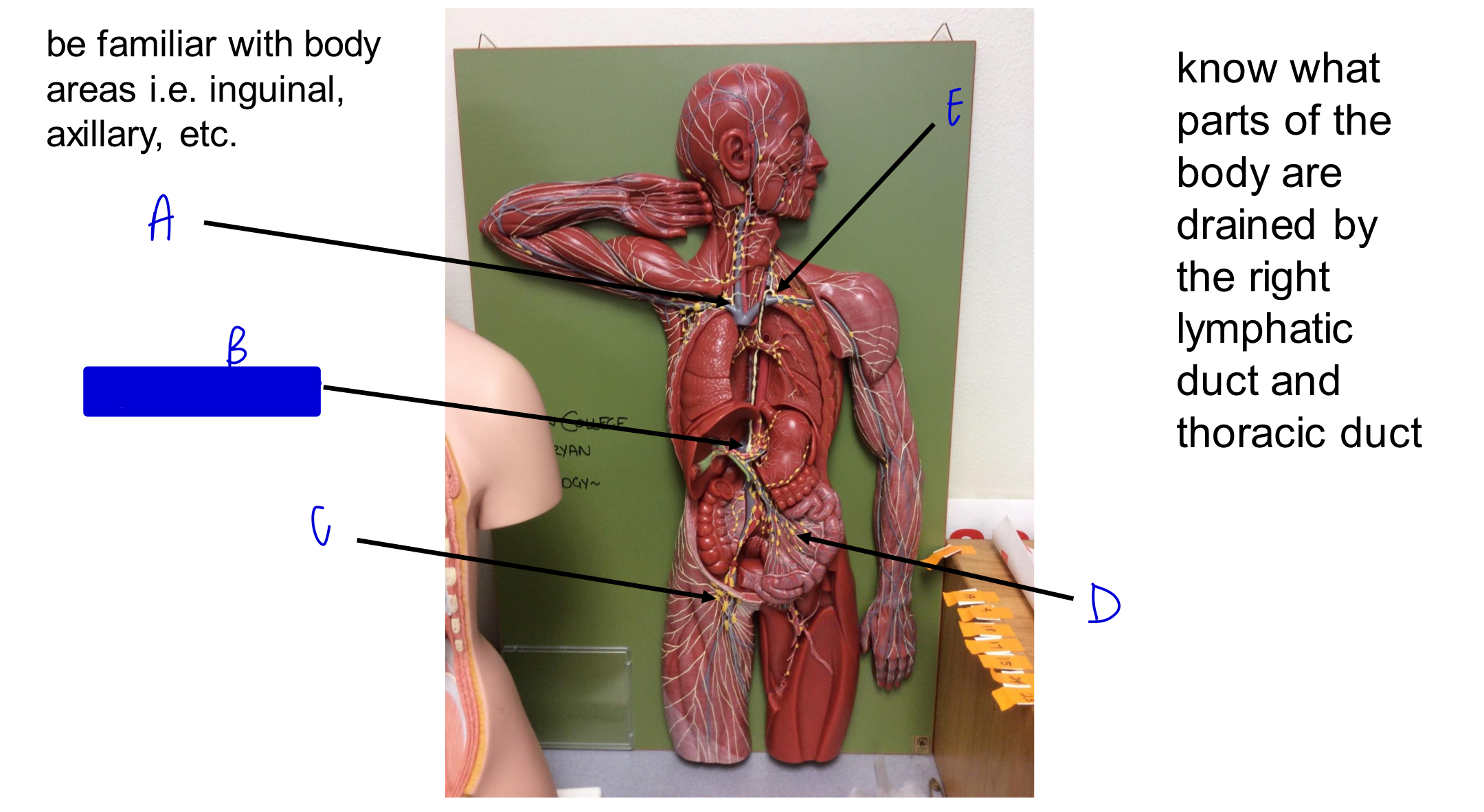
A
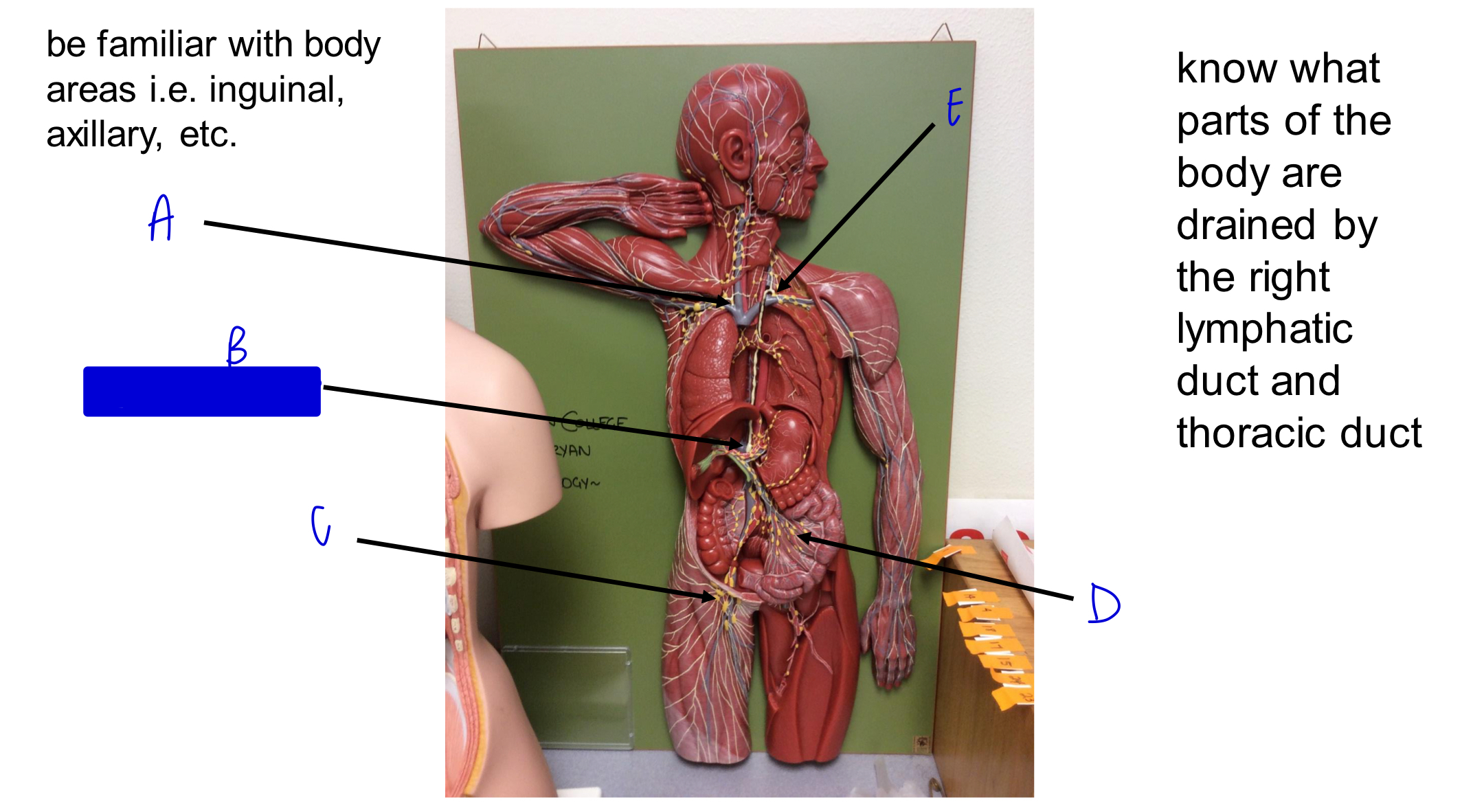
B
cisterna chyli
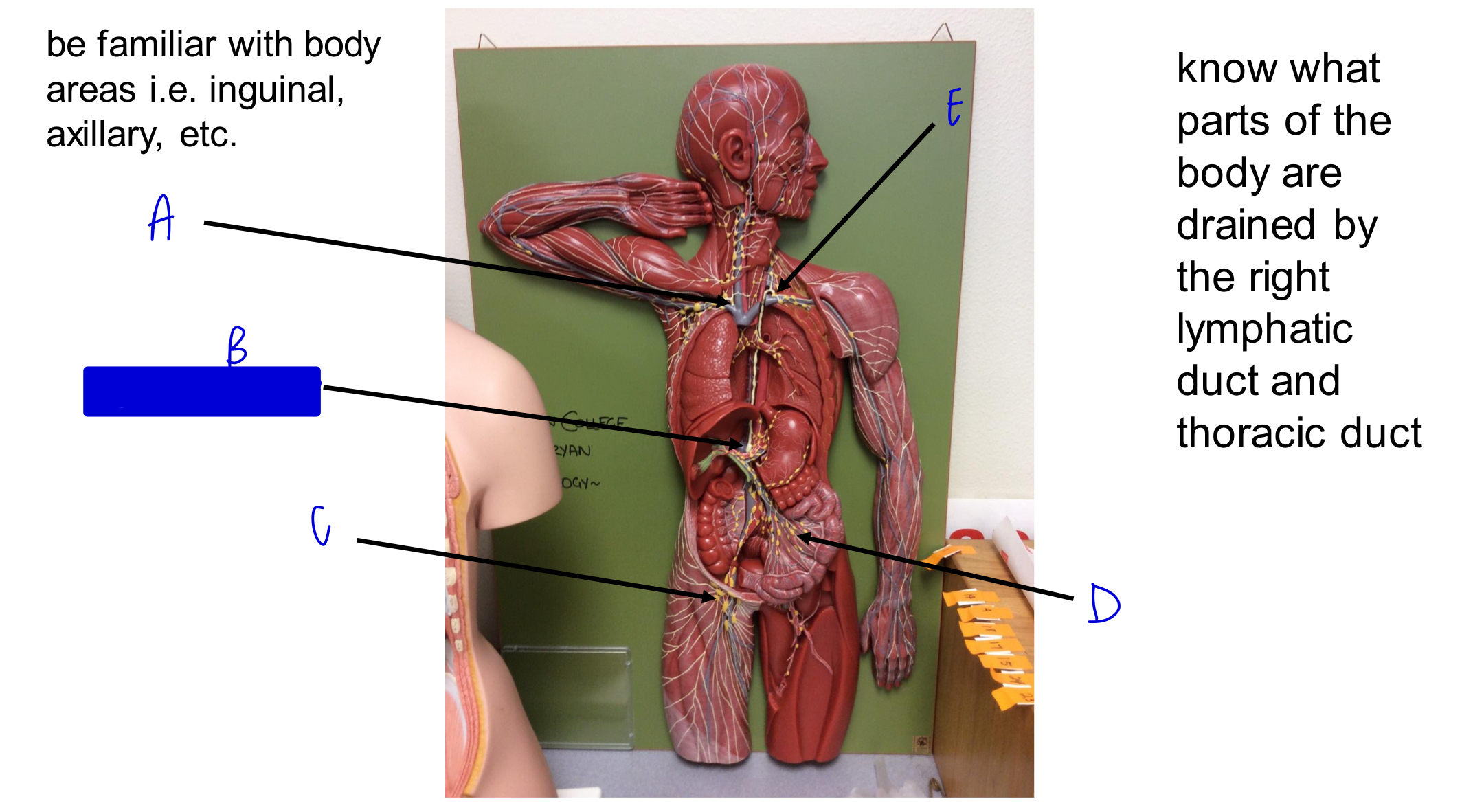
C
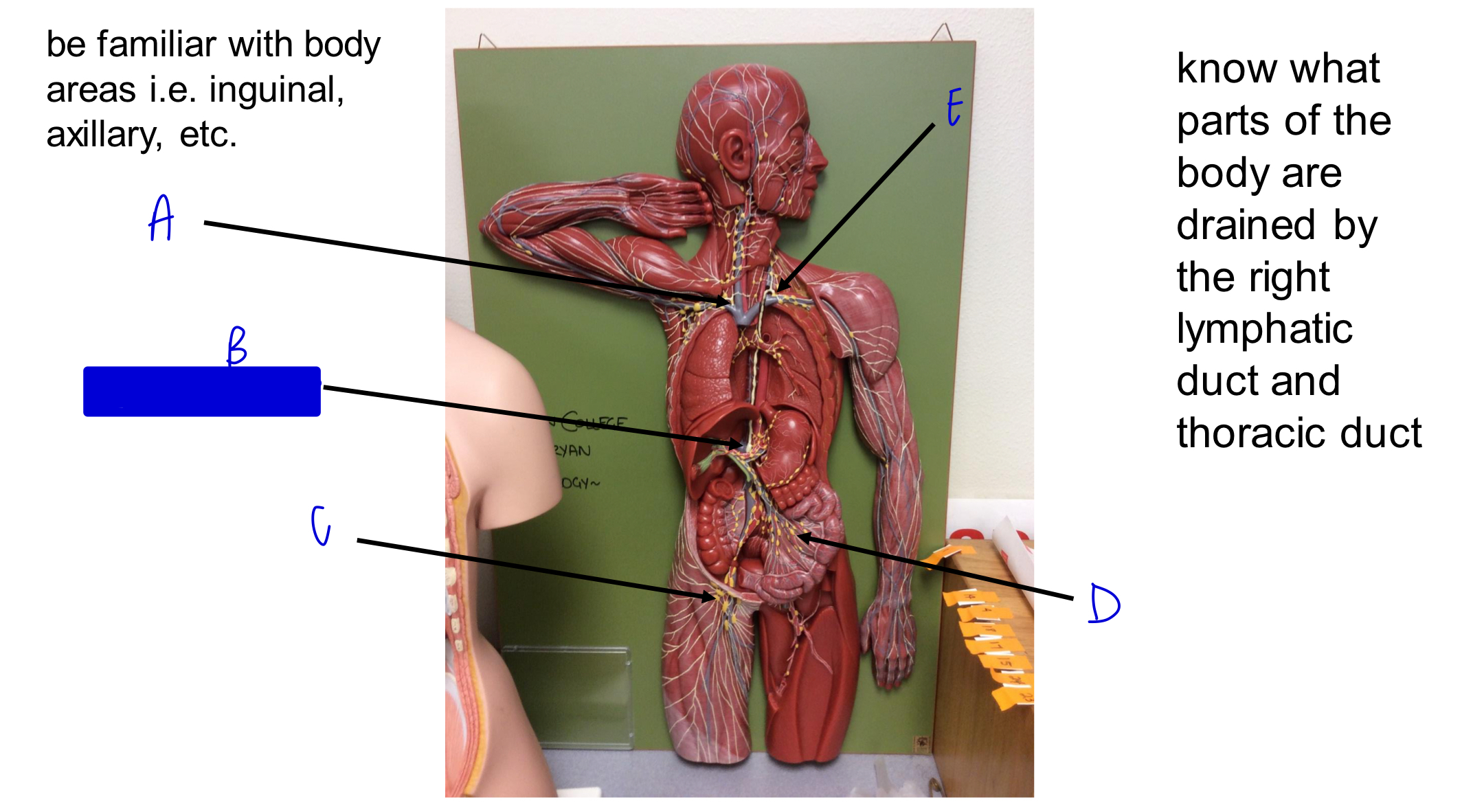
D
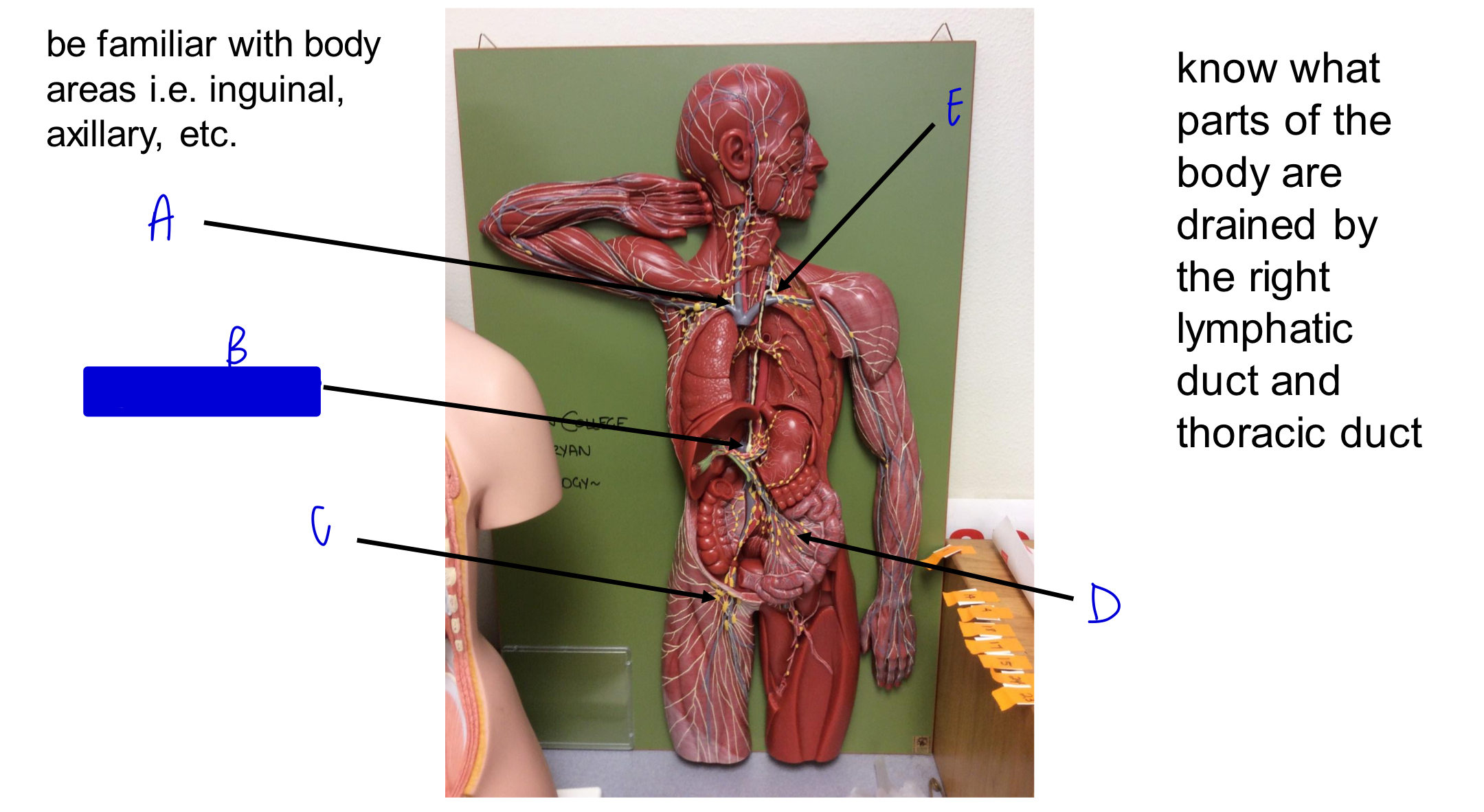
E
?
epiglottis
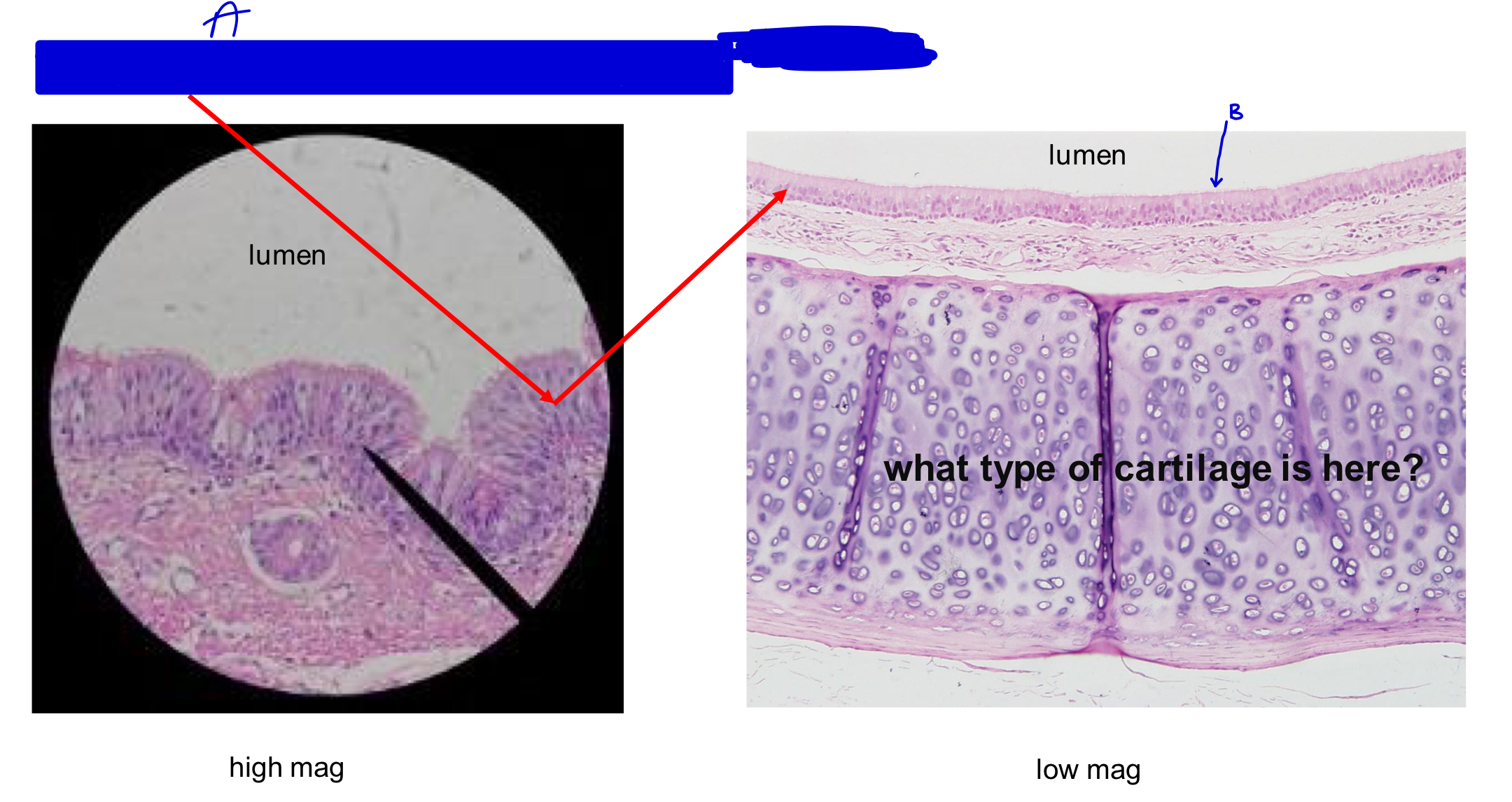
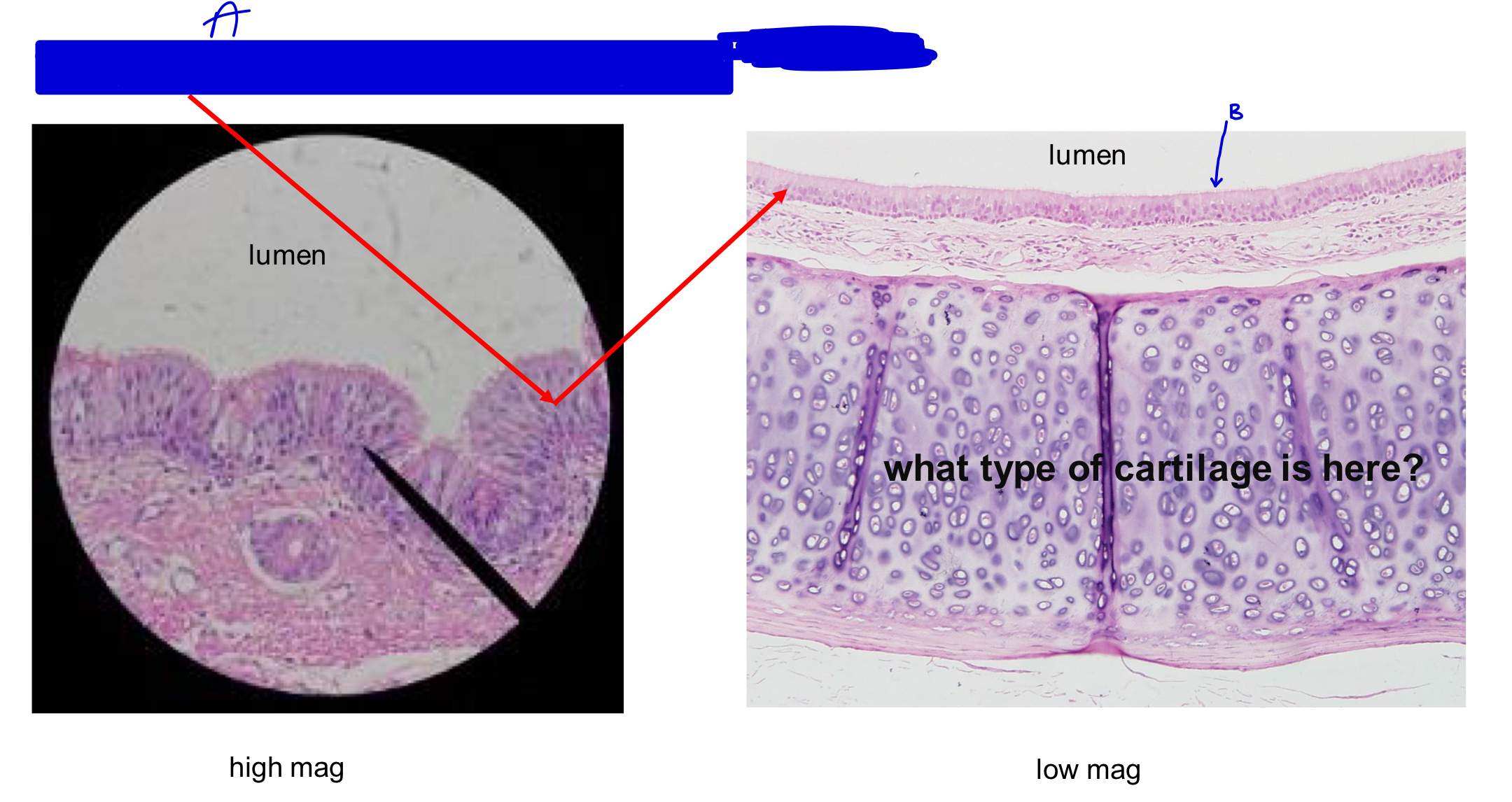
what type of cartilage is here?
