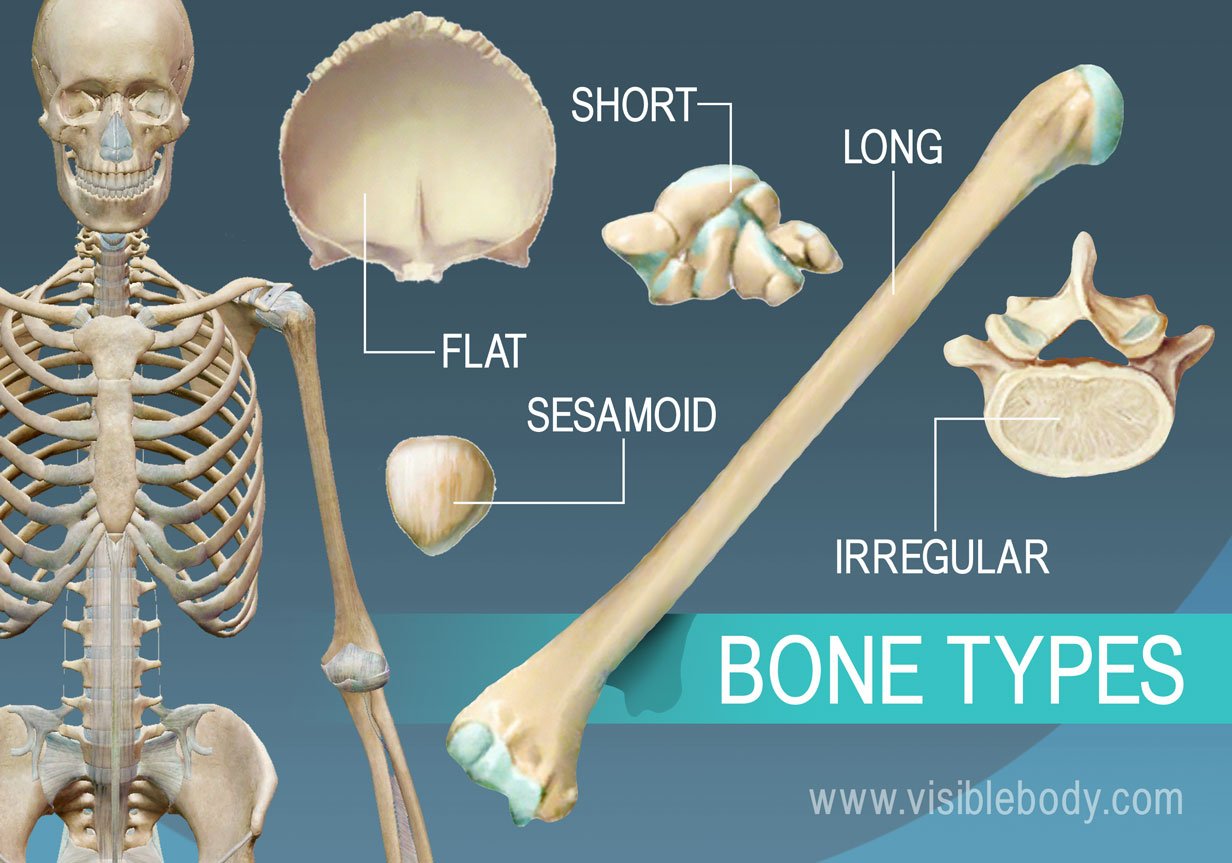
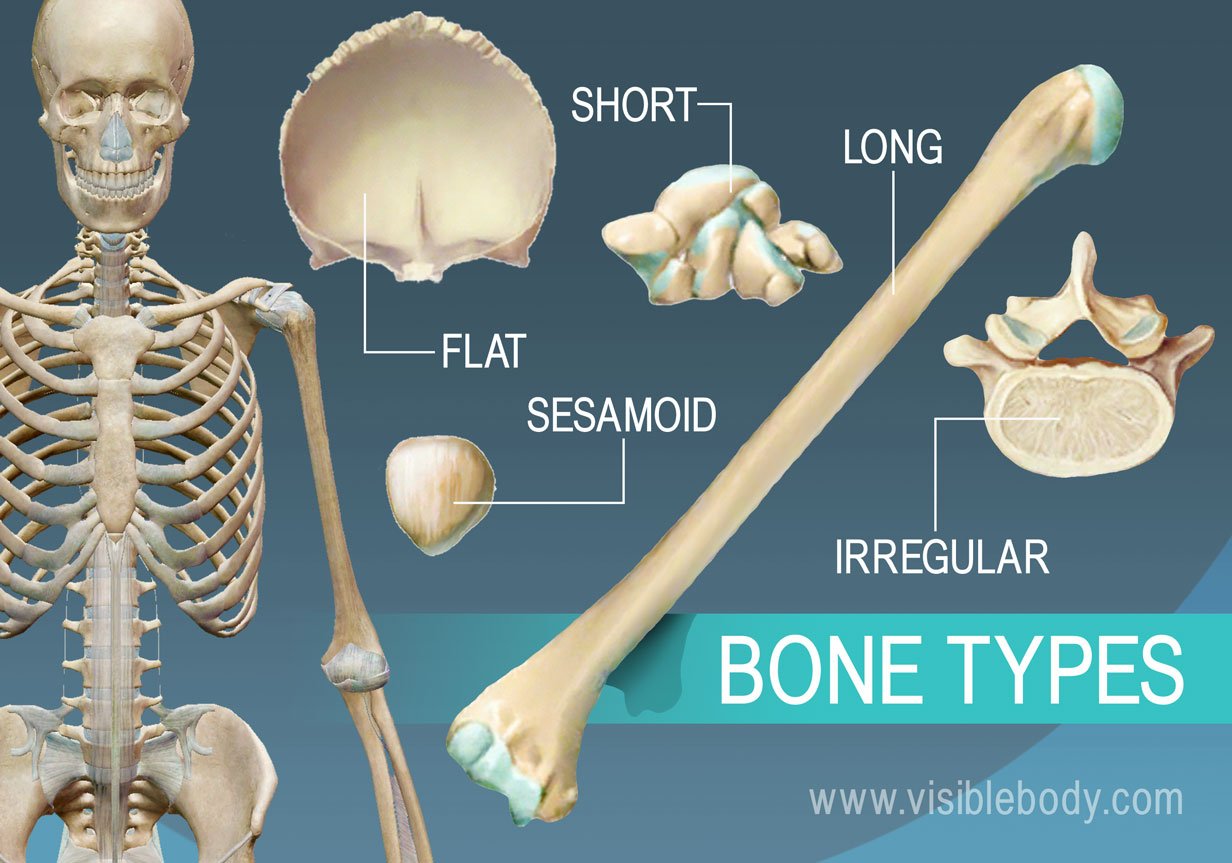
Types of Bones
