Steroidal Anti-inflammatories
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
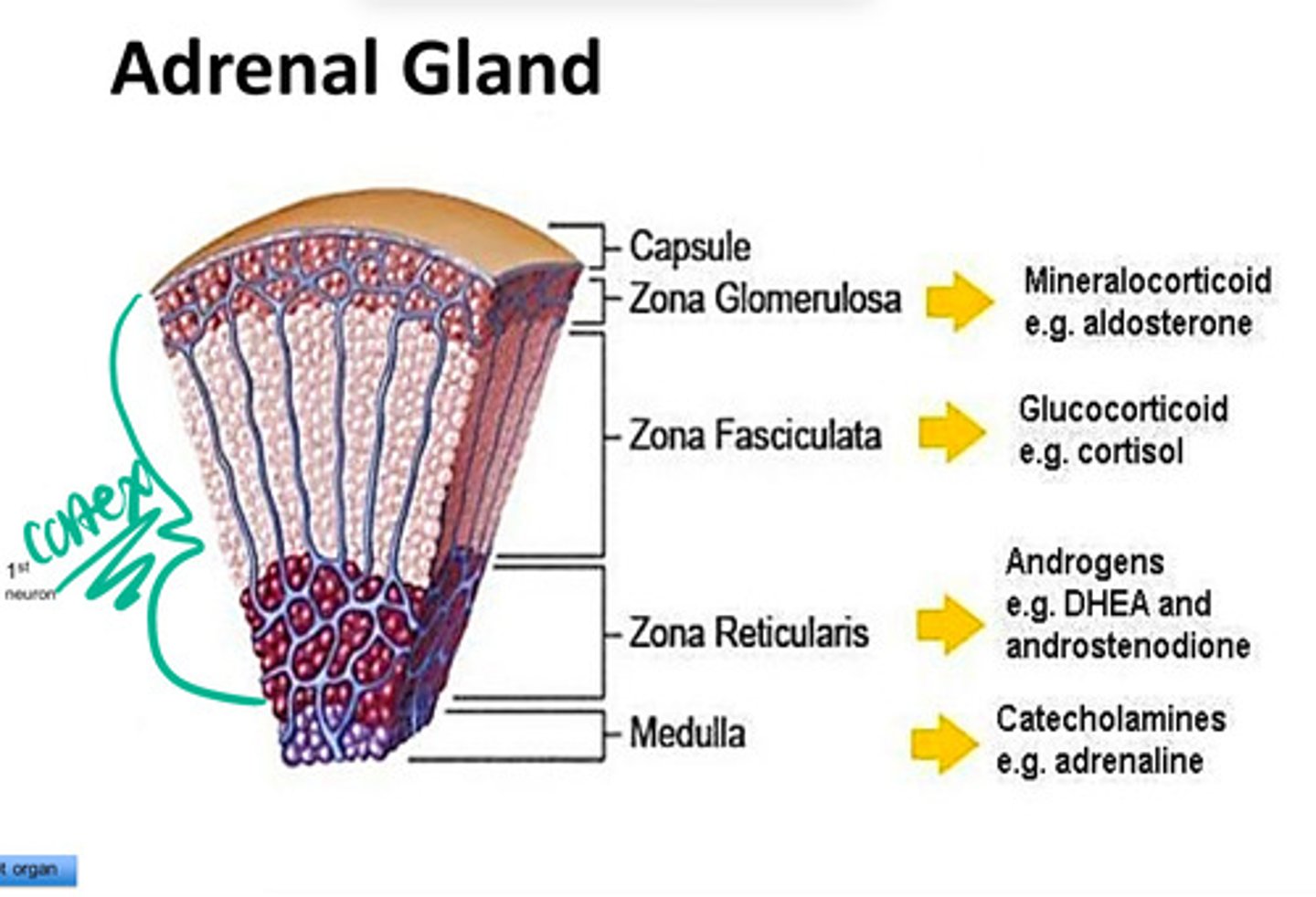
Describe the basic functional structure of the adrenal gland.