hyaline cartilage
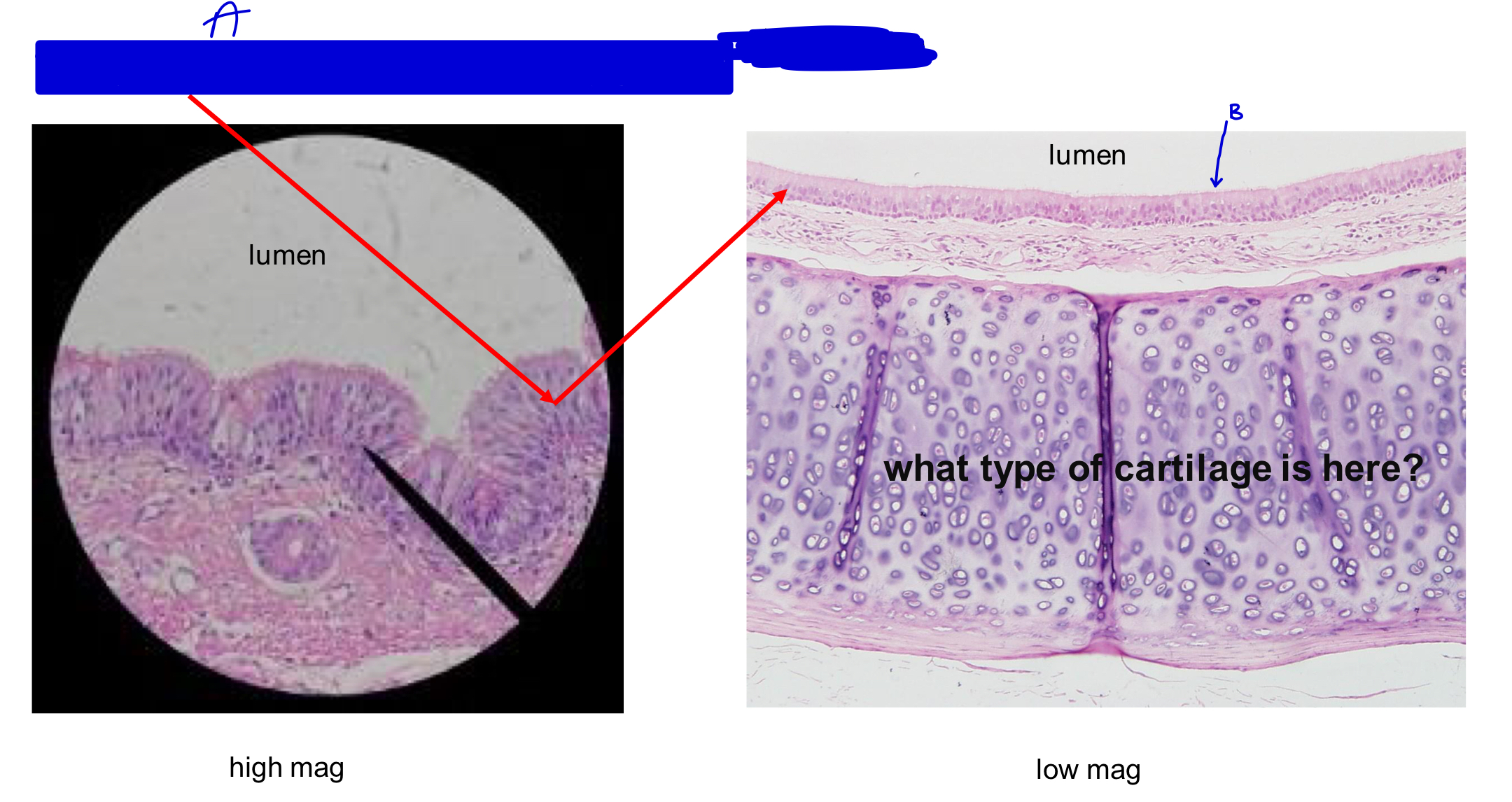
A
pseudostratified ciliated columnar cells
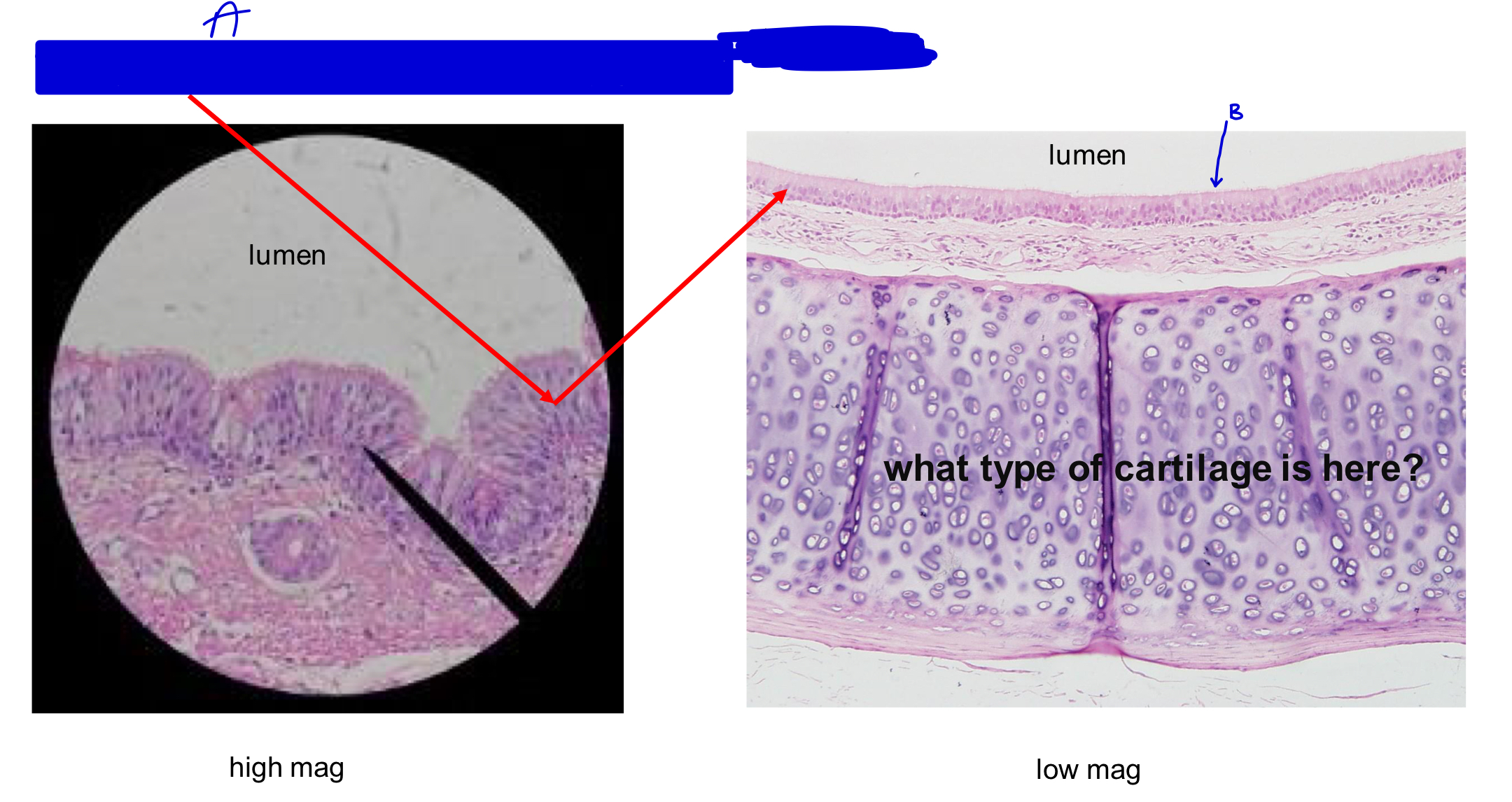
B
cilia (pushes mucus out one direction)
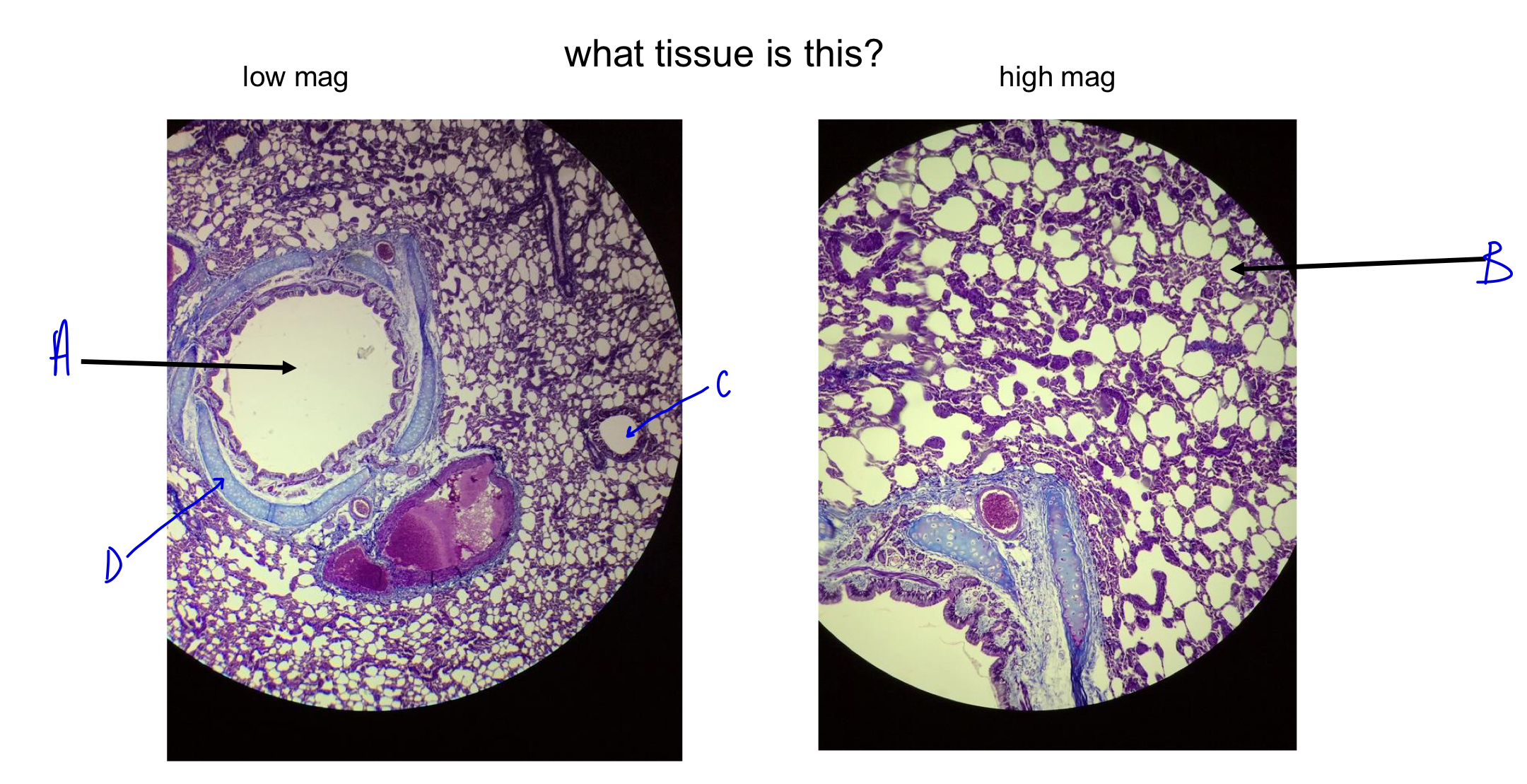
what tissue is this?
lung
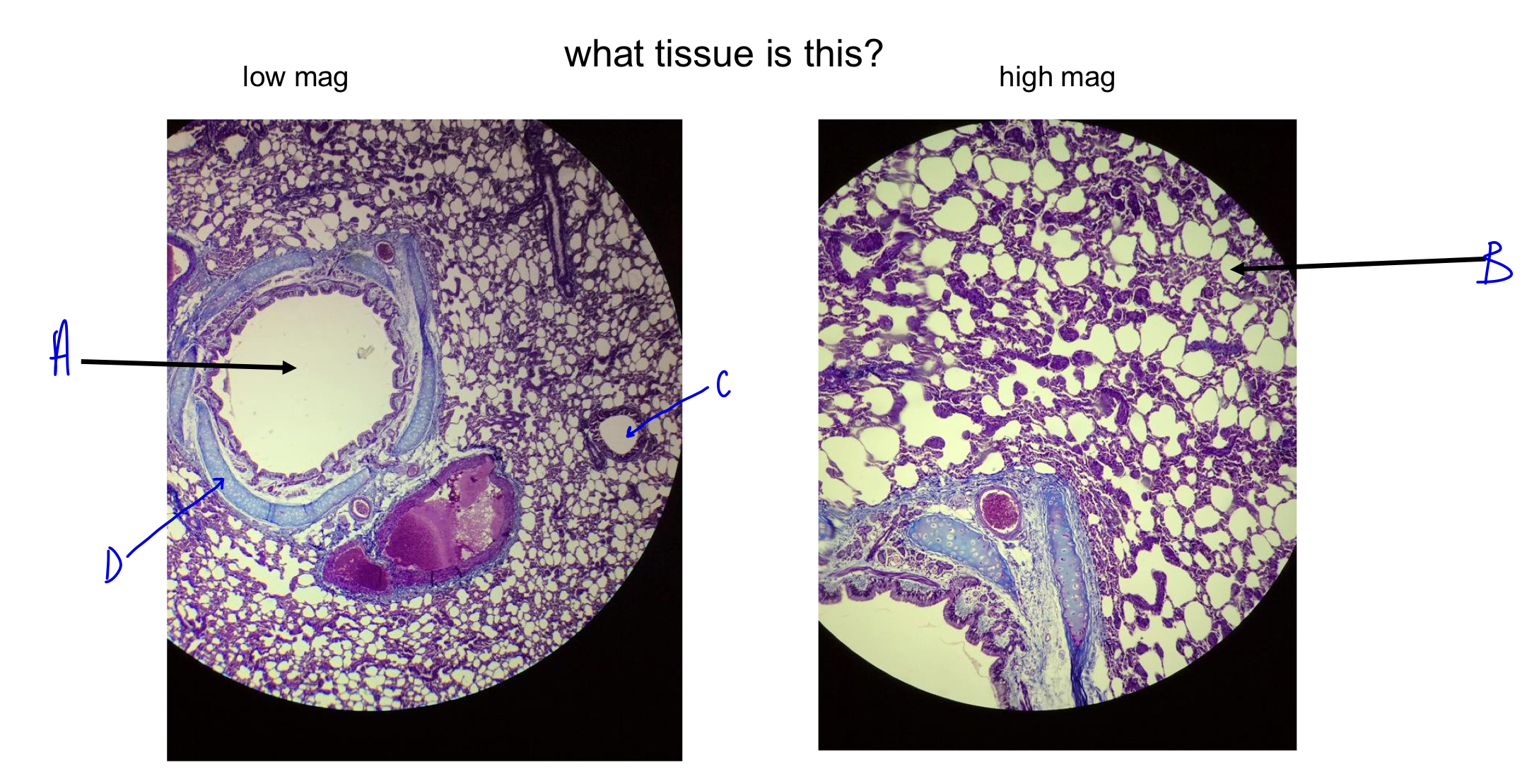
A
bronchi
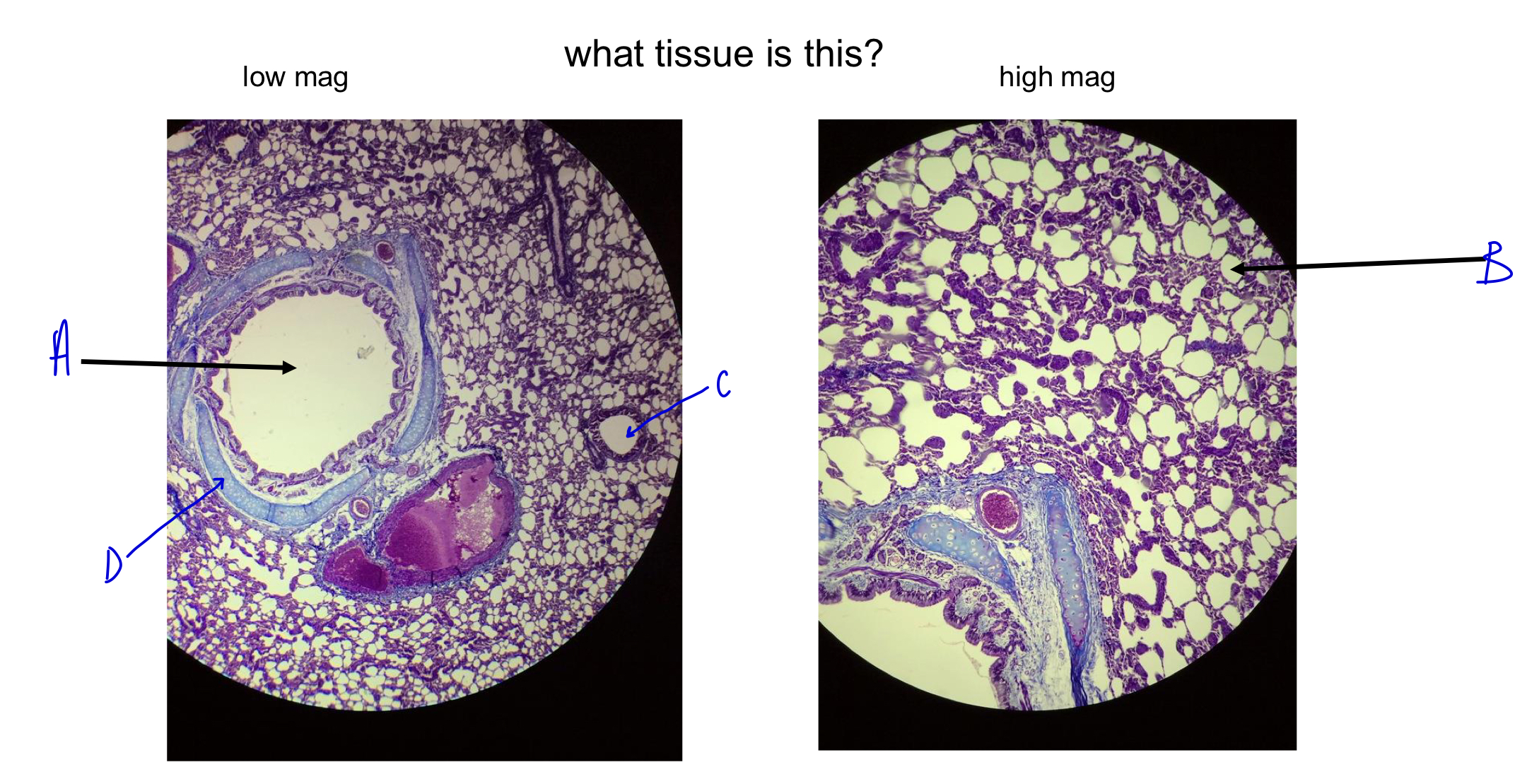
B
alveoli (white dots; gas exchange; wall to wall to maximize gas exchange)
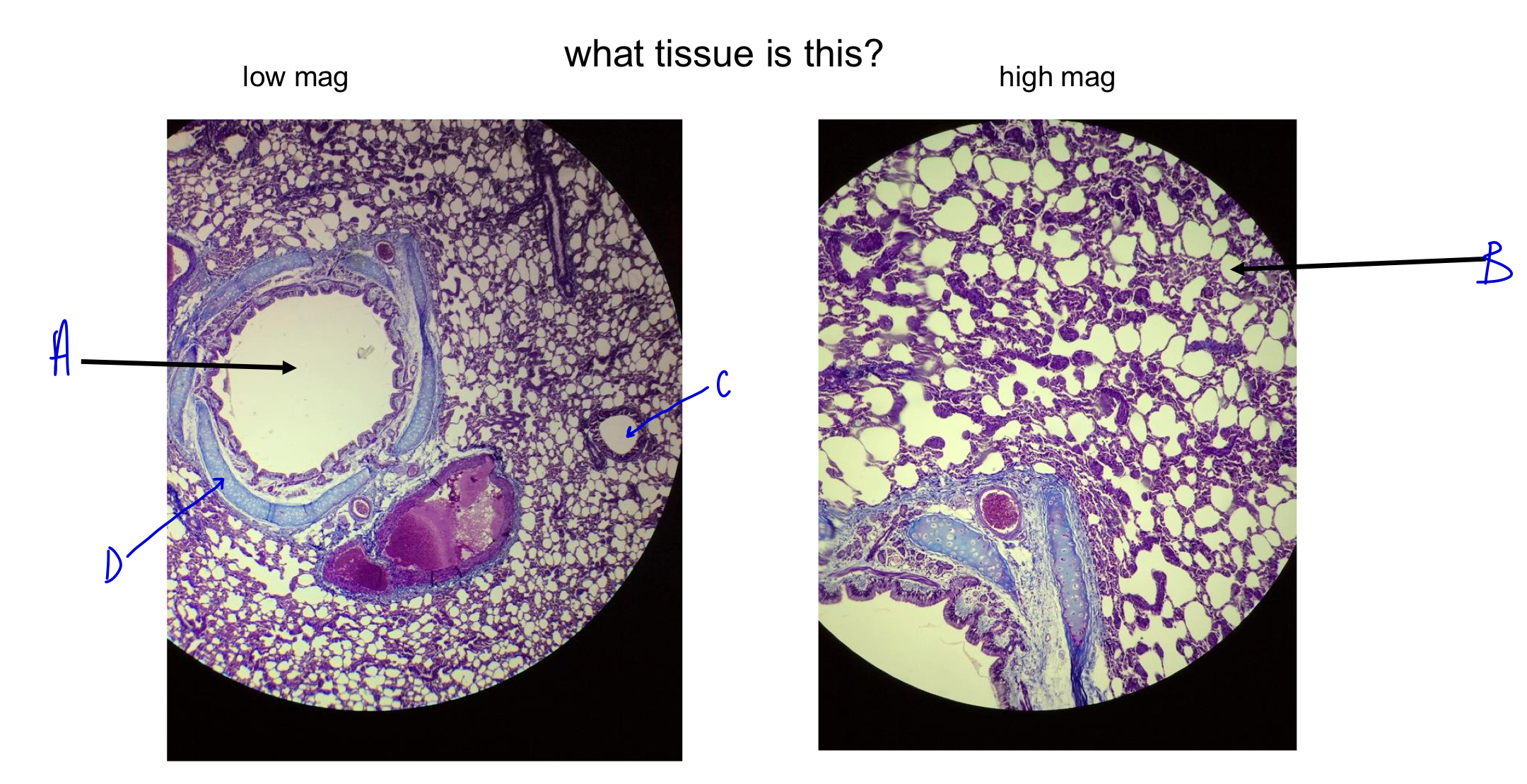
C
bronchi
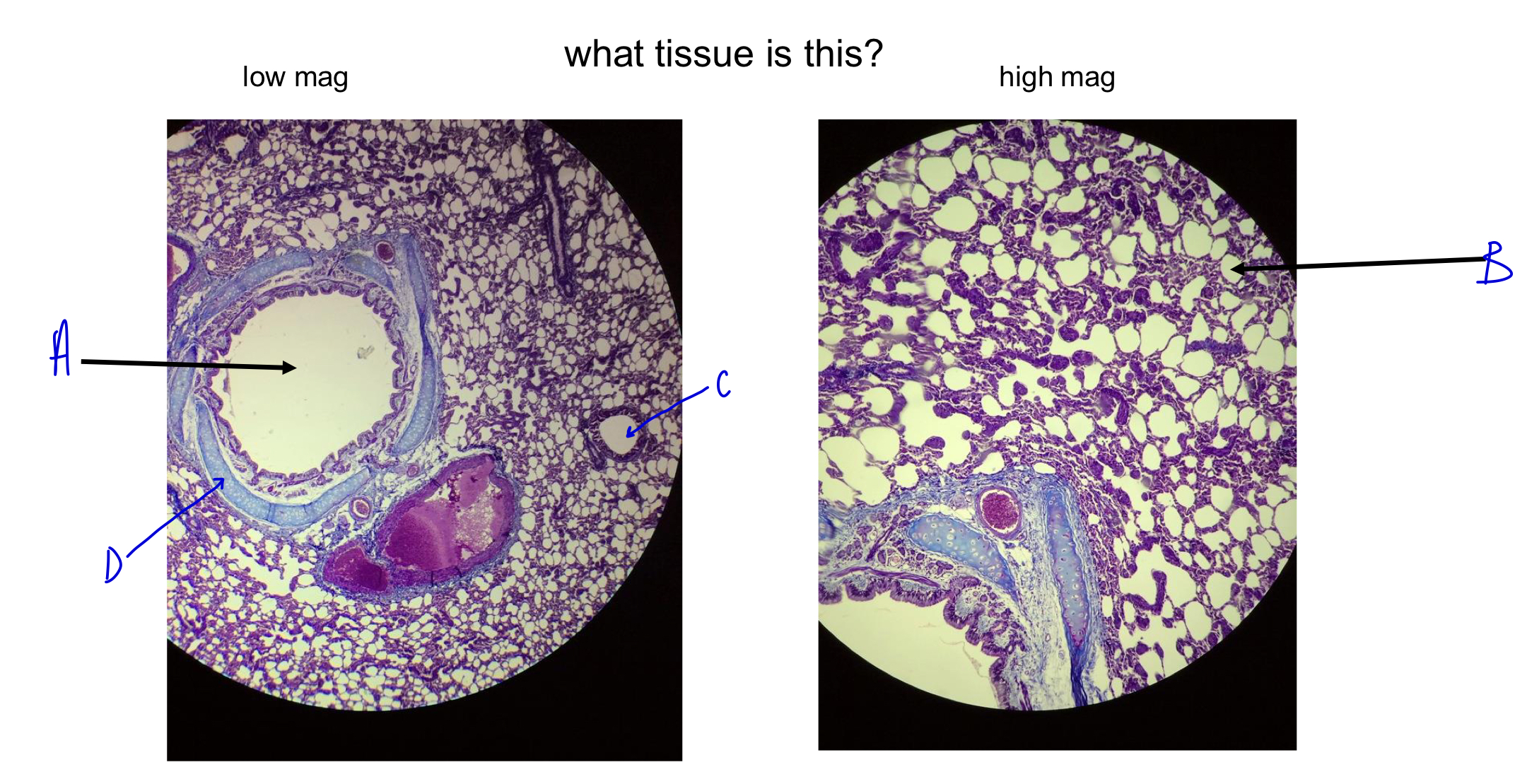
D
cartilage ring around bronchi
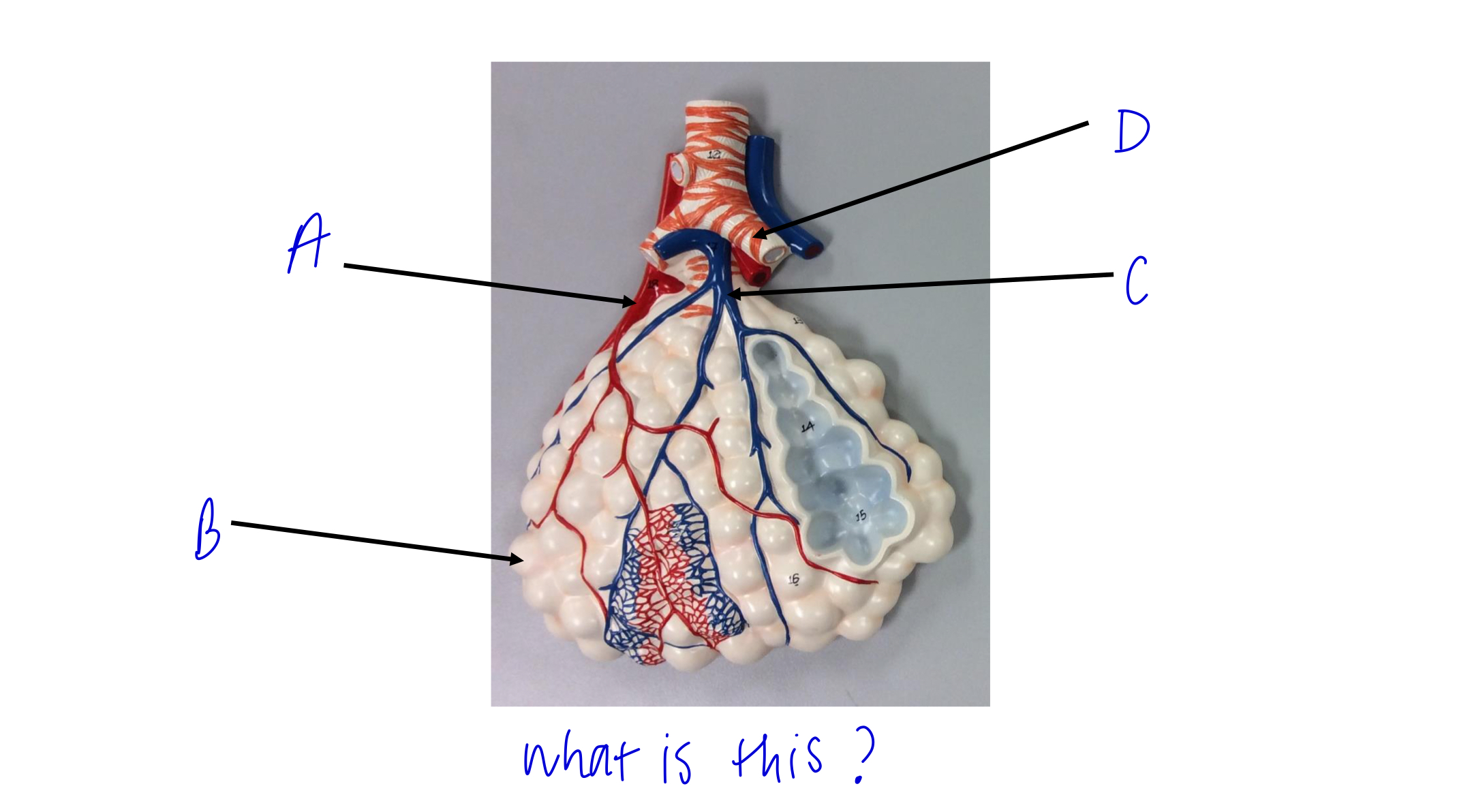
what is this?
