Alkene/Alkyne RXN + Sn1/Sn2/E1/E2
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
H-X (Br, Cl, I)
adds one Br, Cl, I, markovnikov, can rearrange
H2SO4 or H3O+
adds H and OH, markovnikov, can rearrange
H-Br, ROOR
adds one Br, anti-markovnikov
Hg(OAc2), H2O
NaBH4
adds H and OH, markovnikov, no rearrangements bc no carbocation
BH3-THF
H2O2, NaOH
adds H and OH, anti-markovnikov, no rearrangements
H2SO4 or H+, CH3OH
add H and OR, markovnikov, can rearrange
Hg(OAc)2,CH3OH
NaBH4
adds H and OR, markovnikov, can’t rearrange
H2, Pd/C or Pt/C or Ni/C
adds two H’s, syn addition, turns alkenes/alkynes to alkanes
Br2/CCl4 or CHCl2
adds two halogens, anti addition
X2/H2O or ROH
adds halogen and OH or OR, markovnikov (but halogen is on less substituted), anti addition
RCO3H (aka MCPBA)
epoxidation (triangle), syn addition
MCPBA (RCO3H)
H3O+
adds two OH’s, anti addition
OsO4
NaHSO3 or Na2SO3
or
KMnO4 (cold, diluted)/NaOH
adds two OH’s, syn addition
O3
(CH3)2S (aka DMS) or Zn,H2O
splits and reduces to a ketone and aldehyde
O3
H2O2
or
KMnO4 (hot, concentrated)
H3O+
splits and reduces to a ketone and carboxylic acid
acid catalyzed hydration of alkynes
tautomerization of enol and keto
hydroboration-oxidation of alkynes
tautomerization of enol and keto (aldehyde)
ozonolysis of internal alkyne
2 carboxylic acidsoz
onolysis of terminal alkyne
carboxylic acid and CO2
NaNH2
forms new bonds
lindlar’s catalyst (Pd/BaSO4/quinoline)
reduce to cis alkene
Na/NH3
reduces to trans alkene
weak nucleophile/weak base
ROH, RCOOH, H2O
strong nucleophile/weak base
CN-, N3-,Cl-, Br-, I-, RS,- HS-, RSH, H2S, RNH2, R3P
strong nucleophile/strong base
OH-, RO-
bulky bases
t-buO, DBN, DBU, LDA
aprotic solvents
acetone, DMF, DMSO, acetonitrile
3 - weak nuc/weak base
E1 (high temp) or SN1 (low temp)
3 - strong nuc/weak base
SN1
2 - strong nuc/weak base
SN2
1 - strong nuc/weak base
SN2
3 - strong nuc/strong base
E2
2- strong nuc/strong base
E2
1 - strong nuc/strong base
SN2
bulky bases are___
always E2
large, broad trough far to the left (3000-3600)
OH group
medium-sized peak at ~2200 cm-1
nitrile (C≡N)
big, pointy peak at 1700 ± 50 cm-1
carbonyl (C=O)
reduce aldehydes, acid chlorides, and acid anhydrides to primary alcohols
LiAlH4 and NaBH4
reduce ketones to secondary alcohols
LiAlH4 and NaBH4
reduce esters and carboxylic acids to primary alcohols
LiAlH4
KMnO4 or H2CrO4 or CrO3/H2SO4 (Jones reagent)
makes carboxylic acid from primary alcohol
Mg (Grignard reagent - replaces halogen with Mg)
CO2
H3O+
makes carboxylic acid from alkyl halide
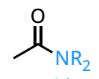
amide
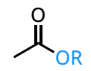
ester
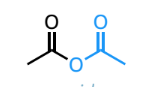
acid anhydride
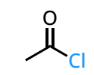
acid halide
increasing reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives
amide - ester - acid anhydride - acid halide
ROH + strong acid
converts carboxylic acid to an ester (fischer esterification)
NaOH
H3O+
converts ester to carboxylic acid (saponification)
reduce esters and acid chlorides to primary alcohols
LiAlH4
reduce amides to amines
LiAlH4
DIBAL-H, -70C
H2O
reduces ester to aldehyde
LTBA
reduces acid chloride to aldehyde
Br2/NaOH
reacts with primary amide to give primary amine
LiAlH4
H2O
nitrile to primary amine
H3O+
heat
nitrile to carboxylic acid