1 - NERVOUS SYSTEM
1/138
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
What is homeostasis?
Maintaining a constant internal enviroment despite internal or external changes in order to maintain optimal conditions for enzyme activity
What has to be kept the same in the body?
body temperature
water levels
blood glucose levels
What is the automatic control system?
stimulus→receptor→coordination centres→effectors→response
What is the stimulus?
change in the enviroment
What is the receptor?
cells that detect stimuli
Where are receptors usually found?
mostly in the sense organs
What do the coordination centres do?
recieves and processes information and organises a response
What are examples of coordination centres?
brain
spinal cord
pancreas
What do effectors do?
they carry out a response
What are the effectors?
muscles and glands
What responses do muscles carry out?
contract
What responses do glands carry out?
secrete a chemical (enzymes/hormones)
How are messages sent to the automatic control system?
signals are sent via the nervous ststem or hormonal system
What is the signal type for the nervous system?
electrical impulses
How does the signal travel in the nervous system?
neurones
What is the speed of the signal in the nervous system?
faster than the hormonal system
What is the duration of the signal in the nervous system?
short lasting
What is the signal type for the hormonal system?
chemical
How does the signal travel in the hormonal system?
blood
What is the speed of the signal in the hormonal system?
slower than the nervous system
What is the duration of the signal in the hormonal system?
longer lasting
What are the 5 senses?
sight, hearing, taste, smell, touch
What is the sense organ for sight?
eyeballs
What is the sense organ for hearing?
ears
What is the sense organ for taste?
tongue
What is the sense organ for smell?
nose
What is the sense organ for touch?
fingertips
What are the receptors for sight?
retinas
What are the receptors for hearing?
auditory hair cells
What are the receptors for taste?
taste receptors / taste buds
What are the receptors for smell?
olfactory receptors
What are the receptors for touch?
pacinian corpuscles (pressure)
pain receptors (pain)
What are the stimulus for sight?
light
What are the stimulus for hearing?
sound
What are the stimulus for taste?
chemicals (in food)
What are the stimulus for smell?
chemicals (in air)
What are the stimulus for touch?
texture
What do nerve cells do?
Carry electrical signals called impulses around the body
What are the 3 types of neurones?
sensory, motor and relay neurones
What do sensory neurones do?
carries impulses from the receptors to the CNS
What do motor neurones do?
carries impulses from the CNS to effectors
What is a relay neurone?
transmits impulse from the sensory to the motor neurone
What are the adaptations of neurones?
long
contrain mylelin sheath
dendrites
Why are neurones long?
so they can reach all parts of the body
What is the myelin sheath made of?
fat
Why do neurones have a myelin sheath?
the fatty myelin sheath insulates the neurones so the electrical impulses can’t pass out of the axon
What is an axon?
What the impulse travels along
Why do neurones contain dendrites?
the branched endings of the dendrites are used to communicate with other neurones
What does the Nervous System do?
they allow you to react to your surroudings and coordinate your behaviour
What does CNS stand for?
Central Nervous System
What does the Central Nervous System deal with?
brain
spinal cord
relay neurones
What does PNS stand for?
Peripheral Nervous System
What does the Peripheral Nervous System do?
all other nerves (sensory/motor neurones)
What is a reflex action?
automatic
rapid
protective responses
innate
Reflex Action Flow Chart
stimulus→receptor→sensory neurone→relay neurone (spinal cord)→motor neurone→effector→response
Voluntary Action Flow Chart
stimulus→receptor→sensory neurone→cordination centre (brain)→motor neurone→effector→response
What is a synapse?
A gap between neurones
Why is it hard for impulses to travel across synapses?
since synapses are a gap between neurones and impulses can’t cross the gap
How do impulses travel across synapses?
nerve impulse arrives at the end of one neurone
this triggers the release of chemical molecules in the synapse
the chemicals diffuse across the synapse and bind to the receptors on the next neurone generating a new electrical impulse
What is the method for the reaction time required practical?
Student A sits with their arm resting on the edge of a table
Student B holds the ruler so that 0 cm on the ruler is level with the top of the thumb of Student A
Student B lets go of the ruler without warning.
Student A catches the metre rule as quickly as possible
Record the number on the ruler where Student A caught it.
Repeat 9 more times
Repeat with Student B now catching the ruler
Both students repeat the experiment with their other hand
What are some things to try and keep the same in the ruler drop test?
Same starting position of the ruler
Same distance between the catcher’s thumb and fingers
Support your arm on the bench the same way
Use the same hand each time
Drop the ruler without warning
What is the starting position of the ruler?
aligned 0cm with the top of the catching thumb
What are some other control variables for tests similar to the ruler drop test?
age
sex
BMI
amount of sleep
What does the Brain do?
