3.1.11- Rate equations
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What does rate of reaction mean?
Rate of reaction- change in amount/concentration of a reactant/product per unit time.
What are the units for rate of reaction?
Units- mol dm^-3 s^-1
How can you calculate the rate of reaction?
Can be found by- measuring the decrease in the concentration of a reactant over time, measuring the increase in the concentration of a product over time.
How can you determine a rate equation? What does a rate equation contain?
Rate equations can only be determined experimentally. A rate equation will have a rate constant (K), the concentration of reagents and the other to which each reactant is raised.
What is the formula for a rate equation?
Rate of reaction = k [P]m [Q]n
Why is the concentration of the products not included?
Concentration of products does not affect the rate of reaction.
How can you find the rate constant using a graph?
The rate constant can be calculated by finding the gradient of a graph that has rate against concentration.
Gradient - Rate/ concentration of product
What happens in the rate equation when one of the concentrations is kept constant?
For example if
Rate = k[NO]2[ H2]
If [ H2] is kept constant
Than any change in the rate of reaction is caused by [NO]
Rate = K1 [NO]2
If [NO] is constant, any change is caused by [H2]
Rate = k2 [H2]
What does an order show?
The order shows how the concentration of a reactant affects the rate of reaction.
What does an order of 0 show?
Order 0 = Change in concentration has no effect on rate of reaction
What does an order of 1 show?
Order 1 = Change in concentration is directly proportional to rate of reaction
What does an order of 2 show?
Order 2 = Change in rate is directly proportional to the square of the concentration of that chemical.
