AP Human Geography: Unit 2: AP review
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
1
New cards
east asia, india
What regions in the world is it most densley populated?
2
New cards
natural/enviromental/physical, economic, social/cultural, political
What factors influence the distribution of a population?
3
New cards
Ecumene
The portion of Earth's surface occupied by permanent human settlement.
4
New cards
Arithmetic Density
The total number of people divided by the total land area.
5
New cards
Physiological Density
The number of people per unit area of arable land
6
New cards
Agricultural Density
The ratio of the number of farmers to the amount of arable land
7
New cards
carrying capacity
the maximum population size that can be supported by the available resources without damaging the enviroment or using natural resources unsustainabiliy
8
New cards
LDCs
Do MDCS or LDCS have higher agricultural density?
9
New cards
social services and infrastructure
How does population distribution and density affect society?
-high population density impacts acess to houses, jobs, water and services like sanitation (medical care)
-easier and cheaper to provide support to clustered populations
-rural areas are harder to support
-high population density impacts acess to houses, jobs, water and services like sanitation (medical care)
-easier and cheaper to provide support to clustered populations
-rural areas are harder to support
10
New cards
economic
How does population distribution and density affect society?
-competition for jobs
-urbanization
-uneven population distribution results in uneven development
-scattered/dispersed population
-lower wages- less access to people-less developed
-competition for jobs
-urbanization
-uneven population distribution results in uneven development
-scattered/dispersed population
-lower wages- less access to people-less developed
11
New cards
political
How does population distribution and density affect society?
- representation in goverment
-electoral districts which have to be roughly equal in population size
- representation in goverment
-electoral districts which have to be roughly equal in population size
12
New cards
natural/enviromental/physical
How does population distribution and density affect society?
- carrying capacity
- high population density: pressure on the arable land, water, resources, food supply
- air and water pollution, depletion of natural resources, use of large amounts of energy, excessive waste
- carrying capacity
- high population density: pressure on the arable land, water, resources, food supply
- air and water pollution, depletion of natural resources, use of large amounts of energy, excessive waste
13
New cards
Population structure
what percentage of population are children, elderly, male, female
14
New cards
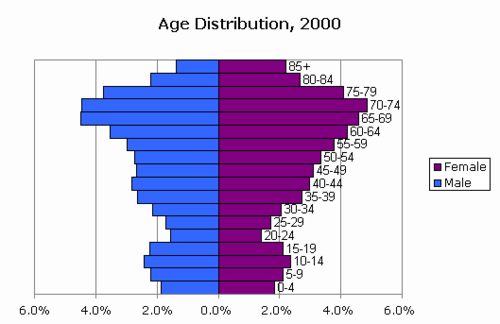
Population Pyramid
A bar graph representing the distribution of population by age and sex.
15
New cards
dependency ratio
the number of people in a dependent age group divided by the number of people in the working age group multiplied by 100 (under age 15 and over age 65)
16
New cards
high
HIGH OR LOW DEPENDENCY RATIO?
- many people not working
- not earning an income
- not paying tax
- working population face higher taxes
- many people not working
- not earning an income
- not paying tax
- working population face higher taxes
17
New cards
sex ratio
the proportion of males to females in a population
18
New cards
Pro-Natalist Policies
increases fertility rate and acclerate population growth (STAGE 4 AND 5 COUNTRIES)
19
New cards
aging population, declining populations, more people in labor force
Why would a popualtion be pro-natalist?
20
New cards
propoganda, financial support, length and paid maternity/paternity leave, free/subsized child care, tax breaks for children
What are some methods populations try to promote pro-natalist policies?
21
New cards
Anti-Natalist Policies
goverment policies to decrease fertility rate and slow down population growth (STAGE 2 COuntries)
22
New cards
over popualtion and rapid growth, limited resources and infrastructure, reduce the risk of famine
WHy would a popualtion enforce anti-natalist policies?
23
New cards
propoganda, financial disincentives and incestives, fines and taxes per child, family planning and contraception
How do popualtions promote anti-natalist policies?
24
New cards
Demography
The scientific study of population characteristics.