alveolar sac
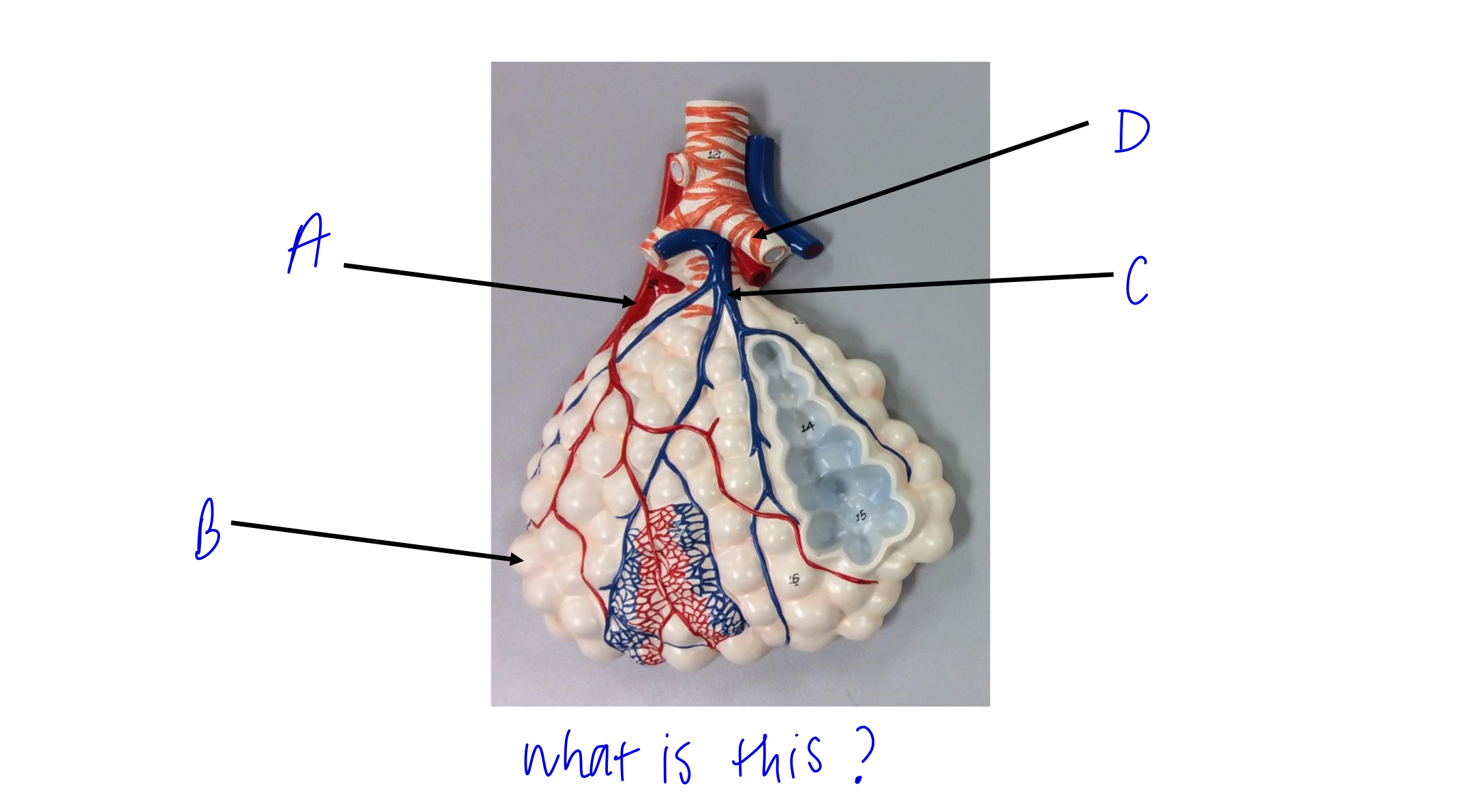
A
pulmonary vein
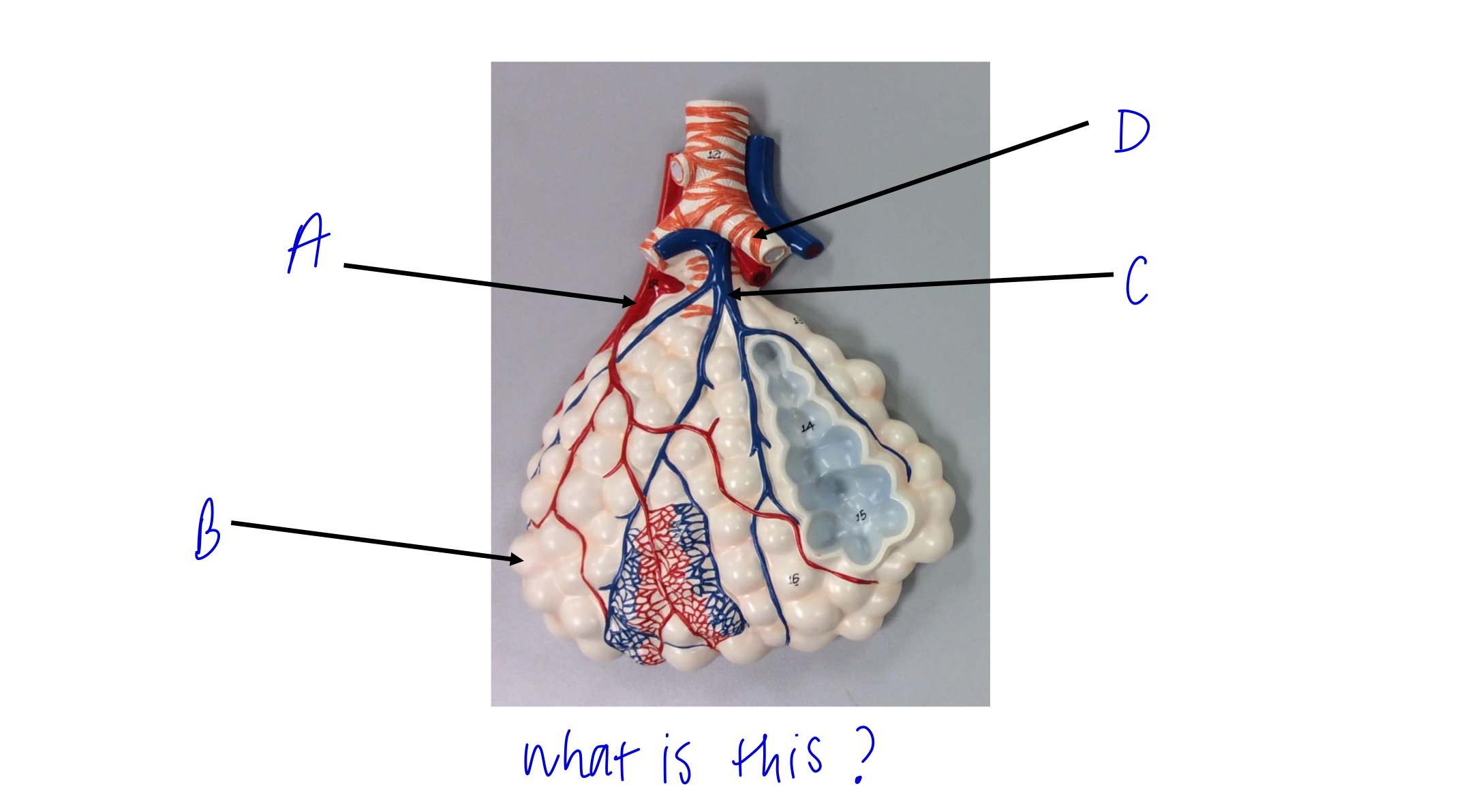
B
alveoli
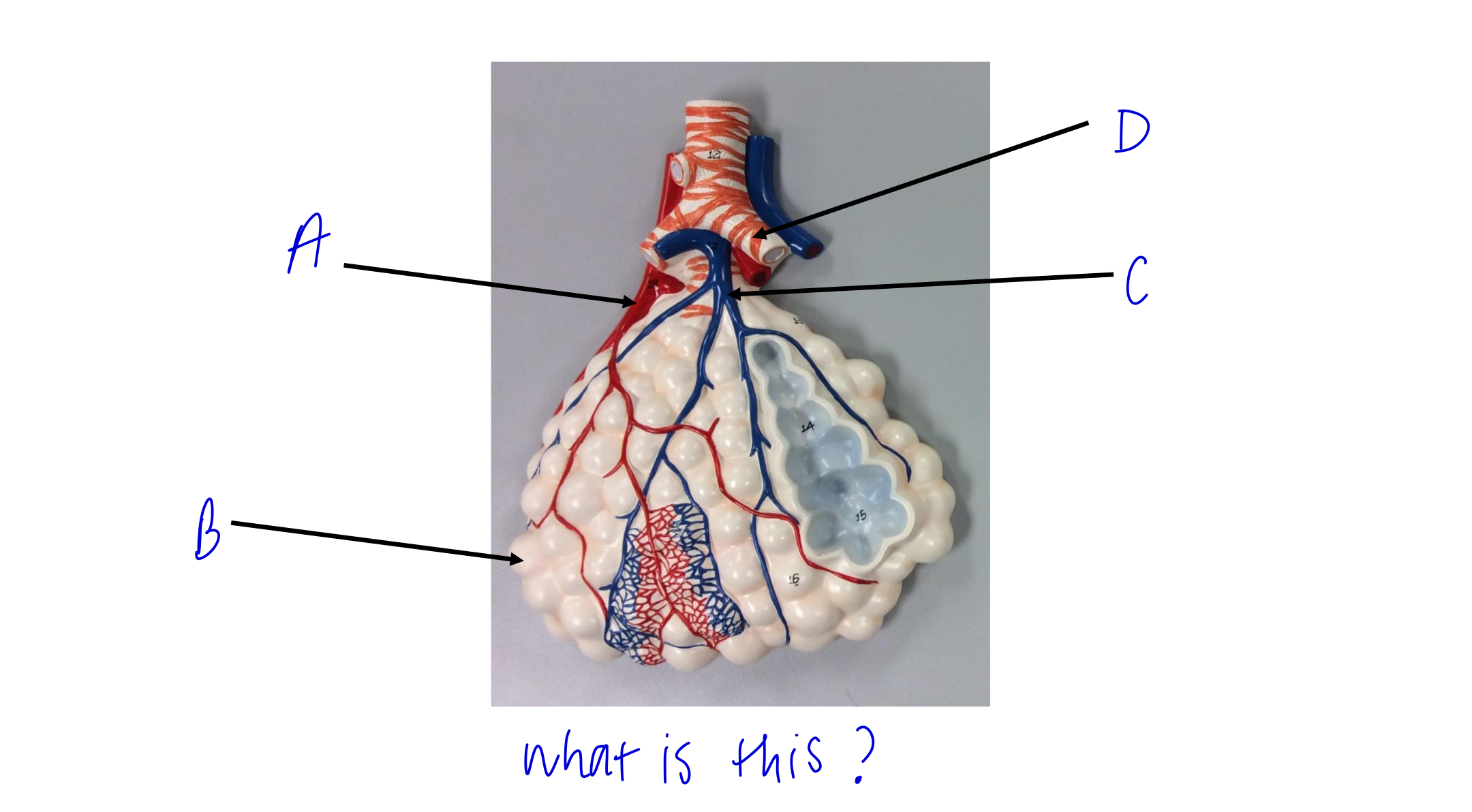
C
pulmonary artery
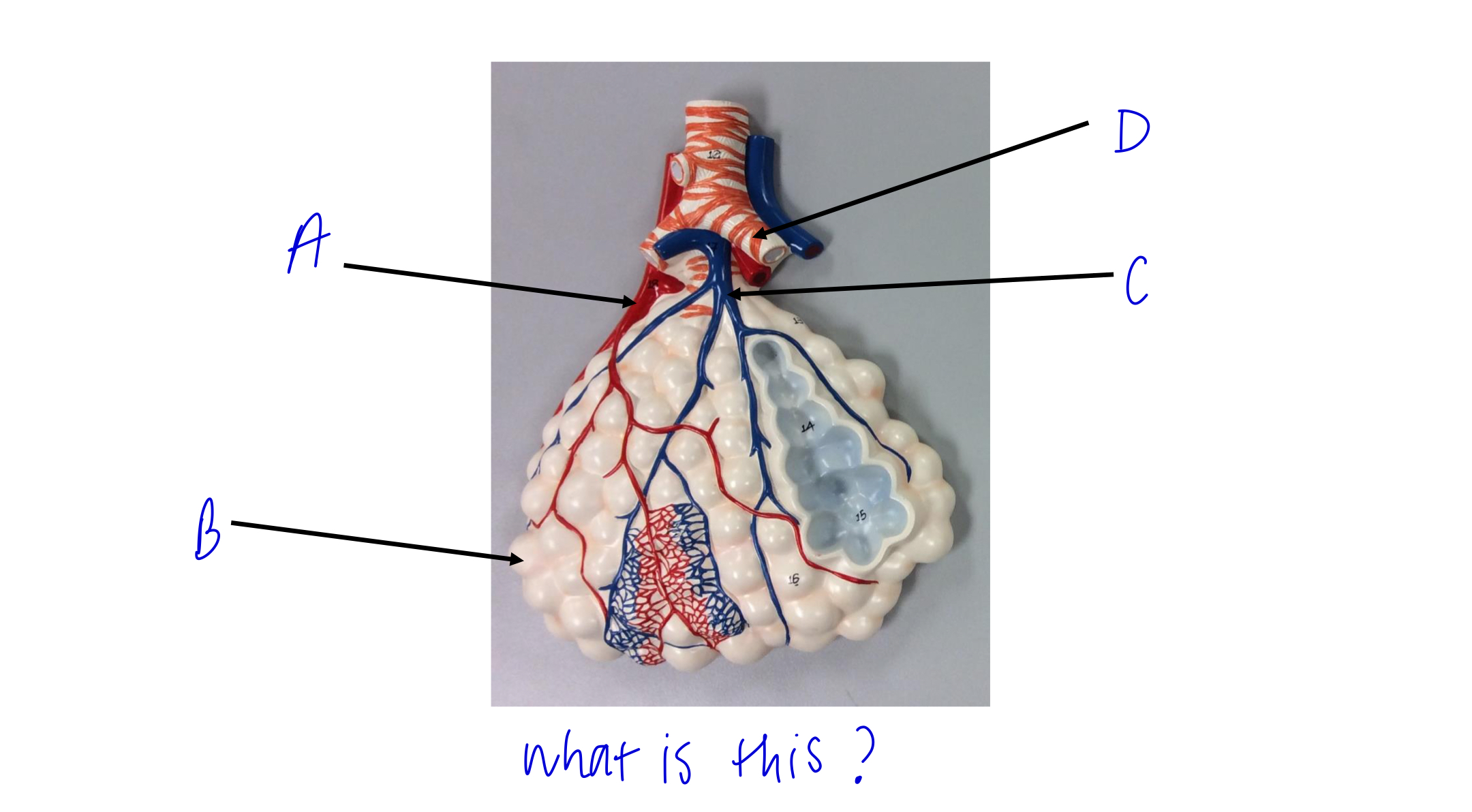
D
cartilage rings holding bronchioles open
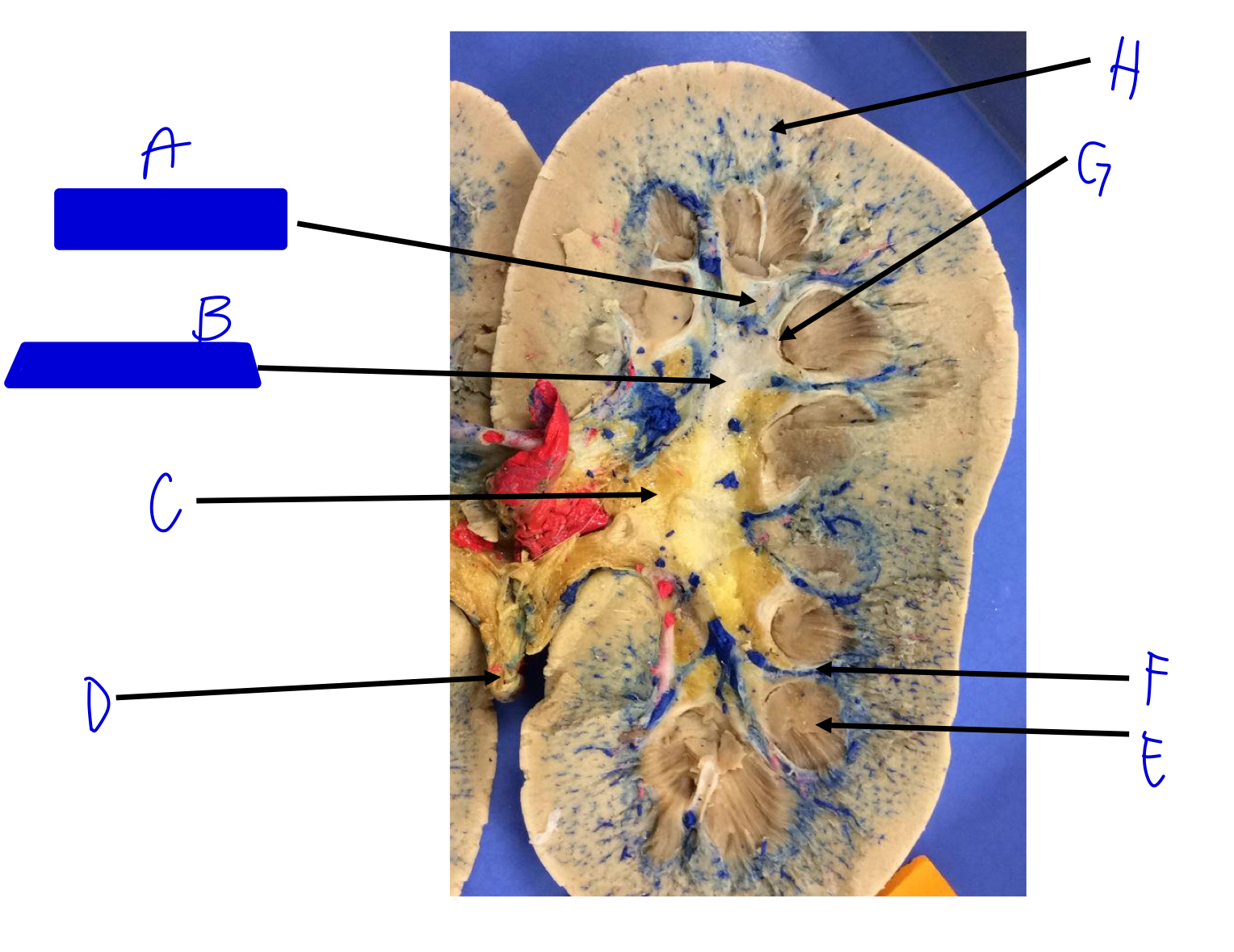
A
minor calyx (merges to major)
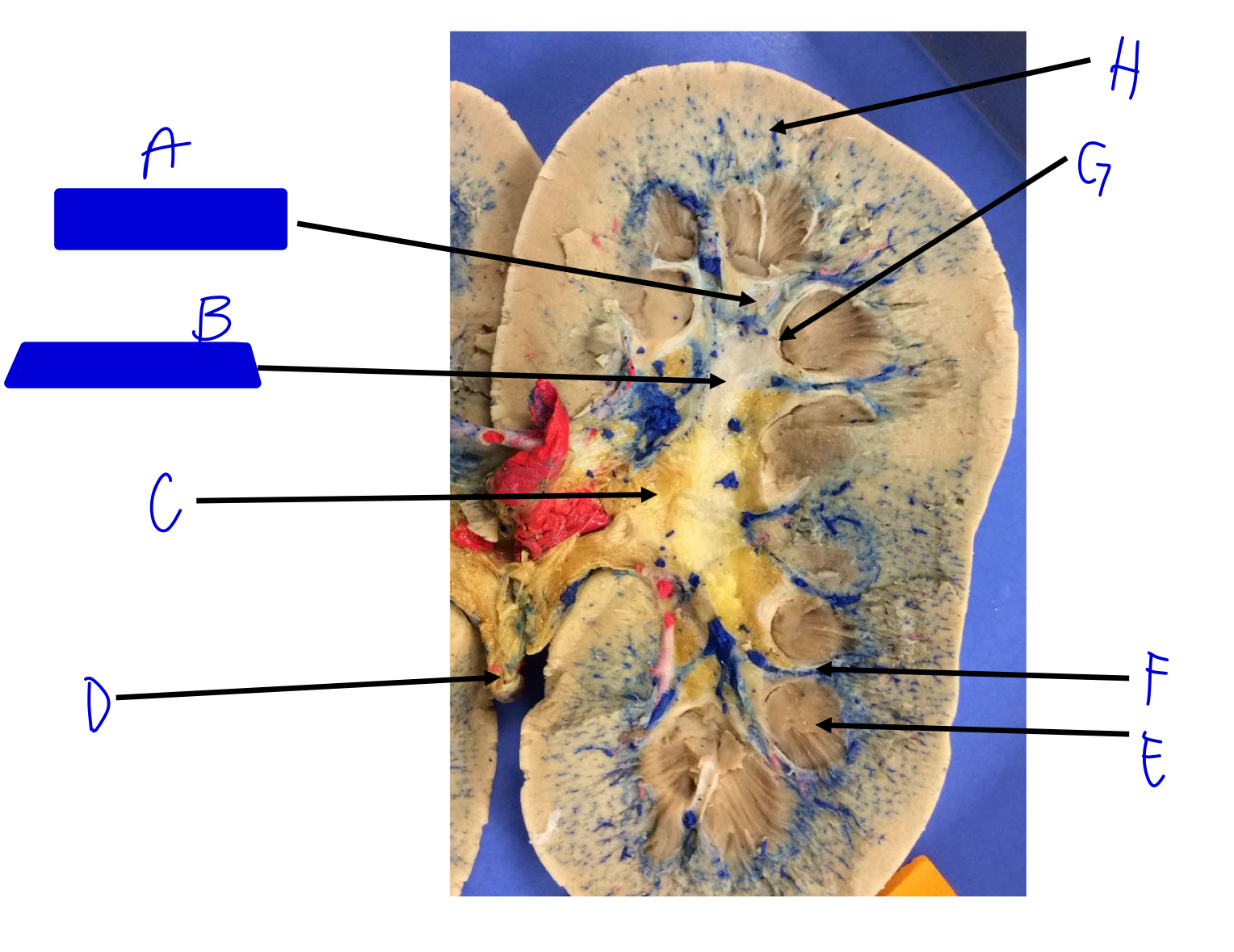
B
major calyx (merges to renal pelvis)
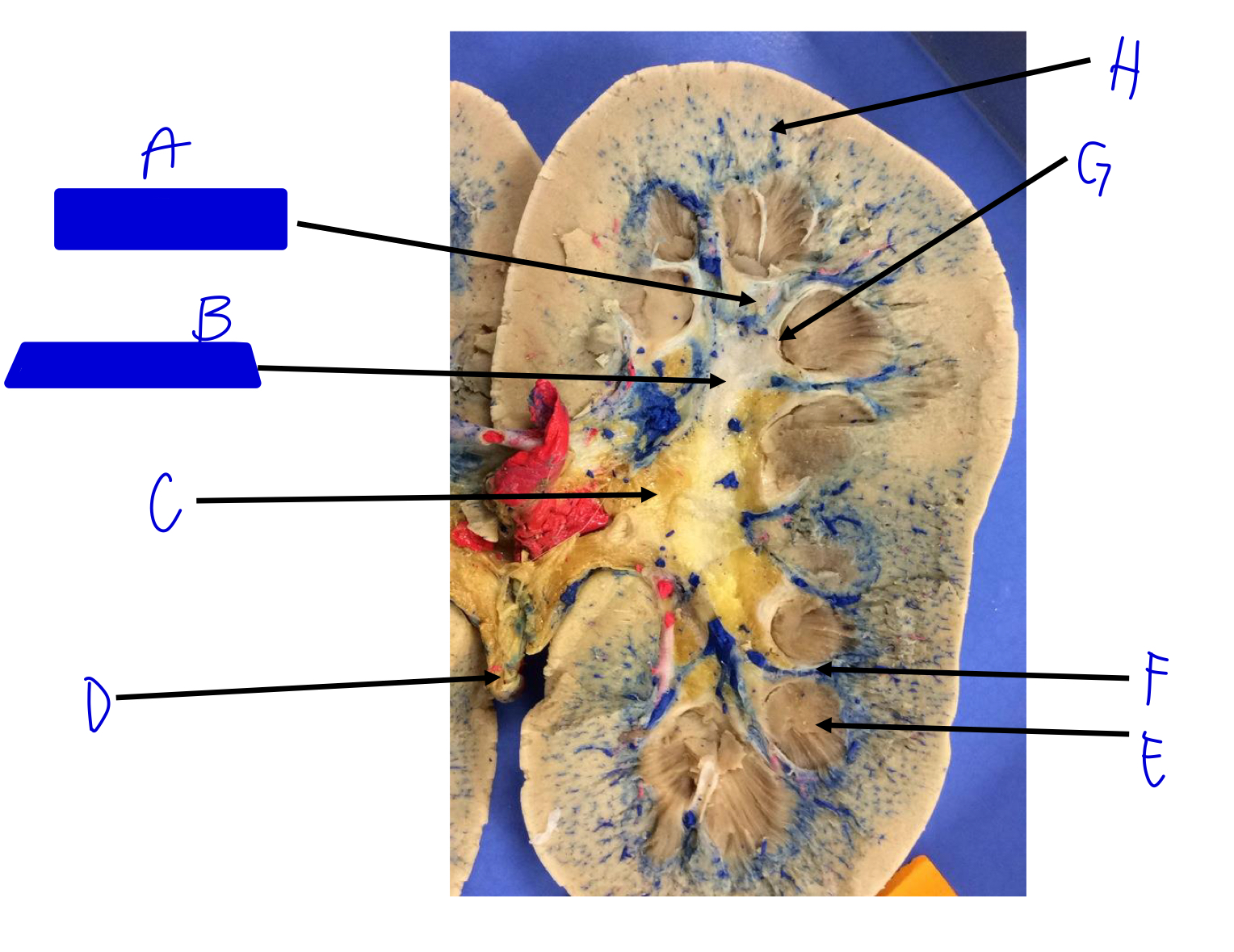
C
renal pelvis
