U3 W8: Surgical client/ pain
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
blurb: preoperative assessment
patient education, head-to-toe assessment, medical history review, lab results review, diagnostic test review, proper identification, allergies, medications, reactions to anesthesia, use of any tobacco or alcohol, spiritual or cultural needs, pain
Preoperative assessment risk, list chronic conditions that pose surgery a risk
COPD, Sleep apnea, coronary artery disease (CAD), congestive heart failure (CHF)
Preoperative assessment risk: malignant hyperthermia
severe reaction to certain medications given during anesthesia
Preoperative assessment risk: Antigoagulants
increases risk of bleeding during surgery
Preoperative assessment risk: alcohol
increases risk of bleeding, infection, heart problems, increased hospitalization
Preoperative assessment risk: Tobacco
increase risk of blood clots, myocardial infarction
Preoperative assessment risk: Age of over 65 can cause
post op delirium, chronic conditions
Preoperative assessment risk: obesity can cause
risk for higher complications like DVT, or breathing complications
Preoperative assessment risk: Smoking can cause
difficulty with anesthetisa, and breathing, slower wound healing, increased infections
Preoperative assessment risk: diet/ nutrition status
a low status means not very good wound healing.
N/V are normal postoperative events bit what would make this more of an issue?
projectile vomiting
s/s of venous thromboembolism(DVT)
warmth, redness, swelling
s/s of pulmonary embolism
shortness of breath, hypoxia, blue/purple
s/s of hypovolemia
low urine output, decreased and thready pulses, dry mucous membranes, tachycardia, hypotension
s/s of hypervolemia
crackles in the lungs, JVD, pitting edema, 3+ bounding pulses
s/s of ateletasis
hypoactive lung sounds, shortness of breath
what lowers the risk of atelectasis
using an incentive spirometer
dehiscence
staples and sutures opening up
evisceration
organs popped from a wound
s/s of an Ileus
Distended abdomen, hypoactive/no abdomen sounds
s/s of oliguria(low urine output)
pitting edema, dry mucous membranes, JVD, this is also a sign of acute kidney injury
What does a nurse do with getting consent from a patient?
a Nurse cannot obtain consent, it can only witness it
what items can the nurse remove when prepping pt. for surgery?
remove dentures, glassing, hearing aids, piercings
the universal protocol
prevents wrong patient, wrong site, wrong surgery
When is time-out given?
before anesthesia
Time-out
correct pt. by name and DOB, correct procedure, consent form for correct site, and marked surgical sitewh
Discrepancies: If marked site and patient say something different (or anything doesn't match
stop the procedure, clarify correct patient and procedure, if it is still wrong, do not continue with surgery
circulating nurse
circulates the operating room(not sterile)
what are the duties of a circulating nurse?
coordinates pt care
verifies identity, assess allergies, checks consent forms
assisting anesthesia provider as needed
safety, positioning, and monitoring of pt
provide supplies
counts instruments
documents information
The surgical environment has these things within it.
cold(65F-75F) humidity(20-60%), sterile technique and attire including gown, mask, gloves, hair cover, shoe covers
Skin preparation
by showering, shaving, cleansing with iodine, chlorhexidine alcohol, scubbing in a circular fashion and move outward, use a new sponge for each area
monitoring local anesthesia
tachypnea/tachycardia, tinnitus, numbness around the mouth, drowsiness, metallic taste, tremors, seizures, coma
report
regional anesthesia
temporary loss of feeling in localized areas of the body
general anesthesia
nervous system suppressant, used in invasive procedures and uses respiratory support
moderate sedation to monitor for
blood pressure, respirations and oxygen saturation
respiratory status in a post operative
primary concern. assessing rate, depth, and oxygen saturation.
hep suction secretions
use an incentive spirometer to prevent pneumonia and atelectasis
cough and deep breathing exercises
assessing Cardiovascular system post op
assess circulation
fluid/electrolyte imbalance(like increased K+lvs)
frequent vital signs
assess extremities, pulses, DVT
prevention: early ambulation, SCDs(Sequential Compression Devices) and TEDs (Thromboembolic Deterrent stockings) positioning
assess the cardiovascular system/ s/s of bleeding
hypotension, tachypnea, changes in LOC, decreased O2, weak thready pulse, tachycardia, decreased urine output
neurological assessment post op
the goal is baseline neuro.
