The Cold War: Containment
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
The Cold War
1945 - 1989 (Berlin Wall collapse) /1991 (Soviet Union ends)
Democratic-Capitalist World (United States) vs. Communist World (Soviet Union+China)
No actual fighting between these nations, but instead competing over who’s better":
Competing for control over post-war Europe
Competing control over newly independent peoples in Asia, the Middle East, Latin America, and Africa
Sports and cultural competitions (Olympics: hockey, gymnastics, chess, ballet)
Technological and military innovations
The Cold War Spheres of Power: Containment
Soviet Sphere: 1945-1948 :The Cold War Begins
USSR fighting in Europe, Latin America, the Middle East
Chinese Sphere: 1949-1953: The Cold War Extends to Asia
China fighting US in Asia
Middle East Sphere: 1945-1950s: American Insertion + Suppressing Nationalists & Soviets
Middle East
The Cold War Eras
1945-1989
Containment: 1945-1953
Mutually Assured Destruction 1952-1968
Detente 1968-1978
Reescalation and End of the Cold War 1980-1989
Containment:
1945-1953 —> emerges post WWII and Potsdam conference
Foreign Policy strategy based on belief:
created by George Kennan
Communism is here to stay, can’t be eradicated
But…we must stop communism from spreading
If left unchecked, Stalin will spread communism across the world (rn focused on weak Western Europe) …we must hold it back like a dam (can’t drain ocean but hold it back)
The Soviet Sphere: Containment
1945-1953
Franklin Roosevelt 1932-1945
Yalta Conference February 1945
Truman assumes presidency 1945-1952
Potsdam Conference July 17-August 2 1945
SHIFT IN FOREGIN POLICY
The Truman Doctrine 1947
Containment:
The Marshall Plan 1948
The Berlin Blockade & Airlift 1948
Franklin Roosevelt
1932-1945
Democrat
Worldview:
Begins his presidency as an isolationist
Pearl Harbor attack: supports US entrance into WWII
War progresses begins to develop a type of Wilsonian world view
Post war: wanted allied victory so world would be managed by 4 regional powers connected internationally Think Justice League!!
United States: The Americas
Britain: Western Europe & Africa & South Asia
The Soviet Union: Eastern Europe
China: Asia
The Yalta Conference
February 1945 (during WWII)
Meeting between the three major allied powers
England: Prime Minister Winston Churchill
U.S.: President Franklin Roosevelt (2 months from death)
Soviet Union: Premier Joseph Stalin
Goals + Plans made:
End War Strategy → Defeat Japan: by U.S.S.R would declare war
Plans for Post-War World → Create the United Nations
Roosevelt believed that the 4 major world powers (US, England, USSR, and China) would lead the organization
Germany and the city of Berlin would temporarily be divided into 4 zones each administered by one of the 4 allies (USA, USSR, Britain, and France) until Germany had transitioned through the peace process.
Truman assumes presidency
Roosevelt dies during 4th term and Truman takes over from 1945-1952
Democrat
Worldview:
Wilsonian
harsher on communism than Roosevelt due to ideological/moralistic values (less gray area, religious = right vs wrong) WILSONIAN
Supported internationalism and American involvement in global affair
Truman administration skeptical of USSR and didn’t want USSR sharing in world power
Potsdam Conference figures
July 17-August 21 1945 meeting after WWII (USSR + US hiding true intentions)
Meeting between the leaders of the 3 allied powers on ending war w/ Japan (Germany has surrendered)
England: new Prime Minister Clement Attlee: elected by labor class focused on domestic policy rather than global affairs
US: President Truman: believes US can achieve world piece by promoting the elevation of US as key in international affairs (hiding that US has tested 1st atomic bomb from USSR not Atlee)
Soviet Union: Premier Joseph Stalin: The USSR is now occupying most of Eastern Europe (public plan in Japan was still land invasion of Japan but Stalin wants in)
Potsdam Conference content
Disagreements:
German Reparations: Stalin wants Germany to pay large reparations; Truman did not want a repeat of the Treaty of Versailles from WWI
Elections in Eastern Europe: Truman wants Stalin to hold free and open elections in Eastern Europe; he refuses
Refuses bc region created Eastern Europe as Eastern Bloc: buffer states that protected Russia region + USSR
nations would rather have rigged elections = run by handpicked leaders who directly answered to the USSR
Post Potsdam Conference
WWII ends swiftly after Potsdam Conference w/ dropping of atomic bomb in Japan -> Stalin now knows US has weapon he doesn’t which paves way for MAD peace (for 3 yrs)
atomic bomb creation began bc of concern for nuclear tech in Germany -> created after war in Europe ends therefore not used in Germany
