b - Elements, mixtures and compounds
1/10
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
element
consist of one type of atom only
e.g. oxygen, copper
mixture
material composed of 2+ elements/compounds
physically mixed together
no chemical bond
properties of mixture are mixture of properties of separate parts
e.g. air (mixture of several gases), crude oil (mixture of hydrocarbons, mostly liquids)
compound
made up of atoms of 2+ different elements joined by chemical bonds
properties often totally different from properties of original elements
e.g. carbon dioxide is compound formed from chemical reaction, one C atom reacts with two O atoms to form molecule of carbon dioxide
Pure substance
Made of single element/compound
Has specific melting + boiling point
e.g. pure ice melts at 0ᵒC, pure water boils at 100ᵒCMixture not pure - will melt/boil gradually over range of temperatures
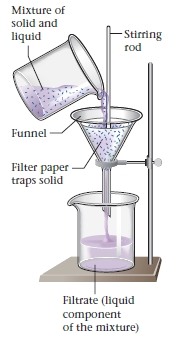
filtration
used to separate insoluble solid from a liquid/solution
Put filter paper in funnel and pour in mixture
Liquid part runs through paper, leaving behind solid residue
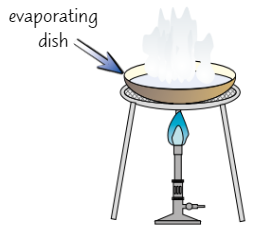
crystallisation
used to separate soluble solid from solution
Pour solution into evaporating dish + gently heat solution
Some water will evaporate, solution becomes more concentratedOnce some water has evaporated/when crystals start to form, remove dish from heat + leave solution to cool
Salt should start to form crystals as it becomes insoluble in cold, high conc. solution
Filter crystals out of solution + leave in warm place to dry
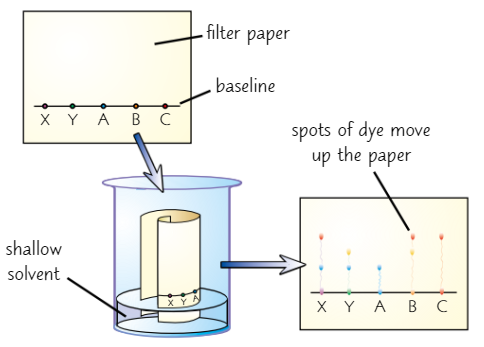
Paper chromatography
used to separate dyes
Draw line near bottom of filter paper (use pencil as pencil marks are insoluble so won’t dissolve in solvent)
Add spots of diff inks to the line at regular intervals
Loosely roll sheet up + put in beaker of solvent e.g. water
Ensure level of solvent is below baseline - don’t want inks to dissolve in solvent
Put lid on container to stop solvent evaporating
Solvent seeps up paper, carrying inks with it
Each dye in inks moves up paper at diff rate + forms spot in diff place
When solvent has nearly reached top of paper, take paper out of beaker + leave to dry
End result is called chromatogram
How chromatography separates mixtures
Different dyes move up paper at different rates
Some stick to paper, others dissolve more readily in solvent + travel quicker
Distance travelled by dyes depends on solvent + paper used
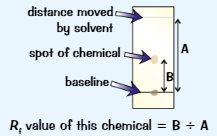
Rf value
Rf = distance travelled by solute/distance travelled by solvent
To find distance travelled by solute, measure from baseline to centre of spot
Chromatography often used to see if certain substance is in mixture
Run a pure sample of substance you think might be in mixture alongside sample of mixture itself
If sample has same Rf values as one of the spots, they’re likely to be same
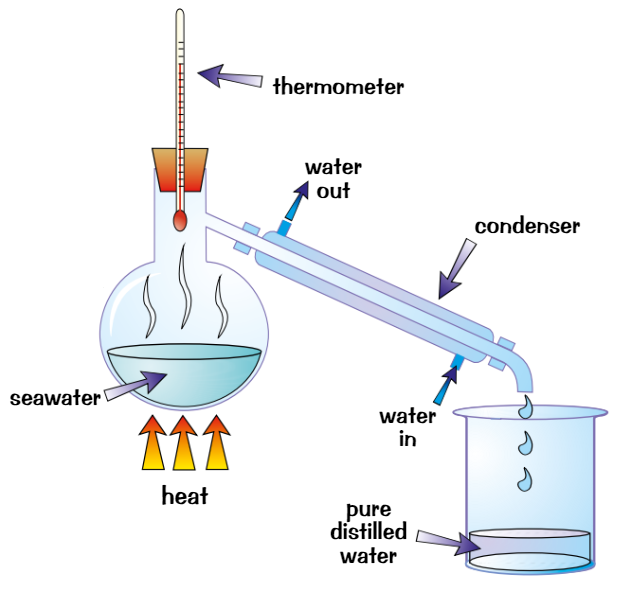
simple distillation
used to separate pure liquid from solution
Heat the solution
Part of solution with lowest BP evaporatesVapour is cooled, condenses + collected
Rest of solution is left behind in flask
Can use simple distillation to get pure water from seawater
Water evaporates, condenses and is collected
Problem: can only be used to separate things with very different BPs
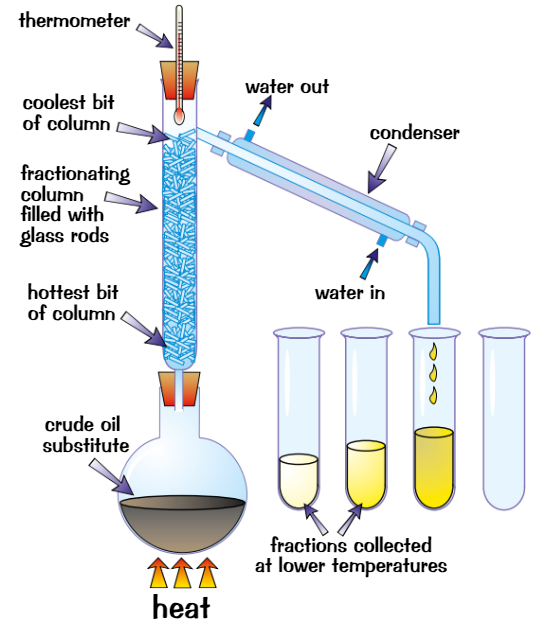
fractional distillation
used to separate mixture of liquids with different boiling points
Put mixture in flask + put fractionating column on top, then heat it
Different liquids have different BPs so evaporate at diff temps
Liquid with lowest BP evaporates first
When temp on thermometer matches BP of liquid, it reaches top of columnLiquids with higher BPs also start to evaporate but column is cooler towards top, so they only get part of the way up before condensing + running back down towards flask
When first liquid has been collected, raise temp until next one reaches the top