Receives and processes information from sensory receptors via sensory neurones
Sends impulses along motor neurones to effectors to coordinate responses
What is the brain made of?
billions of interconnected neurones
What do different regions of the brain do?
carry out different functions
What are the different regions of the brain?
cerebral cortex, cerebellum, medulla oblongata, hypothalamus, pituitary gland
What does the cerebral cortex control?
Consciousness, intelligence, memory and language
What does the cerebellum control?
Controls of muscular movement, posture and balance
What does the medulla oblongata control?
Controls unconscious activities (breathing rate, heart rate peristalsis, swallowing and coughing)
What does the hypothalumus control?
Controls homeostatic mechanisms (body temperature, water potential of the blood)
What does the pituitary gland control?
produces hormones
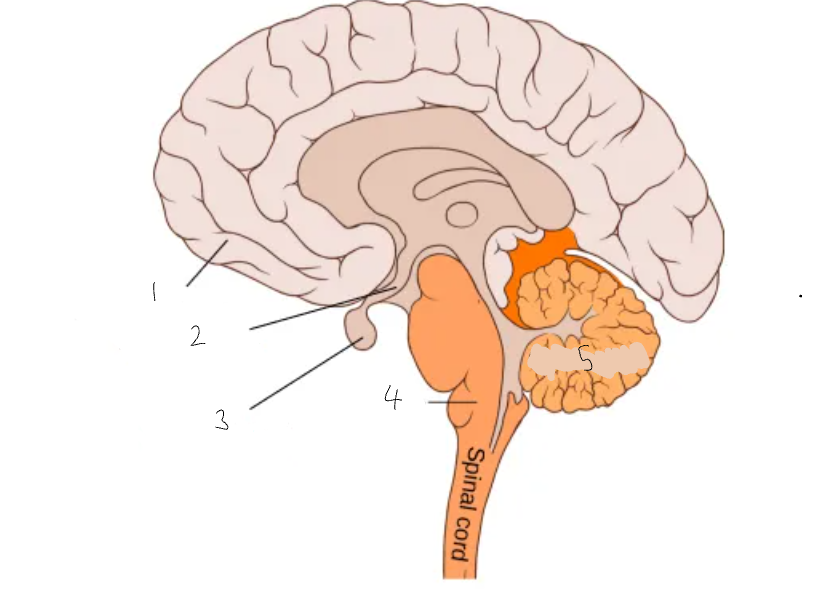
What part of the brain is 1?
cerebral cortex
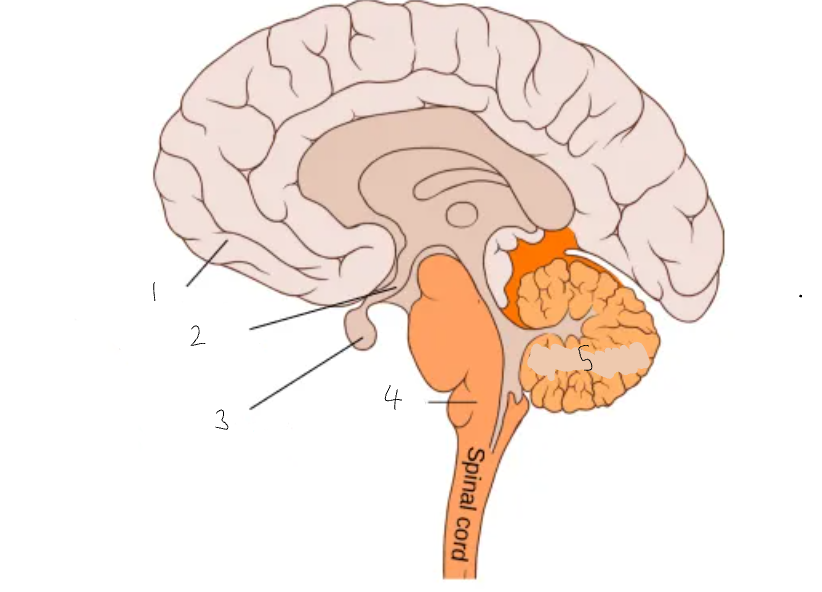
What part of the brain is 2?