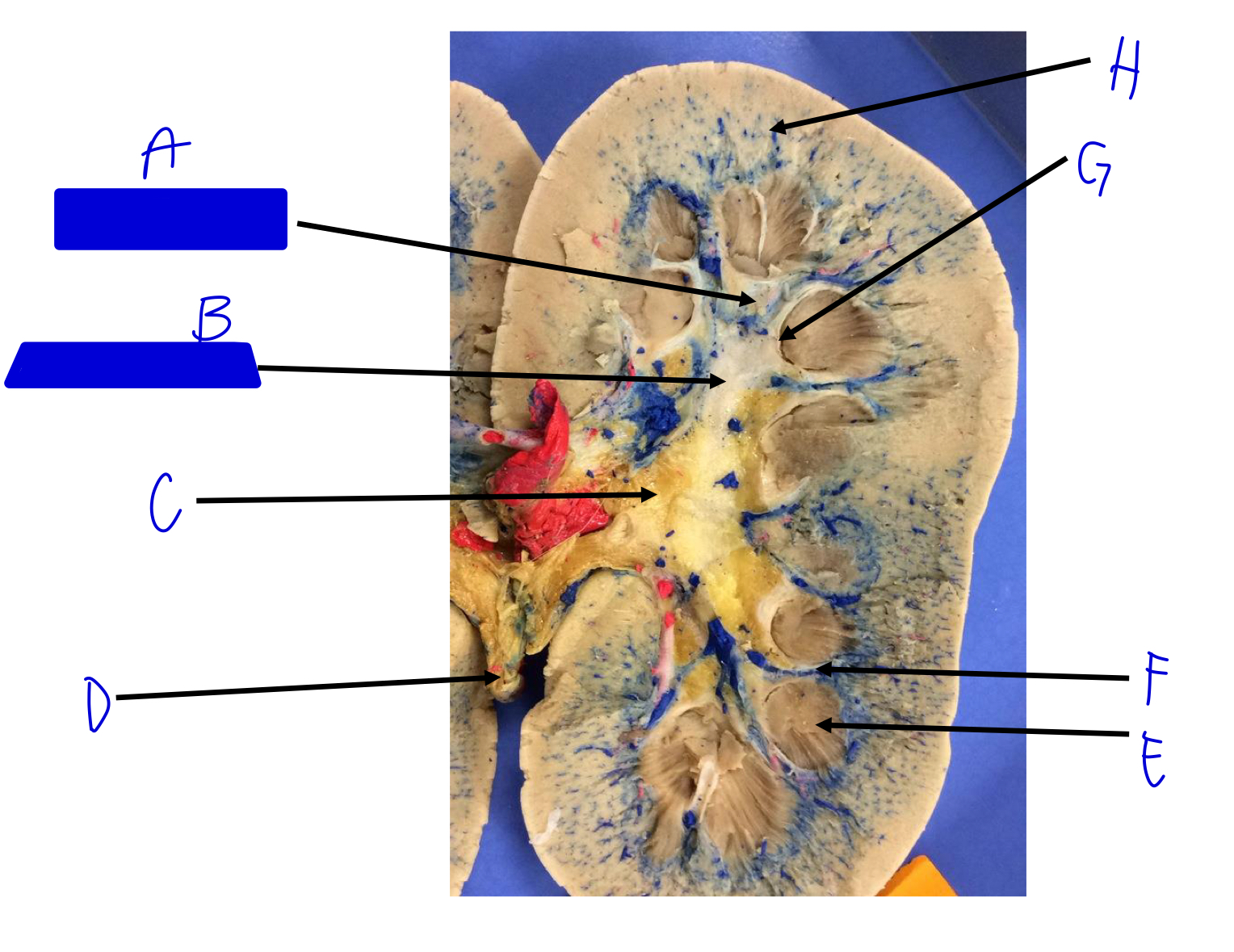
D
ureter (beginning)
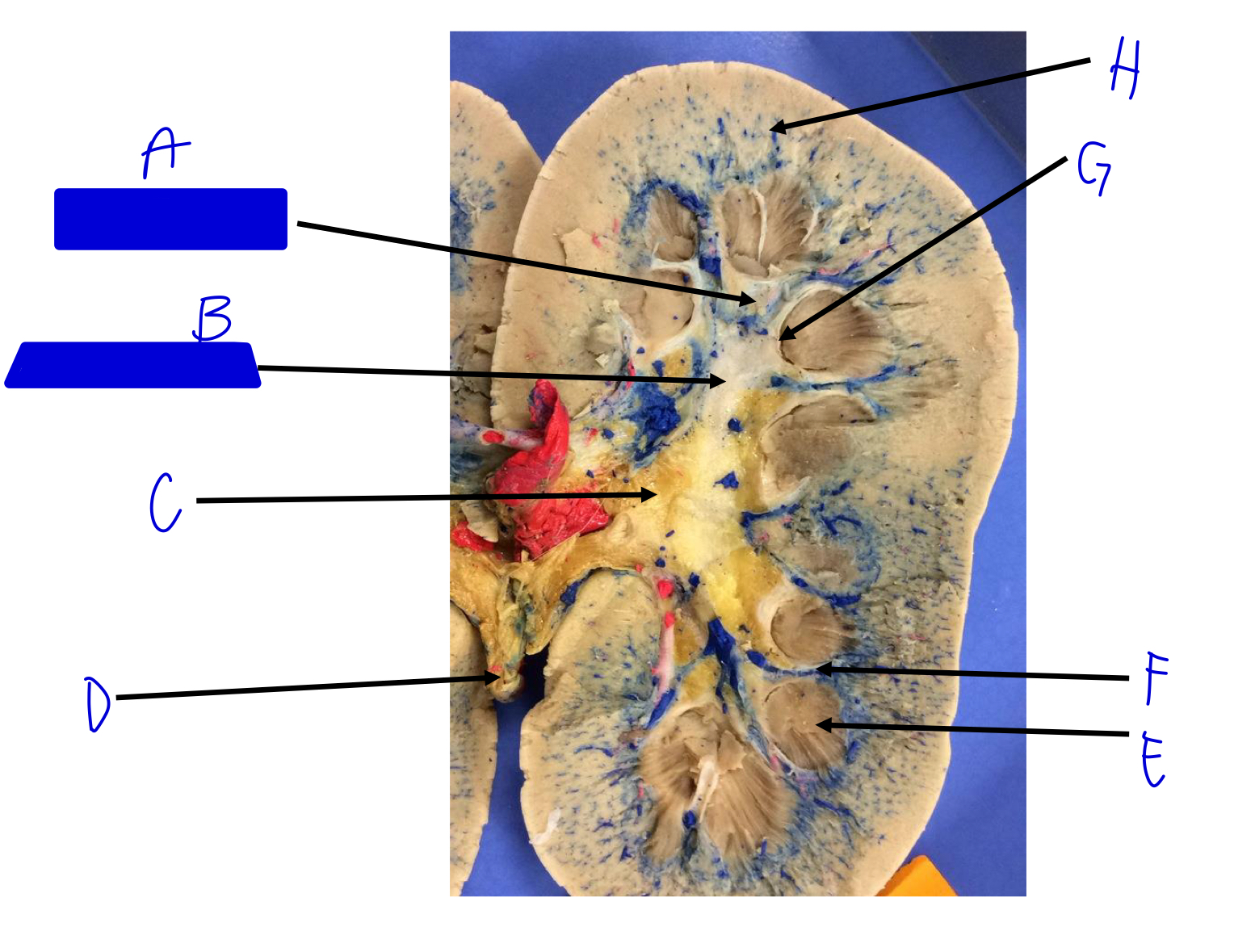
E
renal pyramids
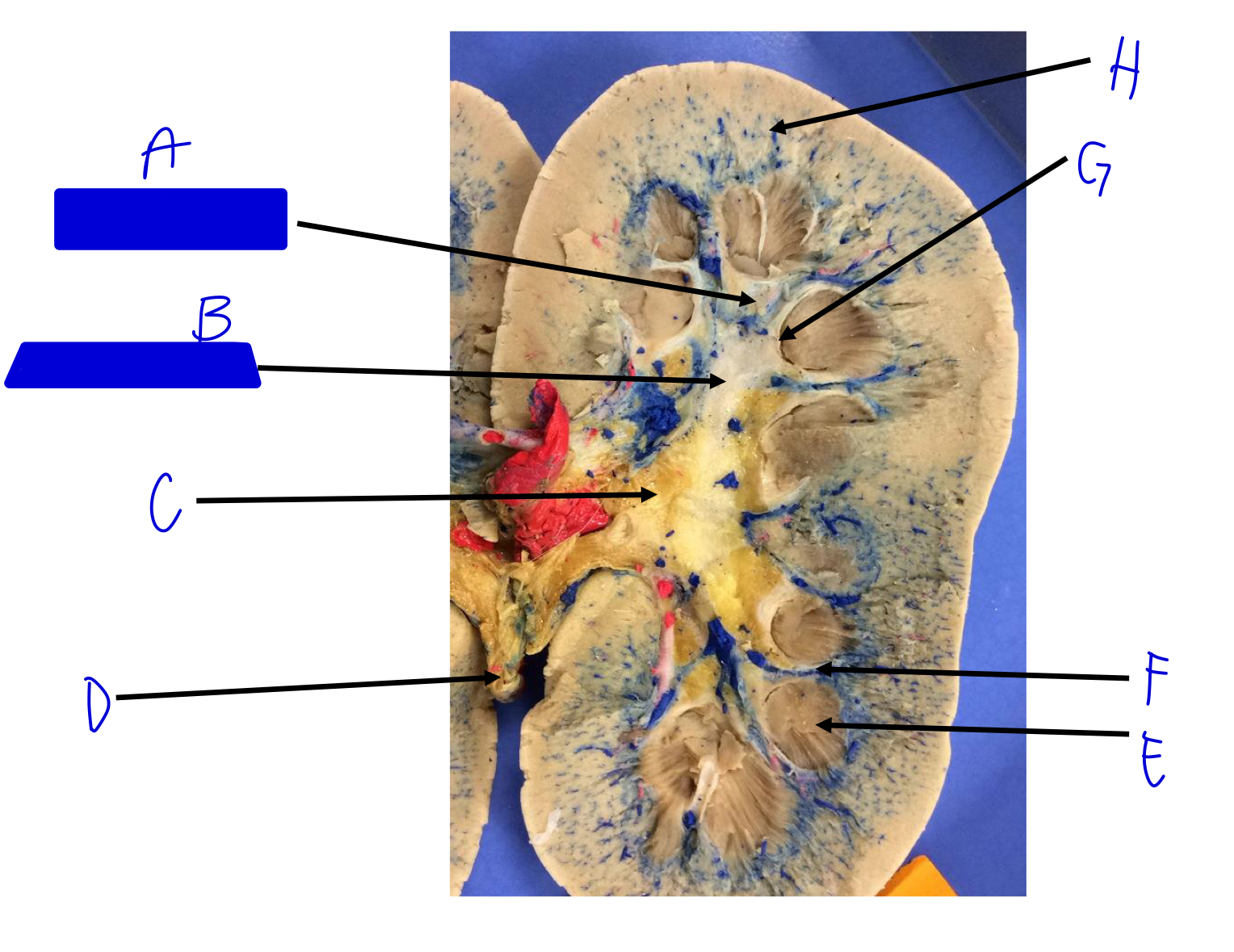
F
renal columns
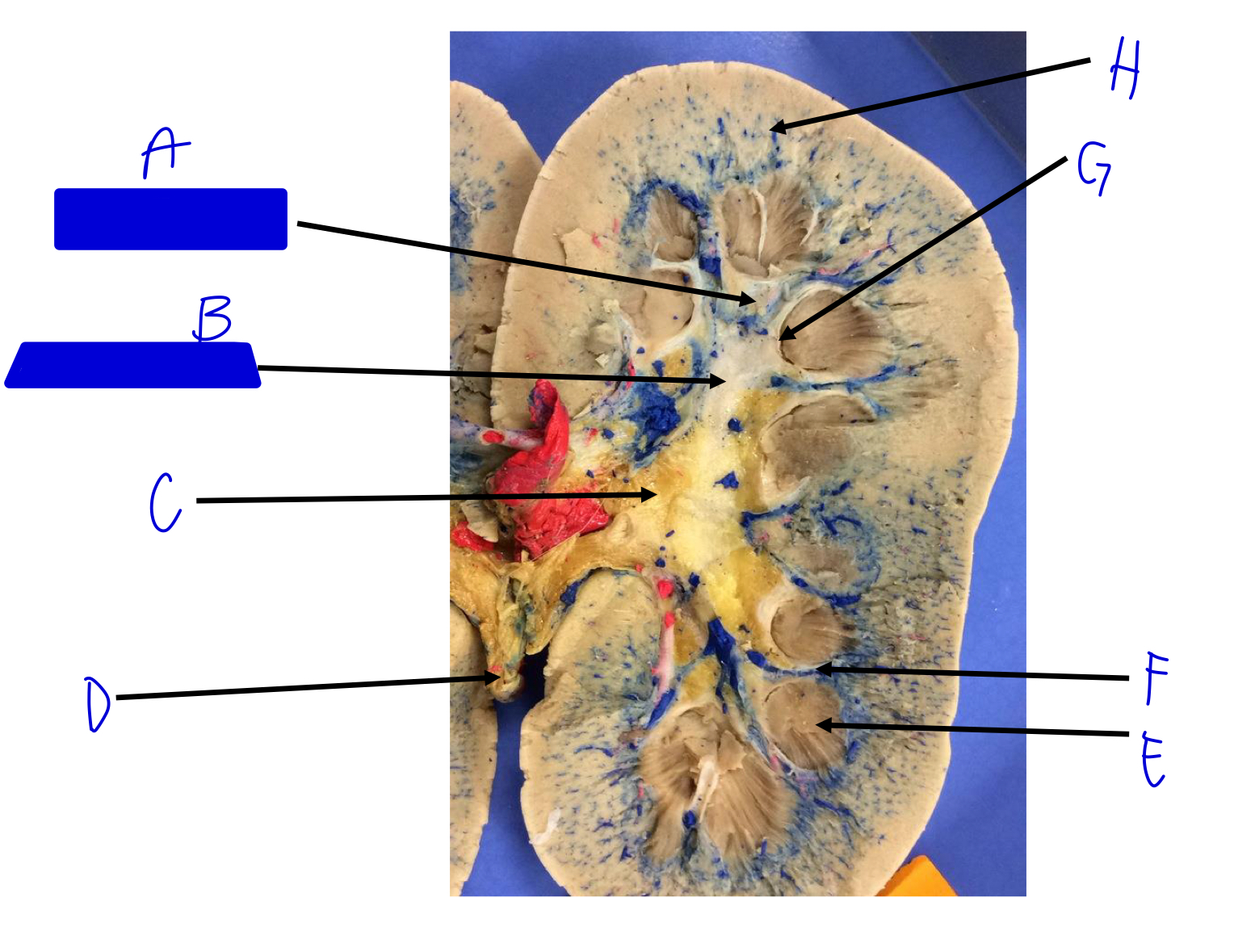
G
renal papilla (the tip; where the urine is)
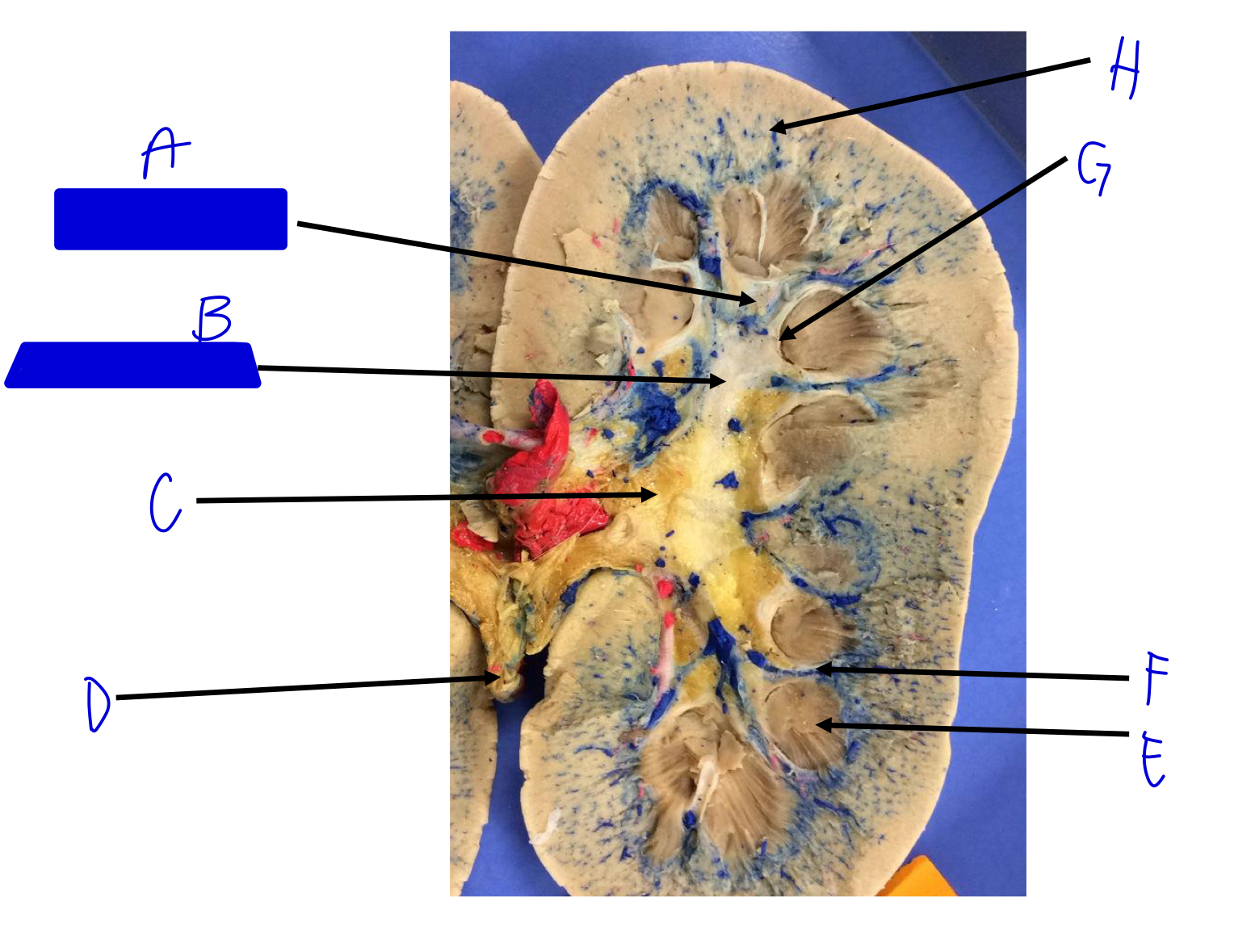
H
cortical radiate arteries and veins (interlobular)
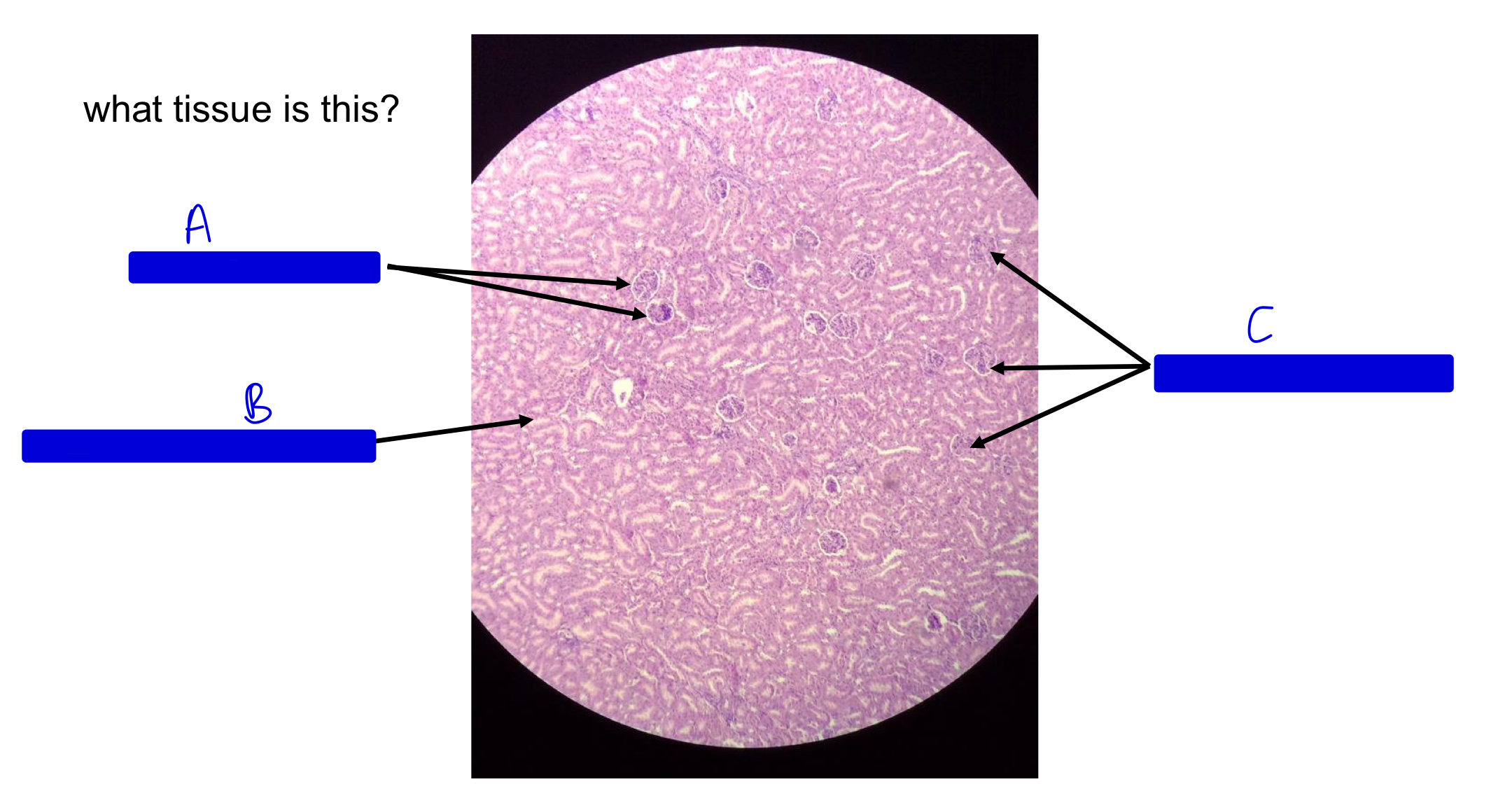
what tissue is this?
kidney
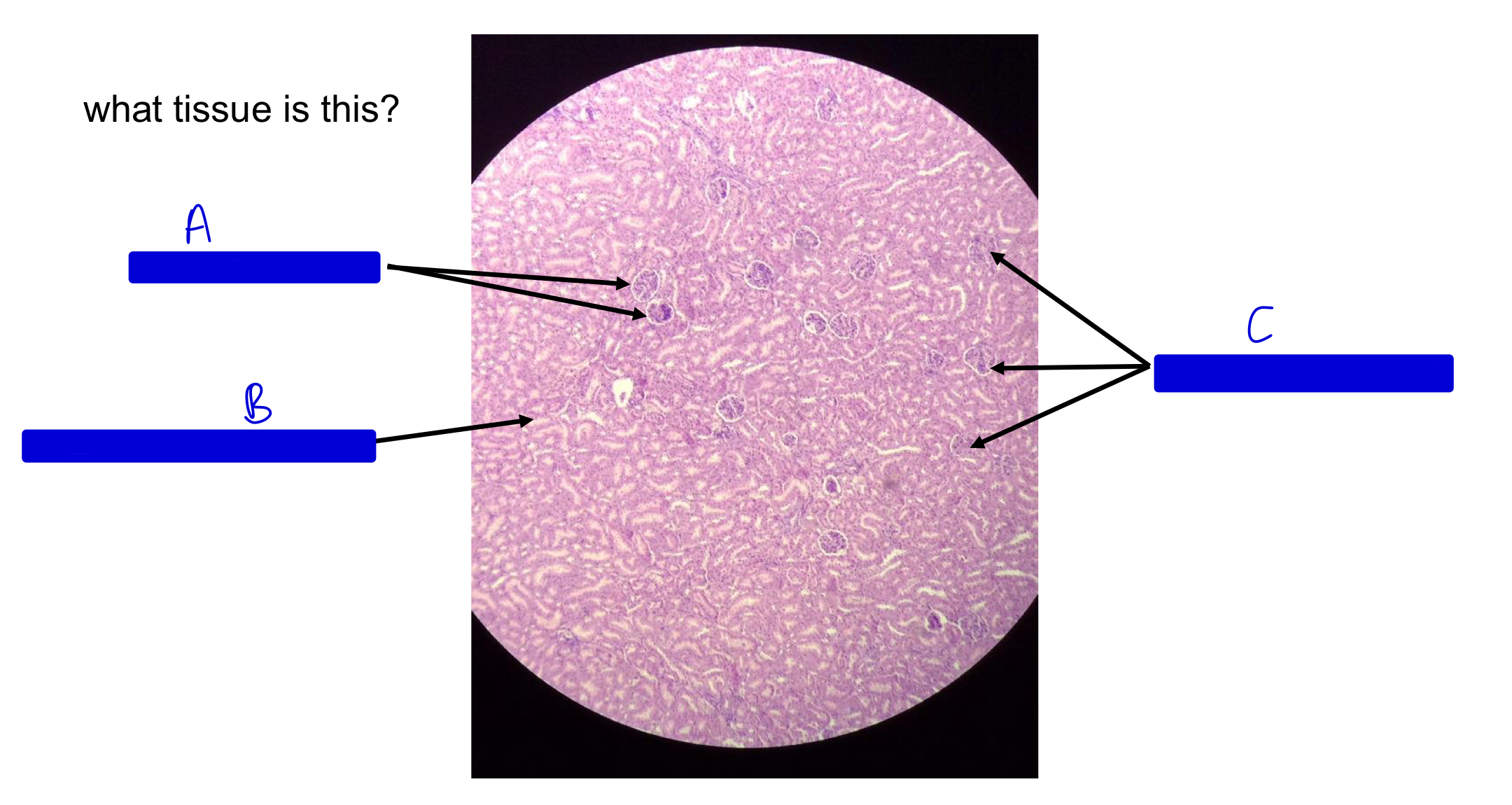
A
JM renal corpuscle (JM by the medulla!)