1/4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
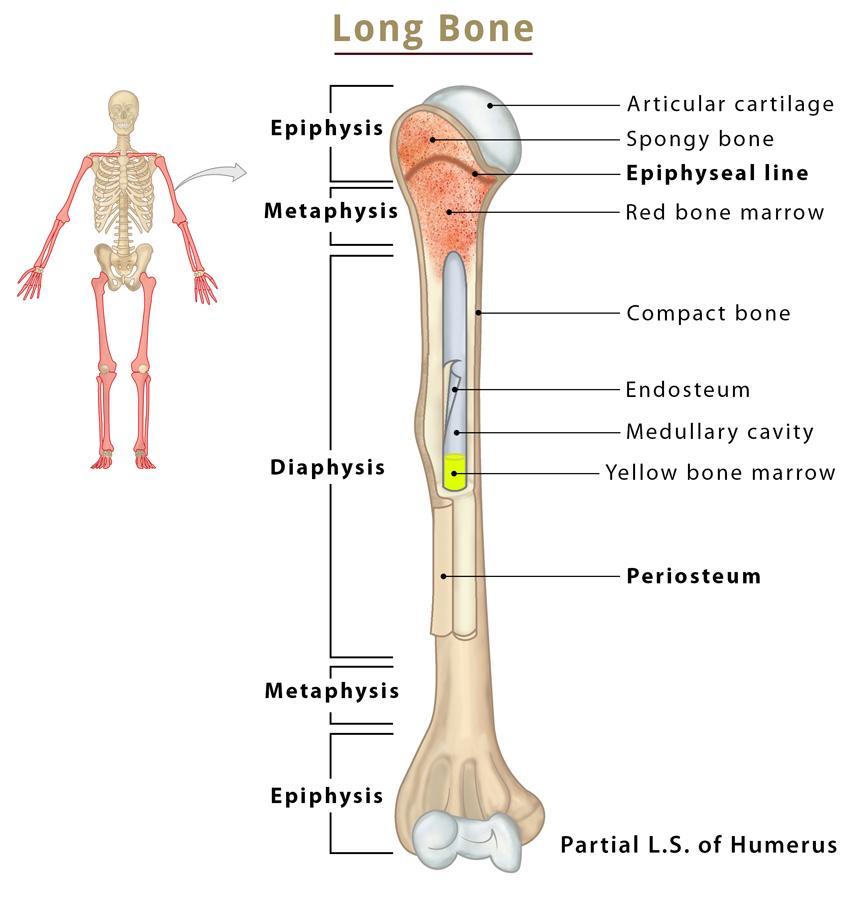
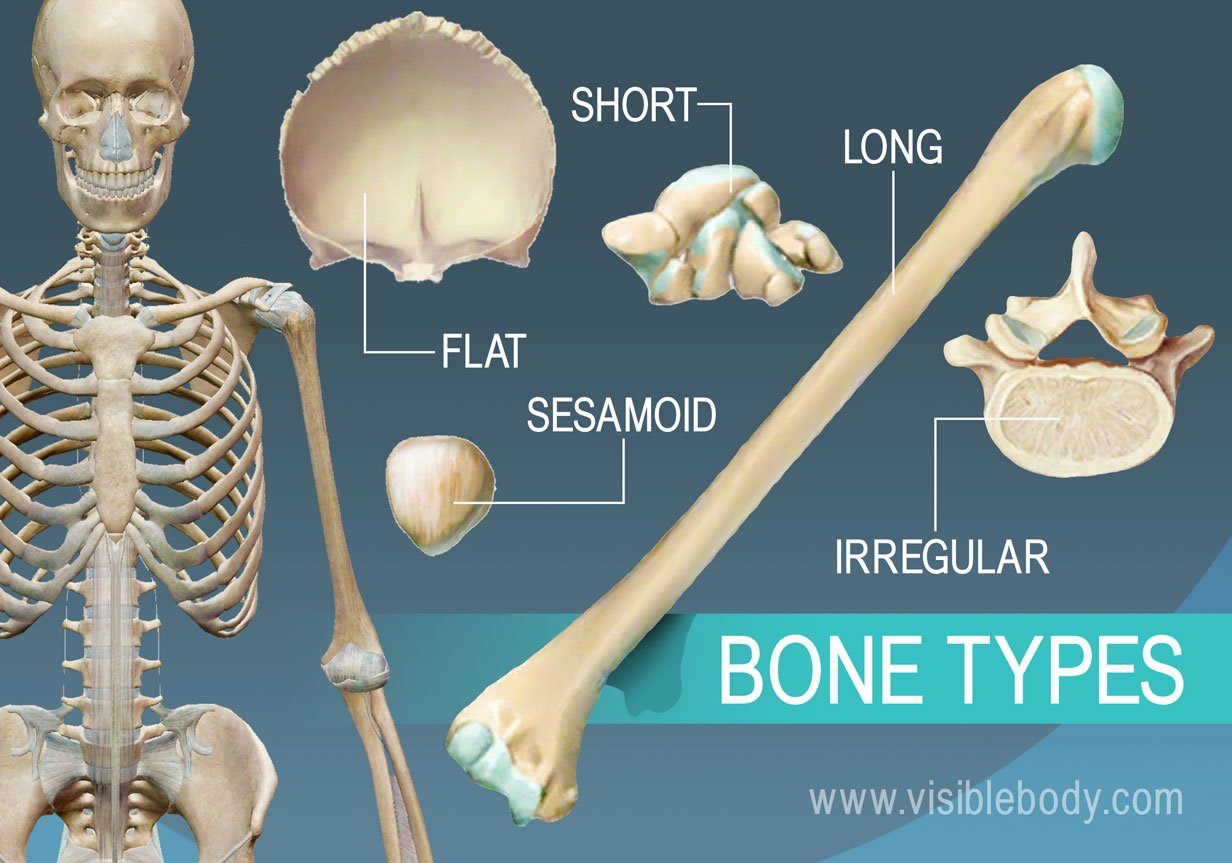
