Environmental Science Unit 1
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
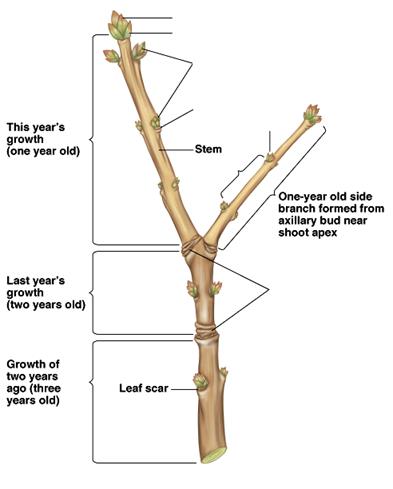
Anatomy of Twig
terminal bud
bud scales
lateral bud (axillary)
lenticel
leaf scar
bundle trace
node
internode
pith
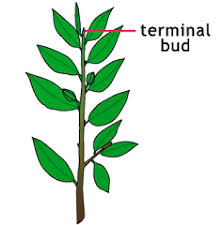
Terminal bud
a bud that is at the tip of a stem/branch
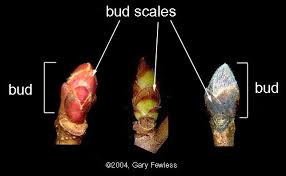
Bud scale
a small modified leaf on the outside of a bud
lateral bud
a bud that is situated along the sides of a branch

lenticel
a corky spot on the bark which originally allowed air into the twig

leaf scar
the scar left on the twig when a leaf falls
bundle trace
Be able to define and describe in detail the 5 main global Environmental Indicators
environmental indicator: something that describes the current state of the environment
Human population
Global temp and CO2 levels
overall food production (soil)
biodiversity
resource depletion (water)
Be able to define and describe in detail what sustainable forestry is?
sustainable forestry: aims to meet human needs for timber and other forest resources in a way that maintains the forest's health for generations to come.
sustainability: living on Earth in a way that allows us to use its resources without depriving future generations of those resources
Be able to define Biodiversity and determine why it is important?
biodiversity: the variety of all living things and their interactions. Biodiversity changes over time as extinction occurs and new species evolve. Scientists often speak of three levels of diversity: species, genetic, and ecosystem diversity.
Be able to define and describe in detail the role trees play in the biosphere and why they are important in the biosphere and the technosphere (human world)?
Trees contribute to their environment by providing oxygen, improving air quality, climate amelioration, conserving water, and preserving soil. Trees supply oxygen for humans to respire and for other animals in nature. They help eliminate the excess CO2 in the atm and are homes/shelters for many small creatures.
Be able to define and describe in detail the difference between conifers, deciduous trees and evergreen trees.
Conifers are trees that have cone and sometimes needles.
Deciduous trees that drop their leaves all at once.
Evergreen trees are trees that don’t loose that their leaves all at once.
Biltmore stick and how to use it
for measuring tree height and diameter (you use that info to get board feet)
use it: diameter
Hold the stick at breast height (4.5 feet from the ground), 25" from your eye, with the back of the stick against the tree you are measuring.
Hold the stick at a right angle to the axis of the tree and keep your eyes level with the stick.
Adjust the stick so that the left or zero is in line of sight with the left side of the tree.
Without moving your head, shift the line of sight to the right hand side of the trunk.
Read the diameter on the stick nearest the point at which the line of sight crosses it.
use it: tree height
Total tree height is measured from the ground to the top of the tree. Merchantable tree height is measured from the stump height to the point at which the tree is no longer usable.
Stand 100 feet from the tree you are going to measure. If the ground is not level, stand on a spot which has about the same elevation as the base of the tree.
Hold the stick vertical, 25" from your eye, with the “Height of Tree” side facing toward you.
Align the base of the stick at the ground (or at your estimated stump height for merchantable height).
Without moving your head, shift your line of sight so you can read the height at the point where your line of sight and the top of the tree intersect (or merchantable height).
This can also be done opposite: Zero the stick at the top of the tree and check height at the ground.
use it: volume
Board Feet: After determining tree diameter and height (in 16 foot lengths), use the chart on the back of the Biltmore stick to determine board feet. Using the “inches” scale along the top, find your tree diameter. Look on the table corresponding to the number of 16 foot log sections you have. The number not in parenthesis will indicate board feet. If you want to determine the volume of one cut log, use the inches scale on the back of the stick to measure the small end inside the bark. The numbers in parenthesis (below your log diameter in inches) list the board feet of one log, 8, 10, 12, 14, or 16 feet long.