25
New cards
East Asia, South Asia, Europe, Southeast Asia
2/3rds of the world's inhabitants are clusetred in four regions, what are they? These areas are generally low lying areas with fertile soil, and temperate climate
26
New cards
Stage 1 DTM
Low growth, High CBR, High CDR, Low NIR, small population
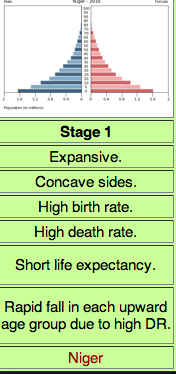
27
New cards
Stage 2 DTM
High Growth, High CBR, Rapidly declining CDR, High NIR
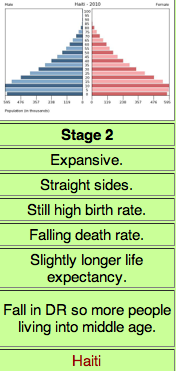
28
New cards
Stage 3 DTM
Moderate Growth, Rapidly Declining CBR, Moderately Declining CDR, Moderate NIR
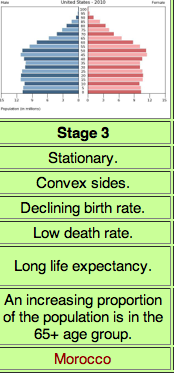
29
New cards
Stage 4 DTM
Low Growth, Very Low CBR, Low or Slightly increasing CDR, Zero or Negative NIR
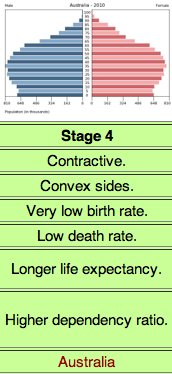
30
New cards
Stage 5 DTM
very low CBR, increasing CDR, declining NIR
31
New cards
Thomas Malthus theory
the idea that population growth is potentially exponential while the growth of the food supply or other resources is linear, which eventually reduces living standards to the point of triggering a population die off.
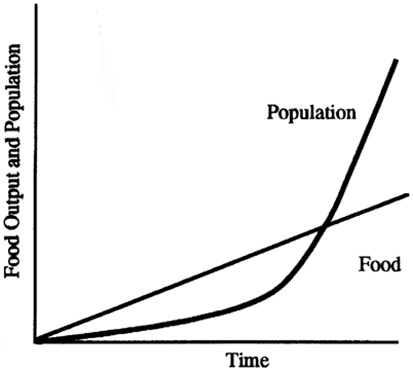
32
New cards
Neo-Malthusians
world population growth is outstripping a wide varity of resources, not just food production
33
New cards
crude birth rate
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
34
New cards
crude death rate
The number of deaths per year per 1,000 people.
35
New cards
infant mortality rate
The percentage of children who die before their first birthday within a particular area or country.
36
New cards
Natural Increase Rate
The percentage growth of a population in a year, computed as the crude birth rate minus the crude death rate.
37
New cards
total fertility rate
The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years.
38
New cards
doubling time
The number of years needed to double a population, assuming a constant rate of natural increase.
39
New cards
Migration
the permanent or semipermanent relocation of people from one place to another
40
New cards
Immigration
the movement INTO a location
41
New cards
Emigration
the movement AWAY (or exiting from) a location
42
New cards
net migration
the difference between the number of emigrants and the number of immigrants in a country
43
New cards
push factors
a negative circumstance, event, or condition that causes people to leave their homelands and migrate to another region (EX: job loss, lack of employment, low wages)

44
New cards
pull factors
positive conditions and perceptions that induce people to new locations from other areas (EX: job oppurtunities, higher wages, seasonal jobs)

45
New cards
friction of distance
the increase in time and cost that usually comes with increasing distance
46
New cards
Demographic Transition Model
A sequence of demographic changes in which a country moves from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates through time.
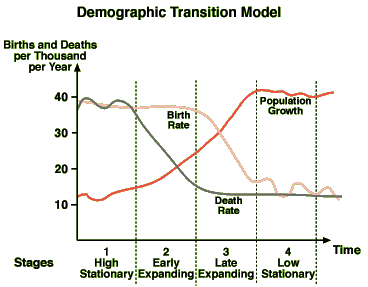
47
New cards
stage 4
WHat is the ideal stage to be in the DTM?