How do you calculate the order?
By using the rate law equation, divide one experiment by the other.
When does K remain constant?
K only remains constant if the concentration of the reactants is the only factor that is changed.
When does K change?
K changes if the temperature or catalyst is used/changed.
What does a higher temperature mean to k?
Higher temperature= more energy = increased rate of reaction = increased rate constant.
What is the arhenius equation?
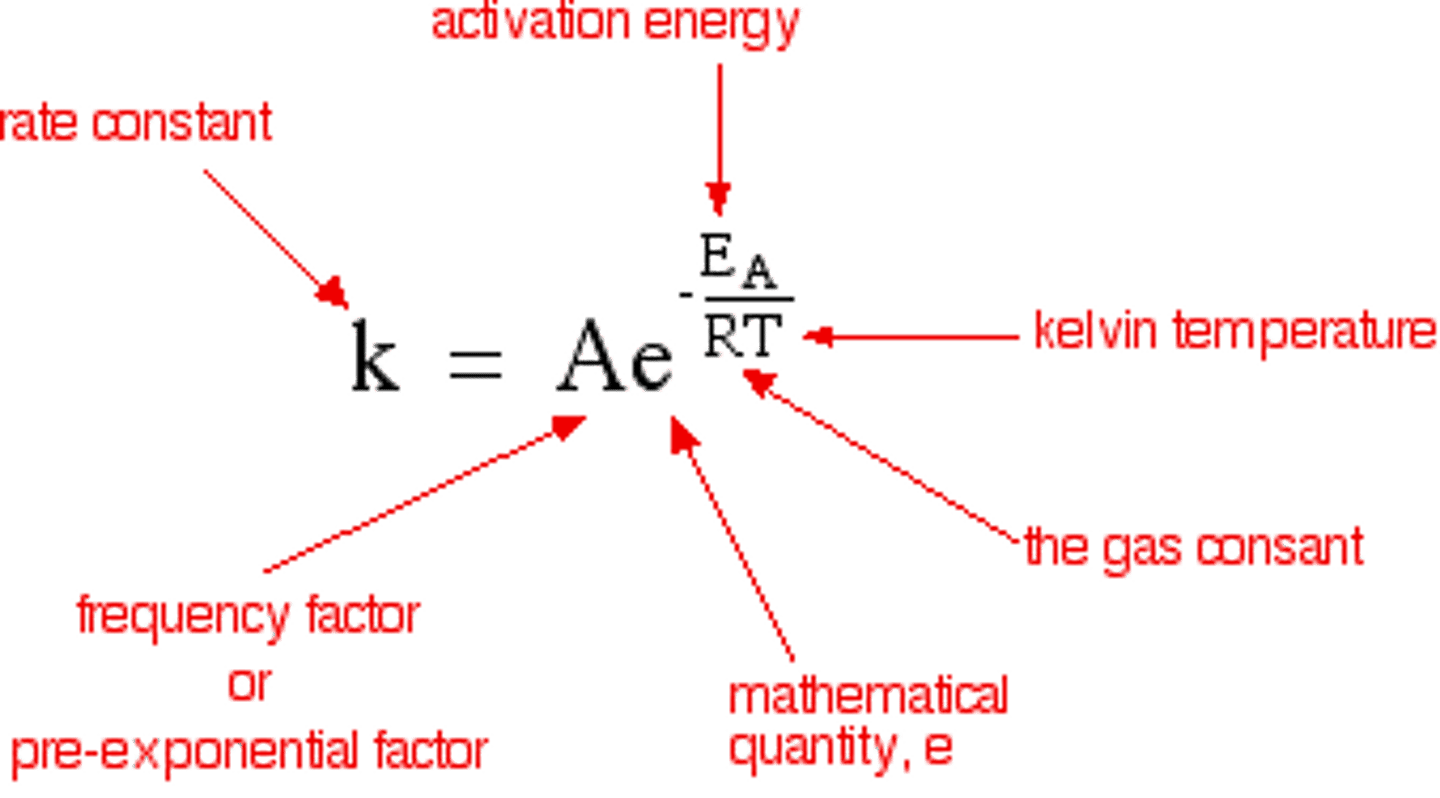
When is the arrhenius equation used?
Arrhenius equation is used to describe reactions with - gases, reactions in solution, reactions that occur on the surface of a catalyst.
What is a simplified equation of arrhenius equation?

How do you rewrite this equation to plot a graph
ln k = (-Ea/R) (1/T) + lnA
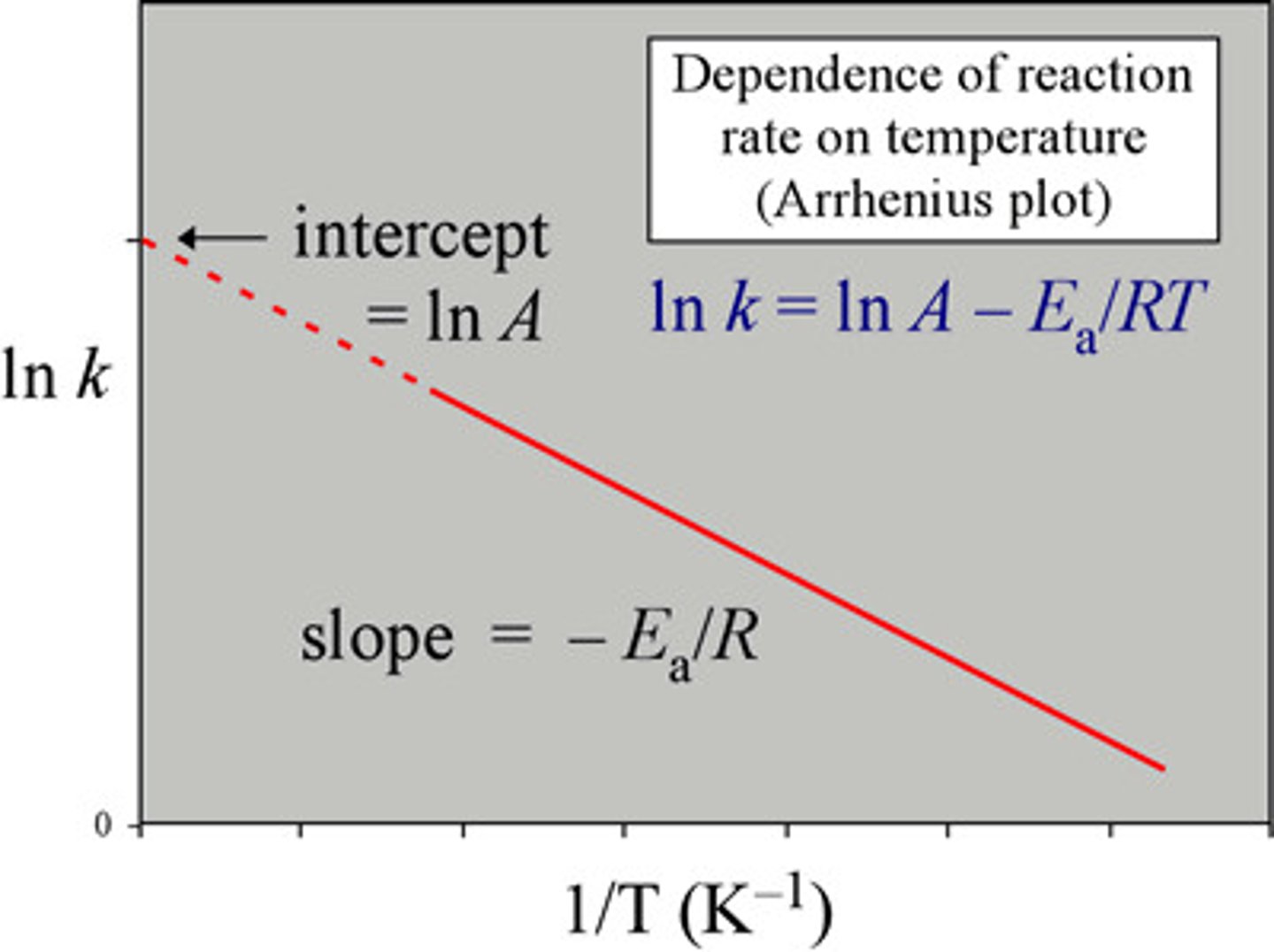
In the Y=m + c form, what does each variable stand for?
y = lnk
x = 1/t
m= -Ea/R (gradient)