Tons: After determining board feet, use the conversion chart on the back of the stick to determine either cubic feet or tons.
Two types are leaves are (1)____ and (2)_____
Different types leaves and branchea are arranged on trees: _____ and ____ penate
and _____ and _______
1) simple: one single leaf
2) compound: many leaflets
single and double penate and alternate and opposite
Red Oak
leaf shape: lobes (bristle tips)
bark: lines on bark (fissures)—> red fissures
acorns (all oak)
used for source of wood —> firewood and hardwood floors
both red and white oak used acorns to make flour
turkeys, deer, squirrels like to eat
White oak
softer acorns
often associated with wetter areas
lobed leaves
white bark and more soft and peely than red oak (instead of fissures)
used for hardwood flooring
Feasible solutions fro improving for humans
systems/machinery that naturally help reduce pollution; eliminating single use plastics and using renewables instead
Be able to define and describe in detail what the NH Envirothon is and how the competition works. Be sure to talk about the different topics covered.
An academic and practical environmental program.
A hands-on, skill-based training presented in a teacher-guided, student-led manner.
Networking with Natural Resource professionals.
A school team that trains locally, then competes state-wide.
Learning about nature in New Hampshire.
Supported by various web and live trainings.
Builds confidence, teamwork, and life-long skills
Each year, volunteer advisers coach teams with assistance from local conservation districts, forestry associations and participating natural resource agencies and organizations. Students are tested on their knowledge in five topic areas: aquatics, forestry, soils, wildlife, and current environmental issues.
Students work and compete as a team of five.
Skills are learned throughout the year but last a lifetime.
The state competition is held in May @NHTI
4 major contributors to global warming
transportation, agriculture, manufacturing, energy production
Witch hazel
shrub/tree with wavy margin leaves that are asymmetrical
has little yellow flowers (in autumn) which allows birds and bees to pollinate
used in skincare (toner)
used for dousing rods
Eastern hemlot
stromata on back of needles
disease called wooly adeldre attacks and suffocates tree
cones very small
conifer that provides shelter and shade
Broad leafed cattails
native plant but acts in an invasive
leads to eutrophication (too many nutrients in the water)
Rhododendron
bush
not invasive
evergreen (doesn’t loose leaves all at once)
good wildlife habitat (hiding spaces)
American Beech
buds: long, pointy, scaly
bark: solid and smooth gray bark (no fissures)
provides food in form of beech nuts
lance shaped leaves (vains run in parallel)
tend to hold dead leaves in winter
havent fully adapted and dont produce absessic acid
cherry tree
serated on outside
contians arsenic
lance shaped leave
rust fungus on back
black locust
protects themselves by thorns
thick bark when older (deep fissures)
used for firewood (good for outdoor furniture)
White pine
five needle fasciate
softwood (floors)
cones 3-5in
produces lots of pollen
trembling aspin
heart shaped
largest tree on planet
flattened petiole
big tooth aspin
big teeth (bigger leaves than tremble)
very similar to trembling
paper birch
triangular shape leaf (serated)
will burn when wet
little lines on bark —> lenticels (transpiration and respiration occurs here)
musclewood
grows in wetlands
triangular and look and feel like muscles
staghorn sumac
invasive native species
edible berries
eastern red cedar
grown in fields with secondary successions
scaly and good for insect repelling
black locust
twigs have thorns (alternate)
Juniper
scaled (sharper not as flat as cedar)
makes bad tea
autumn olive
has become invasive (much less diversity)
can grow where its open to sun
2nd succession (will shad out other trees)
weeping willow
leaves narrow lance shape
buds have no scales
reduction in diversity
norway maple
invasive
look at smooth bark
have v-shaped and U-shaped
sugar only has U-shape
polmate and opposite leaves
basswood
bottom of leaf (asymmetrical) and serated and heart shaped
will grow straight and tall
tight grains
American elm
double serated
dutch elm disease eliminated lots of elm
sandpaper feel
scotch pine
3 needles per fascal (red has 2)
bark is orange
males have pollen
dead branches fall off
gray birch
really triangular leaves
long point on leaves
double serated
male and female catkins: great for birds
not peely like white birch