integumentary assessments post op
assess dressings for excessive bleeding, and monitoring for infection: pain, redness, inflammation, temp above 100.4, increased WBCs, tachycardiap
pain management
use of a PCA and nonpharmacological interventions like distractions, music, breathing, heat/cold, repositioning
positioning post op
reposition frequently, prevents blood clots, pneumonia, atelectasis, and muscle weakness, you can splint with a pillow during coughing for chest /abdominal incisions to reduce pain and protect wound
gastrointestinal complications post op
auscultating bowel sounds and asses for N/V
early ambulation to promote gastric motility and prevent ileus
abdominal surgeries are at high risk for ileus(because the surgons’s were manipulating the GI system)
Renal complications post op
monitoring output, strict I&O, assessing for skin turgor, mucous membranes, eyes, skin tenting for dehydration
Safety considerations:
Increased Risk for Falls
Due to grogginess, pain, weakness post-op. Older patients (>65) are more susceptible
Interventions: for the risk of fall pts
Keep room free of tripping hazards, monitor for medications causing dizziness (e.g., opioids)
Nausea/Vomiting & Aspiration: interventions
Raise head of bed to prevent aspiration, Keep patients upright for at least one hour after meals, Cut food into small bites
monitor for confusion or delirium
keep patient safe during their LOC
Acute pain
last 6 months or less, sudden onset, has an end, anticipated or predictable
Chronic pain
sudden or slow onset, constant without anticipated end, can be arthritis, back pain, migraine, headaches
nociceptive pain (damage from an outside source
skin, bones, joints, muscles, connective tissue, internal organs, skin or subcutaneous fat, damage to body tissue, sharp, stabbing, throbbing, “shocking pain”
neuropathic pain(damage from the nerve cells)
nerve pain, diabetic neuropathy(feels like pins and needles), phantom limb pain, spinal cord injury, intense, shotting, burning, “pins and needles”