Post WWII = Cold War Containment under Truman
1945-1953
Foreign Policy strategy based on belief:
created by George Kennan
Communism is here to stay, can’t be eradicated
But…we must stop communism from spreading
If left unchecked, Stalin will spread communism across the world (rn focused on weak Western Europe) …we must hold it back like a dam (can’t drain ocean but hold it back)
Truman Doctrine
TURNING POINT: 1947
The United States would provide political, military, and economic assistance to ALL democratic nations under threat from external or internal authoritarian forces (truman does NOT force democracy on nations, but if u have shown desire for it then US steps in)
Differences: under containment US will now
get involved in regional conflicts that DONT involve America
engage in far-away conflicts
us economic aid (not just military) w/o necessarily anything in return
(side note: Trump is denying this policy)
The Marshall Plan
1948: Containment in action example 1
A US program providing economic aid to help rebuild Western European economies after WWII to prevent the spread of communism
response to communist uprisings that result from lack of gov post WWII + poverty (which makes communism appealing)
goal: promote democracy
$12.5 billion allocated to the program -> 150 billion today
benefited US still bc selling American goods + companies in Europe
Proposed by U.S. Secretary of State George Marshall
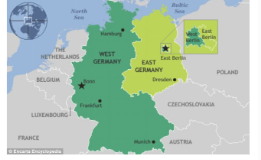
The Berlin Blockade & Airlift 1948
1948: Containment in action example 2
1st Major Cold War Crisis: West Berlin (independent) was a threat to Stalin + control over East Berlin/Germany (communist) =
Blockade (action): Implemented by Stalin around Western Berlin to prevent food, electricity, ppl from Eastern Germany from entering the region
re-sparked negotiation over control of the city
Airlift (response): Western allies organized the Berlin airlift to carry supplies to the people of West Berlin to override blockade
At the height of the airlift, one plane reached West Berlin every thirty seconds
1 year later: blockade lifted
Significance:
Formal division of Germany became permanent into West (democracy) and East (communist) + Berlin
Creation of NATO: North Atlantic Treaty Organization (international (like UN thru yalta conference))
Link democracies together against communism: Western Europe, the US, Canada
The Chinese Sphere: Containment
The Cold War Extends to Asia 1949-1953
Turning Point: Mao Zedong comes to power
NSC-68 1950
The Severing of Diplomatic Ties With China 1950
Involvement in French Indochina War 1950-1954 (not yet Vietnam War)
Geneva Peace Accords 54
The Korean War 1950-1953 (Civil War)
Turning Point: Mao Zedong comes to power
Mao Zedong and the communists win the Chinese Civil War and declare the ppl republic of China = a NEW zone of communist conflict in Asia a big country w/ large population (need a new damn for this eruption)
Will they become big power? What’s China x USSR relationship?
Soviet Union developed and tests the first nuclear bombs= NEW managment strat?
US no longer has the technological upper hand
NSC-68
1950: Truman Administration Regroups → response to Mao Zedong
National Security Council creates report NSC-68
Goal: Reassess containment policy given this context
Conclusions: militarizes containment + commitment to Truman Doctrine
1. US will still show up ANYWHERE using any MEANS (there r now more places + means)
2. Expansion of military budget (current + innovation) to be prepared in military
3. Economic assistance (including military, esp. Local groups)
Implementation of NSC-68: Examples of US strat now involving Asia + military commitment to capitalism
The Severing of Diplomatic Ties with China in 1950
Involvement in the French Indochina War 1950-1954 (not yet Vietnam)
The Korean War 1950-1953
The Severing of Diplomatic Ties with China
1950: US refuses to acknowledge that Mao + communist parties are legitimate = US refuses to engage w/ him
logic: freeze them out
Not the best strat: don’t know what opponent thinks, believes, doing = all information is only based on spies, media, inaccurate sometimes
Involvement in the French Indochina
1950-1954:
Action: Nationalist (Communist ideologies) Ho Chi Minh becomes leader of Vietnamese civil war of independence against France
US concern: Domino Theory: fear that the countries of Asia would fall like dominos as the communist ‘contagion’ spread throughout the continent
Refute: US supports France w/ military aid (Wilsonian proponent of the spreading of democracy and national sovereignty, supported colonialism when it stood against communism)
The Geneva Peace Accords of 1954 ends war provided for the temporary partition of Vietnam at the 17th parallel
North Vietnam: communist regime, supported by the USSR led by of Ho Chi Minh.