c= lnA
(y-intercept)
How do you calculate the activation energy?
Calculate the gradient.
What can you do to calculate the overall rate of a reaction or the order of a reactant?
Plot a concentration time graph or set up multiple experiments with different concentrations of the product and measure the rate of reaction.
What does a zero order concentration time graph look like?
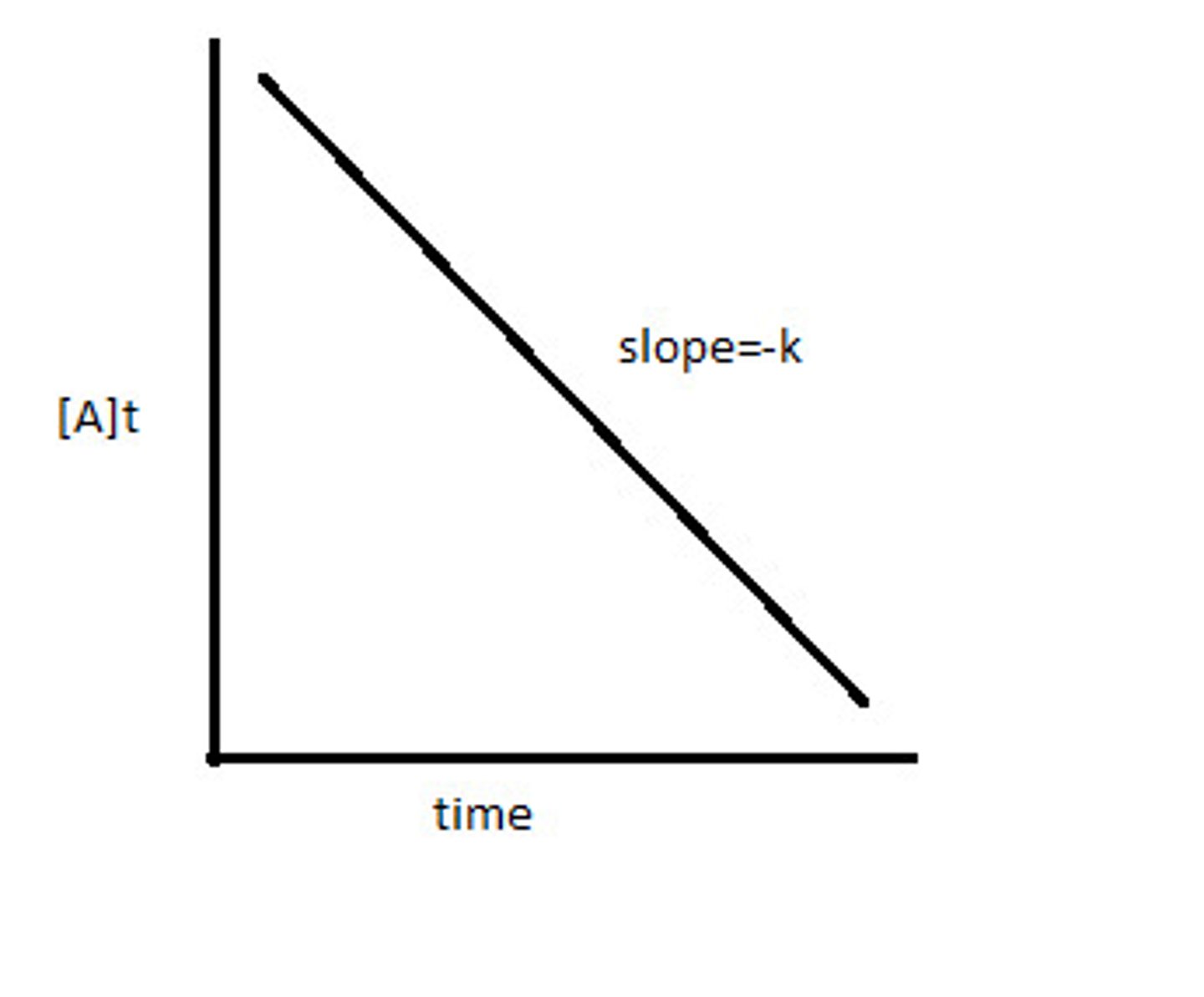
What does a first order concentration time graph look like?
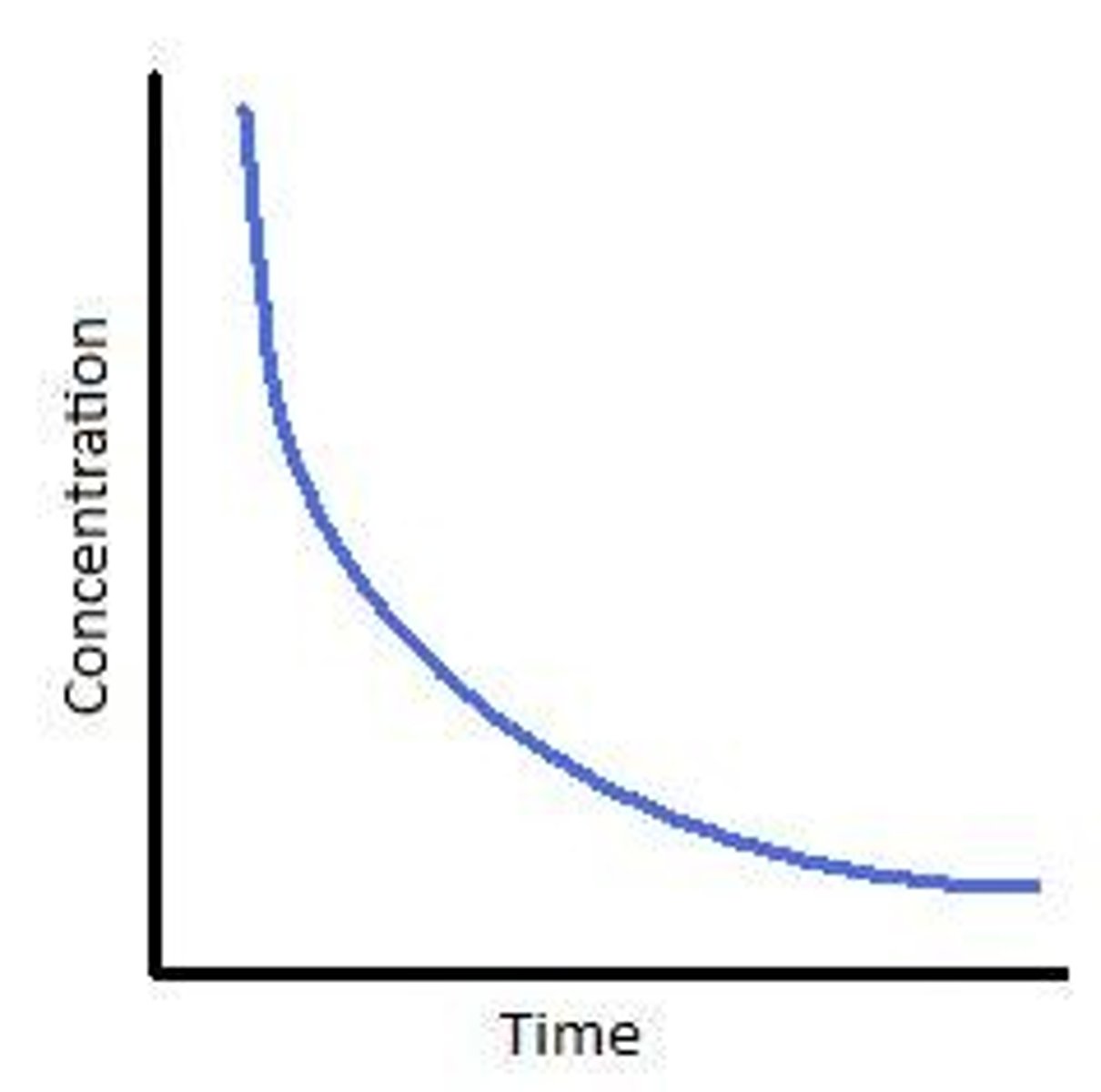
What does a second order concentration time graph look like?
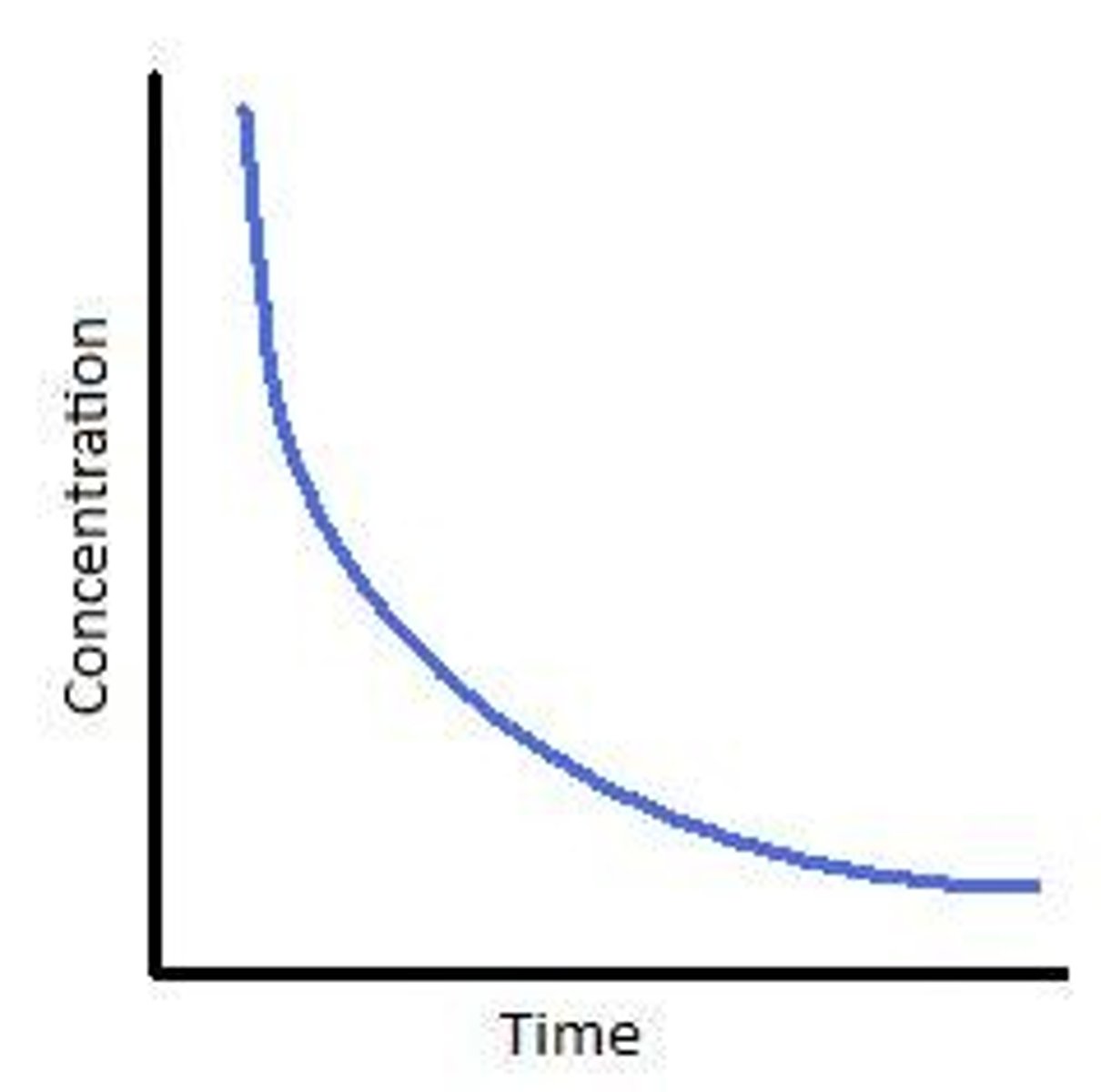
Describe the second order graph in comparison to the first order graph
Second order- concentration decreases more steeply with time, concentration of reactant decreases more steeply with time than first order.
How do you find the initial rate of reaction using the graph?