48
New cards
Epidemiologic Transition Model
A model highlighting the distinctive causes of death in each stage of the demographic transition
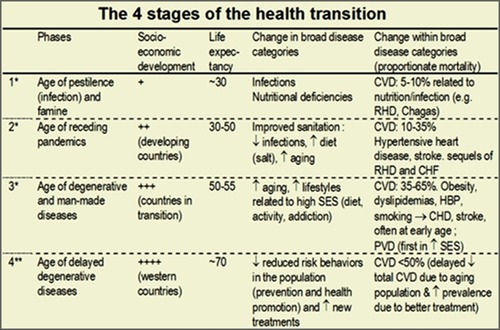
49
New cards
intervening obstacle
Barriers that hold migrants back from continuing to travel
50
New cards
intervening opportunity
an oppurtunity that causes migrants to voluntarily stop traveling
51
New cards
Voluntary Migration
TYPES OF MIGRATION
people migrate due to their own choices
people migrate due to their own choices
52
New cards
Involuntary (forced) migration
TYPES OF MIGRATION
people relocate due to fears of violence or survival
people relocate due to fears of violence or survival
53
New cards
Transhumance
TYPES OF MIGRATION
a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures (EX: farmers, nomads, much of spain)
a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures (EX: farmers, nomads, much of spain)
54
New cards
enslaved person
being forced to work for someone unpaid. (EX: atlantic slave trade, human trafficking)
55
New cards
Refugees
FORCED MIGRATION
someone who has been forced to flee his or her country because of persecution, war, or violence (EX: syrians, afghanistan)
someone who has been forced to flee his or her country because of persecution, war, or violence (EX: syrians, afghanistan)
56
New cards
transnational migration
TYPES OF MIGRATION
migration from one country to another (EX: U.S to China)
migration from one country to another (EX: U.S to China)
57
New cards
Internal Migration
TYPES OF MIGRATION
movement of people from one area to another within a country (EX: move from mInneaplois to mankato)
movement of people from one area to another within a country (EX: move from mInneaplois to mankato)
58
New cards
Chain Migration
TYPES OF MIGRATION
immigrants migrate to a location based off of familys/friends
immigrants migrate to a location based off of familys/friends
59
New cards
step migration
TYPES OF MIGRATION
migration that occurs in steps to reah a destination through small movements (EX: migraton from rural)
migration that occurs in steps to reah a destination through small movements (EX: migraton from rural)
60
New cards
Rural-urban migration
TYPES OF MIGRATION
people moving from rural to urban areas (EX: industrial revolution)
people moving from rural to urban areas (EX: industrial revolution)
61
New cards
Guest Worker Migration
TYPES OF MIGRATION
someone who has permission to live temporarilly in a country (EX: people from LDCs)
someone who has permission to live temporarilly in a country (EX: people from LDCs)
62
New cards
assylum seeker
FORCED MIGRATIOn
someone who has migrated to another country because of persucution; want to seek sancutuary (EX: rwandans)
someone who has migrated to another country because of persucution; want to seek sancutuary (EX: rwandans)
63
New cards
migration selectivity
how likely someone is to migrate based on age, income, and socio-economic factors
64
New cards
Ravenstein's Laws of Migration
MODELS OF MIGRATION
1. migration is typically short in distance
2. migration occurs in steps
3. urban areas attract both long-distance and rural migrants
4. every migration generates a counter-migration
5. young, single, adult males are more likel to migrate than females (Women will migrate shorter distances)
6.(most) migration is due to economic factors
1. migration is typically short in distance
2. migration occurs in steps
3. urban areas attract both long-distance and rural migrants
4. every migration generates a counter-migration
5. young, single, adult males are more likel to migrate than females (Women will migrate shorter distances)
6.(most) migration is due to economic factors
65
New cards
gravity model
MODELS OF MIGRATION
Closer places attract more migrants than distant places. Gravitational pull: lrage places attarct more migrants than smaller
CRITICISMS: doesnt include migration selectivity, factors like age and education. Human behavior doesnt always follow a specific pattern
Closer places attract more migrants than distant places. Gravitational pull: lrage places attarct more migrants than smaller
CRITICISMS: doesnt include migration selectivity, factors like age and education. Human behavior doesnt always follow a specific pattern
66
New cards
Zelinsky Model of Migration Transition
MODELS OF MIGRATION
attempts to predict migration based on stages of development. involves external migration with stage 2 and intraregional migration with many stages
CRITSICMS: doesnt take account for push/pull factors besides economy/development. no data is used.
attempts to predict migration based on stages of development. involves external migration with stage 2 and intraregional migration with many stages
CRITSICMS: doesnt take account for push/pull factors besides economy/development. no data is used.
67
New cards
-colonial settlements in the 17th and 18th century
- mass european immigration is 19th and 20th century
- asian and latin america late 20th and early 21st century
- mass european immigration is 19th and 20th century
- asian and latin america late 20th and early 21st century
What are some historic migration flows in the U.S?
68
New cards
internally displaced person
Someone who has been forced to migrate for similar political reasons as a refugee but has not migrated across an international border
69
New cards
1) increases in the population, with adverse effects on existing social institutions; 2) increases in demand for goods and services; 3) displacement of nationals from occupations in the countryside and in the cities
What are some consequences of migration?
70
New cards
Remittances
Money migrants send back to family and friends in their home countries, often in cash, forming an important part of the economy in many poorer countries