hypothalamus
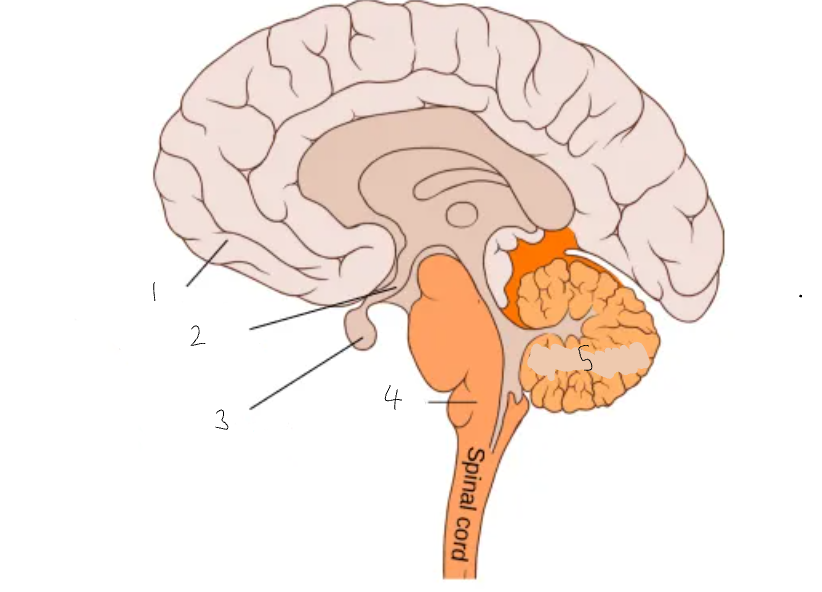
What part of the brain is 3?
pituitary gland
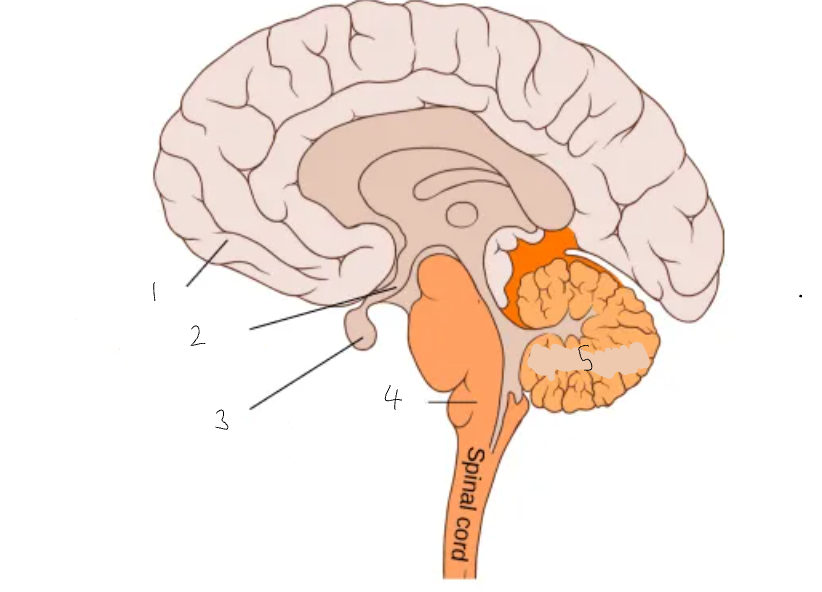
What part of the brain is 4?
medulla oblongata
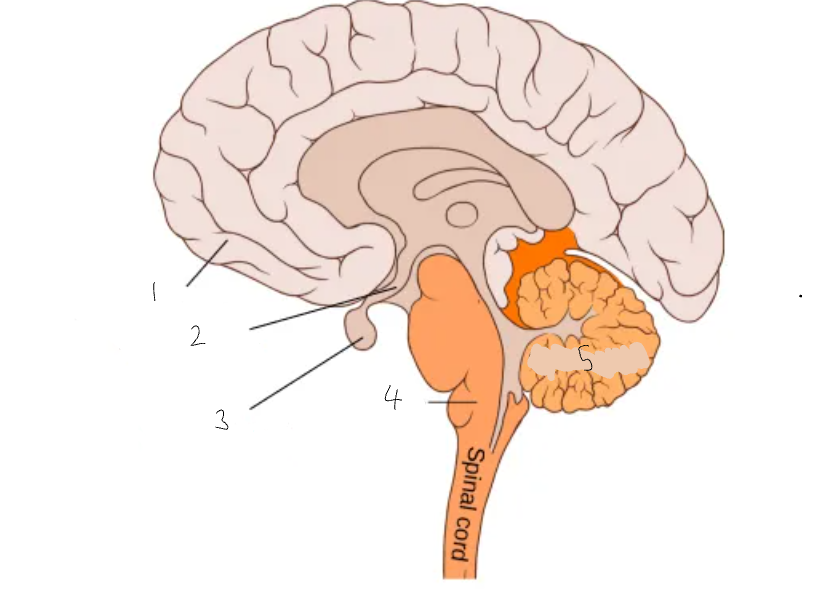
What part of the brain is 5?
cerebellum
How did scientists find out about the structures and functions of the brain?
studied people with brain damage
electrically stimulating different parts of the brain
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scans
What is the width of the brain?