To find the rate at the start of a reaction find the gradient at the initial concentration. Do this by drawing a tangent.
What does a zero order rate of reaction vs concentration of reactant graph look like?

What does a first order rate of reaction vs concentration of reactant graph look like?
Rate = K[A]
![<p>Rate = K[A]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/529fda33-2787-42a2-9327-e84220cbe702.jpg)
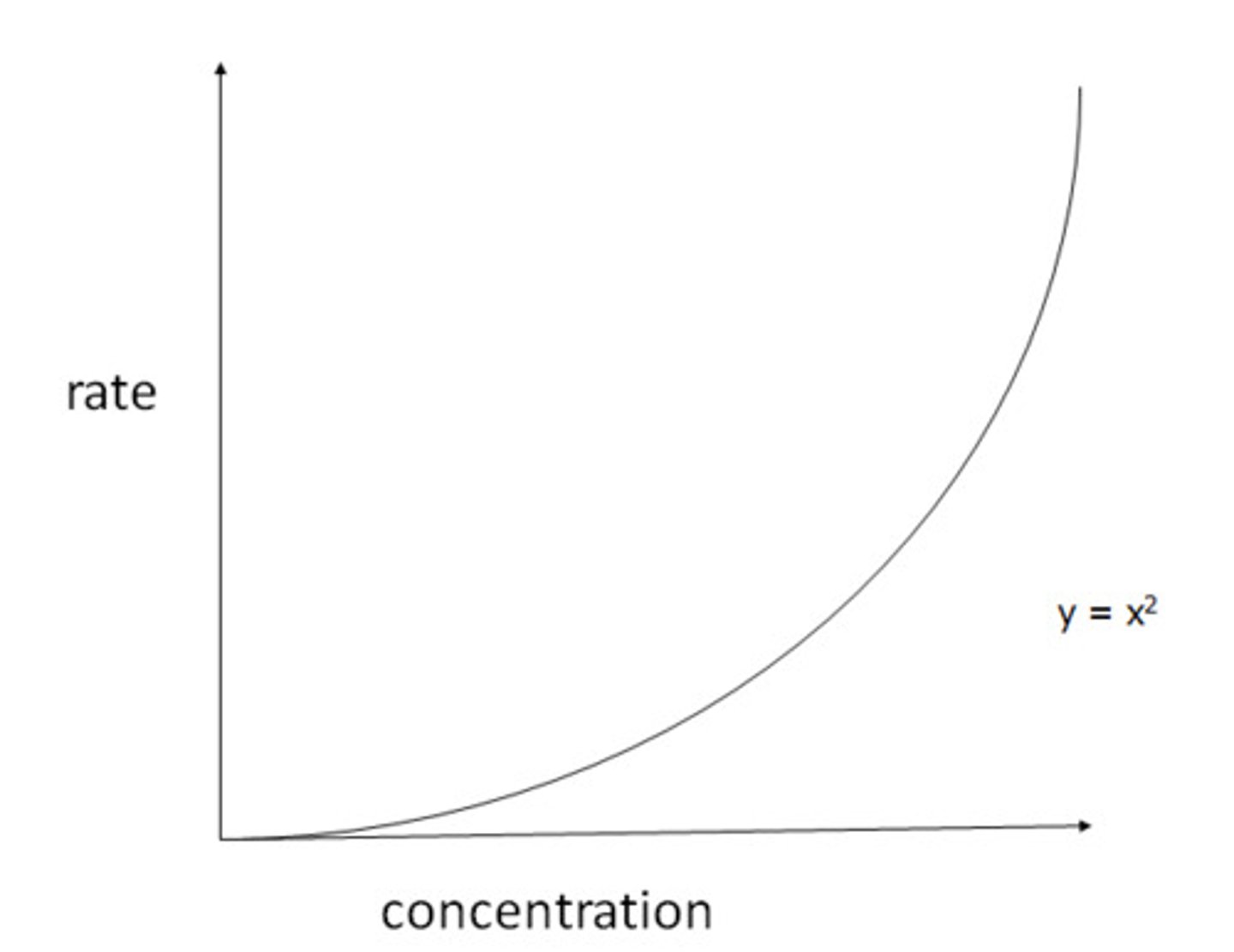
What does a second order rate of reaction vs concentration of reactant graph look like?
What step is the rate determining step?
The slowest step in a reaction is the rate determining step.
What does the slowest step include?
The slowest step in a reaction includes all the reactants that have an impact on the reaction rate when their concentrations are changed.
What reactants appear in the rate equation?
All reactants that appear in the rate equation will also appear in the rate-determining step
