The Etruscans and the Foundations of Rome through the Republic
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Greek Settlements in Sicily and South Italy (8th-3rd C. BC), Etruscans (8th-2nd C. BC), Rome's Foundation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms

fresco (true fresco)
painting on lime plaster either dry (fresco secco) or wet (Buon fresco / true fresco); also a painting executed in either method
3 points of background for early Italy:
1) Greek settlements in Sicily and South Italy thrived from 8th-3rd centuries BC
2) Etruscans flourished from 8th to 2nd centuries BC
3) Rome is traditionally said to have been founded in 753 BC although we have evidence that goes back much earlier
Poseidonia (founded ca. 600 BC)
Greek colony founded around 600 BC in southern Italy, later known as Paestum
Temple of Athena (500)
Temple of Hera I (550)
Walls
Agora
Tomb of the Diver (480)
Temple of Hera II (470-460)

Poseidonia: Temple of Athena
500 BC
y = 2x+1 (ideal)
stair cases
travertine and sandstone
porch framed by ionic columns
1st mix of doric and ionic
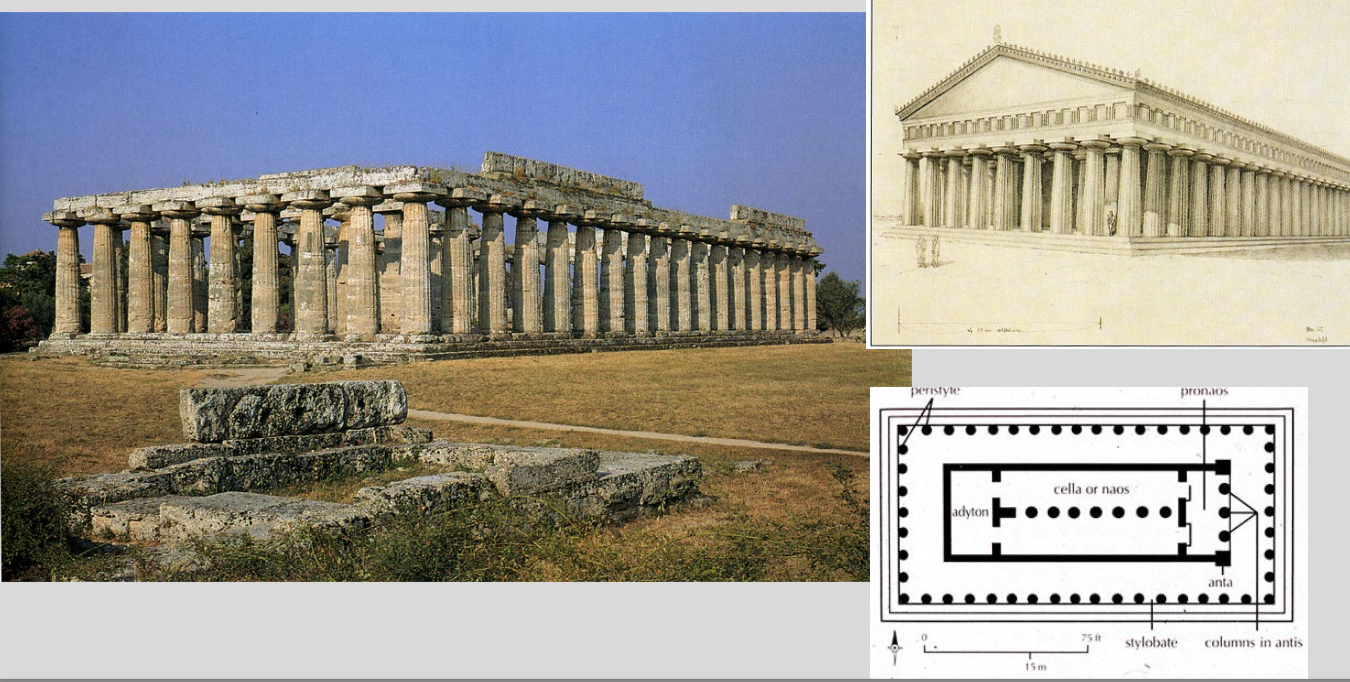
Poseidonia: Temple of Hera I
550 BC
Doric
columns down center
travertine and sandstone
not ideal (y≠2x+1)
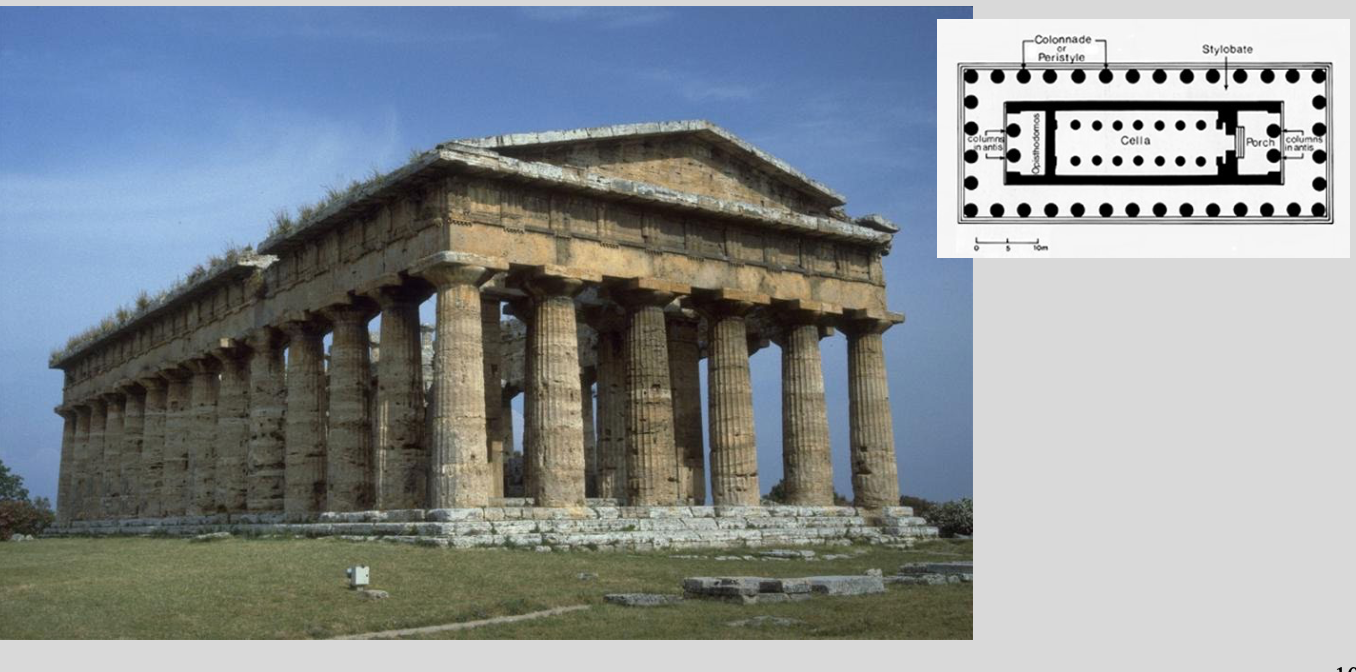

Poseidonia: Temple of Hera II
470-460 BC
ideal GREEK temple
Poseidonia: Tomb of the Diver (480 BC)
480 BC
fresco on travertine
frescoes on all sides with images of feasts & games
top of a diver and a dead tree
kottabos
game in which one flings wine dregs from a cup at a target
Etruscans (list 6 points) CCUCGS
culture based on city-states
1st complex native society in Italy before Romans
uncertain origins maybe Turkey / Italy always
extensive contact with Mediterranean world
heavy borrowing and adoption of Greek traditions
Made sarcophagus of terracotta
sarcophagus
coffin used to hold a body (or ashes) of deceased; Etruscan ones were often made of terracotta
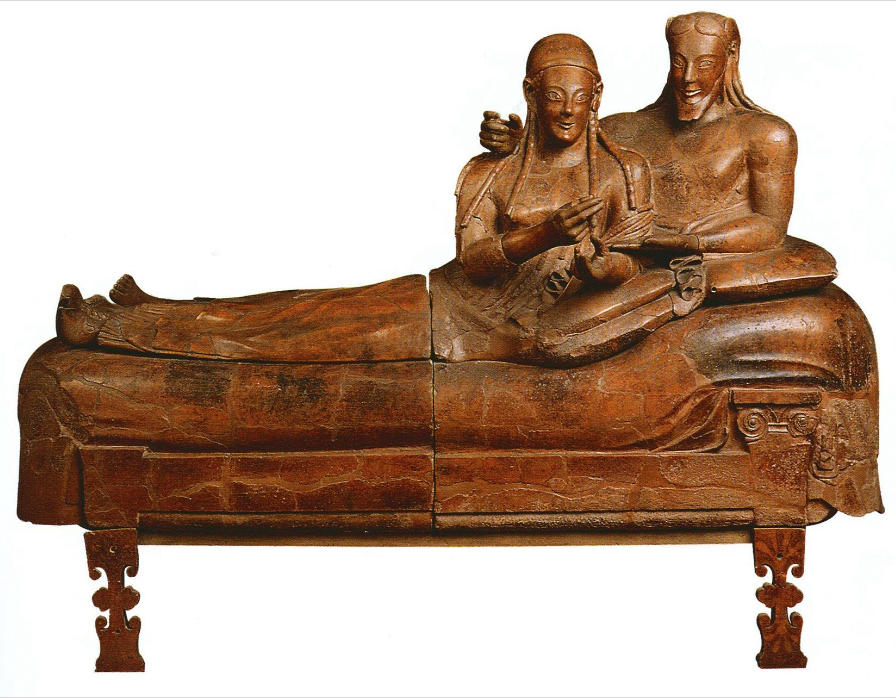

Etruscan Sarcophagus Lid from Caere (525 BC)
1) Greek 5th century archaic smile