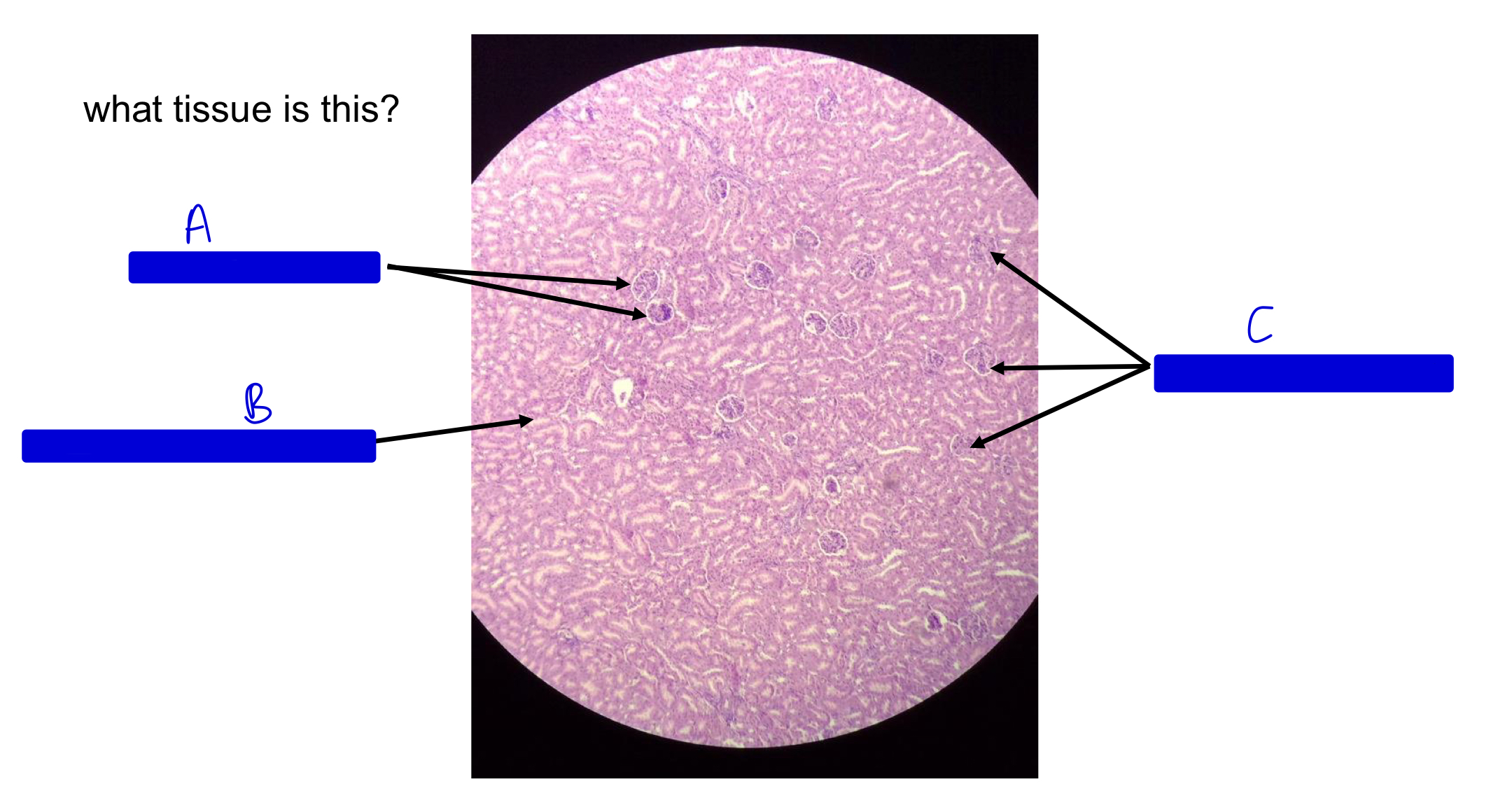
B
collecting ducts in medulla
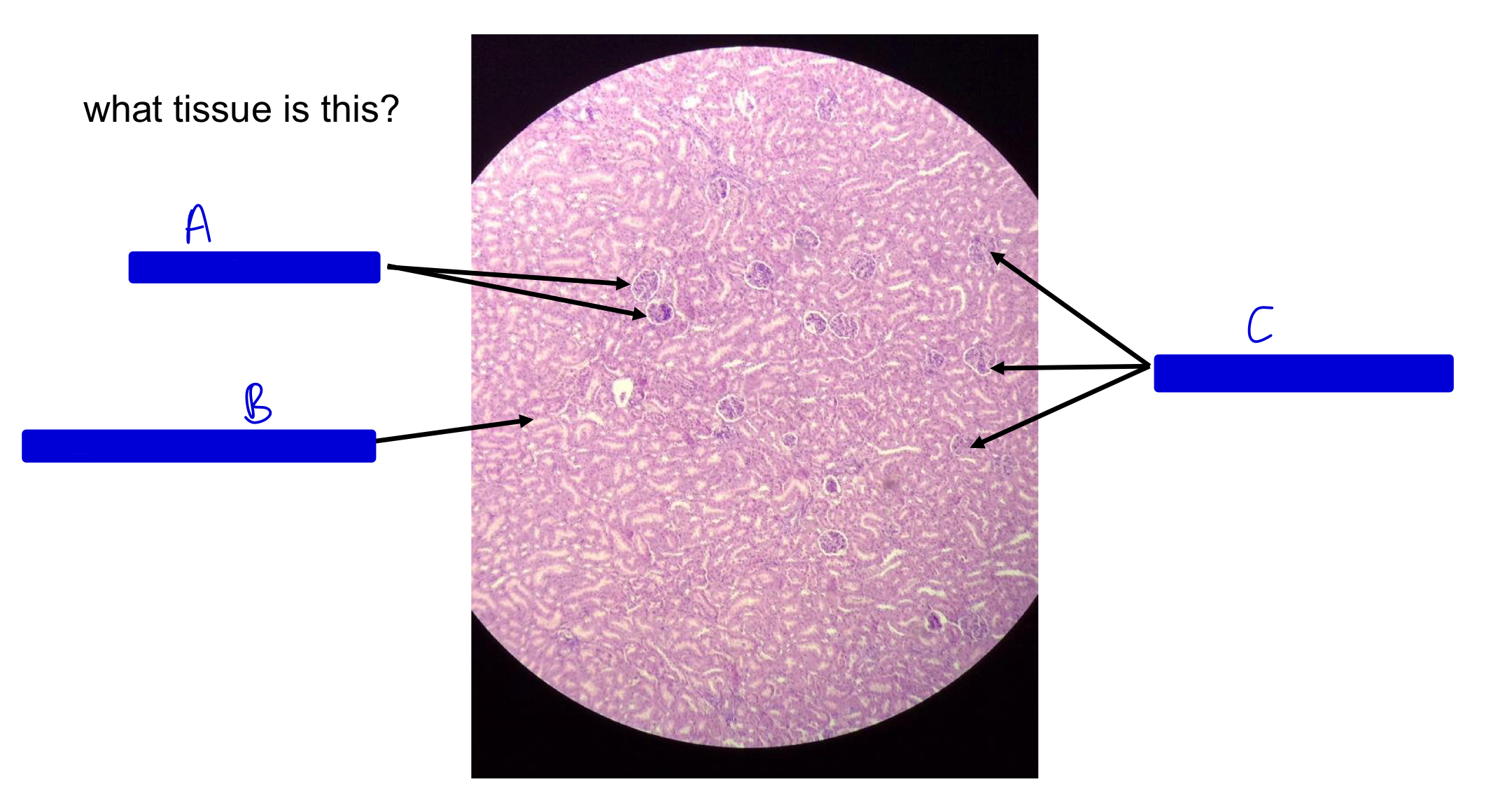
C
cortical renal corpuscle (far from medulla; cortex side!
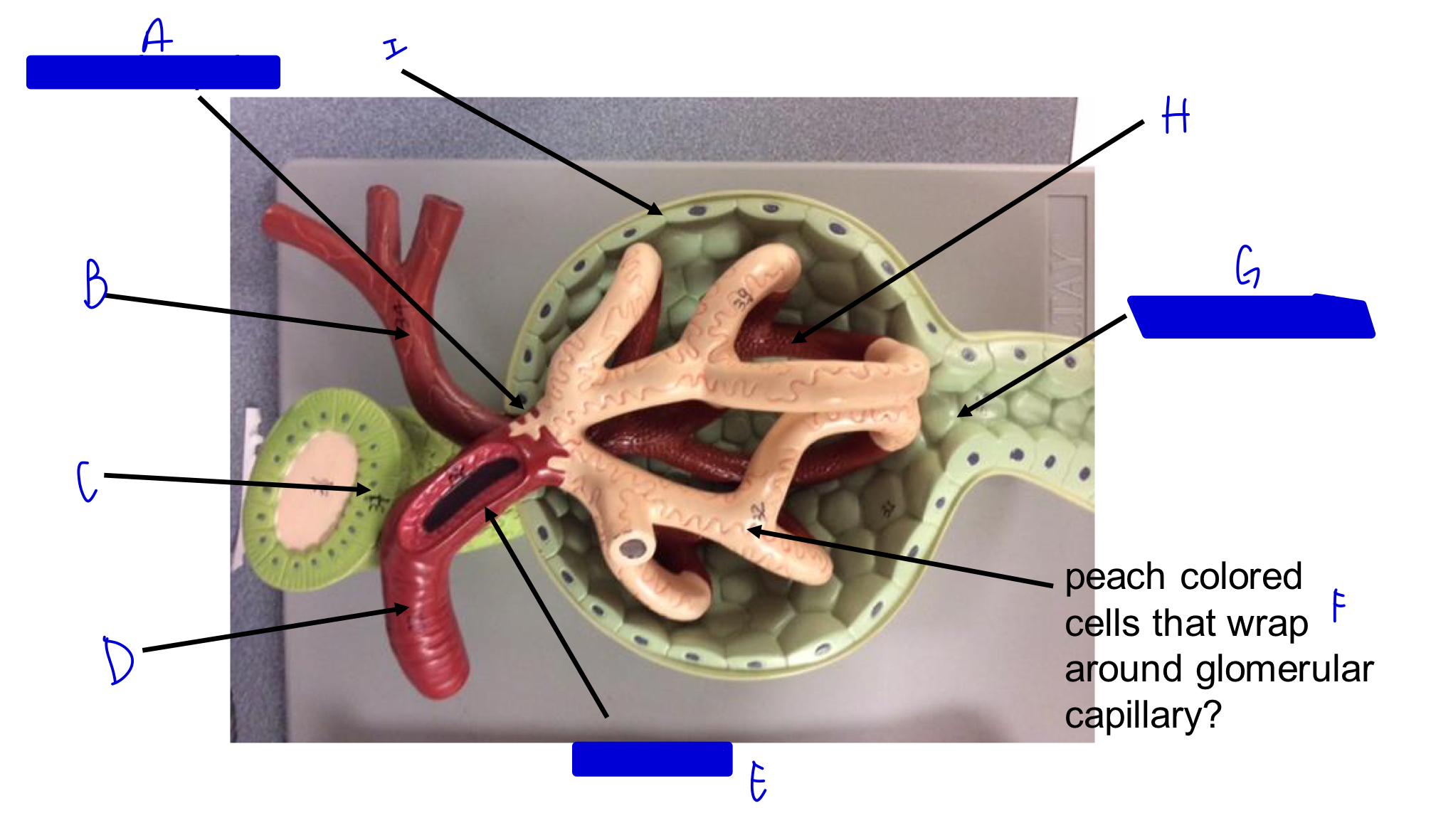
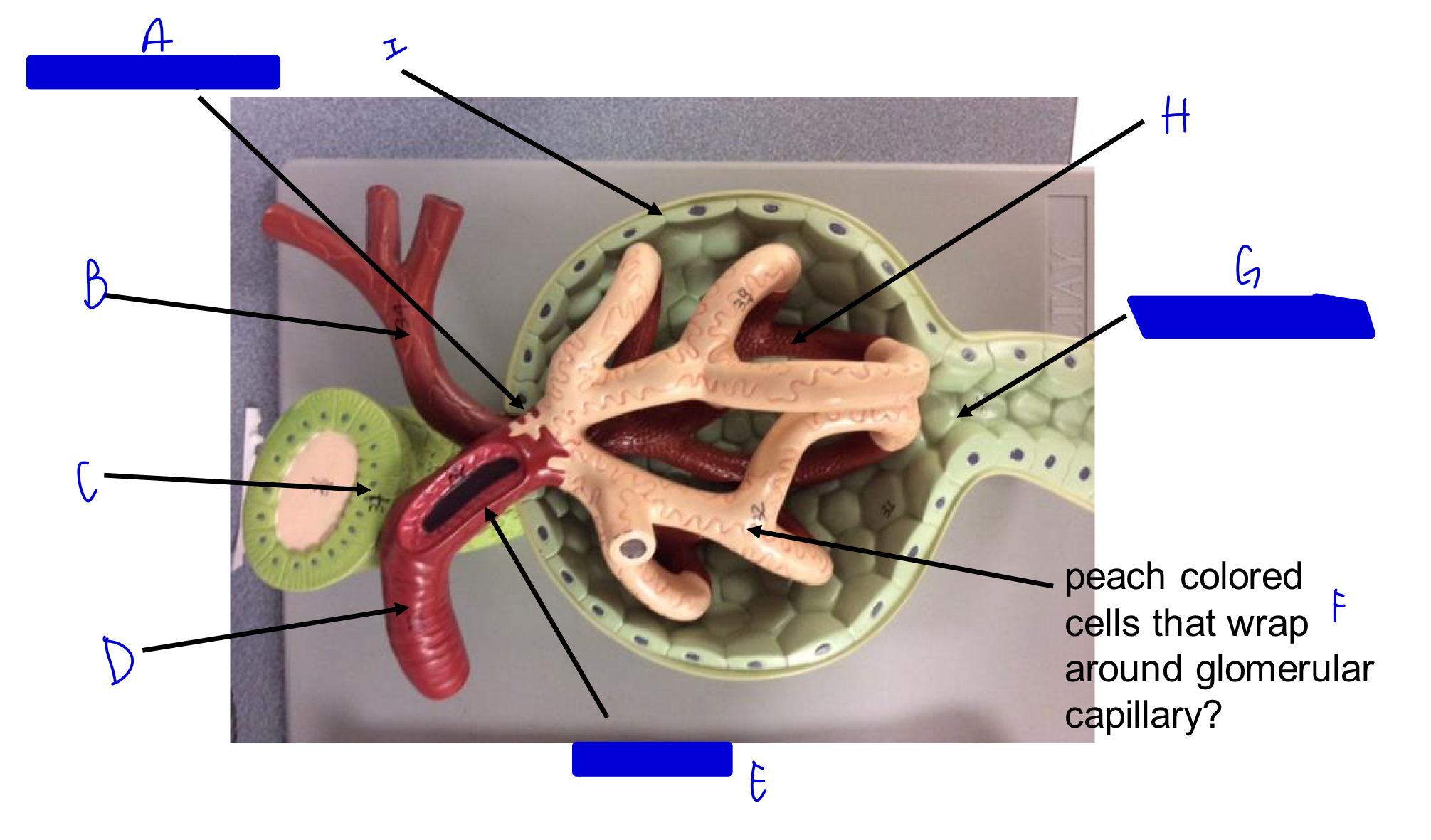
A
vascular pole
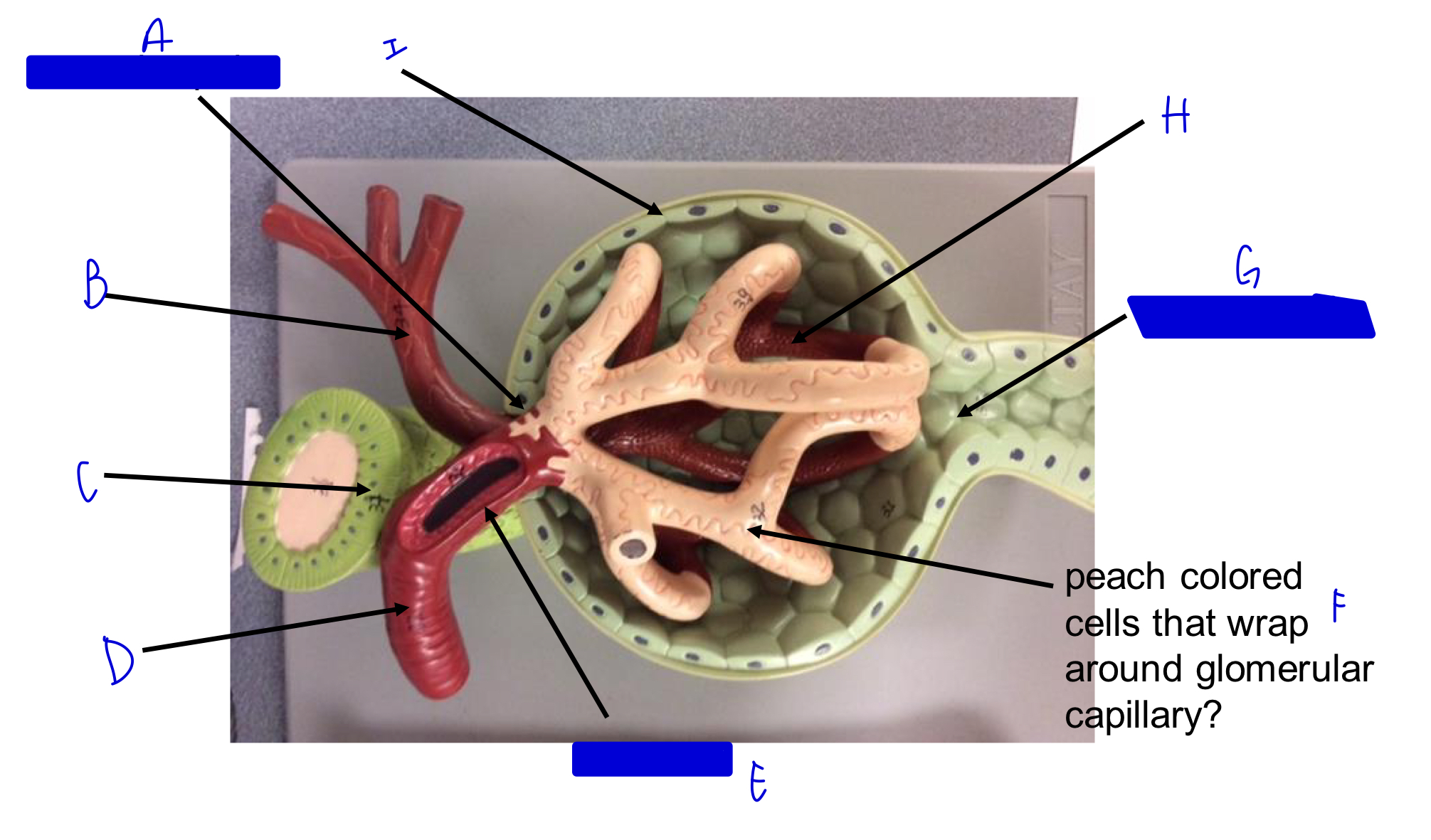
B
efferent arteriole
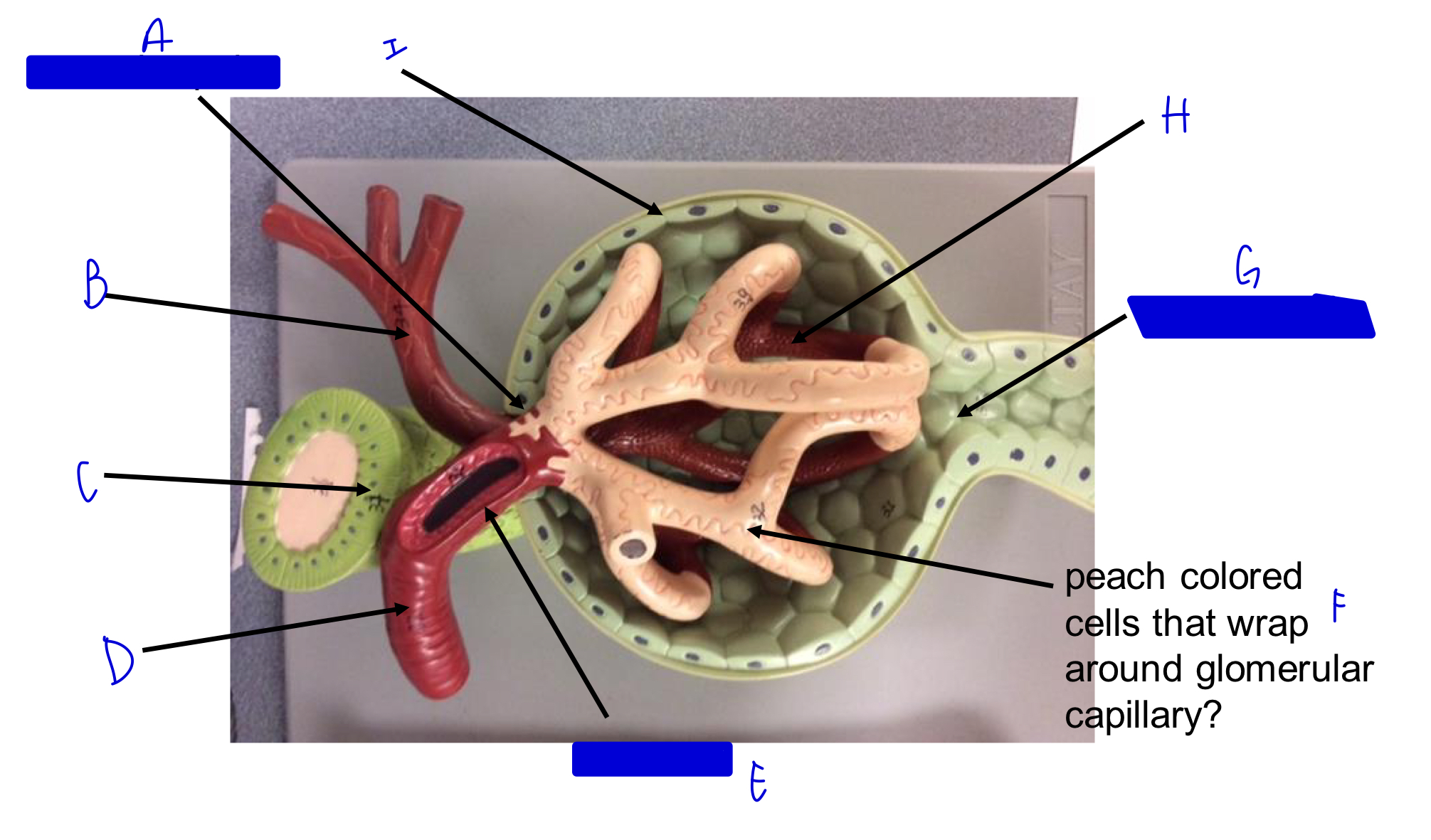
C
macula densa *
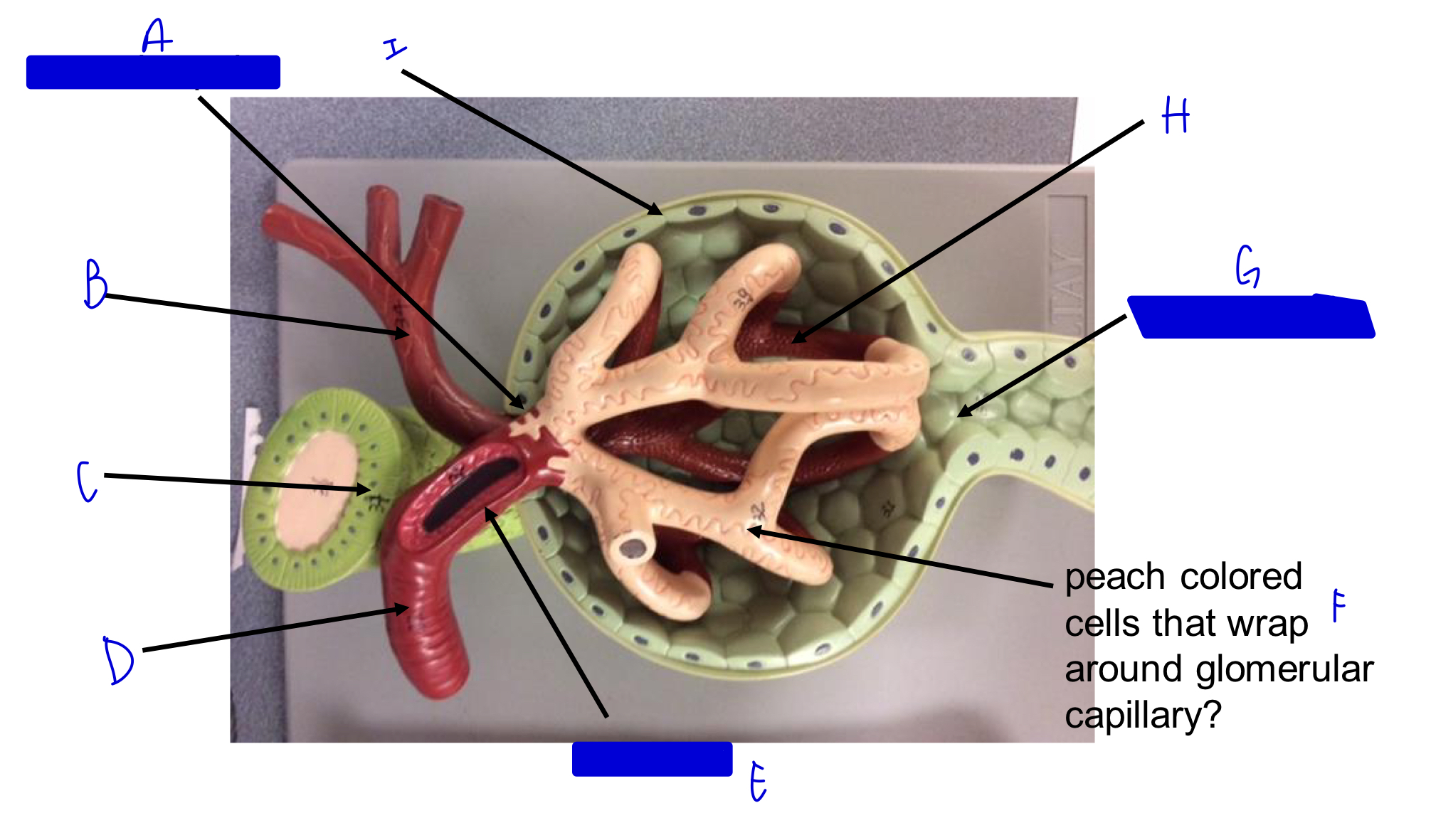
D
afferent arteriole
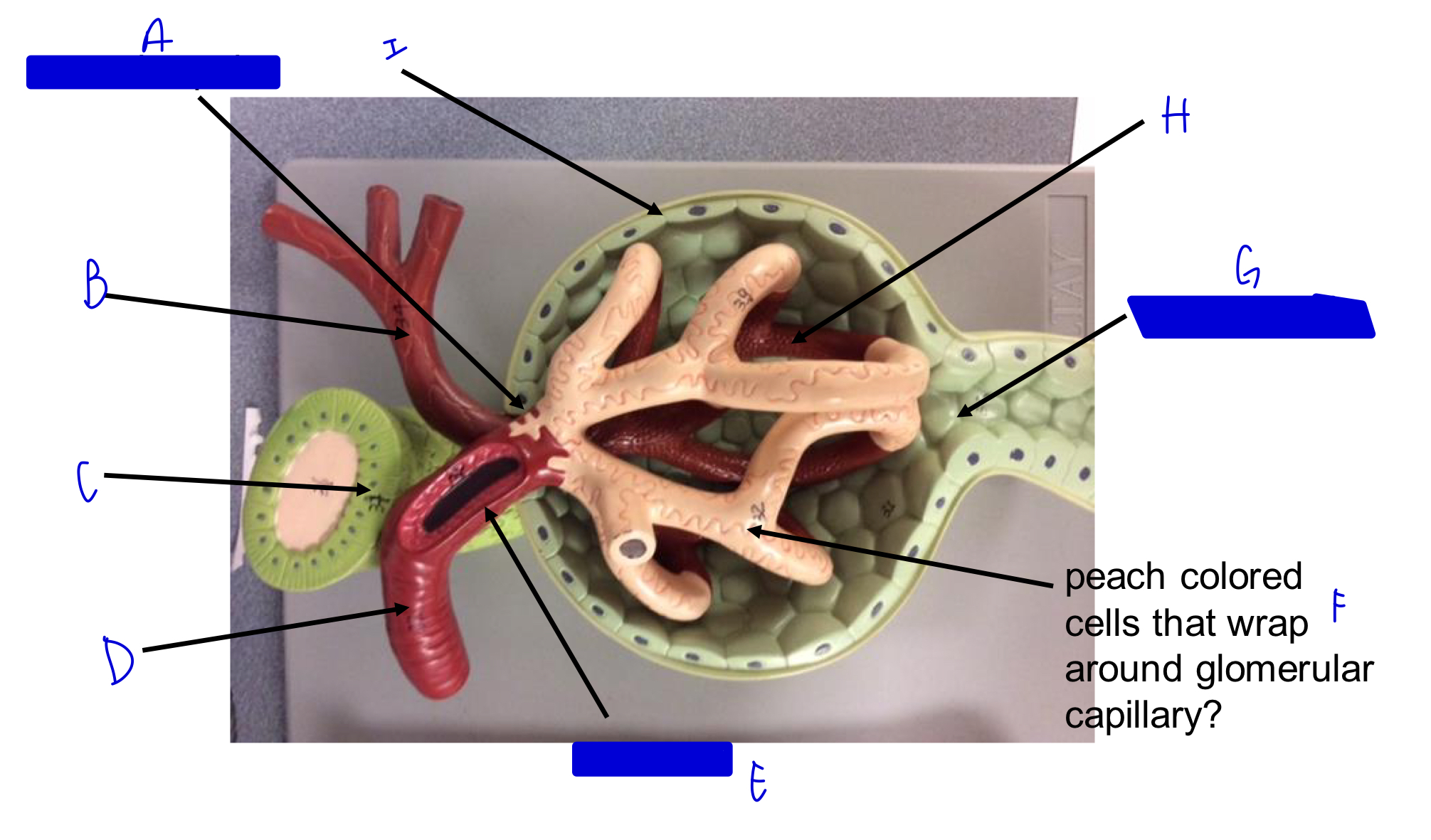
