Nuclear Cardiology review
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Nuclear Cardiology Review slideshow
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
What Radiopharmaceuticals are used in Nuclear Cardiology
Thallium-201
Tc-99m Sestamibi (Cardiolite)
Tc-99m Tetrofosmin (Myoview)
PET: Rubidium-82 chloride, Oxygen-15 water, Nitrogen-13 ammonia
What is the dose for dipyridamole/persantine?
0.56mg/kg in 50ml of saline over 4min
What is the dose for adenosine?
0.140mg/kg/min for four minutes
What is the dose for regadenosine/lexiscan?
0.4mg (5.0 ml)
When is the tracer injected for a pharmacological test using adenosine/adenoscan?
During 3rd minute of infusion
When is the tracer injected during a pharmacological stress test using regadenosine/lexiscan?
20-30sec post injection of pharmacological drug
When is the tracer injected for a stress test using dipyridimole/persantine?
3-5min post completion of injection
When is the tracer injected during a chemical stress test using dobutamine/dobutrex?
1min after max tolerated dose
infusion should continue for at least 1 min
What medication can be given to reverse the side effects of coronary vasodilators during a chemical stress test?
Aminophylline
What can be given to reverse the side effects of dobutamine/dobutrex?
Beta blockers
Name two radiopharmaceuticals used to assess viability
Thallium-201 and F-18 FDG
What are three advantages of Tl-201 imaging?
Redistribution into ischemic tissue over time
increased lung activity after exercise is a marker for CAD
absence of significant hepatobiliary activity.
What are four disadvantages of Tl-201 imaging?
Long half-life limits dose
low dose results in poor count rate
low energy poorly suited for imaging
gated SPECT problematic because of redistribution.
Are Tl-201 studies typically gated or nongated? why?
nongated
due to redistribution
What is reinjection in Tl-201 imaging?
Injecting 1-1.5 mCi of Tl-201 prior to rest imaging to demonstrate reversible ischemia more readily, increasing senstiivity of stress/redistribution
When does imaging begin after stress with TI-201?
5-10 minutes post injection
What happens if you wait too long to image after stress with TI-201?
False negative result due to redistribution
When is imaging performed for rest images with TI-201?
3-4 hours post injection
What are the instructions for the patient between stress and rest imaging when using tl-201?
Patient should fast or have a light meal only (clear liquids) and avoid physical activity.
Why should the pt be instructed to fast or have a light meal of clear liquids only between stress and rest scans usign tl-201?
eating between scans can have a negative effect on redistribution
Glucose ingestion results in increased clearance of tl from myocardium
What are seven advantages of Tc agents over Tl-201?
Tc-99m has more optimal energy
higher injected dose = more photons = better sensitivity
higher target-to-background ratio
more rapid acquisition
improved resolution
more favorable dosimetry
fixed distribution provides flexibility and permits SPECT gated studies
What are the disadvantages of Tc agents over Tl? (4)
Slightly lower blood clearance than Tl
Two doses required
activity in the liver, biliary, and bowel can cause artifacts
Myocardial extraction lower than Tl
T/F: its important that pts continue to exercise for at least 1 minute post injection of the tracer
true
How are tc agents produced?
generator/kit
What is the half life of Tc agents?
6.02 hrs
What is the energy of Tc agents?
140keV
What is the mechanism of localization of Tc agents?
passive diffusion
What is the mechanism of localization for Tc Agents?
Passive diffusion
By which route is Tc-99m Sestamibi cleared from the body?
Hepatobiliary - large intestine
How is Tc-99m Tetrofosmin cleared from the body?
Hepatobiliary - gallbladder
What is a typical dose of Tc-99m Sestamibi?
10-30mCi
What is a typical dose of Tc-99m tetrofosmin?
5-24mCi
How do the doses compare when using a 1-day protocol vs a 2-day protocol?
1-day: smaller dose used in 1st imaging study and larger dose in 2nd imaging study
2-day: larger dose used for both studies
What are the imaging times post-injection for Sestamibi and Tetrofosmin?
Stress: 15-60 minutes post injection
Rest: 30-90 minutes post injection.
What are the advantages of tetrofosmin over Sestamibi in MPI imaging?
imaging can begin earlier bc:
rapid uptake
faster background from liver and Lung
What is the critical organ of sestamibi?
large intestine
What is the critical organ of tetrofosmin?
gallbladder
How long after injection can images be acquired?
up to 4 hrs post inj
How is imaging time selected when using Sestamibi and tetrofosmin for MPI imaging?
to minimize interfering liver, GB and bowel activity
What is the dual isotope procedure for MPI imaging?