2) rigid Egyptian style and unnatural position
terracotta
fired clay
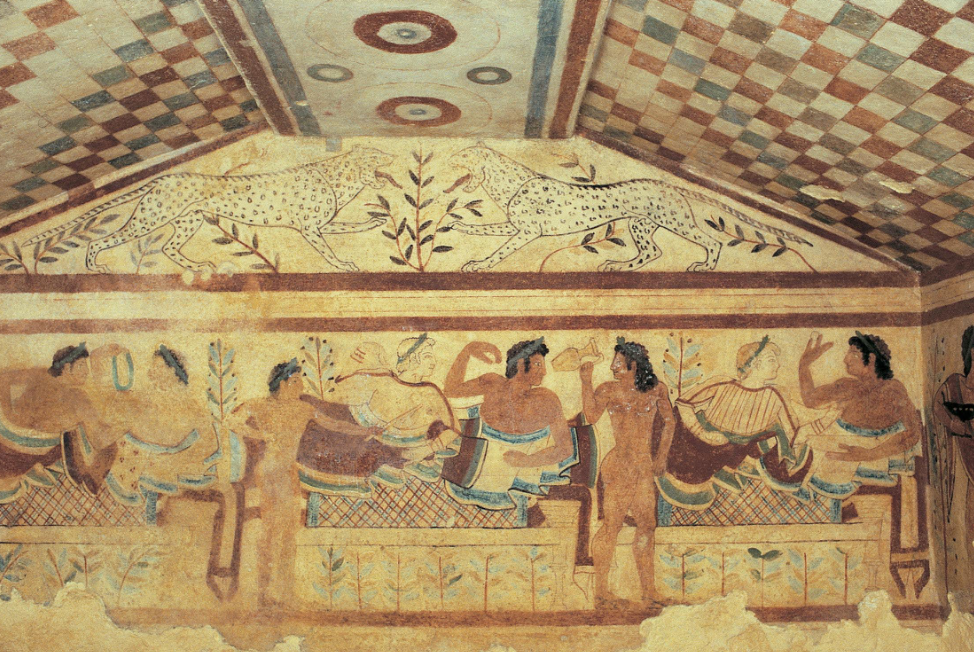

Etruscans in Tarquinia: Tomb of the Leopards (472 BC)
tufo - rock that covers tomb
fresco
Egyptian poses
Leopards warding off danger
Dining scene
shift to classic but not quite
Important Dates Rome
10th c. BC: Iron Age habitation evidence of burials on Capitoline & Paletine Hills
753 BC: traditional date of Rome’s founding
753 - 509 BC: “regal period”
509 BC: explosion of kings
509 - 27 BC: Republican period
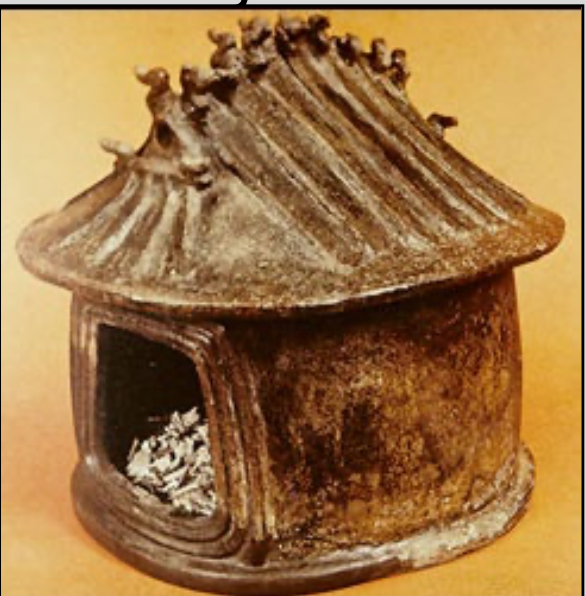

Iron Age cremation burials in “Hut Urns”
terracotta
10th-8th centuries BC
models of actual houses in the Forum valley
forum
public square / marketplace used for judicial and other business
wattle and daub
dried mud held together by straw
Building projects in 6th century BC (regal period)
fill in the Forum
Build Cloaca Maxima
Build Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus
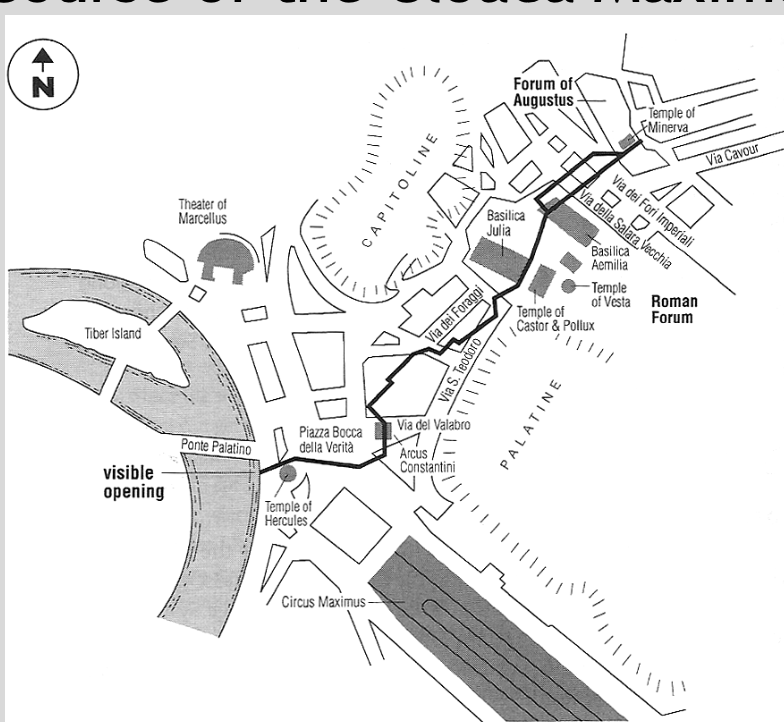
Cloaca Maxima
“Great Drain”; drain and sewer that ran from the Forum Augustum through the low-lying areas of Ancient Rome, winding between the Quirinal, Viminal, and Esquiline Hills
Italic / Roman Temple (vs. Greek Temple)
Italian / Roman
On a high podium
Emphasize the front; columns and steps on the front side
Tripartite cellas (a cella that is split into three side-by- side chambers)
Greek
Not on a high podium
Peripteral; steps and columns on all sides
Usually not tripartite cellas
cella
the inner chamber of a temple, typically a simple rectangular room that houses the cult statue of the deity
podium
a raised platform or base that serves as the foundation for a structure , most famously a temple
Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus (aka Capitolium) (509 BC)
vowed by Tarquinius Priscus
mostly completed by Tarquinius Superbus
dedicated in 1st year of the Republic of Rome
NOT GREEK but TUSCAN / ITALIAN
gridded columns NOT outlined
wall on the back
cella in back not middle
stairs
3 gods, 3 altars: Jupiter, Juno, Minerva