Evolution exam 1 terms
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Organic evolution
Small changes in gene frequency in a population over time are sufficient to explain historical and current patterns of organismal diversification
Homology
Possession by two or more species of a trait inherited from an equivalent trait in a common ancestor.
What is the age of the earth?
~4.6 billion years old
Covergence
Trait adapted to similar function but different origin
Homoplasy
Classification based not on shared ancestry
What were darwin’s 4 postulates?
variation amoung individuals
Variation is heritable
Only fraction of offspring survive
Individuals w/ favorable traits will produce more offspring than others
Heritability (h²)
Proportion of variation in character that is caused by action of genes
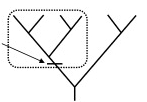
Monoplyly
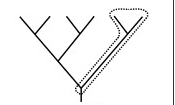
Paraplyly
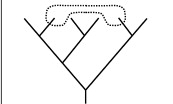
Polyphyly
Synapomorphy (Synopomorphic character)
Derived character state shared by two or more taxa
Parsimony
Fewest changes in phylogenetic tree
Outgroup
Information about ancestral state
Reversal
Removal of a trait from a phylogenetic tree
Molecular clock
Used to date evolutionary events.Molecules evolve at a constant rate such that the amount of divergence is equivalent to the time since two species diverged
Darwinian evolution
Slow and gradual process causes selection for beneficial mutations leading to adaptation. Sufficient mutations need a long time to accumulate.
Biological species concept (BSC)
Species are groups of actually potentially interbreeding natural populations that are reproductively isolated from other such groups.
Phylogenetic species concept (PSC)
Species have separate evolutionary characteristics. Any character can be defined as a species.
Morphospecies concept
Species are grouped based on degree of morphological similarity
What three components need to happen to get speciation?
fragmentation and isolation of populations
Divergence
Reproductive isolation
Allopatric speciation
Evolution of genetic and reproductive barriers between populations that are geologically separated. Gene flow is eliminated.
Vicarient speciation
A type of allopatric speciation that is a sudden geological event which causes change in different species
Peripatric speciation
A type of allopatric speciation in which a large group in which a small subgroup moves to a different location and becomes a separate species (Founder effect)
Parapatric speciation
Reproductive isolation between populations that are continuously distributed in space
Primary integration
A type of parapatric speciation in which an environmental barrier that is strong and sudden to differentiate species contracts gene flow via selection
Secondary contact
A type of parapatric speciation in which a group is originally allopatric becoming two different species but then hybridization occurs and the group becomes parapatric after they aren’t selected
Sympatric speciation
Divergence leading to speciation occurs in presence of substantial gene flow
What was the earliest life form?
The ribozyme
What are the 4 eons?
Hadean (4.6 BYA), Archean (3.6 BYA), Proterozoic (2.5 BYA), Phanerozoic (540-current day)
What are the three sites with the best fossil preservation?
Ediacaren Fauna (Australia), Burgess shale (Canada), and Chengjiang (China)
Punctuated stasis
Predicts that there’s no change until species evolve
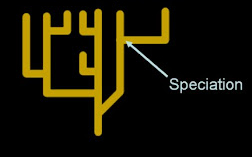
Gradualism
Slow accumulation of differences which causes different species
Caldogenesis
Evolutionary change that produces speciation
Anagenesis
Evolutionary change that does not involve speciation