Heredity and Gregor Mendel's Principles of Genetics
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Gene
It is the sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and determining a trait.
Alleles
The different forms of a single gene.
Dominant allele
Whose appearance dominates over other alleles for the same trait.
Recessive allele
That does not show when a dominant allele is present.
Homozygous
Has two identical alleles for a gene (true-breeding).
Heterozygous
Has two different alleles for a gene (hybrid).
Genotype
Gene pair for a trait.
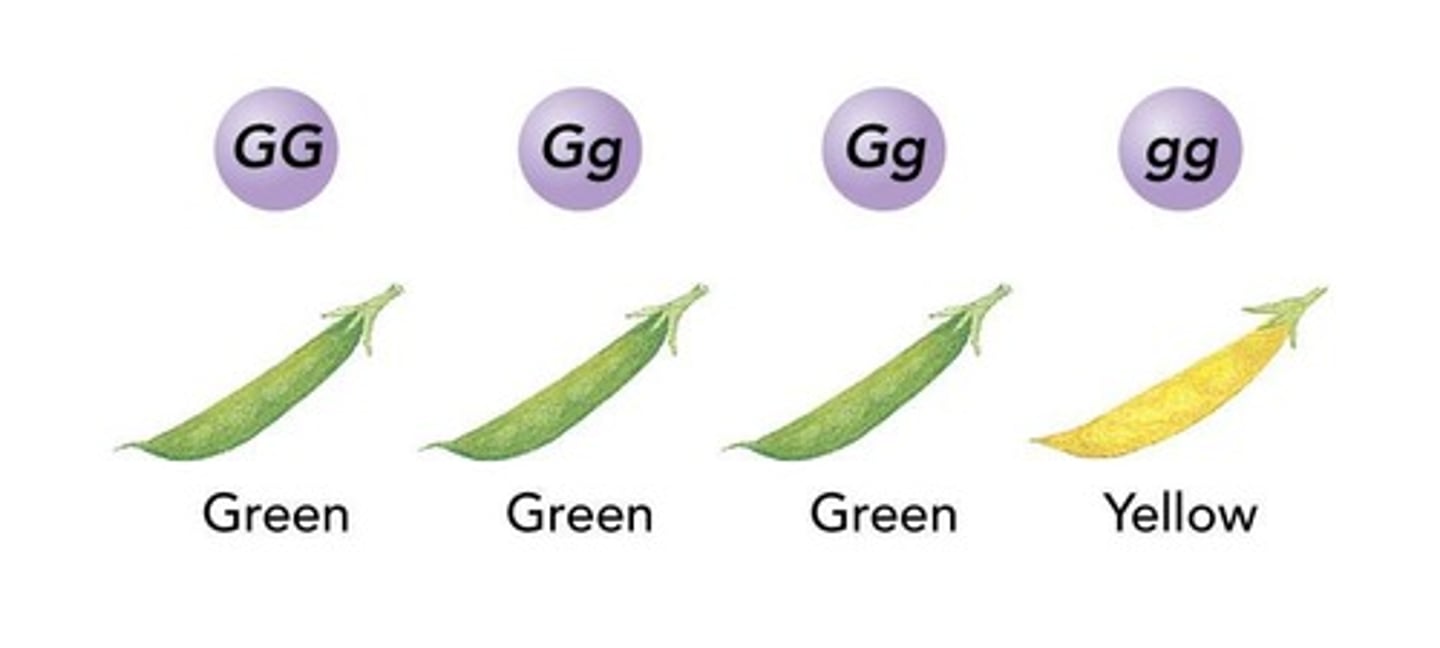
Phenotype
The observable physical characteristics (appearance) of an allele pair.