-capsule
-cortex
>Zona Glomerulosa --> produces mineralocorticoid
>Zona Fasciculata --> produces glucocorticoid
>zona reticularis --> produces androgens
-Medulla --> catecholamines
chromaffin cells
neuroendocrine cells w/in the adrenal medulla that release catecholamines (epinephine/adrenaline, norepinephrine/noradrenaline)
Describe the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis
Hypothalamus releases corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) --> stimulates anterior pituitary gland to release adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) --> stimulates the adrenal gland to release cortisol
*regulated via negative feedback ==> increased cortisol inhibits release of CRH from hypothalamus
Mineralocorticoid
corticosteroids released from the zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex ==> regulates Na+/water & K+ retention/excretion
Glucocorticoid
corticosteroids released from the zona fasciculata of adrenal cortex
-changes carbohydrates & protein metabolism
-fat redistribution
-suppression of inflammation, immune function, & allergy response
-mood changes
-alters calcium absorption & excretion
-reduces the growth of new cells --> not recommended to prescribe to kids
Why shouldn't glucocorticoids be prescribed to children to manage inflammation?
b/c glucocorticosteroids reduces the growth of new cells (thus they stunt the growth of kids)
What is the body's immediate response to stress?
sympathomedullary pathway ==> hypothalamus activates adrenal medulla --> releases adrenaline & noradrenaline into bloodstream --> fight or flight; reinforces the pattern of sympathetic activation -->>> energy
What is the body's response to chronic stress?
Hyp-pit-adrenal axis ==> higher brain centers activate hypothalamus --> hypothalamus releases corticotrophin (CRF) --> pituitary gland releases adrenocorticotrophic (ACTH) --> adrenal cortex releases corticosteroids -->>> increased metabolic rate, increased Na+/water retention, & blood vessels more responsive to NE
Adrenal Insufficiency
disorders in which the adrenal glands do not produce enough corticosteroids ==> Adrenal Crisis due to mineralocorticoid & glucocorticoid deficiency
*glucocorticoid deficiency ==> low or absent cortisol --> decrease in liver function + decrease in stomach enzymes --> extremely low blood sugar + vomiting, diarrhea, cramps + low fluid volume --> shock --> coma &/or brain death
* mineralocorticoid deficiency ==> low/absent aldosterone --> Na+/water loss from kidneys + heart irregular + decreased cardiac output --> low fluid volume + low blood pressure --> shock --> coma &/or brain death
ex: Addision's Disease
Addision's Disease
adrenal insufficiency disease due to autoimmunity against adrenal glands ==> extremely decreased glucocorticoids & mineralocorticoids --> extremely low blood sugar, blood pressure, blood volume -->>> coma & death
What are the effects of glucocorticoid deficiency?
low or absent cortisol --> decrease in liver function + decrease in stomach enzymes --> extremely low blood sugar + vomiting, diarrhea, cramps + low fluid volume --> shock --> coma &/or brain death
What are the effects of mineralocorticoid deficiency?
low/absent aldosterone --> Na+/water loss from kidneys + heart irregular + decreased cardiac output --> low fluid volume + low blood pressure --> shock --> coma &/or brain death
Corticosteroid Excess
syndromes characterizes by overactive adrenal cortex (hyper secretion of corticosteroids)
*symptoms (CUSHINGOID)
-cataracts
-ulcers
-dermal thinning, red straie (red stretch marks)
-hypertension, hyperglycemia
-infections --> c.steroids are immunosuppressant
-avascular necrosis
-glycosuria
- osteoporosis & obesity --> characteristic dorso cervical fat pad = buffalo hump
-immunosuppression
-diabetes
Cushing Syndrome
corticosteroid disease due to pituitary gland tumor ==> hyper stimulation of adrenal cortex --> hyper secretion of c.steroids
How are corticosteroids classified?
-duration of action
>short acting --> hydrocortisone, cortisone
>intermediate-acting --> prednisone, triamcinolone, methylprednisone
>long-acting --> dexamethasone & betamethasone
-activity
>both glucocorticoid & mineralocorticoid activity --> hydrocortisone & cortisone
>only glucocorticoid activity --> prednisone & dexamethasone
-potency (as compared to hydrocortisone)
>dexamethasone 25x more
>prednisone 4x more
>methylpredisolone 5x more
>hydrocortisone 1x more
How is hydrocortisone classified?
-short-acting corticosteroid
-has both glucocort & minerolcort activity
-has the same potency has hydrocortisone
How is cortisone classified?
-short-acting corticosteroid
-has both glucocort & minerolcort activity
-has the standard potency that all other c.steroids are compared to
How is prednisone classified?
-intermediate-acting corticosteroid
-only has glucocorticoid activity
-4x as potent as hydrocortisone
How is methylprednisone classified?