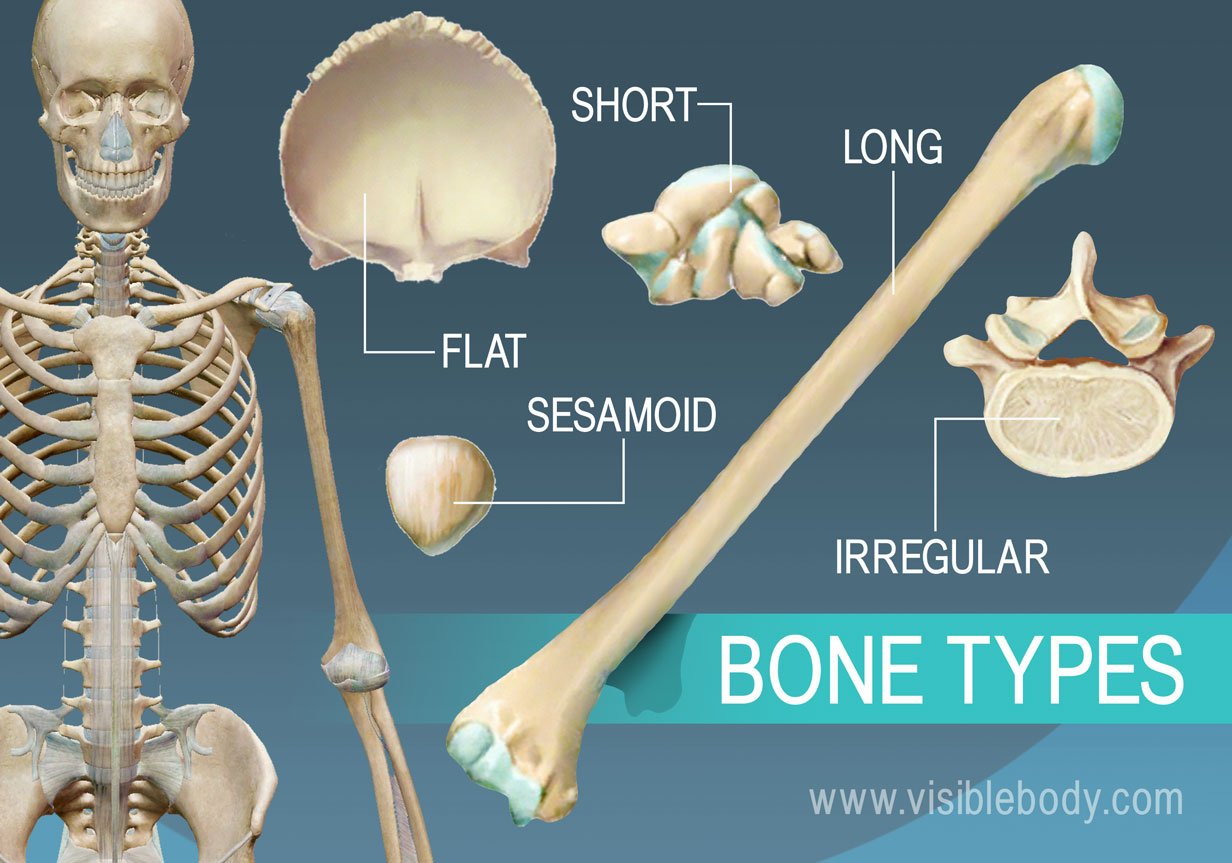
Long bones
Long bones are characterized by their elongated shape and primarily consist of a shaft and two ends. They are mainly found in the limbs, such as the femur and humerus.