2.5mCi of Tl-201 @ rest
wait 10-15min before imaging
22-25mCi of Tc-based agent @ stress
wait time varies btween 30-60min (depending on isotope)
What is the advantage of the Dual isotope method?
advantage of combining unique characteristic of Tl to assess myocardial viability
Name three PET MPI Radiopharmaceuticals
Rubidium-82 chloride
Oxygen-15 water
Nitrogen-13 ammonia
Which PET MPI radiopharmaceutical is not cyclotron produced?
rubidium??
In PET MPI Interpretation, what indicates Ischemia?
A defect on stress with normal rest
In PET MPI Interpretation, what indicates MI?
A defect on both stress and rest
For an MPI test to be “adequate”, patients should achieve at least ____of their maximum HR
85%
How is a pts 85% of their max HR calculated?
(220-patients age) x .85 =
Exercise is limited to a HR of 120-130/min for which patients?
pts who had recent MI
When using the exercise protocol for pts who had a recent MI, their max heart rate should be limited to:
120-130/min
What is the target HR for a 50yr male pt?
139
[(220-50) x .85 = 139 bpm]
At what radiation limit does the treadmill need to be shut down?
>2mR/hr
Name three Coronary Vasodilating Agents, including their chemical name.
Dipyridamole (Persantine)
Adenosine (Adenoscan, Adenocard)
Regadenoson (Lexiscan)
What is the biological half life of Dipyridamole (Persantine)?
hours
What is the biological half life of Adenosine (Adenoscan, Adenocard)?
10 sec
What is the biological half life of Regadenoson (Lexiscan)?
30min
Which coronary vasodialator(s) is preferred, and why?
Adenosine or regadenoson bc they have short biological half life compared to dipyridamole
What type of agent is dobutamine (dobutrex)?
Cardiac Positive Inotropic and Chronotropic Agent
When would Dobutamine typically be used instead of a coronary vasodilating agent?
When a patient has asthma, or is actively wheezing
What are some alternative names for Gated Blood Pool Imaging?
MUGA (multigated blood pool acquisition)
RVG (radionuclide ventriculography)
ERNA or RNA (equilibrium radionuclide angiography)
Name the 5 indications for a MUGA study
Assessment of cardiac function in chemotherapy patients
detection or assessment of CAD
MI
detection or assessment of CHF
Evaluation of function in patients with valvular disease
What are the two most common indications for RVG’s/MUGA’s/gated blood pool imaging?
evaluate ventricular function and EF in pts having chemotherapy
What result from a RVG study would be an indication to discontinue chemo?
If there is a drop of EF of >15%
What are the three methods for tagging Tc-99m labeled RBC's, and their labeling efficiency percentage?
In vitro (95%)
Modified (90%)
In vivo (85%)
T/F: before a MUGA procedure, An ECG rhythm strip should be obtained before injection. And why or why not?
true
Rapid a-fib or frequent PVC’s are a contraindication to the study.
What are the absolute contraindications for MUGA studies?
Rapid atrial fibrillation or frequent PVC’s
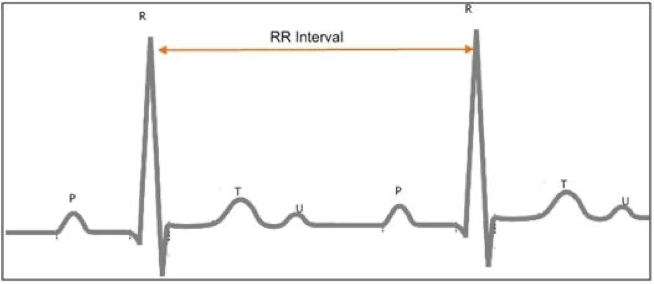
If there is a Tall P or T-wave (double gating) on the ECG, what can be done to troubleshoot?
move leg lead closer to heart
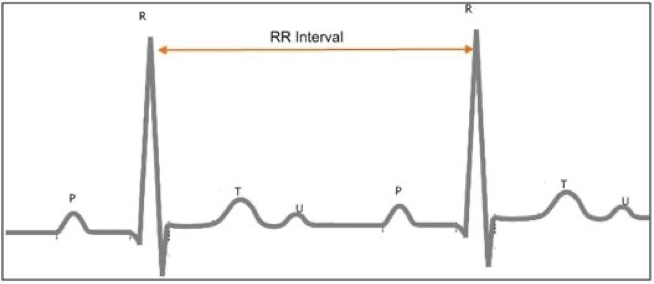
What can be done if the R-waves are inverted?
leads are criss crossed (?)
