Lecture #14 | Fusion Proteins and Designer Drugs: PML-RAR & Retinoids BCR-ABL & Gleevec
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
How Proto-oncogenes Become Oncogenes
Deletion or point mutation in coding sequence: Results in a hyperactive protein made in normal amounts.
Gene amplification: Leads to normal protein greatly overproduced.
Chromosome rearrangement caused by ionizing radiation:
Nearby regulatory DNA sequence causes normal protein to be overproduced.
Fusion to actively transcribed gene greatly overproduces fusion protein, or fusion protein is hyperactive.
Oncogenic Fusion Proteins Overview
Product of chromosomal translocations.
Contain new properties due to modular nature of protein domains.
Frequently found in leukemias.
Often involve:
Transcription factors (e.g., PML-RAR).
Signal transduction pathway (e.g., BCR-ABL).
Can be targets for cancer therapy:
Retinoids target PML-RAR.
Gleevec targets BCR-ABL.
Translocations in Acute Leukemias
Many translocations are present in various acute leukemias and involve oncogenes.
Specific translocations are repeatedly found in cancers from different people.
Why leukemias?
Translocation in T cells
Translocation t(15;17), PML-RAR
Reciprocal translocation between chromosome 15 & 17.
Found in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL).
Caused by bimolane, a topoisomerase II inhibitor used as a medical treatment in China.
Fuses retinoic acid receptor (RARα) to PML.
PML: zinc fingers and coiled-coil domains.
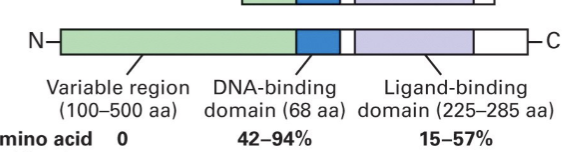
RARα: DNA and ligand binding domains (DBD, LBD).

Retinoic Acid Receptor -- RAR
~460 amino acids.
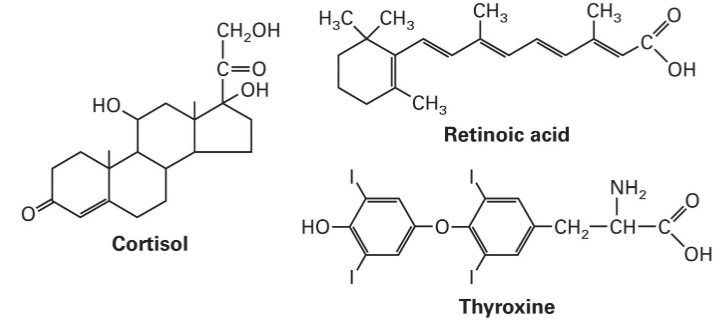
Retinoic acid (RA) studied for over a century.
RARs studied since late 1980s.
RA is formed from dietary Vitamin A in dairy products, fish liver oils, and β-carotene from plants.
RA is essential for normal development and plays a critical role in differentiation, cell growth, and death.
RA has tumor suppressive activities via its ability to promote differentiation and apoptosis.
too much RA is teratogenic (causes birth defects).
RAR is a member of a superfamily of ligand-dependent transcription factors (nuclear receptors, NR).
RAR forms heterodimers with retinoid X receptor (RXR).
Dimers bind retinoic acid response elements (RAREs).
In the absence of RA, RAR binds co-repressors.
N-CoR (SMRT) forms a complex with Sin3A & HDAC.
Upon ligand (RA) binding, RAR undergoes a conformational change.
Co-repressors are released.
Co-activators with HAT activity are recruited.
The Mediator complex binds and interacts directly with the basal transcription machinery which initiates transcription.
Many target genes of RAR have been identified with roles in development, metabolism, differentiation, et
All have RARE
Nuclear Receptors domains
DNA binding domain (DBD):
2 zinc fingers, each consisting of 4 Cysteines.
Ligand binding domain (LBD):
ligand binding pocket (LBP) – hydrophobic.
activation function (AF-2) – binds Co-activators (& Co-repressors).
N-terminal activation function (AF-1):
ligand-independent, binds Co-activators, interactions with LBD.
Ligands for nuclear receptors
Unligated
RAR:RXR binds RARE and co-repressors with HDAC activity.
Ligated RAR
recruits co-activators with HAT activity and then Mediator complex (SMCC/TRAP/DRIP).
PML – Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein
Identified in 1977 as part of the PML-RAR fusion protein, before RAR was cloned.
PML contains 3 ring fingers, a zipper motif and a coiled-coil region that promotes oligomerization.
increase activity and stability
Ability to oligomerize is critical to the oncogenic function of the fusion protein.
PML-RAR fusion protein function: Alters Expression of RA-Responsive Genes
PML-RAR has the same DNA binding specificity as RAR.
Dimerization with RXR is not needed for PML-RAR to bind DNA.
PML provides a dimerization motif with its coiled coil region.
PML-RAR has the same affinity for RA as wildtype RAR, but more RA is required to remove the co-repressor.
Co-repressor with HDAC bound.
Treatment with high doses of RA leads to Co-activator with HAT bound.
PML-RAR blocks cells in pro-myelocytic (pre-differentiation) stage unless high doses of RA are given.
low = physiological concentrations
high = pharmacological/therapeutic concentrations → for leukemia cells
PML-RAR fusion protein function: Causes Nuclear Bodies to Disintegrate
PML is found in nuclear bodies (NB), heterogeneous, dynamic macromolecular structures in the nucleus:
Sequester and release proteins
Mediate post-translational modification of proteins
Promote specific events in response to cellular stress
Associate with transcriptionally active regions of the genome
Role in apoptosis, senescence, tumor suppression, telomere length
PML interacts with several proteins in NBs, including p53, an important tumor suppressor protein.
BCR-ABL Fusion Protein (overview)
Translocation t(9;22) between c9 and c22 (Philadelphia chromosome).
Present in 90% of CML (chronic myelogenous leukemia) and 10-20% ALL (acute lymphoblastic leukemia).
Gleevec – designer drug
BCR-ABL fusion protein has constitutive kinase activity and phosphorylates new substrates
BCR-ABL Activity
stimulates proliferation via Ras/MAPK: interacts with SH2 of adaptor GRB2 → activates Ras → GF-independent cell growth
activates Src: Increase motility Decrease adhesion
suppresses apoptosis: activates PI3K pathway
activates JAK/STAT: cytokine pathway
Gleevec
miracle drug
very effective at treating CML
highly specific with few side effects
in the ATP binding pocket of the
tyrosine kinase domain of BCR-ABL
Prevents ATP from binding and the kinase from transmitting the signal
New properties of Bcr-Abl make it a good anti-cancer target
locks BCR-ABL in the inactive form
Downsides to Gleevac
Patients can develop resistance to Gleevac via mutations in the Gleevac binding site
Does not work when a mutation has locked Abl into the active state
Dasatinib, another Src kinase inhibitor, does bind the active form
Inhibitors of Src family kinases are used to treat cancer of the lung, colon, stomach, and other leukemias