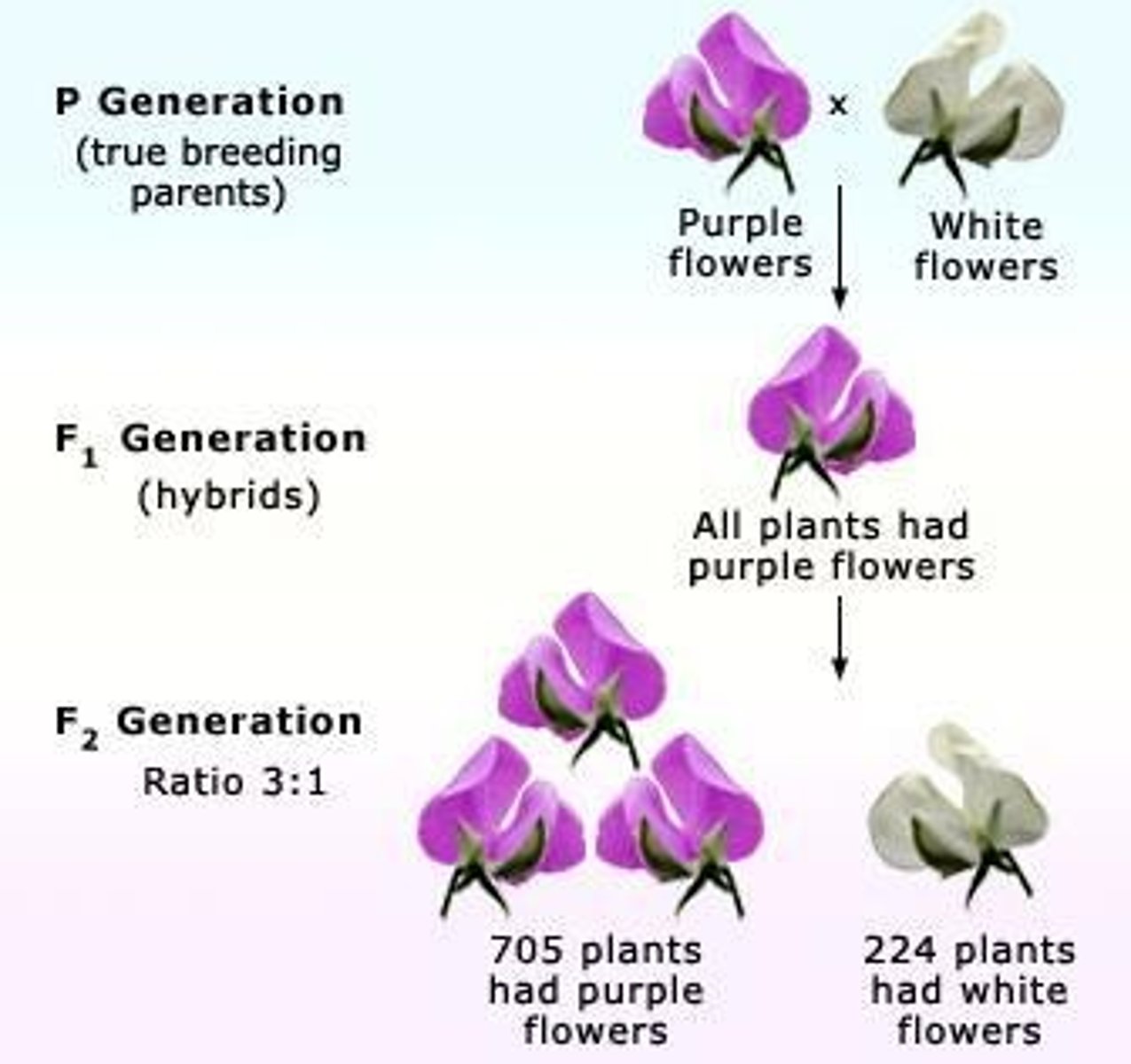
P generation
Parental generation.
F1 generation
Offspring from P generation.
F2 generation
Offspring from F1 generation.
Law of Segregation
Alleles separate from each other when gametes form in meiosis.
Law of Independent Assortment
Alleles for different genes usually separate independently of each other.
True-breeding
Organisms that produce offspring identical to themselves.