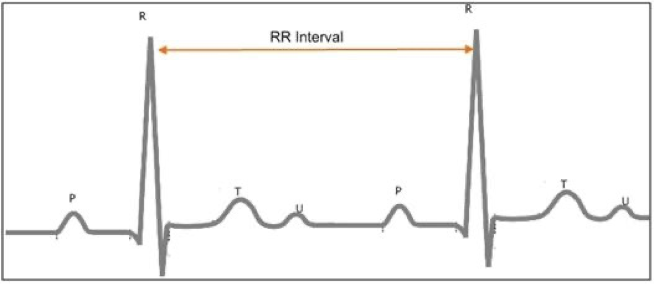
How can you increase the R-wave height on an ECG strip?
move black and red leads closer
During a gated study, 24 images per cardiac cycle are obtained. What is the length of time per image?
a)3.8 msec
b)38 msec
c)4.1 msec
d)41 msec
38 msec
What is the Ejection Fraction Formula?
EF = (Net diastolic counts - net systolic counts) / net diastolic counts
x 100
Calculate EF if ED = 90,400, and ES = 40,000
55.7%
What is the normal range for LVEF?
55-75%
What is the normal range for RVEF?
>40%
What level of decrease in LVEF in Chemotherapy Patients could indicate cardiotoxicity?
Decrease in LVEF below 50% or drop in LVEF of 5% or more
What is a normal range of increase for LVEF on a stress MUGA or first pass study?
Should have 5 % increase in LVEF from rest to stress
What causes an overestimation in EF?
Too much background subtraction
What causes underestimation in EF?
Too little background
including the left atrium in the left ventricle ROI in systole
Name the four indications for a First Pass Study.
Evaluation of patients with left ventricular dysfunction
interventricular shunts
myocardial ischemia
infarction.
What are advantages of a First Pass Study?
Tracer activity is limited to one chamber at a time, making it easy to define ROI’s
background is decreased
rapidly completed.
What are the disadvantages of a first pass study?
counting statstics are low bc of count rate limitations on rountine gamma cameras
Special high-count rate capable cameras are optimal but not widely available
What radiopharmaceutical is used for a First Pass Study?
Almost any Tc-99m radiopharmaceutical (besides MAA)
Why is Tc-99m pertechnetate or Tc99m DTPA prefered for a first pass study?
bc is Rapidly excreted through the kidneys
Using a MPI Tc agent, first pass study can be followed by a ______
gated SPECT
Using Tc-99m labeled RBCs, a first pass study can be followed by a ______
MUGA
What is visualized during a good bolus injection path on a first pass study?
sequential visualization of the superior vena cava, right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary artery to lungs, pulmonary veins, left atrium, left ventricle, and aorta
How is Hibernating Myocardium defined?
Severely, chronically ischemic tissue that is viable but appears to be nonfunctioning and has decreased perfusion
Why is it important to identify hibernating myocardium?
Because hibernating myocardium has a high likelihood of benefiting from revascularization.
What 2 PET radio pharmaceuticals can be used for viability imaging?
Tl-201
F-18 FDG
Which PET radiopharmaceutical is considered the gold standard in Viability?
F-18 FDG
What is the TI-201 Imaging Protocol for Viability studies?
dose: 2.5-3.0mCi of Tl @ rest (no stress)
Imaging 10-15 minutes post injection
redistribution (delay) images at 3-4 hours
if indicated: 24-hour delay or reinjection,
If ischemic areas fill in on initial 3-4hr delay viability images using Tl-201, what is done next?
nothing - exam is complete
If ischemic areas do not fill in on initial 3-4hr delay viability images using Tl-201, what is done next?
perform 24hr delay images or reinjection protocol
How are viability images usign Tl-201 interpreted?
Tl-201 uptake on delay or after injection = viable myocardium
How is F-18 FDG produced?
cyclotron
What is the positron range of F-18 FDG?
0.3mm
What is the mechanism of localization of F-18 FDG?
metabolic trapping
What is the critical organ of F-18 FDG?
bladder
What is the SNM ideal blood glucose for viability imaging?
between120-160 mg/dl
What should be done if BS is less than 120mg/dl?
administer oral glucose
What is the Viability Imaging protocol using FDG ?
glucose, if indicated
dose: 5-15 mCi F-18 FDG
IV inj. 45 min post glucose loading
PET images 30-60 minutes post-injection