E
JG cells that wrap around the afferent arteriole *
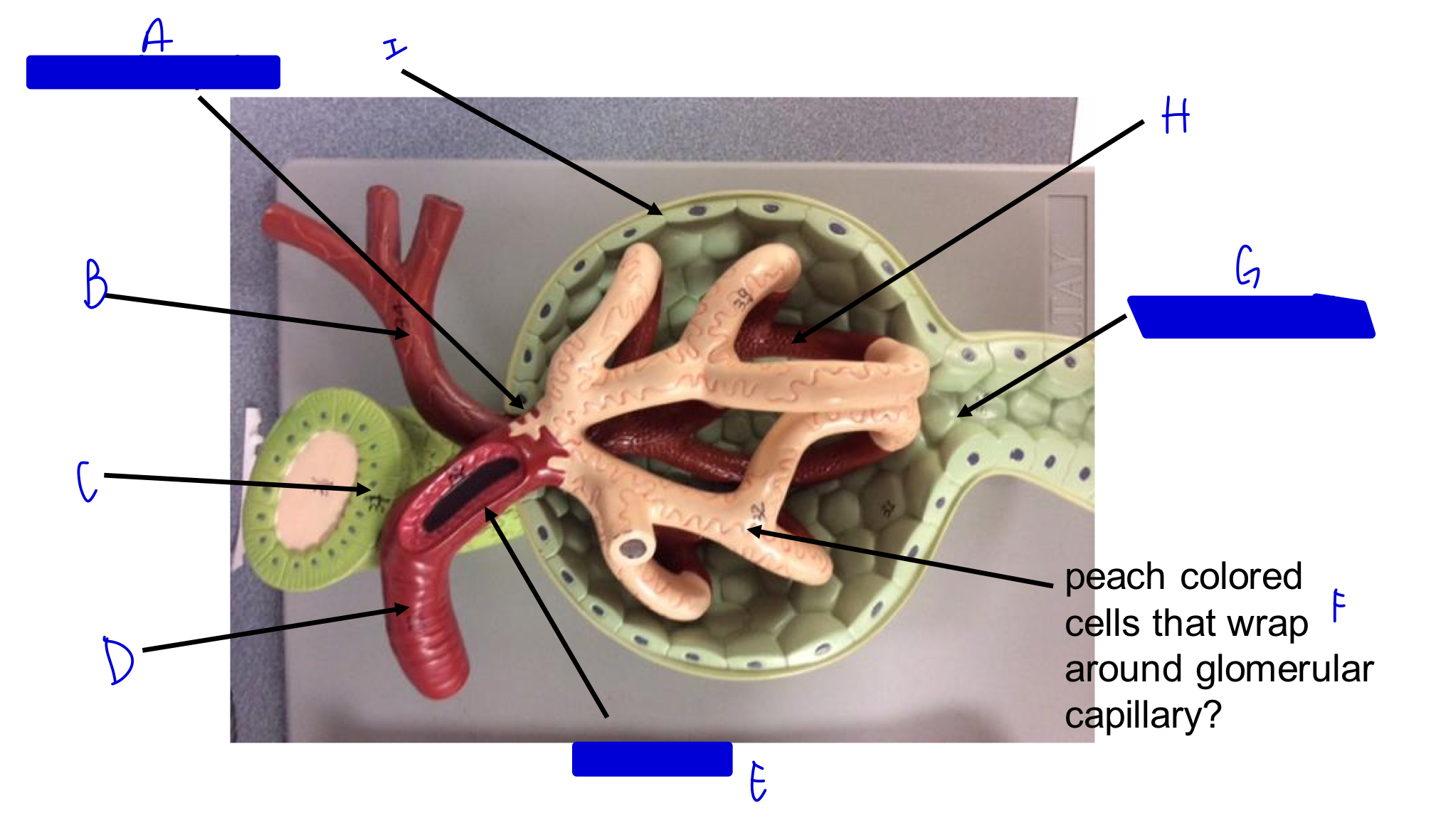
F
podocytes (look like feet)
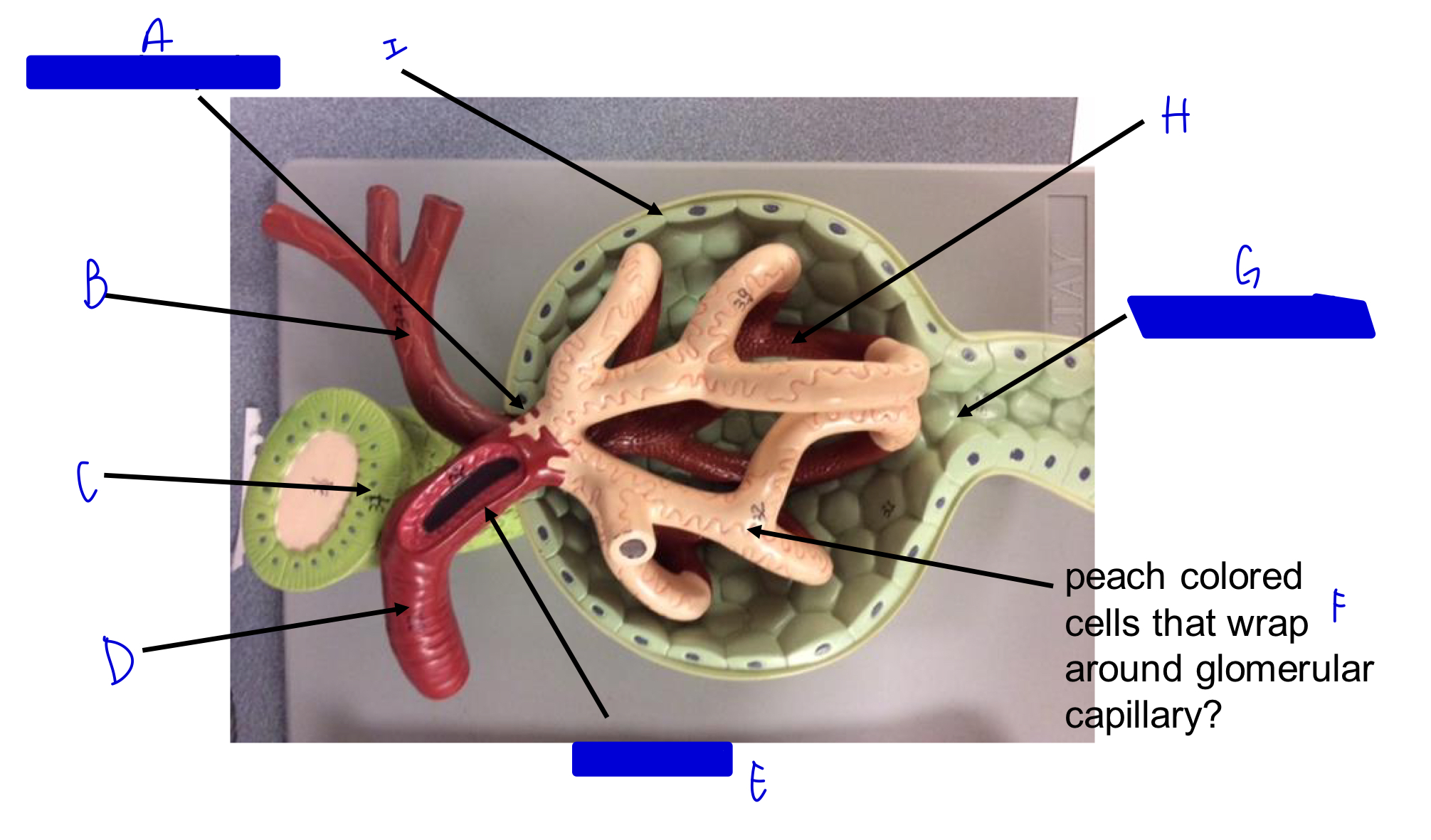
G
urinary pole
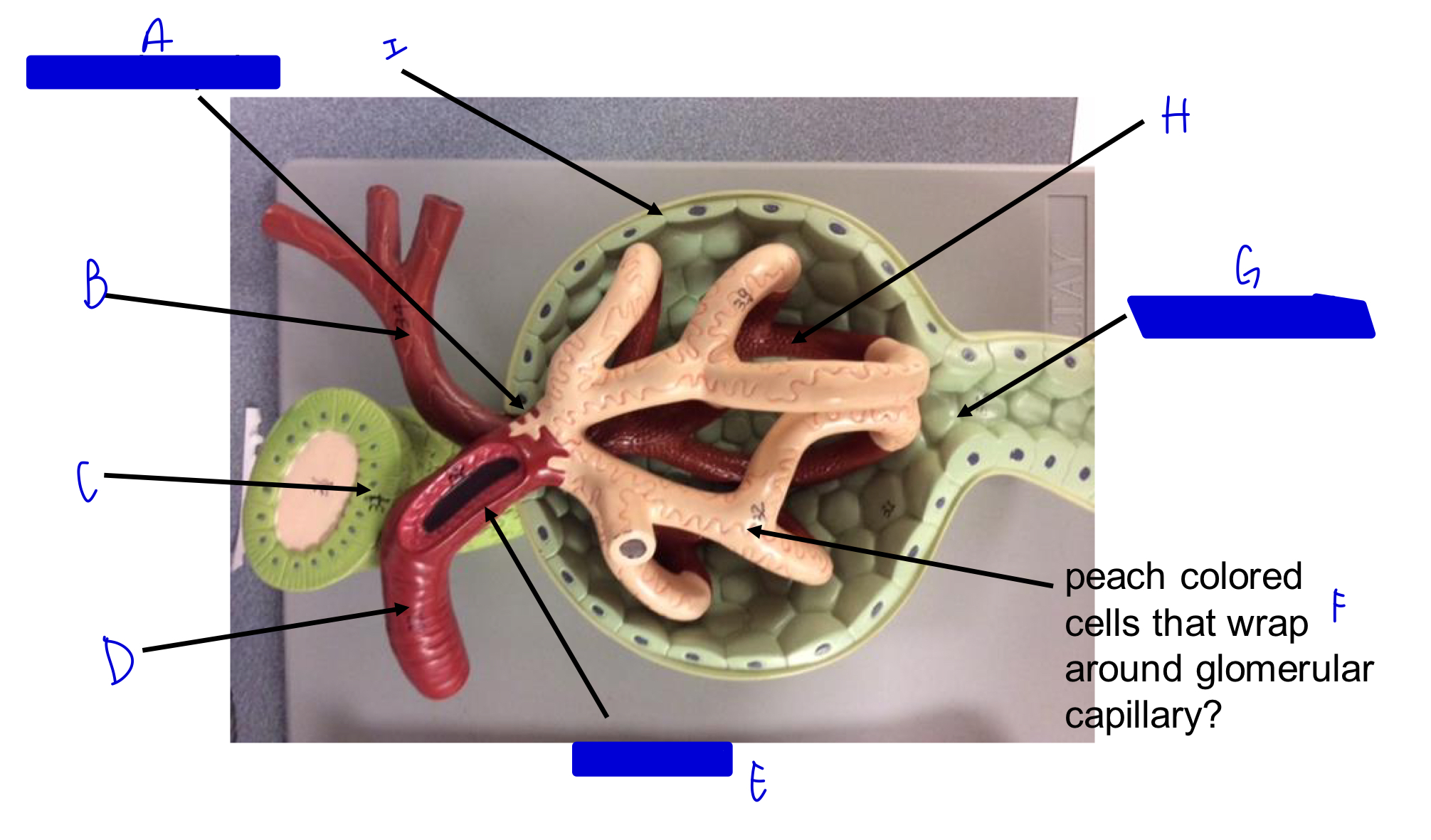
H
glomerular capillary
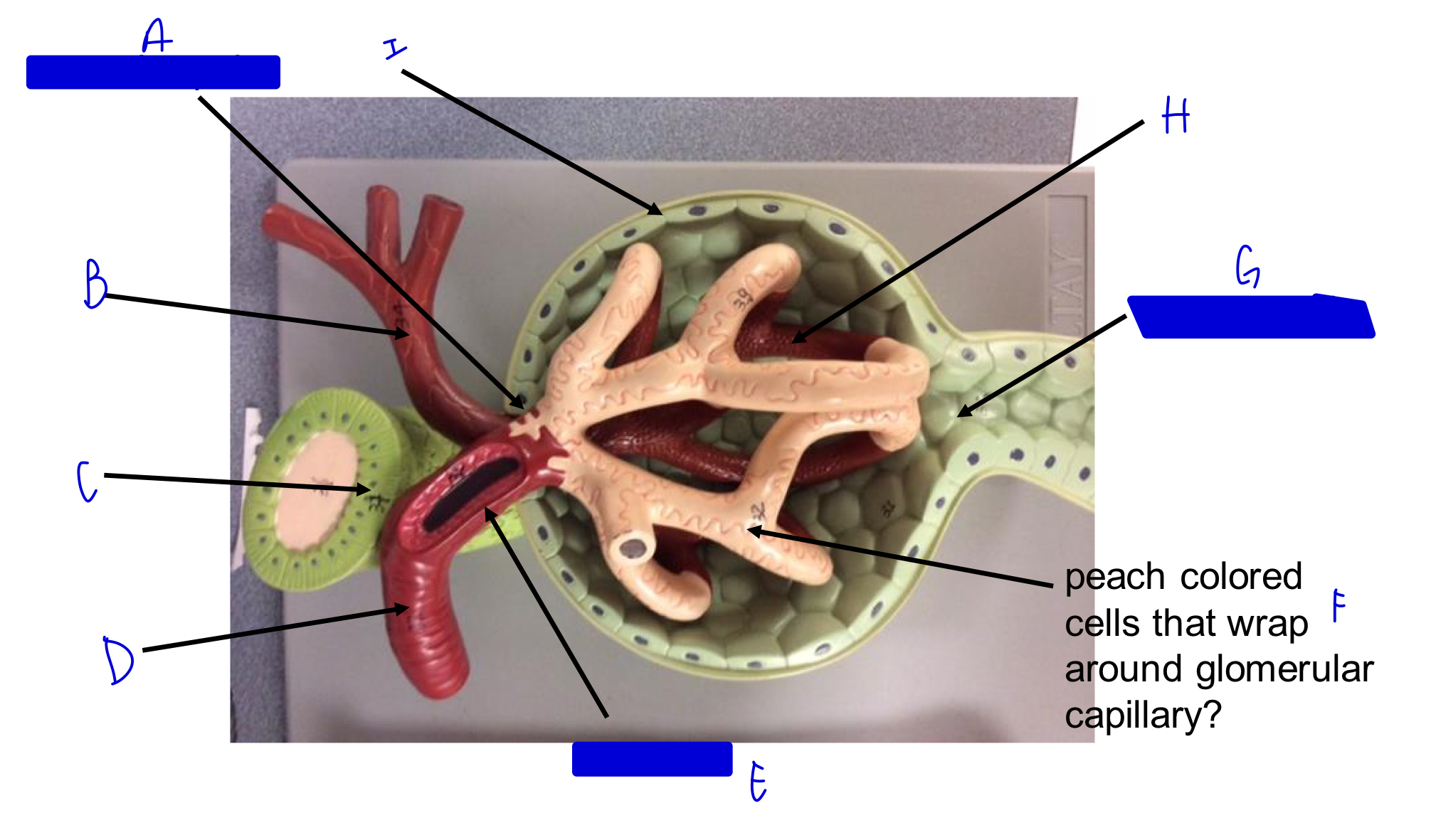
I
capsule
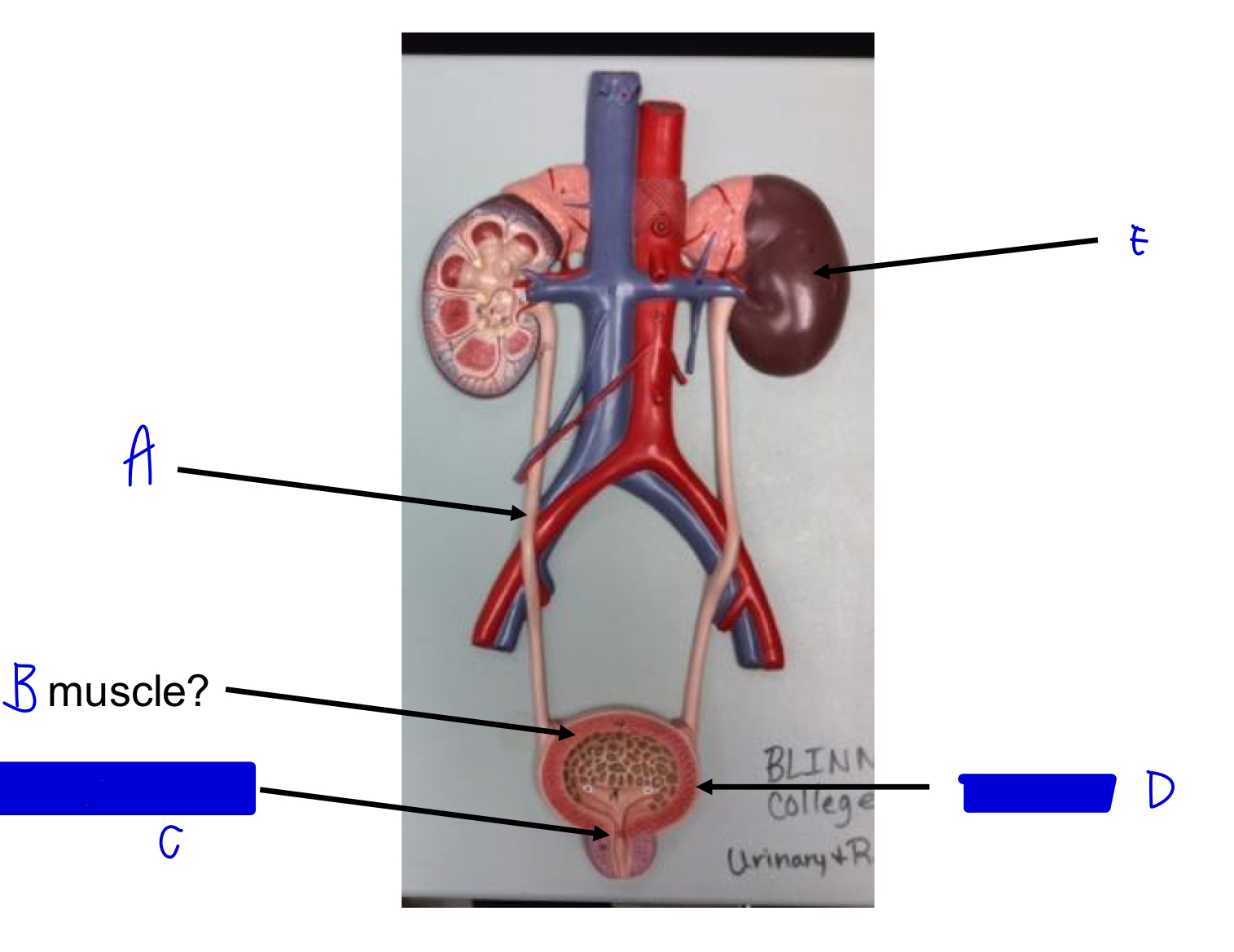
E
kidney
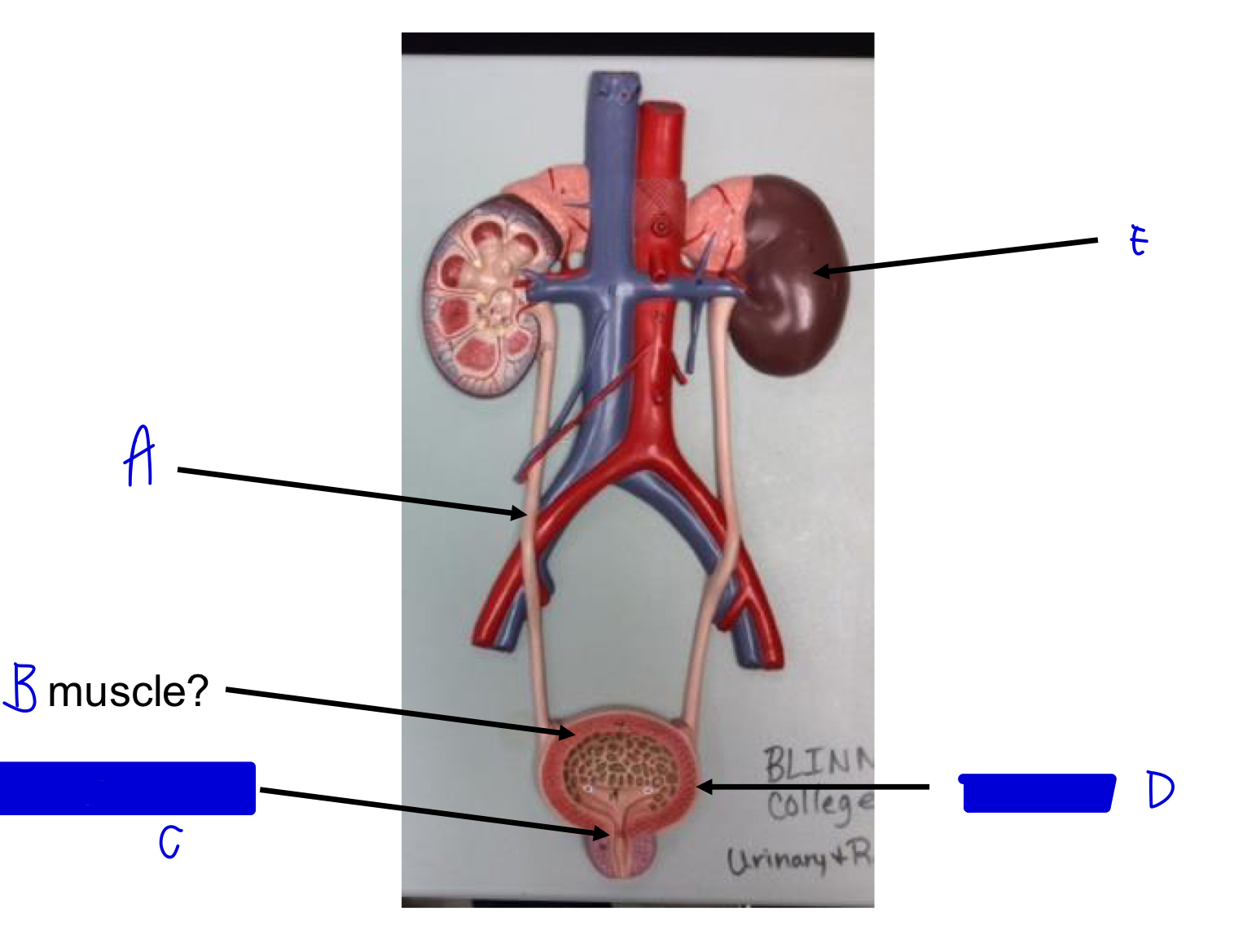
D
urinary bladder
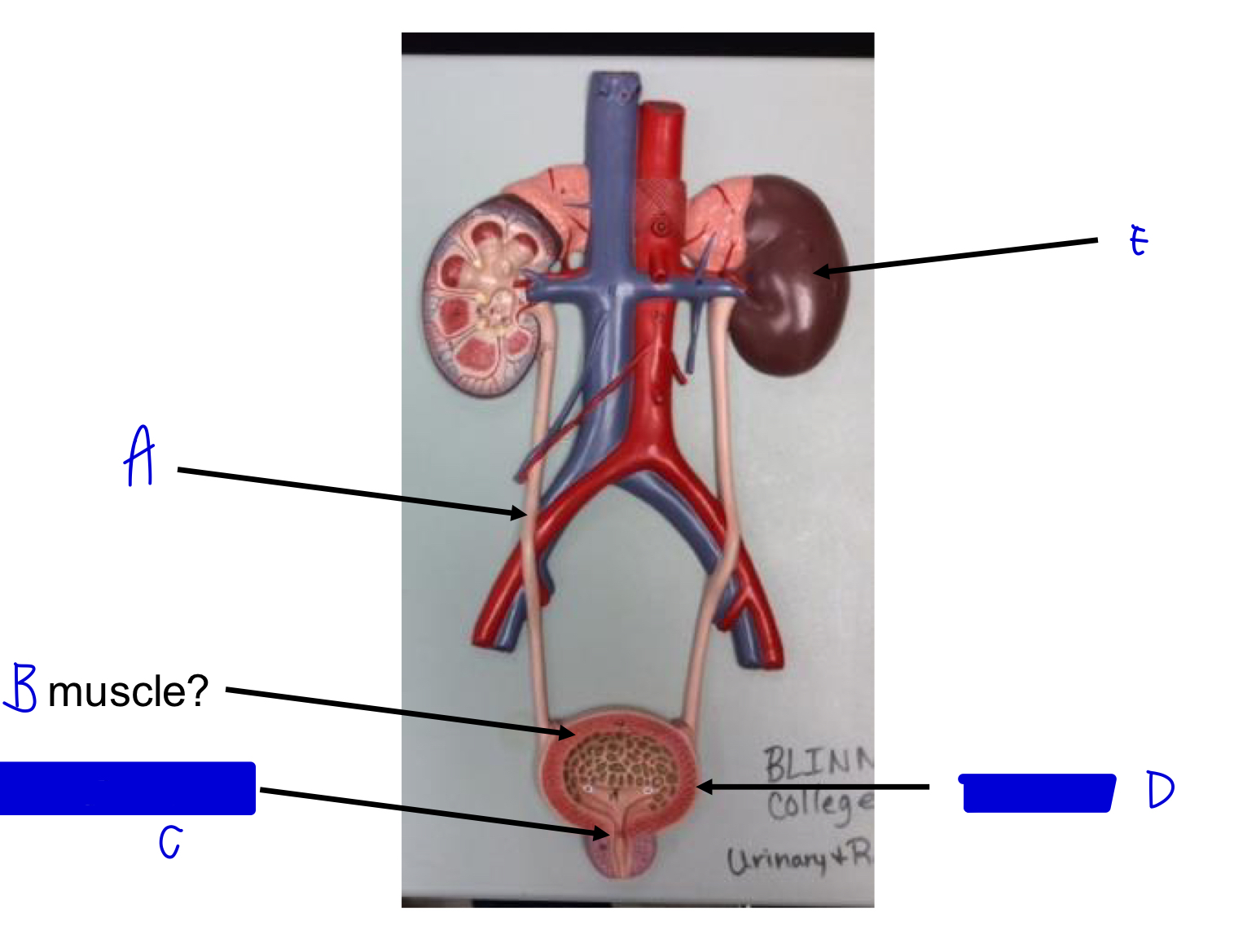
C
internal urethral sphincter (skeletal!)