South Vietnam: Republican government, led by President Ngo Dinh Diem (Diem is killing Bundists, US eventually teams w/ his brother to kill him)
Note: The Americans' involvement in civil unrest in Vietnam was just beginning and would continue to grow and expand for another 20+ years
The Korean War
After Japan was defeated in WWII, the Soviets and the United States divided control over Korea.
The Soviet Union occupied Korea NORTH of the 38th parallel
The United States occupied Korea SOUTH of the 38th parallel
The Soviets supported a communist government in the North: Kim al Sung
The United States supported a democratic government in the South: Syngman Rhee
Originally, the U.S. and Soviet Union intended to establish a stable unified Korea and to withdraw their military forces in time
1950: North Korea (Kim al Sung) invaded South Korea, marking the start of the Korean War (per Stalin's advice: testing the waters to see how US will respond)
Success! In 3 days North Korea has captured South Korean capital of Seoul → continued South
Other Countries support:
the US sends troops to South Korea (first military engagement in Cold War)
China also sent apx 80,000 troops to fight alongside the North Koreans against US = south retreats
General George MacArthur wants to carry out massive air strikes against China, including the use of nuclear bombs + asks Truman
Truman refused: to keep this localized
He wanted to avoid a wider and more dangerous war (bc we believe soviets + China are allies)
SOLUTION: Truman told MacArthur to negotiate reestablishing the 38th parallel to end war
MacArthur then publicly criticized Truman’s war strategy (this was odd for the time) = Truman fired MacArthur in 1951
Armistice: ending the war signed July 27, 1953
terms: cease-fire and a fixed demilitarized zone at the 38th parallel to serve as a buffer between North and South Korea that remains today
Notice: The boundaries of North and South Korea are set at the 38th parallel. The same boundary before the war! → war never rly ended, still military stationed at boundary, elaborate communication (easier to keep communist control w/ war threat)
The Middle East Sphere: Containment
US insertion in region + suppressing nationalist & Soviet influence
1945-1950s
The Creation of Israel 1948
Iran:
Under the Shah 1941-1979
Rise of Mossadegh 1951
re-establishment of the Shah 1953
Context in Middle East post WWII
After WWII, the Middle East saw the rise of Arab nationalist movements as many nationalistic (self-sovereignty) who wanted independence
Concerning to England and France–the main two colonial powers–but also to the United States bc might loose:
nationalist groups to the USSR
access to reasonably priced oil/access entirely
So: US tries to create allies of Jewish states in the region (Israel)
The Creation of Israel
1948: United Nations recognized Israel as a nation
Nation formed as Jewish homeland out of other Arab states
America is first country to recognize state of Israel bc:
Arab nations won’t: bc Britian gave their land + desired independence to Israel w/o consulting them
Beneficial to America: access to region, Israel = counterweight to Arab Nationalism + USSR influence
America now supports other pro-American, anti-nationalist-Soviet regimes
Iran
Iran Under the Shah
1941-1979:
Pro-Western leader who endorsed Westernization and modernization
Pro-America and seen as an American ally
Iran seen as key US ally in Middle East
Rich in oil that it was willing to sell to the US
Opposed the Soviet Union
The fact that the nation shared a border with the Soviet bloc meant that it was an important barrier state for Soviet influence in the region
Iran Rise of Mossadegh
1951:
Mohammad Mosaddegh (pitch: benefit ppl not self, not America)
Elected by parliament in 1951
Believed in Iranian sovereignty and nationalism
Nationalized the oil industry so citizen’s benefit
Mosaddegh’s power and his policies troubled US: feared that he would cut off American access to cheap oil, make the nation more independent from American influence
Re-establishment of the Shah
1953:
Mossadegh is taked out of power and given back to Shah for American benefit
Britian and the US orchestrated a coup to take Mossadegh out of power
The US didn’t formally acknowledge its role in the Coup until 2016
The coup was successful, and Mosaddegh was imprisoned and then put under house arrest → Power in Iran was returned the pro-American Shah