140mm
What is the lenght of the brain?
167mm
What is the height of the brain?
93mm
What is the weight of the brain?
1.4kg
What are some problems with the brain?
The brain is very complex and delicate and can be easily damaged
Many processes involve different neurones and different types of chemicals are released at synapses, which makes it very difficult to investigate and treat brain disorders
Drugs can’t always pass through the membrane surrounding the brain to reach it
Surgery may cause unintended damage
What is the eye?
a sense organ that contains receptors which are sensitive to light intensity and colour
What is the sclera?
white outer layer of the eye, which is tough and strong so the eyeball is not easily damaged
What is the cornea?
curved transparent region at the front of the sclera to allow light through
Why is the cornea curved?
to refract (bend) the light so that it focuses on the retina
What is the pupil?
hole through which light enters the eye
What is the iris?
contains muscles that control pupil size by contracting and relaxing which controls the amount of light that reaches the retina
What is the lens?
clear disc that further focuses the light to produce a clear image on the retina
What are the suspensory ligaments and ciliary muscles?
they hold the lens in place and change the shape of the lens to focus light onto the retina
What is the retina?
contains receptor cells that are sensitive to light intensity and colour
What are the receptor cells in the retina called?
photoreceptors
What do photoreceptors do?
they convert light energy into electrical energy
What is the optic nerve?
it carries electrical impulses from the retina to the brain
What is the blind spot?
where the optic nerve leaves the eye because there is no retina there
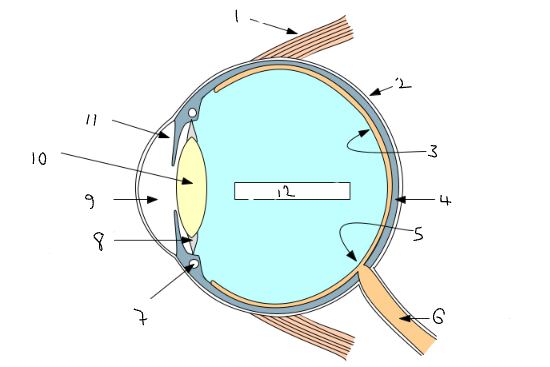
What part of the eye is 1?
muscle to move the eye
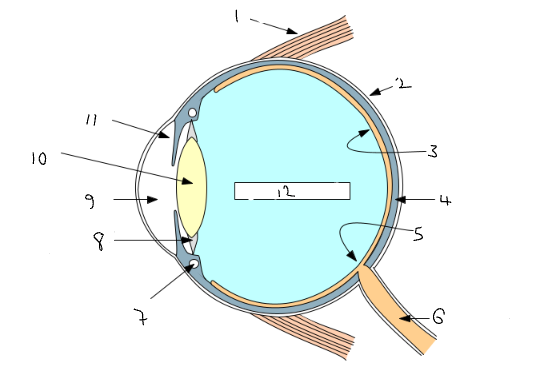
What part of the eye is 2?
sclera
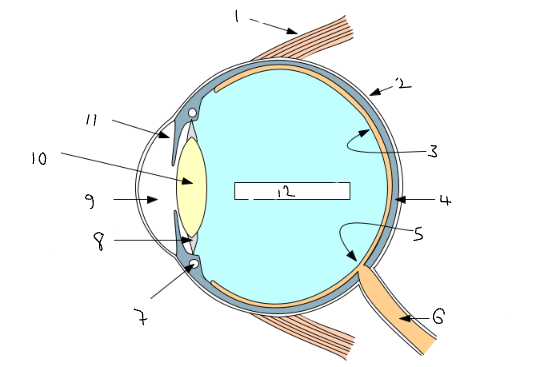
What part of the eye is 3?
retina
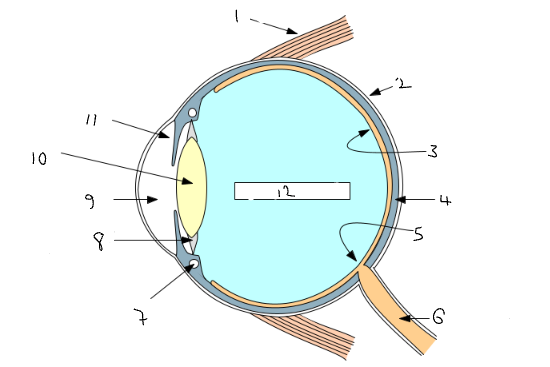
What part of the eye is 4?
choroid