Cyclic Intermediates and Dyes
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
not finished
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
William Perkin
Who discovered the first practical synthetic dye (mauve) while trying to synthesize quinine from aniline contaminated with toluidine?
1856-1873
Sir William Perkin discovered the first practical synthetic dye in what year range?
Coal tar or aniline dyes
Synthetic dyes are also called as “___” or “___”.
1914
In ___, Germans produce almost 87% of the world’s dye.
World War I
During ___, the United States established a domestic industry for dyes.
1978
In ___, several major American companies recently lost a significant percentage of their domestic market to Swiss, German, Japanese, and Italian competition.
Intermediates
Dyes have complicated structures which are made by reactions involving its building blocks called ____.
Intermediates
These are aromatic compounds with substituent groups such as -NH3, -OH, -NO2, and -SO3H.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Reacting dyes with intermediates can alter the reactivity of cyclic compounds and sometimes, the color of the dye.
False
(Explanation: Intermediates are not limited only to the dye industry. It is also used in all types of organic work where complex structures are built up. Examples are making agricultural chemicals, pesticides, pharmaceuticals, and rubber chemicals.)
TRUE OR FALSE. Intermediates are limited only in the dye industry.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. The whole procedure of intermediate manufacture is generally labor intensive, which makes it difficult for the United States to compete.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Organic and inorganic materials are both important in manufacturing dyes and intermediates.
Petroleum
Aromatic hydrocarbon
Intermediates
Dyes
What is the correct raw material sequence of dye production?
True
TRUE OR FALSE. The demand of the dye industry for raw materials to make intermediates or precursors of intermediate played a major part in bringing about the change from beehive to by-product coke ovens.
Benzene, toluene, naphthalene, anthracene, xylene, and some paraffins and olefins
The major hydrocarbons used in making intermediates are now the specialized aromatized naphthas from catalytic refining of selected petroleum crudes. What are these major hydrocarbons?
Ethylbenzene
What cyclic intermediate that was originally extracted from coal tar produced the highest amount in thousands of kilograms from 1972 to 1980?
True
TRUE OR FALSE. There are no unit operations involved in manufacturing intermediates.
Aryl substances
Chemical conversions of cyclic intermediates and dyes are mainly concerned with ___; those with aliphatic and naphthenic substances.
Isomers
Identify what chemical conversion is being described.
Mono-substitution produces one isomer in benzene but multiple isomers in naphthalene and anthraquinone.
With poly-substitution, the number of possible isomers increases substantially.
Obtaining the desired isomer is critical for achieving specific reactivity, color, or physiological effects. It requires great chemical skill due to factors like substitution patterns, solubility effects, and the directing effects of substituents.
Nitration
Identify what chemical conversion is being described.
Historically, before high-pressure techniques were available, it was the standard method to introduce an amino group onto an aryl ring for dye synthesis.
The amino-substituted compound could undergo diazotization with NaNO and then be coupled with another compound to form the azo dye chromophore.
Nitro groups
These groups are rarely present in final dye products, as they are typically reduced to more reactive amines during the dye formation process.
Sulfuric acid in nitration
(Additional information: It increases solubility of the hydrocarbon in the reaction mix, thus speeding up the reaction. It also promotes the ionization of the nitric acid to give NO2+, the nitronium ion which is the nitrating species.)
It reduces the ionization (HNO3= H+ + NO3), which increases as the water-producing reaction dilutes the reaction mixture. It also acts as an energy reservoir to prevent destructive rapid temperature rise and provides a vehicle to convey heat to the jacket and/or coil.
Reduction to aniline
(Additional information: Reduction to aniline competes with direct aniline production via ammonolysis.)
What is the main use of nitrobenzene produced from the nitration of benzene?
Nitration
(Additional information: After the reaction, the nitrobenzene product is separated from the spent acid by decantation, washed with dilute alkali, and the spent acid is sent for recovery.)
Identify what chemical conversion is being described.
It is carried out in large batch nitrators (3,000 to 5,000 L) or small continuous units at around 50 degrees Celsius, with a short reaction time of 15-20 minutes and high yields of up to 98%.
Sulfonation
Identify what chemical conversion is being described.
It is a nucleophilic substitution reaction where its primary sulfonating agent is sulfuric acid, but SO3, chlorosulfonic acid, metallic sulfates, and sulfamic acid are also occasionally used.
Sulfonation
Identify what chemical conversion is being described.
It is typically carried out in a heated sulfonator made of corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel, with agitation, condensation, and fume control systems.
Exothermic
In sulfonation, the reaction is ___ and water is formed, so excess sulfuric acid is used to maintain high acid concentration, and water removal (e.g.: azeotropic distillation) is crucial for driving the reaction forward.
