IGSCE Biology - Exretion
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What do the lungs excrete?
Carbon dioxide and water
What does the skin excrete?
Water and salt by sweating
What do the kidneys excrete?
Urea, water and ions from the blood. This is called urine.
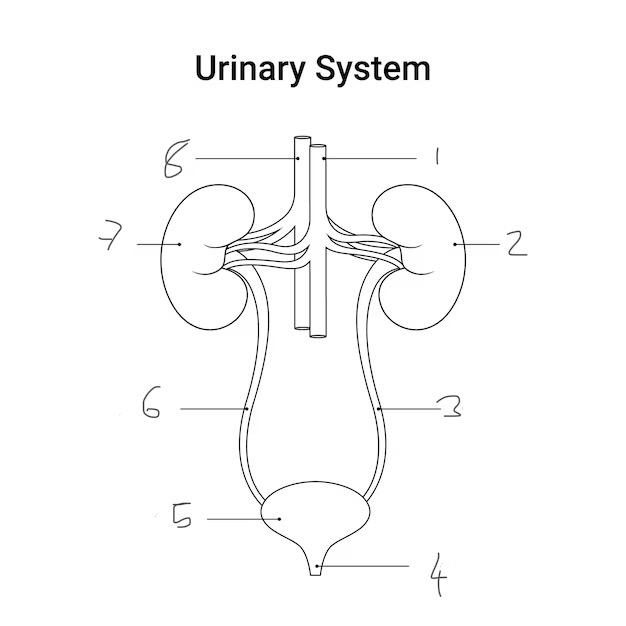
Label this diagram
Vena cava
Left kidney
Left ureter
Urethra
Bladder
Right ureter
Right kidney
Aorta
renal vein + vena cava = blue
renal artery + aorta = red

How does the kidney carry our its role of excretion?
The kidneys filter the blood to get rid of harmful substances, particularly urea, which is produced in the liver from the breakdown of amino acids
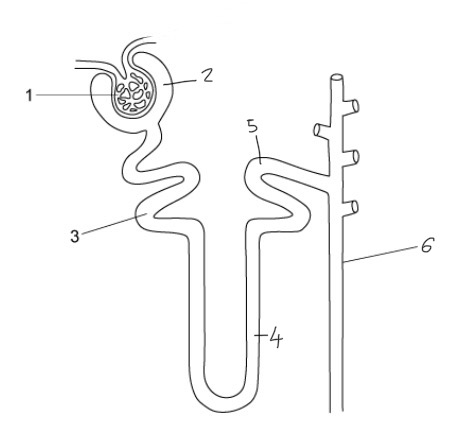
Label this diagram
Glomerulus
Bowman’s capsule
Proximal convoluted tubule
Loop on Henle
Distal convoluted tubule
Collecting duct
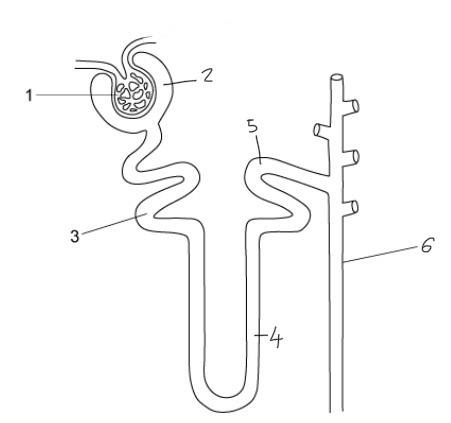
Ultrafiltration
The blood arriving at each glomerulus is under high pressure.
Small molecules cross over into the kidney nephron whereas large molecules stay in the blood.
The fluid moves along the nephron, it is known as the glomerular filtrate
Selective reabsorption
glucose (and other useful small molecules) mustn’t stay in the nephron and leave in the urine (it’s needed for respiration)
It is reabsorpted into the bloodstream from the proximal convoluted tubule
This happens via active transport - there are lots of mitochondria in the cells lining this part of the nephron.
osmoregulation (reabsorption of water in the loop of henle)
the wall of the nephron is permeable to water
The surrounding are has low water potential and therefore the some water will leave via osmosis.
Osmoregulation (hormonal control of water)
the body can control the water content of the blood using the kidney.
Special cells in the hypothalamus of the brain can detect the amount of water in the blood.
If you are dehydrated, the cells in the hypothalamus can cause the pituitary gland to release a hormone called the anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
This then travels through the blood to the kidney where it make the walls of the nephron more permeable to water and therefore more water is reabsorpted into the blood.
This make the urine more concentrated (less water excreted.)
Opposite happen when there is a normal amount of water in the blood.