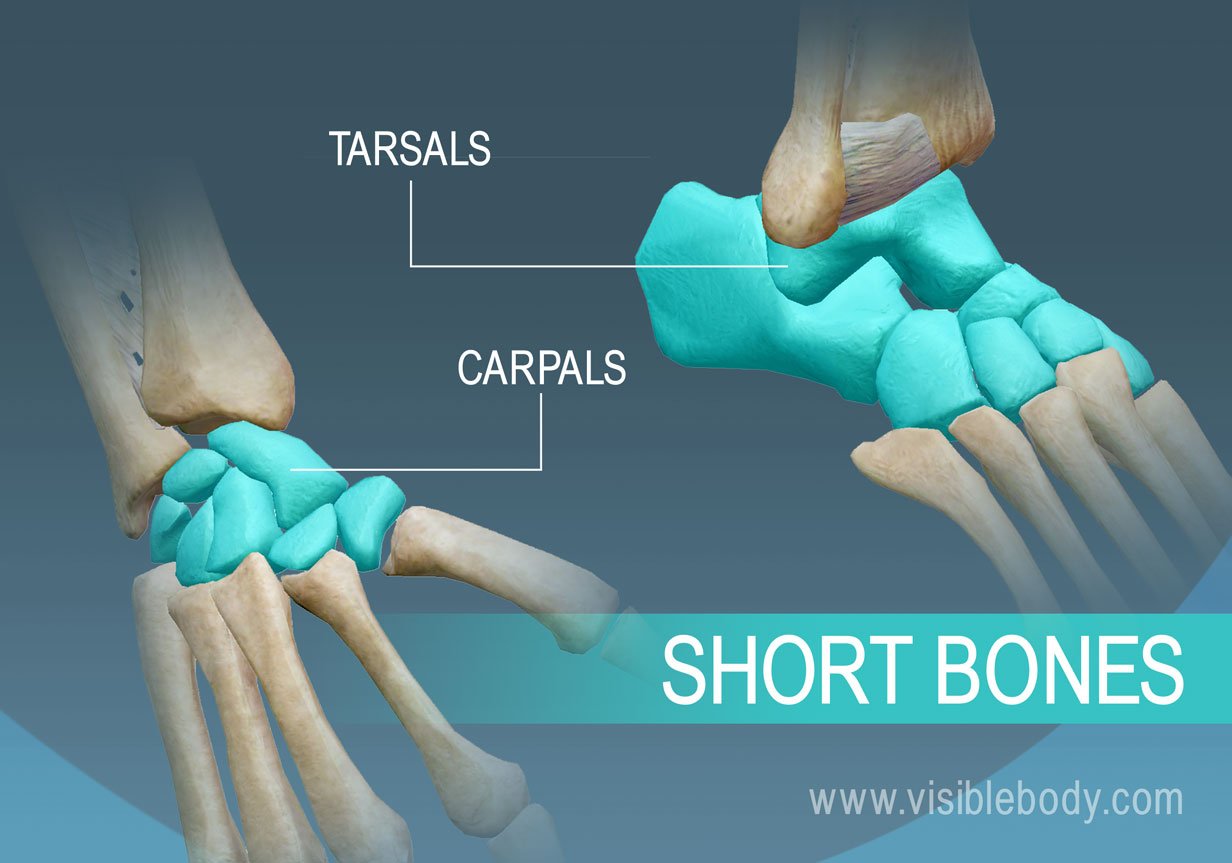
Short bones
Short bones are roughly cube-shaped and provide stability and support while allowing for some motion. Examples include the carpals in the wrist and tarsals in the ankle.
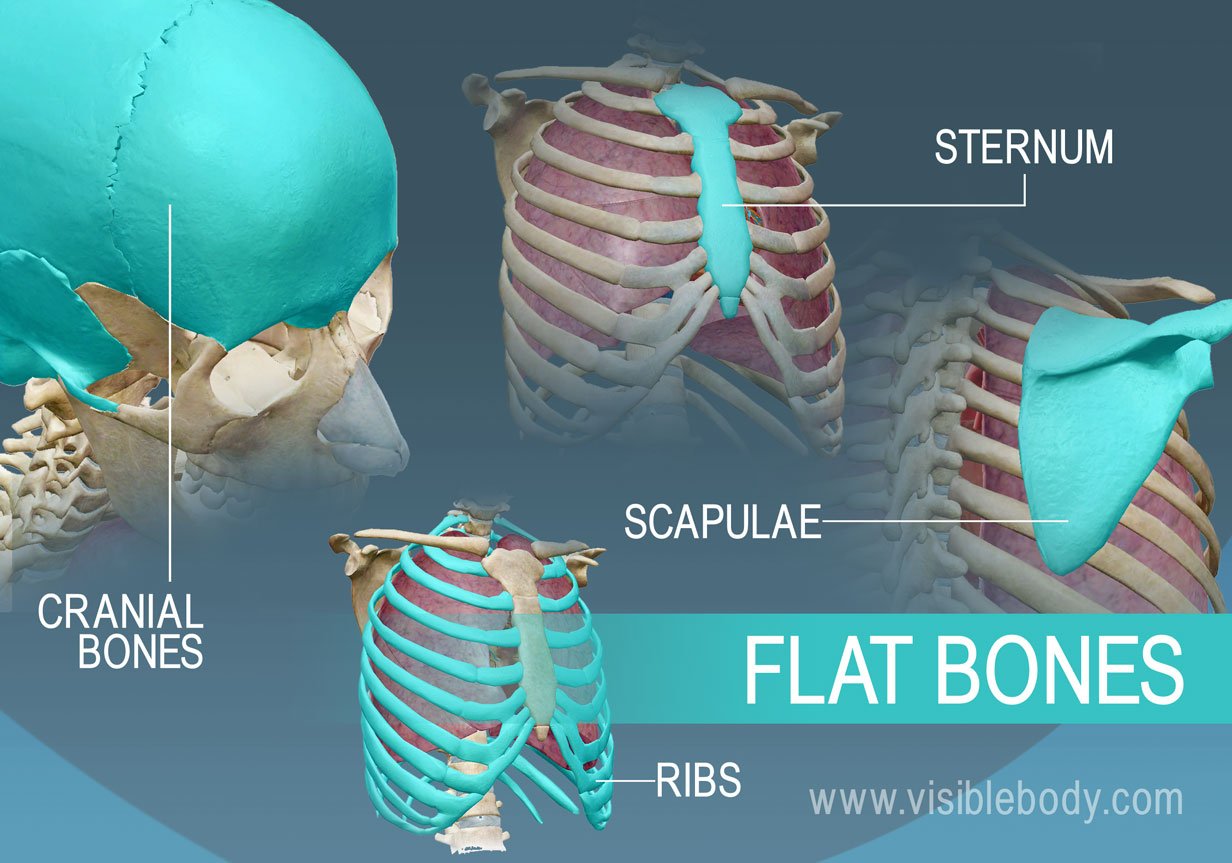
Flat bones