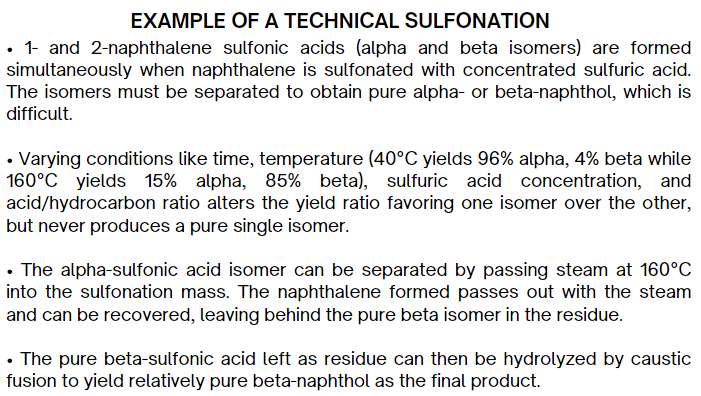
READ!!!
READ!!!!
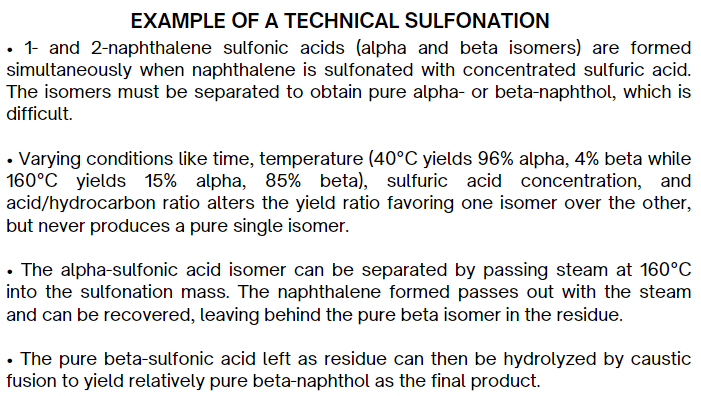

Separations are based on some considerations. What are these six considerations?
Amination by reduction
Identify what chemical conversion is being described.
It is a method for introducing amino groups onto aryl compounds by reducing nitro groups, historically done without high pressure vessels or modern catalysts.
Amination by reduction
Identify what chemical conversion is being described.
Common reducing agents were iron and acid, zinc and alkali, sodium sulfide/polysulfide, sodium hydrosulfite, electrolytic hydrogen, and metal hydrides.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Using metals as reductants creates difficult processing issues like expense and dealing with spent metal.
309 million kg
In 1982, ____ of aniline were produced, with 55% used for making p,p’-methylene diisocyanate, 20% for rubber chemicals, and 10% for intermediates and dyes.
Catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene
Most aniline was produced via ____ with hydrogen gas.
Amination by ammonolysis
Identify what chemical conversion is being described.
It involves replacing nuclear substituents like -OH, -Cl, or -SO3H, with -NH2 using ammonia.
Amination by ammonolysis
Identify what chemical conversion is being described.
It is a cost-effective route for producing amines compared to reduction methods using expensive reagents like iron, zinc, or hydrogen gas.
Amination by ammonolysis
Identify what chemical conversion is being described.
The process requires an agitated pressure vessel made entirely of iron (stainless steel is rarely necessary) to handle the ammonia and high temperatures or pressures involved.
Halogenation
Identify what chemical conversion is being described.
It is almost always chlorination; however, the only difference is due to the significantly lower cost of chlorine compared to other halogens.
Chlorination
Identify what chemical conversion is being described.
It can occur through addition to an unsaturated bond, substitution for hydrogen, or replacement of another group like -OH, or -SO3H.
Chlorine and hydrochloric acid
These are commonly used for causing substitution or addition reactions on aromatic ring compounds.
False
(Explanation: Chlorination reactions are less orderly.)
TRUE OR FALSE. Nitrations and sulfonations are less orderly than chlorination reactions in hot, dilute aqueous solutions.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Halogenations are highly exothermic reactions.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Anhydrous conditions allow the use of steel or nickel alloy equipment because of the reaction’s corrosive nature.
Chlorobenzene
It enjoys a modestuse as a solvent and for the manufacture of nitrochlorobenzene. Moreover, it is manufactured by passing dry chlorine through benzene using ferric chloride as a catalyst.
8:5:1
The reaction rates favor production of monochlorobenzene over dichlorobenzene by ___ providing that the temperature is maintained below 60 degrees Celsius.
Distillation
What process separates the monochlorobenzene and leaves mixed isomers of dichlorobenzene to be disposed?