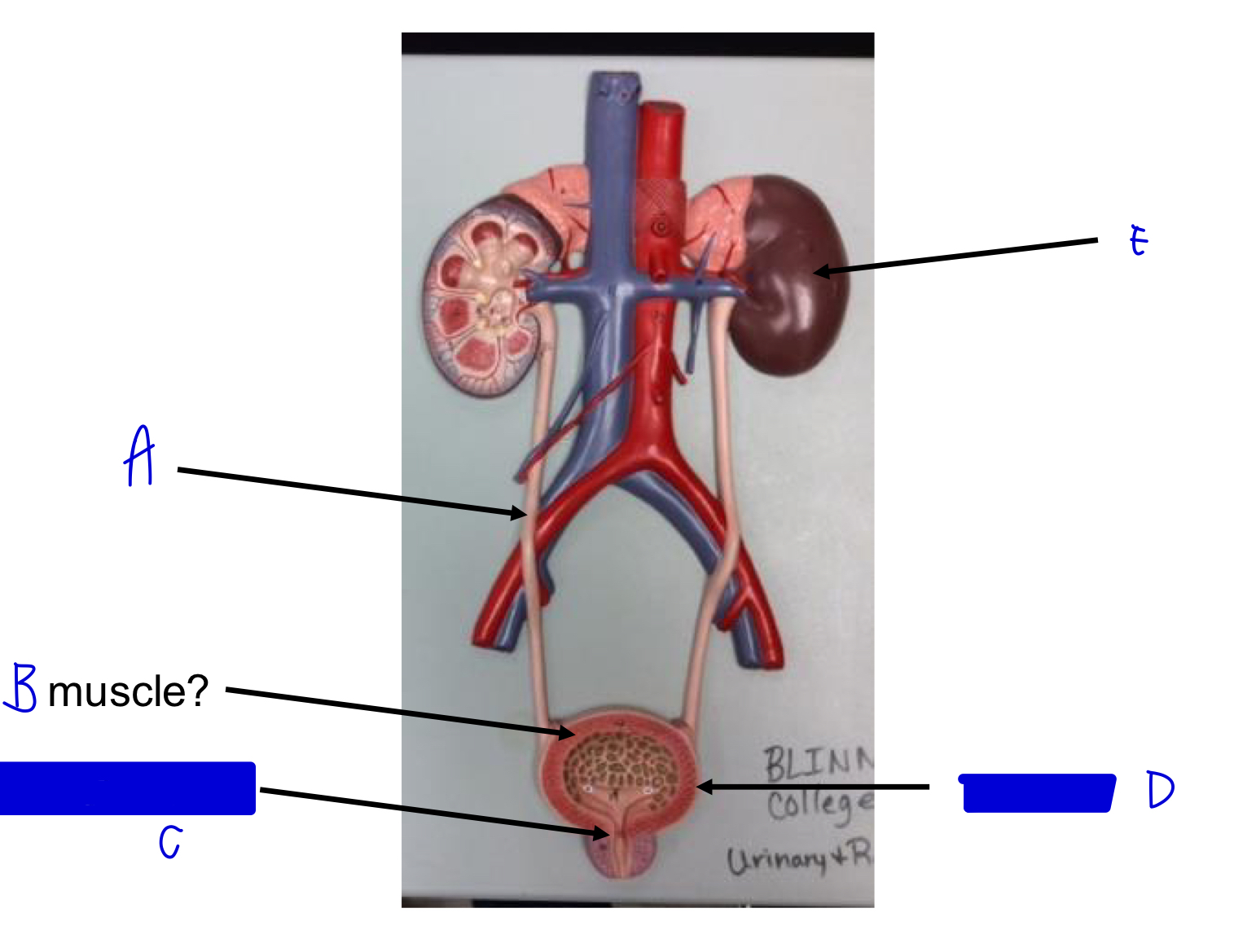
B
detrusor muscle (smooth!)
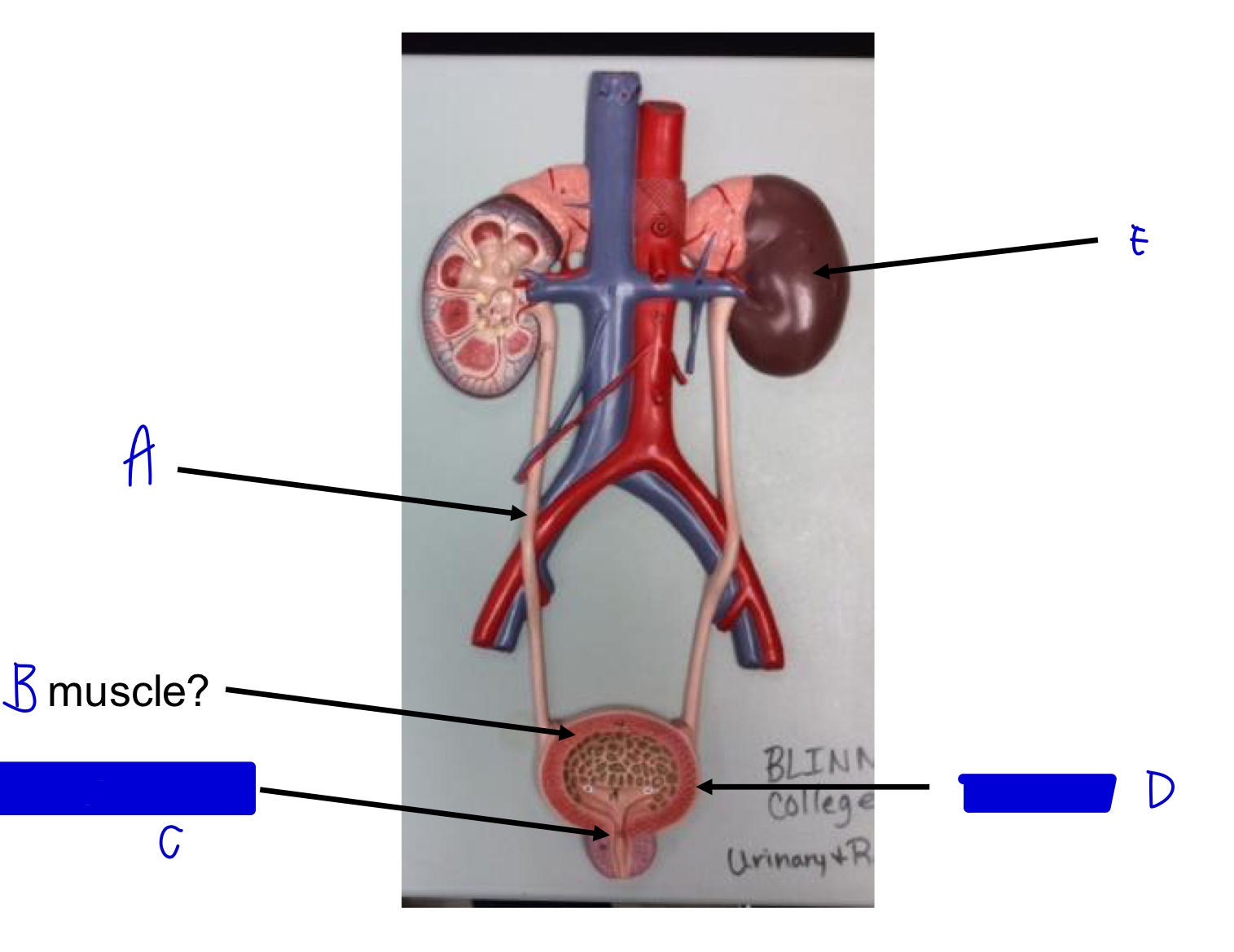
A
ureter
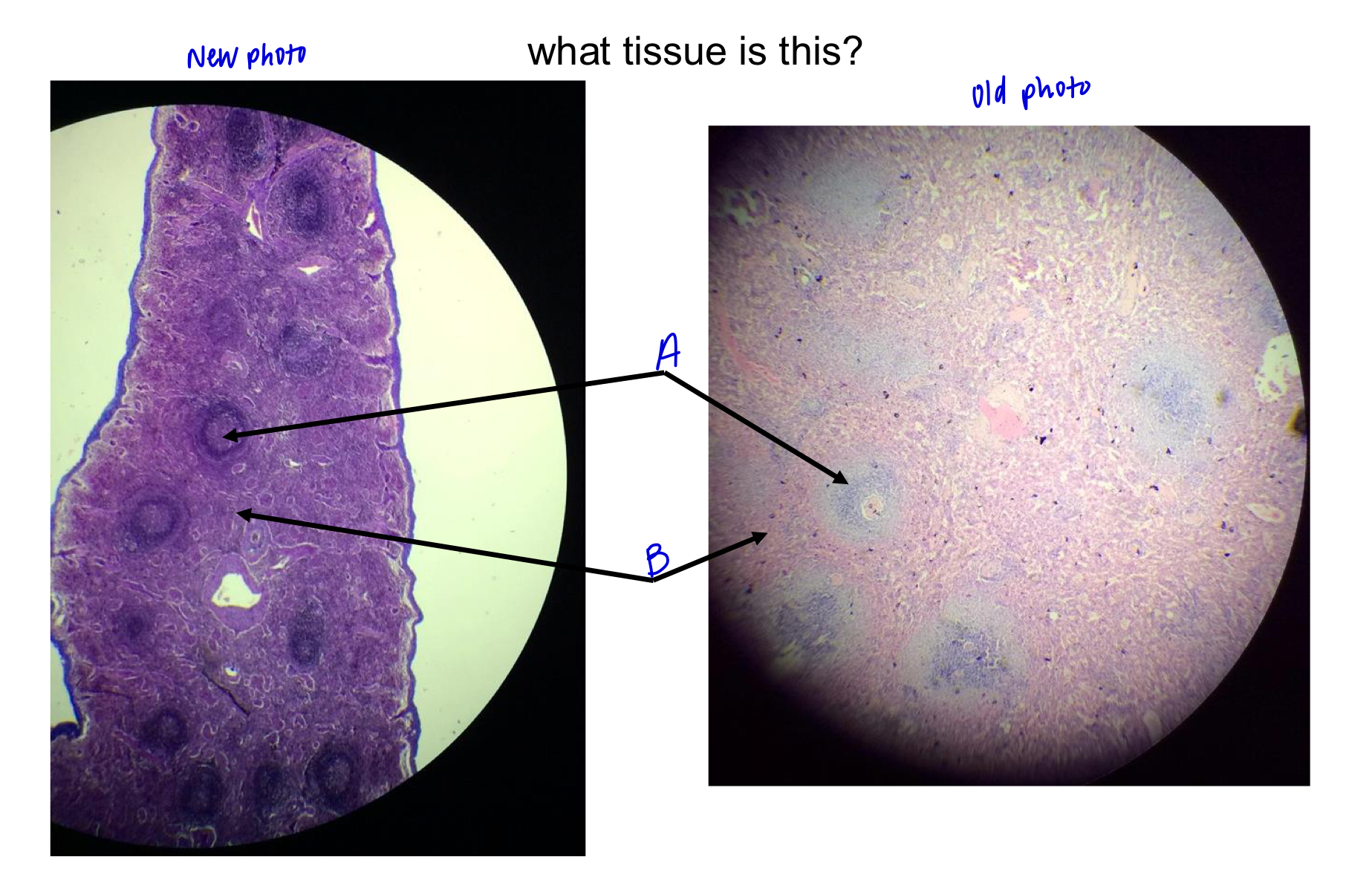
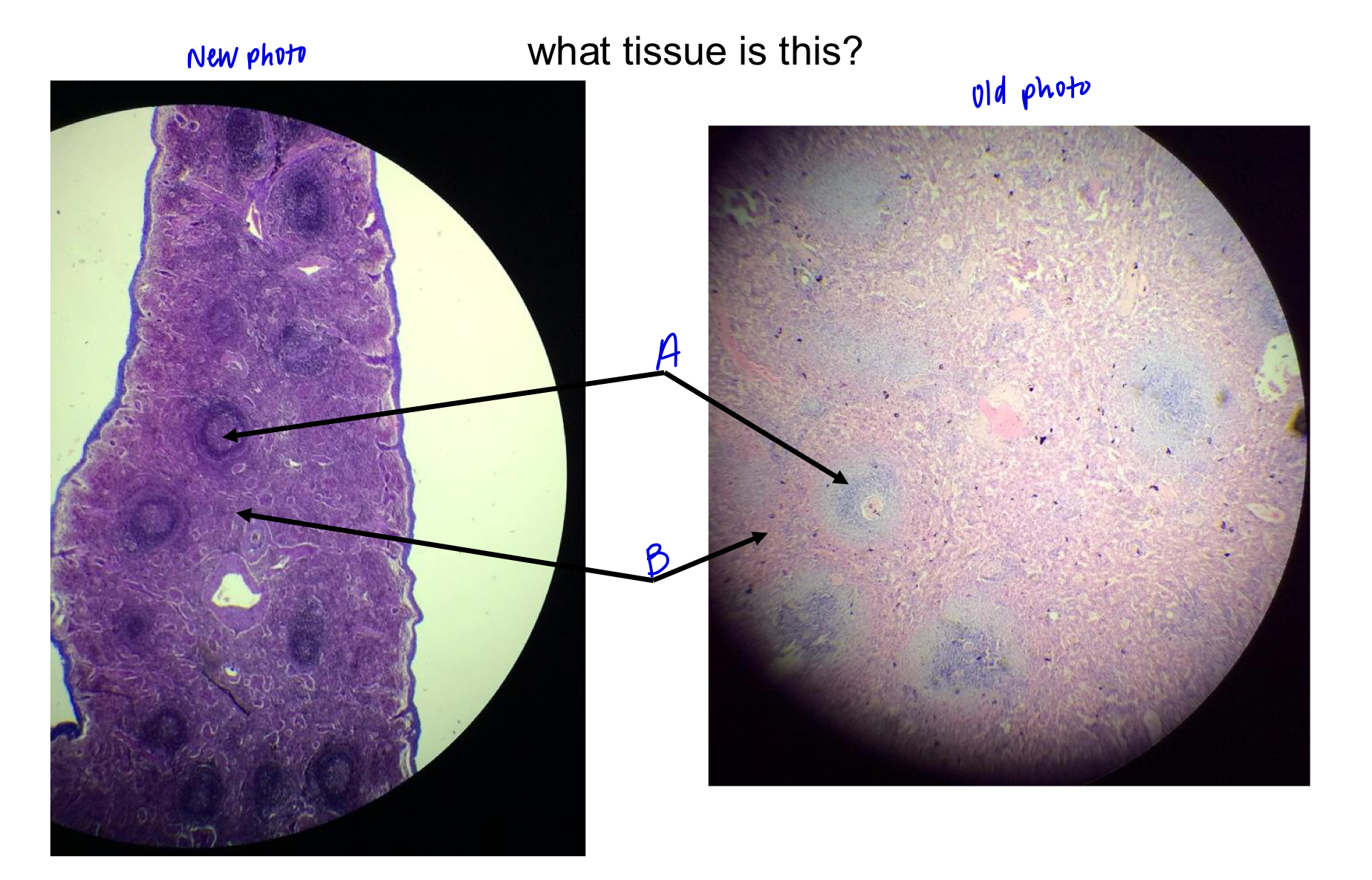
the thymus gets smaller are you get older and the nodules start to
spread out.
the thymus is where _____ of T lymphocytes takes place.
maturation
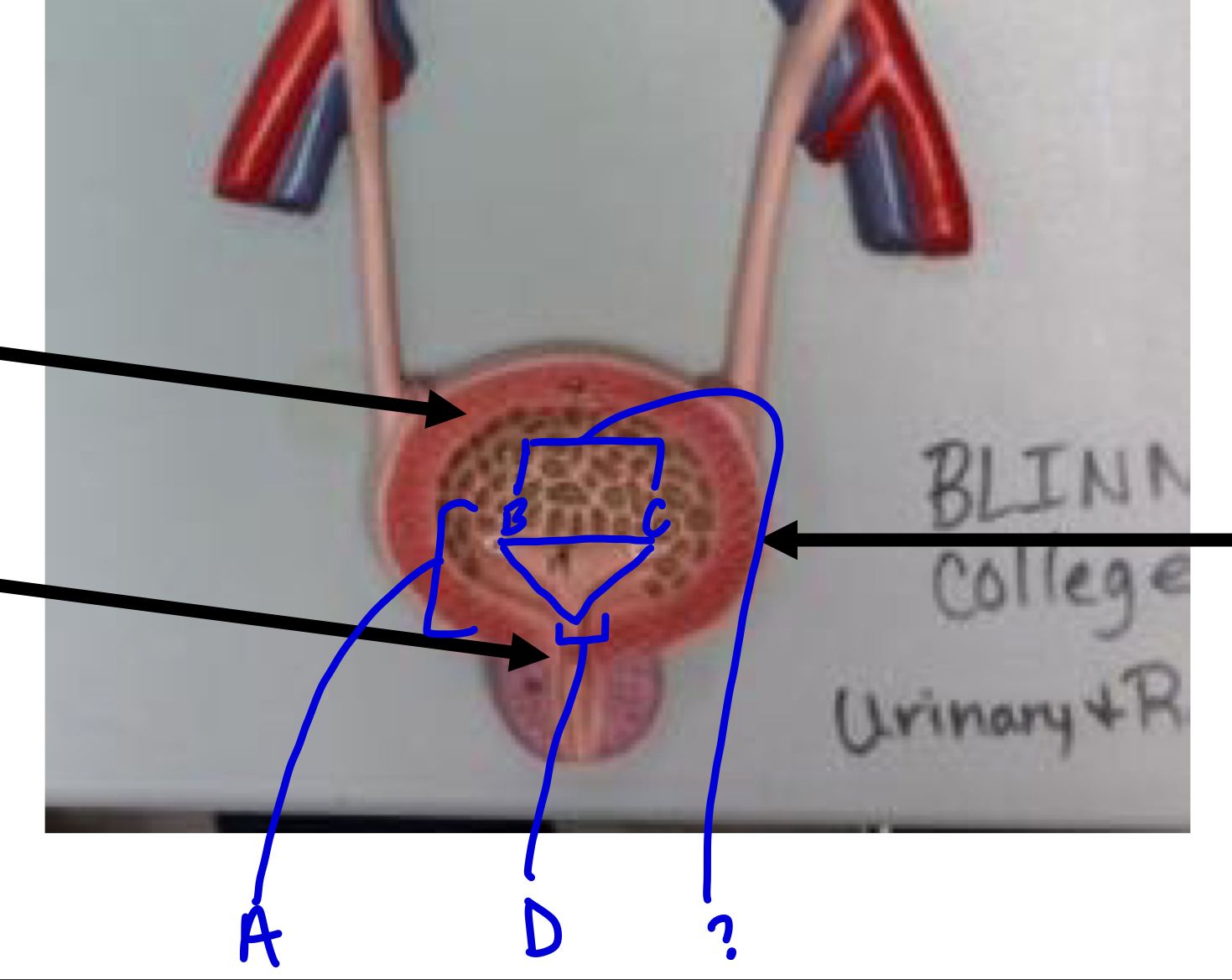
A
trigone
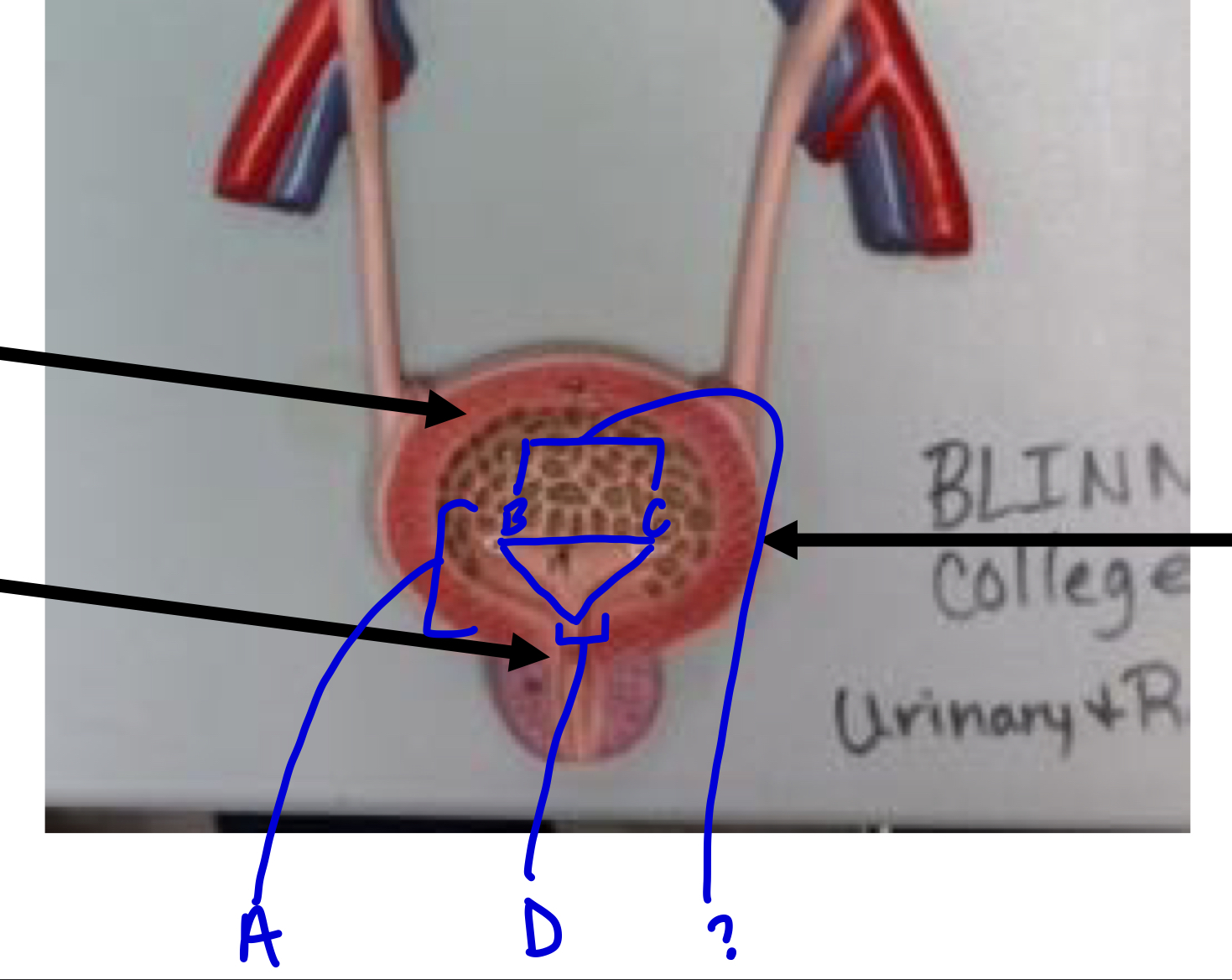
?