What happens to zero order reactants and intermediates in the rate determining step?
Zero order reactants and intermediates will not be present in the rate determining step.
What can you tell from the rate equation about the rate determining step about the number of molecules involved?
The rate equation is:
Rate = k [NO2]2
From the rate equation, it can be concluded that the reaction is zero order with respect to CO (g) and second order with respect to NO2 (g)
This means that there are two molecules of NO2 (g) involved in the rate-determining step
What does overall order mean?
Add up all the powers.
What does it mean if a molecule is not present in the chemical reaction equation but it appears in the rate equation?
If a molecule is not present in the chemical reaction equation but does appear in the rate equation it is a catalyst.
What are the two required practicals?
Measuring the rate of reaction by an initial and continuous rate method.
How do you measure the rate of reaction by an initial rate method.
The iodine clock reaction
Describe the iodine clock reaction
A small amount of sodium thiosulfate and starch (the indicator) are added to an excess of hydrogen peroxide and iodide ions in acidic solution. The sodium thiosulfate reacts instantaneously with any iodine produced. One all the sodium thiosluphate has reacted, any iodine produced will stay in the solution and the starch will turn the solution a blue/black colour. Varying the concentration of iodine or hydrogen peroxide will give different times for the colour change
How do you measure the rate of reaction by a continuous rate method.
Magnesium and HCL
How can you calculate the rate of reaction with a continuous rate method?
Draw a graph of volume of has collected by time. Draw a tangent at t=0 to get the initial rate of reaction.