Flat bones are thin, broad bones that provide protection for internal organs and a surface for muscle attachment. Examples include the skull, ribs, and sternum.
Irregular bones
Irregular bones have complex shapes that do not fit into the other categories. They provide support and protection while allowing for flexibility. Examples include the vertebrae and certain bones of the face.

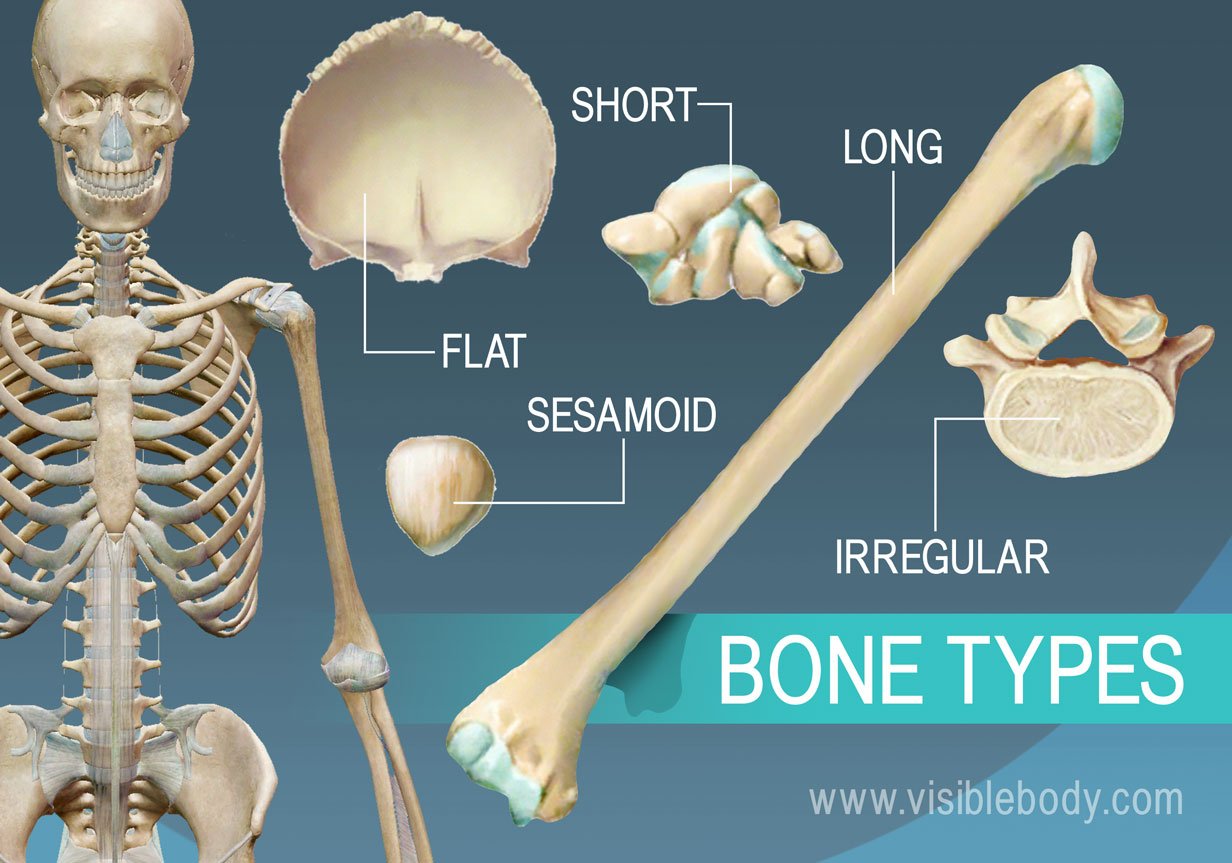
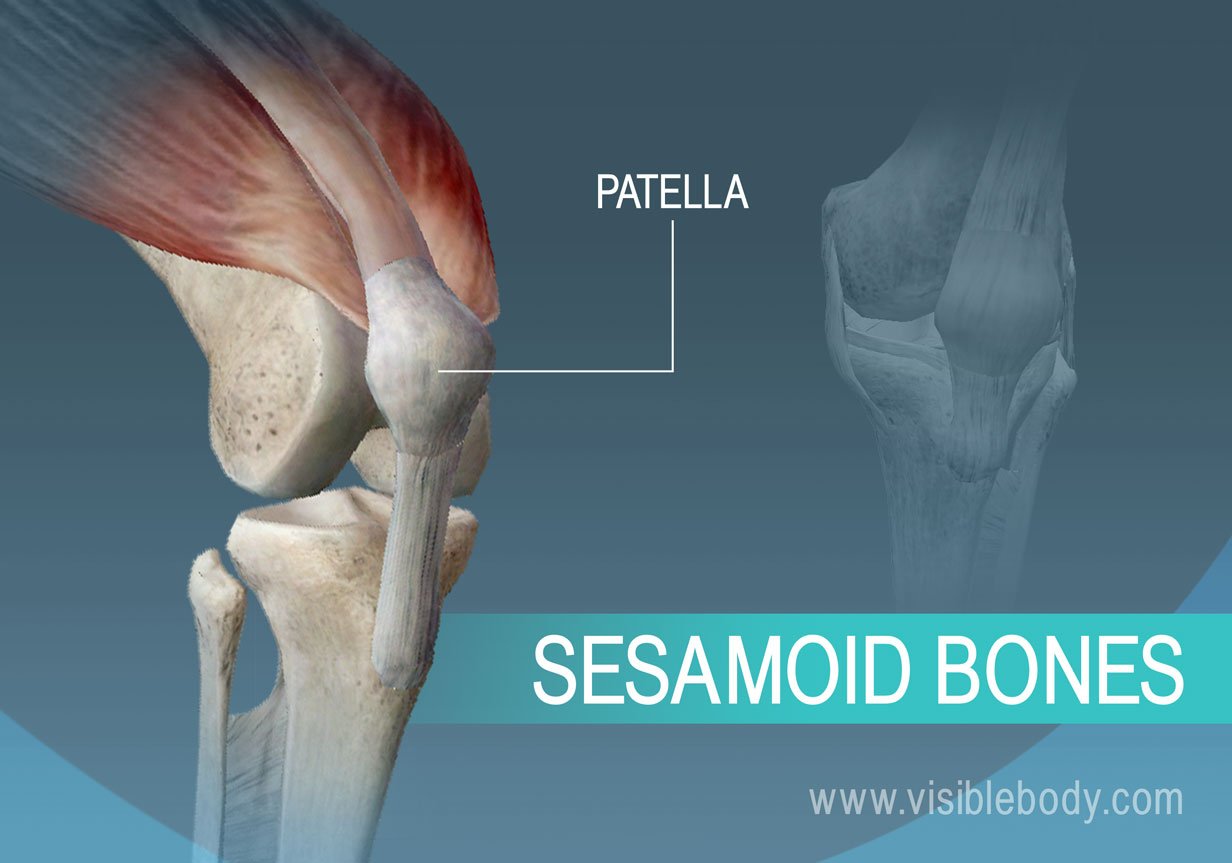
Sesamoid bones
Sesamoid bones are small, round bones embedded within tendons that help to protect tendons from stress and wear. A common example is the patella (kneecap).