-intermediate-acting corticosteroid
-5x potent as hydrocortisone
How is dexamethasone classified?
-long-acting corticosteroid
-only has glucocorticoid activity
-25x has potent as hydrocortisone
How is betamethasone classified?
long-acting corticosteroid
Therapeutic Uses of Corticosteroids
-corticosteriod replacement (Tx adrenal insufficiencies)
-arthritis
-asthma
-inflammatory bowel disease
- non- infectious various skin conditions --> can't use on skin infection b/c c.steroids are immunosuppressant & will make the infection worse
-immunosuppression
-allergy
-antiemetic --> stop vomiting
What is the mechanism of action of analgesic & antipyretic effects of corticosteroids?
inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins & leukotrienes ==> inhibits phospholipase A2 from converting phospholipid into arachidonic acid (a. acid is metabolized to prostaglandins & leukotrienes
How are corticosteriods anti-inflammatory & immunosuppressive?
-stabilize lysozyme membranes
-decrease the release of inflammatory mediators
-decrease capillary permeability
-interfere w/ complement pathway activation
-interfere w/ formation of inflammatory mediators
Dental Uses of Corticosteroids
-systemic steroids --> oral lesions due to noninfectious inflammatory disease, 3rd molar EXT, for minor/major surgeries to reduce edema, pain, trismus (can't open the mouth), & TMJ disorder
-topical steroids--> noninfectious ulcerative diseases in oral cavity, inhibit inflammatory rxn, decrease redness & edema
Synalar and Lidex
topical steroid paste used in dentistry to treat noninfectious ulcerative diseases in oral cavity, inhibit inflammatory rxn, decrease redness & edema
What are some major side effects of corticosteroids that are directly applicable to dental care?
-bigger dose of c.steroids needs to be prescribed to Tx oral/dental related inflammation in patients who have been taking steroids within the past year ==> b/c pt's have already been taking steroids, they have stopped producing endogenous steroids via negative feedback (hyp-pit-ad axis regulation) --> won't produce own cortisol due to stress of dental procedure --> will need higher dosing of steroid prescription to manage inflammation (give high dose prior to procedure or right after & then taper down to normal maintenance dose)
-immunosuppression==> pts on c.steroids have decreased immunity = higher risk of infection. Pts who take steroids will need antibiotic therapy before/following oral surgical procedures
-suppression of beneficial inflammatory process ==> slow wound healing post dental/oral surgical procedures & suppressed inflammatory response may mask early symptoms of disease = interfere w/ proper diagnosis
True or False: Patients who have been routinely taking steroids will require less corticosteroid therapy to manage inflammation prior to major dental procedures.
False ==> bigger dose of c.steroids needs to be prescribed to Tx oral/dental related inflammation in patients who have been taking steroids within the past year b/c pt's have already been taking steroids, they have stopped producing endogenous steroids via negative feedback (hyp-pit-ad axis regulation) --> won't produce own cortisol due to stress of dental procedure --> will need higher dosing of steroid prescription to manage inflammation (give high dose prior to procedure or right after & then taper down to normal maintenance dose)
True or False: A Patient who has stopped routinely taking corticosteroids 6 months ago still does not have fully normal functioning adrenal glands
True ==> if taking steroids within the past year, patients have stopped producing endogenous steroids via negative feedback (hyp-pit-ad axis regulation)
*adrenal fxn won't return to normal until up to a year after cessation of steroid therapy
What are some precautions dentists should consider when prescribing corticosteroids regarding their immunosuppressive action?
-pts taking steroids may have increased susceptibility to infection ==> may be necessary to provide antibiotic therapy for pts on long term steroids when an oral surgical procedure is planned
-pre-existing minor or superficial infections may become systemic
-quiescent infections may become active (ex: contraindicated in patients w/ latent TB)
-a normally nonpathogenic organism may cause systemic disease
-use of corticosteroid inhalers associated w/ increased occurrence of oral candida
What are some precautions dentists should consider when prescribing corticosteroids regarding their anti-inflammatory action?
-suppression of beneficial inflammatory process ==> slow wound healing post dental/oral surgical procedures & suppressed inflammatory response may mask early symptoms of disease = interfere w/ proper diagnosis
What are some general considerations regarding corticosteroid use?
-multiple adverse side effects due to wide ranging effects & potencies of these drugs ==> limit use to emergency use & short-term therapy at the smallest effective dose (should opt to use NSAIDs when possible)
-do not prescribe as analgesic (due to side effects)