Hybrid
Offspring resulting from the cross of two true-breeding plants.
Cross-Pollination
When Mendel cross-pollinated two true-breeding plants with different traits.
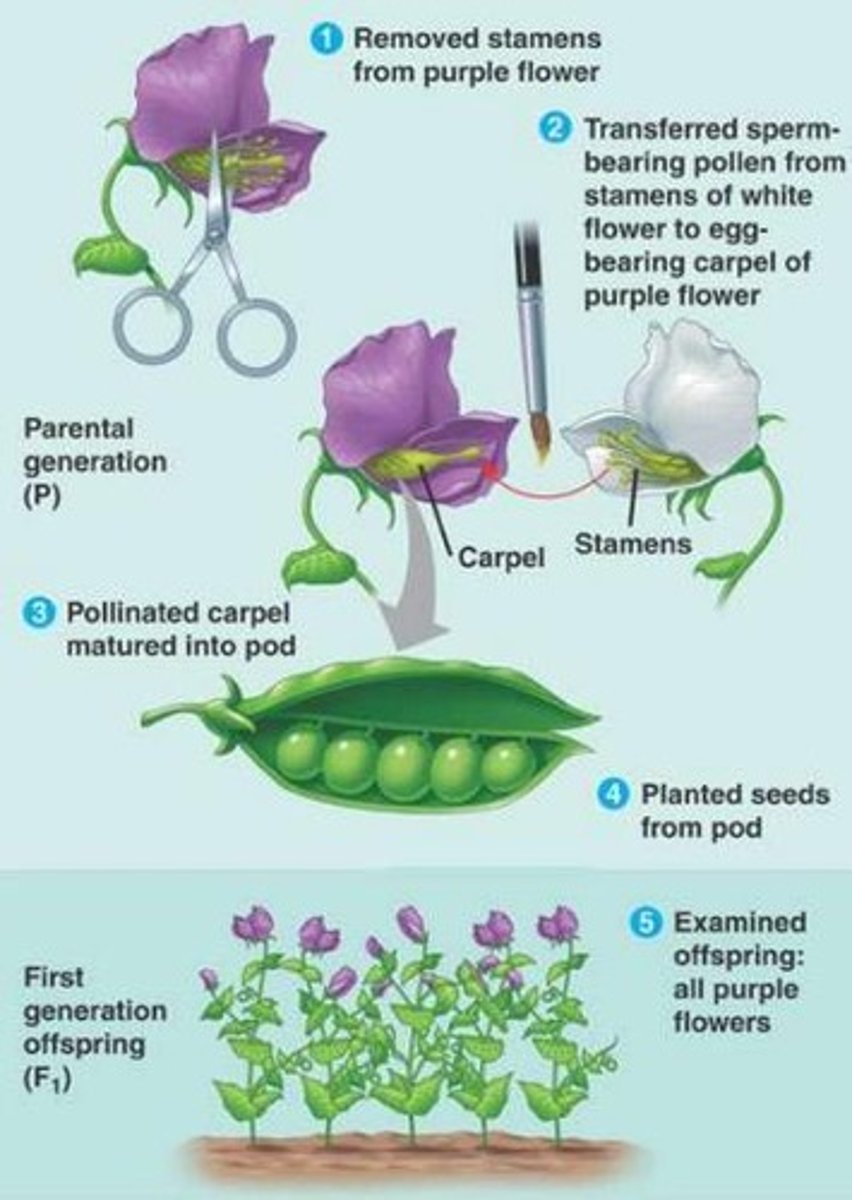
Phenotype of purple flower
Purple flower.
Genotype if purple is dominant
PP or Pp.
Genotype if it is a recessive trait
pp.
Mendel's conclusion about inheritance
Inheritance is determined by 'factors' (now called genes) that are passed down from parent to offspring.