Cancer pain
comes from a tumor, the bone, or the treatment of these these things. could also be caused by post surgical, radiation or chemotherapy induced neuropathy
Age considerations: children
pain may be ignored, but their behavior and physical signs will show their pain.
FLACC
pain scale for children 2 months to 7 years, rated by observation
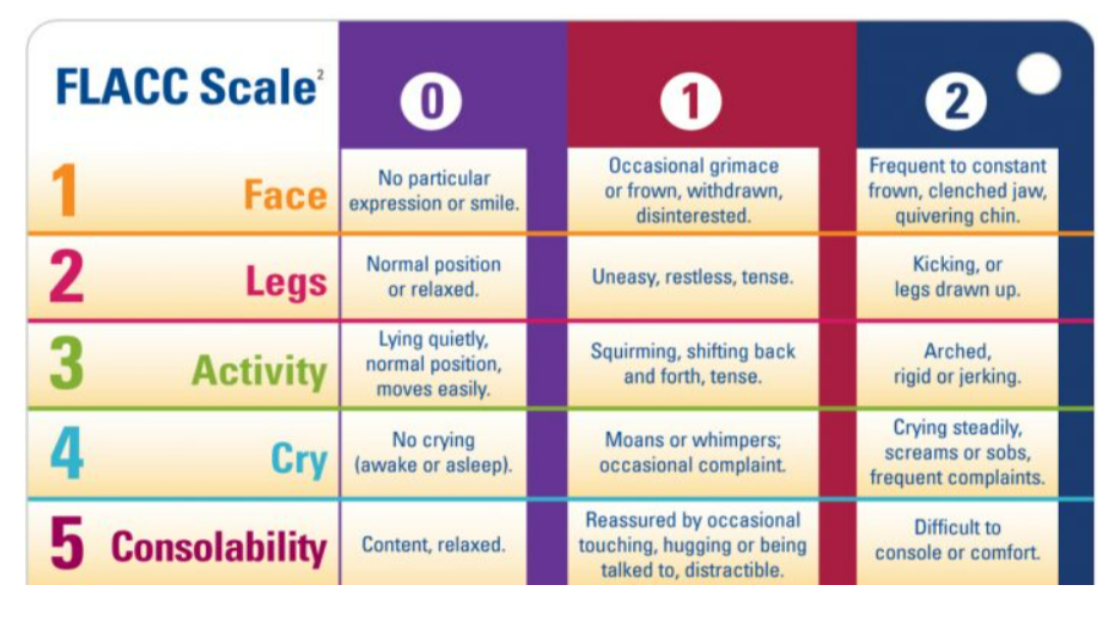
wrong BAKER faces
for children 3 and up to rate their pain

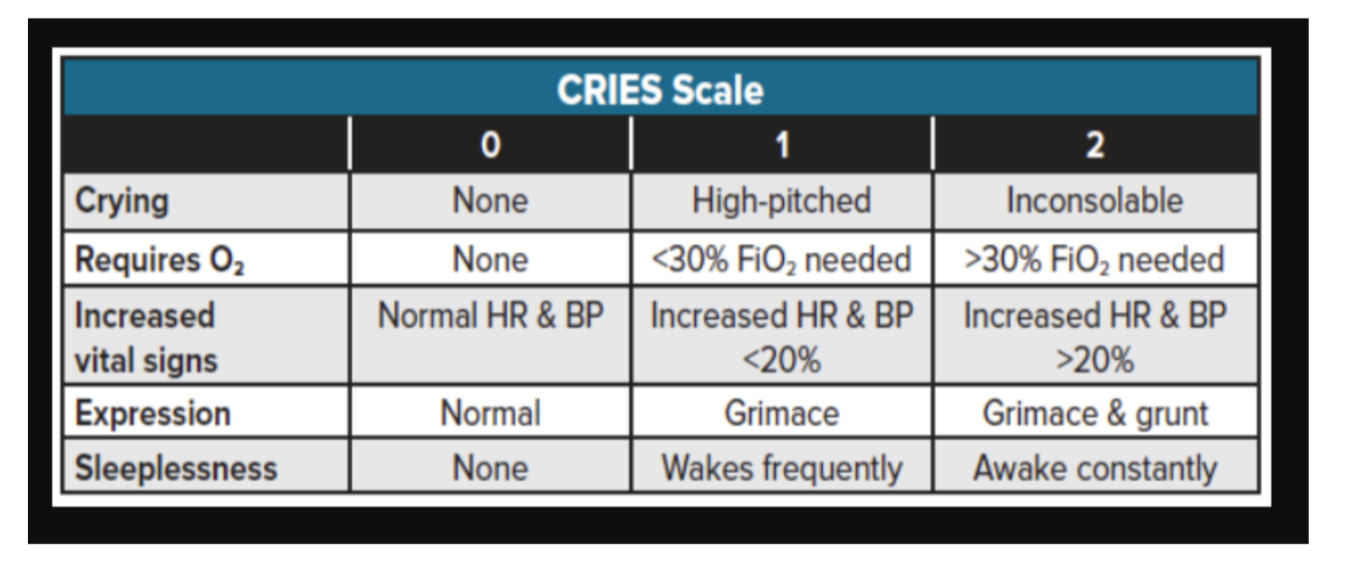
CRIES
for infants born 38 weeks of greater.
age considerations: older adults
back pain may be consistent, neuropathy pain, decreased pain tolerance, chronic illness, arthritis
age considerations: special needs
may not be able to express their pain so look at their behavior, like grimacing, guarding, crying, restlessness
objective signs of pain
Can be measured/observed
by the nurse
Crying
Sweating
Restlessness
Grimacing
Guarding
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Hypertension
Preipitating cause
This refers to what makes the pain worse or brings it on
Quality
This asks what the pain feels like
EX: aching, stabbing, sharp, throbbing, dull, burning, cutting, gripping, tearing, pounding, and shocking pain
Region
This identifies where the pain is located and if it spreads to other areas
Severity
This assesses how severe the pain is, often rated on a scale of zero to ten
Timing
This asks how long the pain has been going on (its onset and duration)
pharmacological Interventions for pain
Opioids
Premedicate before painful procedure
Try to prevent breakthrough pain
Treat pain before it becomes severe
Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA pump)
NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen, Aleve, Advil)
Acetaminophen
Monitor for respiratory depression in opioids & bleeding in NSAIDs
Some cultures may refuse opioids
nonpharmacological interventions for pain
Positioning (turn Q2)
Relieve bony prominences
Cold
Heat
Massage
Distraction
Therapeutic touch
Splint post-op incision with a pillow