ureters
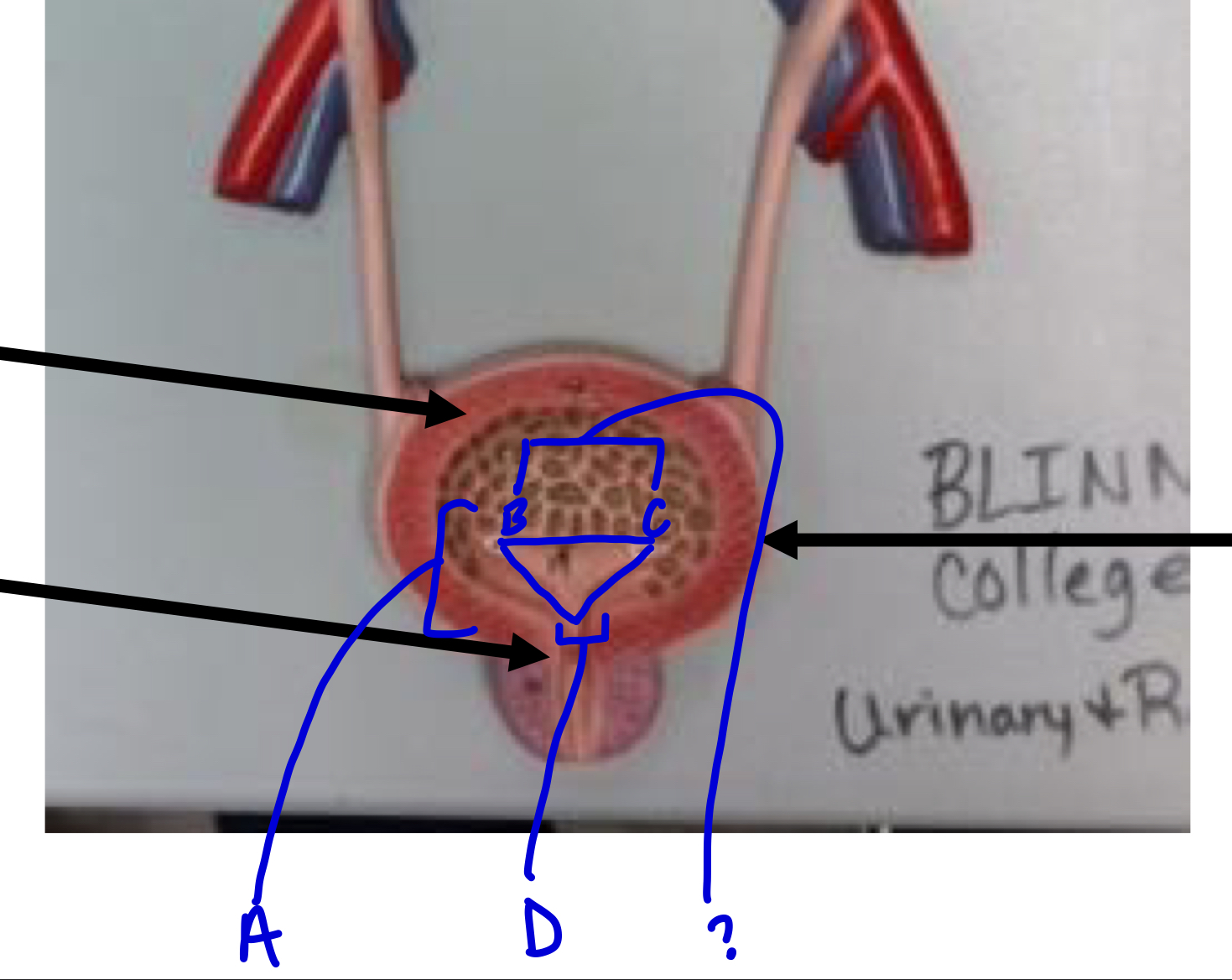
D
urethra
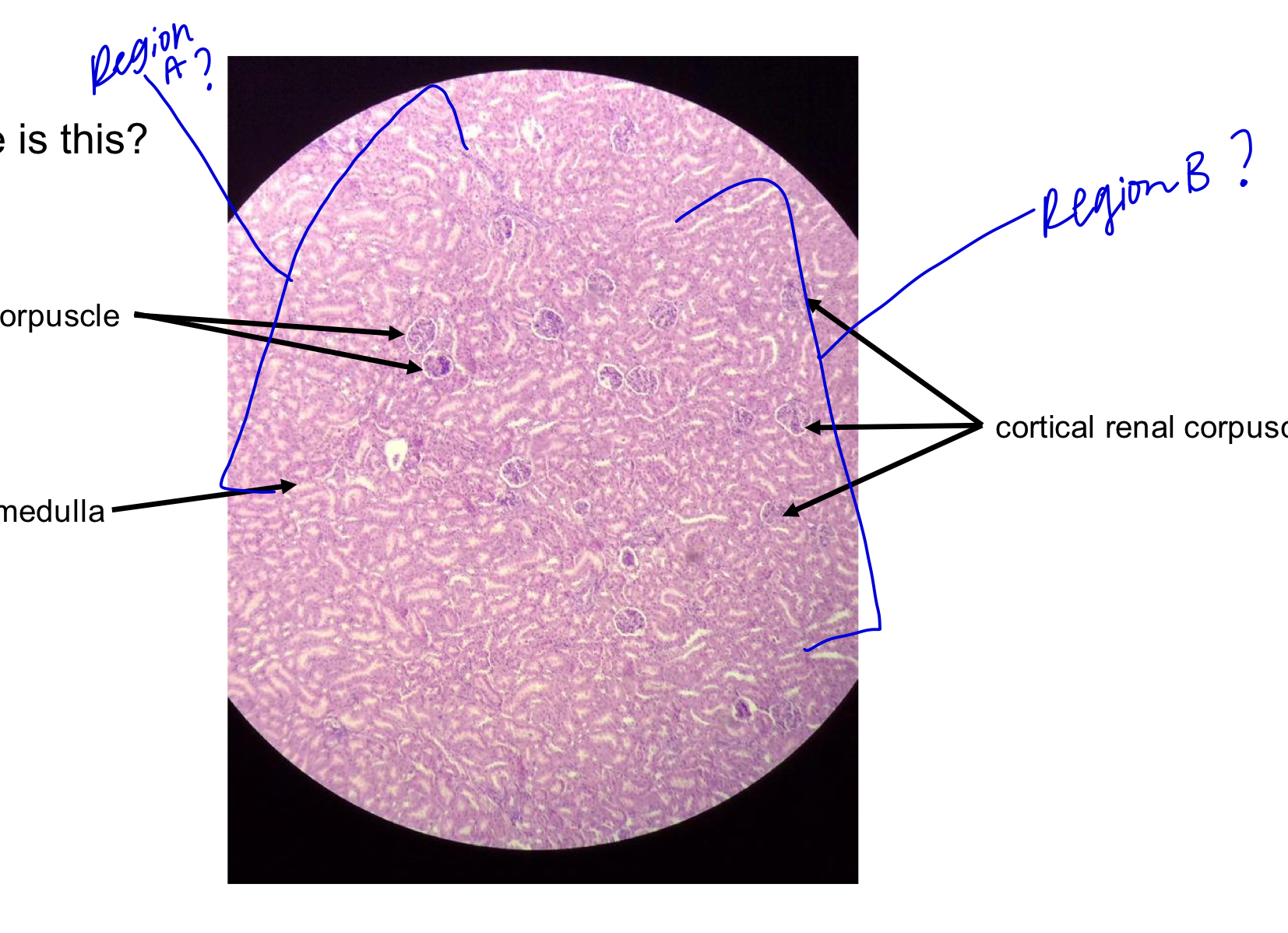
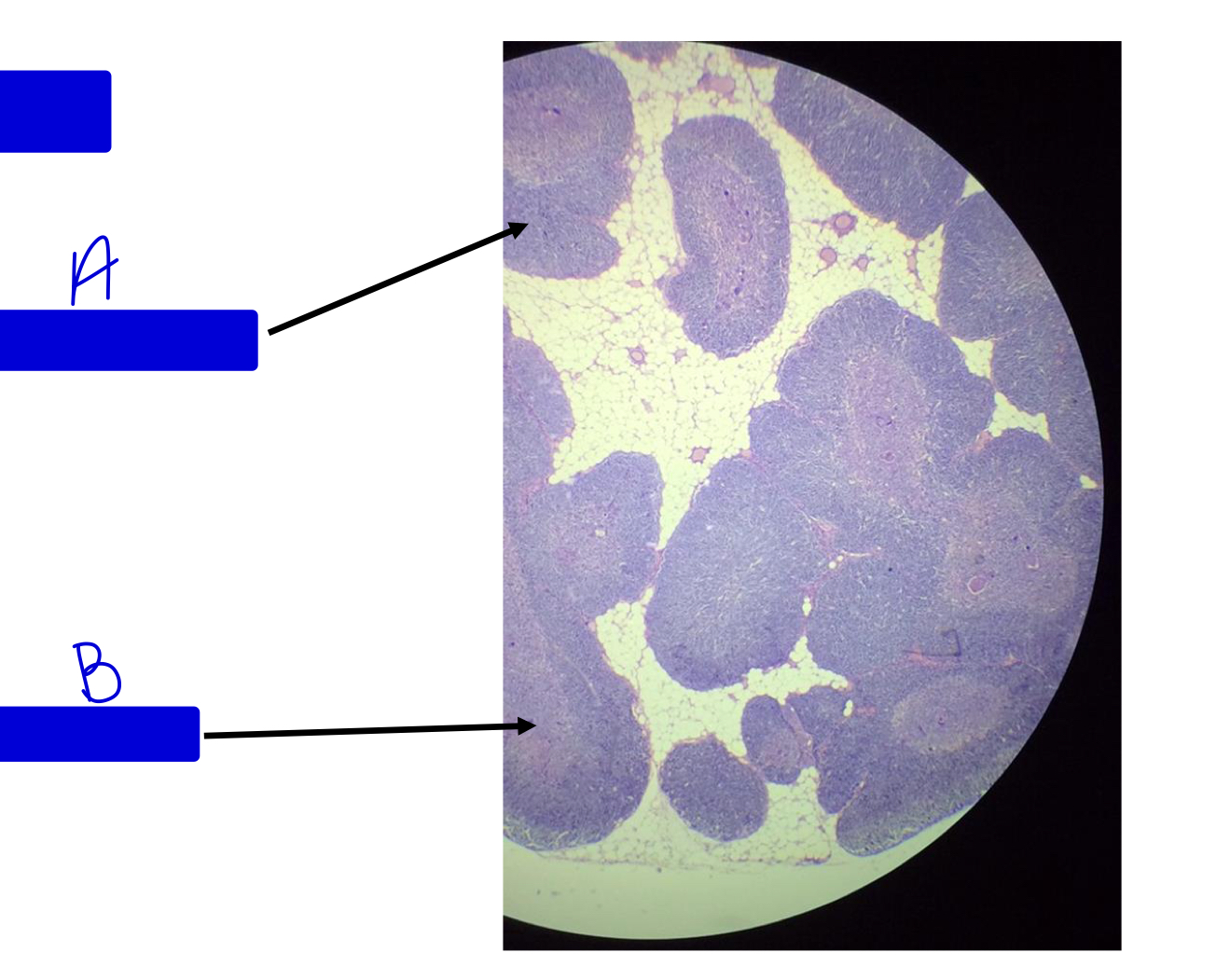
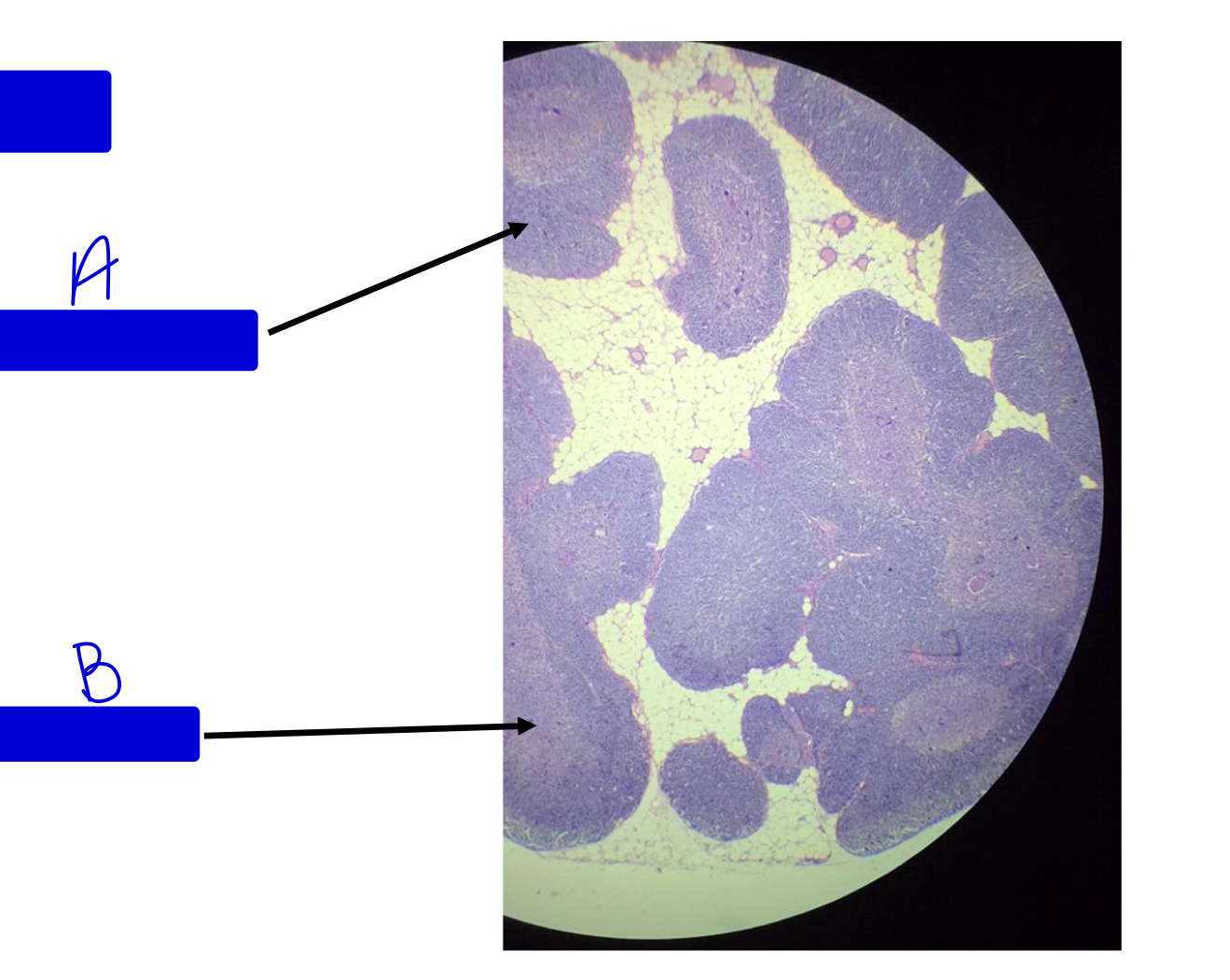
region A
medulla
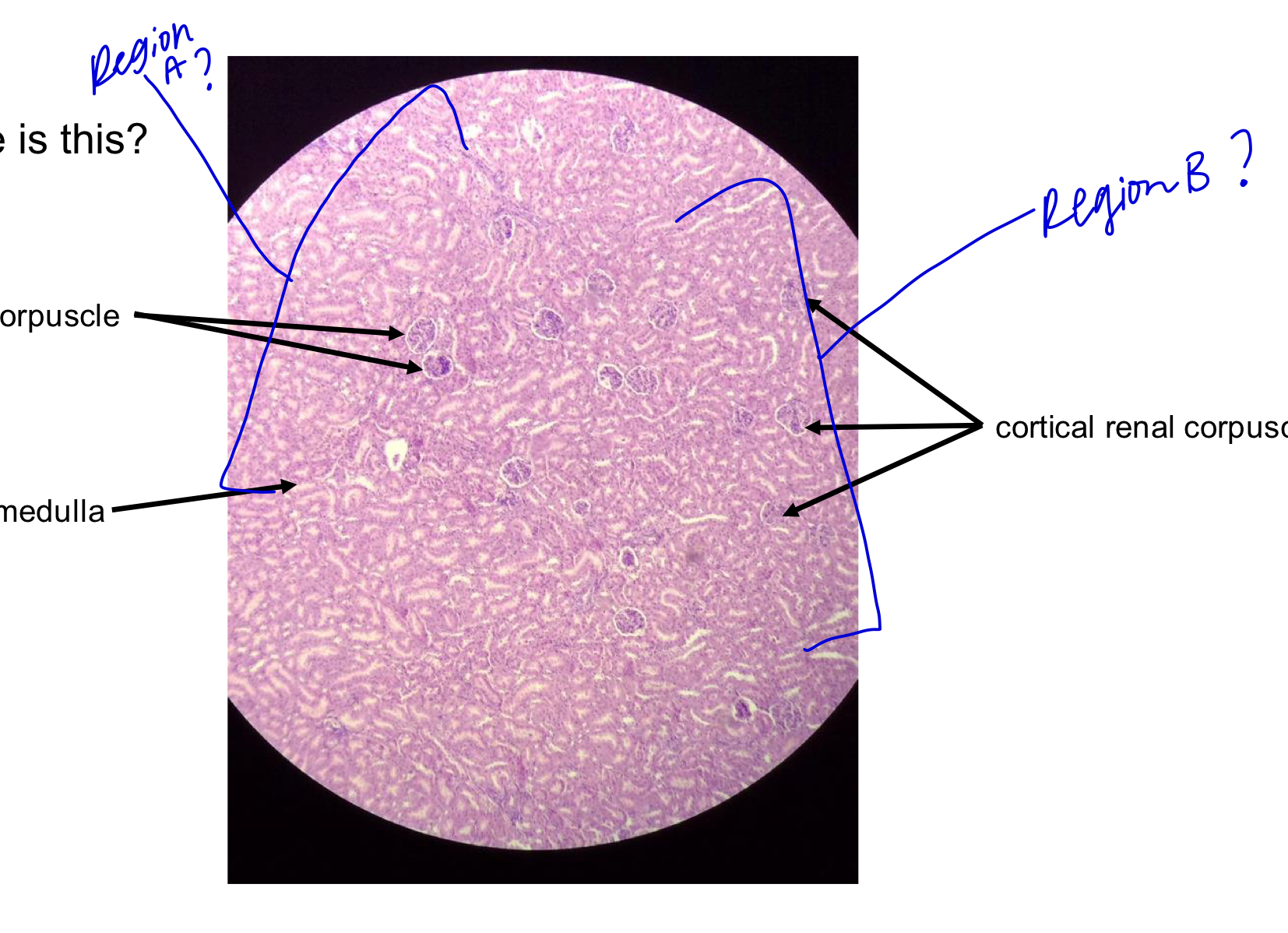
region B
cortex
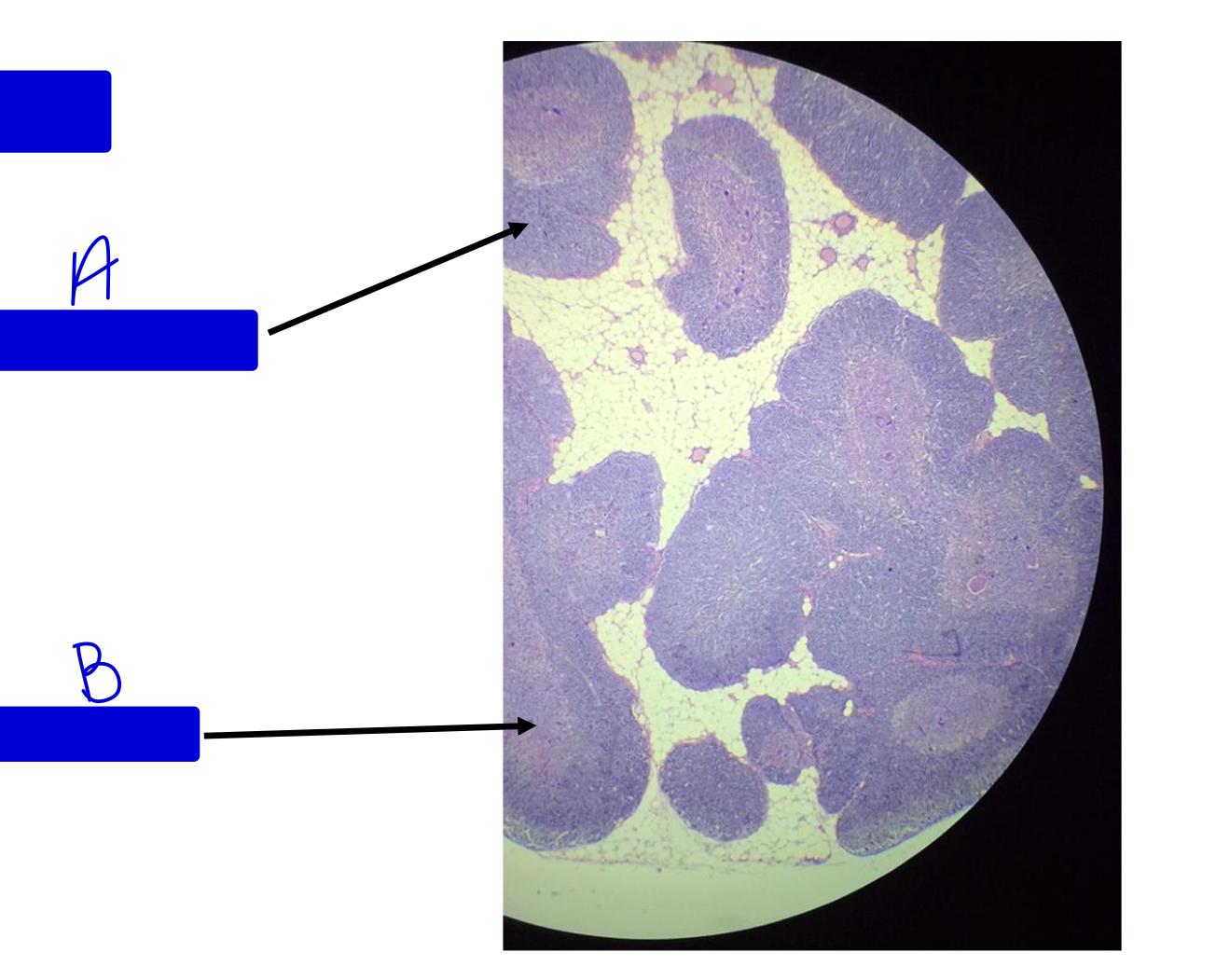
What tissue is this?
thymus
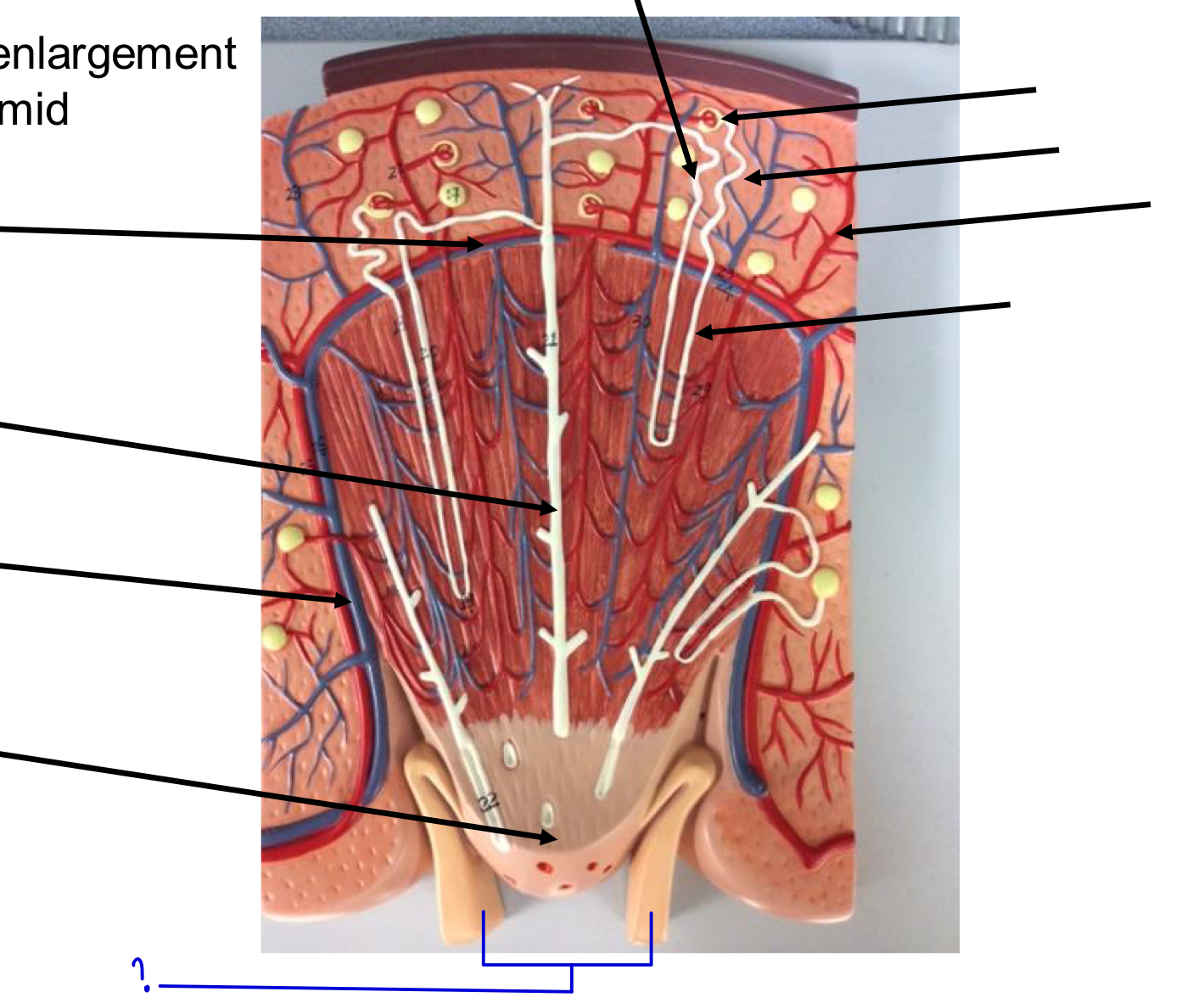
?
minor calyx
what tissue is this?
trachea
what is this?
Glomerulus in nephron
the trachea is not collapsable.
the wall of the trachea is collapsable but it is glued to rings of cartilage to support breathing so it cannot be collapsable
the bronchi is held open by
rings of cartilage
what parts of the body are drained by the right lymphatic duct?
right side of head and neck, right arm, and right side of thorax
where does the right lymphatic duct deliver deliver lymph to?
right subclavian vein
what parts of the body are drained by the thoracic duct?
left side of head and neck, left arm, left side of thorax, and body regions inferior to the diaphragm
where does the thoracic duct deliver lymph to?
left subclavian vein
largest lymphatic vessel?
thoracic duct
lymphatic vessels from different regions of the body drain into larger
lymphatic trunks