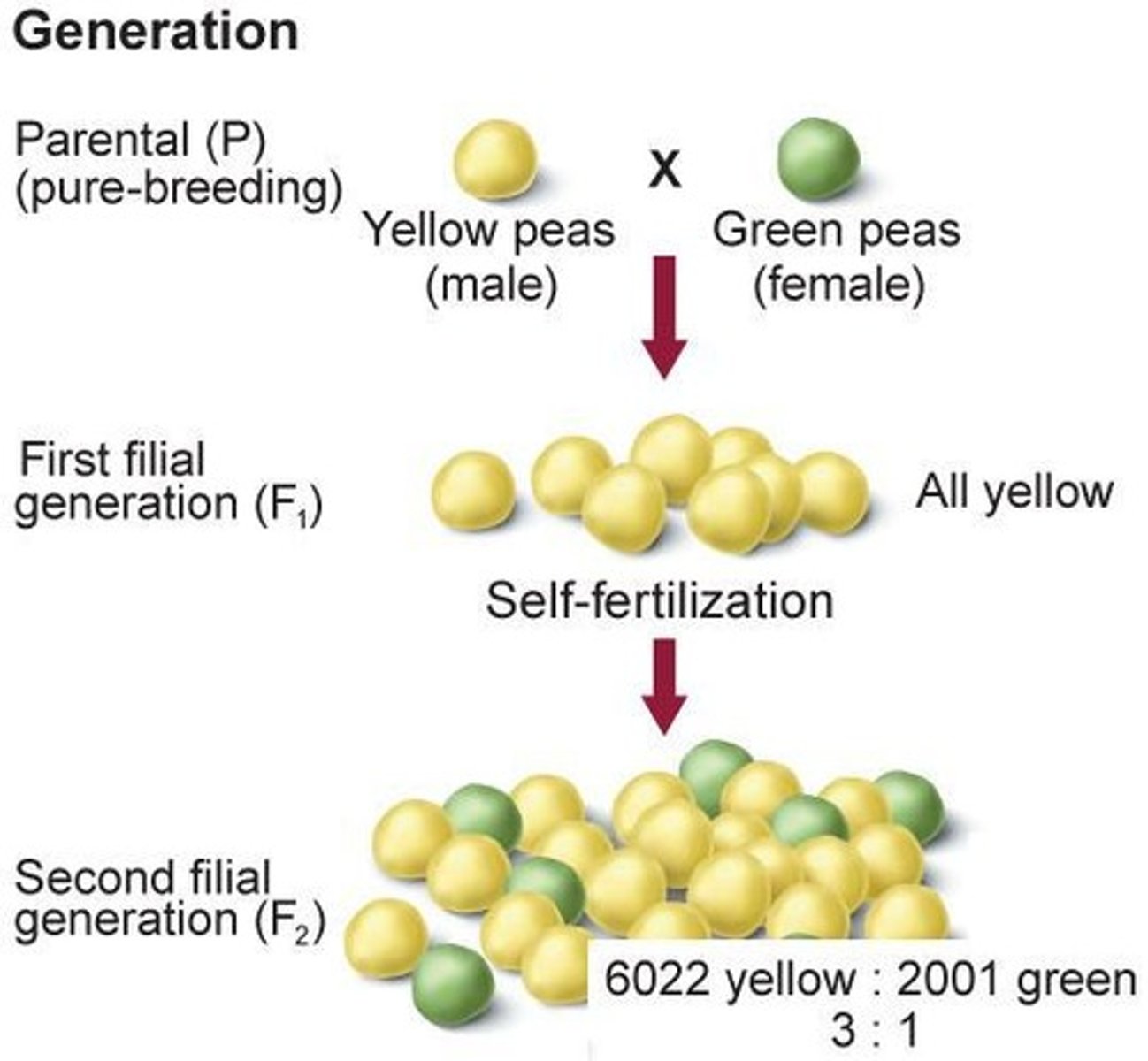
Proportion of F2 offspring that were yellow
1/4.
Proportion of F2 offspring that were green
3/4.
Example of allele trait abbreviation
T = tall, t = short.