practical techniques questions
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Why are crystals rinsed with a small amount of ice cold water?
Rinsed to remove impurities that remain in solution
Ice cold - prevents crystals redissolving
Why are the crystals put in a warm oven
To ensure water of crystallisation is not removed
2 possible reasons why yield is less than 100%
solid lost when heated in basin
Remains in solution
Crystals remain on filter paper
Transfer losses from reaction flask
Water of crystallisation lost during drying process
How could not using a lid affect the calculated value of n
some of the salt y could be lost from crucible during heating
Mass lost is greater n is greater than expected
Explain how decreasing amount of time heating could affect the value of n
mean not all water has been removed
N is less than expected
Why is sodium carbonate used in iodine clock reaction?
Quench the reaction neutralising remaining H2SO4
Explain why filter paper and funnel are warmed in an oven
make sure the solution doesn’t cool down
Prevent crystallisation
Would reduce the yield of product
How does allowing the filtrate to cool and recrystallise and filter the crystals under a reduced pressure remove impurities from crystalline product
Step 4: product less soluble in cooler solvent soluble impurities stay in solution
Step 5: filtering under reduced pressure removed more of the soluble impurities
Devise an experiment to determine Ka for a solution of ethanoic acid of unknown concentration
Measure pH at regular intervals
Plot pH against volume
Use graph to find pH at half equivalence point
At half neutralisation pH = pKa Ka = 10-pH
Some of the crystals jumped out of crucible while it was being heated
Crystals jumped out of crucible
value of z increases
Bc more mass than expected
Prevented by placing a lid on crucible or heating to a constant mass
Not all water of crystallisation lost
less mass
Prevented by heating to a constant mass
This means value of z decreases
Why do you cool the mixture before adding the conc H2SO4 drop by drop
reaction is v exo
Why do you add a few anti bumping granules
smooth bubbling
Surface for bubbles to form
Why do you heat under reflux
Prevent the loss of volatile substances
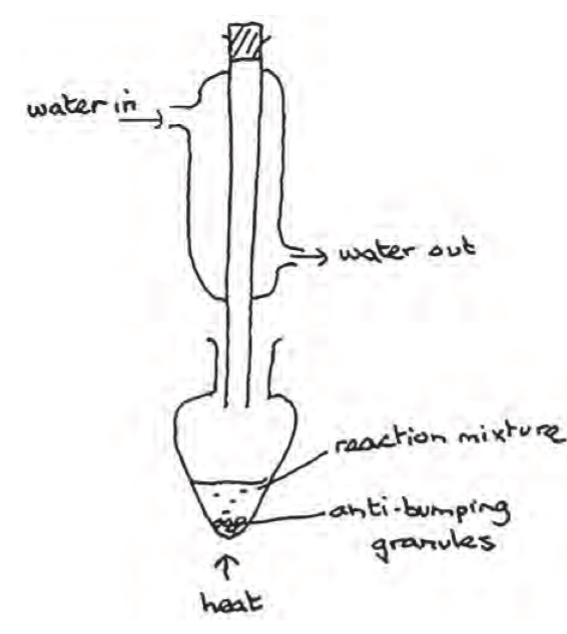
Identify 3 errors and what the effect is
there is a gap between condenser and flask + products will escape
Water is flowing the wrong way doesn’t fill with water
There is a stopper on condenser there will be a build of pressure
Explain why brown vapour forms
Bromide ions oxidised
State the position of the aqueous layer in the separating funnel
Aqueous layer on top
Why do you add sodium hydrogencarbonate
To react with HCl
Why do you invert the funnel and open the tap
To avoid build up of pressure
Why do you add anhydrous sodium sulfate and swirl the flask until the liquid becomes clear
Drying agent
Give a suitable range over which to collect the pure 1-bromobutane in recrystallisation step
99-101
Why would you have a yield less than 100%
recation is incomplete
Not all crystallised
Why do you have a higher yield than expected
impurities in crystals
Crystals were not dry
Give 2 reasons why the wire is made of nichrome
Unreactive
Uncoloured
Why is fresh conc HCl used in second stage of flame test
contaminated with residue of previous tests
Why is HCl used in 2nd stage of the flame test
acid is contaminated
Describe how you would ensure that all the sodium hydroxide was transferred to volumetric flask
rinse beaker
Transfer washings to volumetric flask
State why the procedure has to be restarted rather than using a test pipette to remove excess water
Remove some of dissolved NaOH
Give 2 steps needed before the student takes the initial burette reading
eyes are level with bottom of meniscus
Remove the funnel
Give the effect of any on the value of the first titre
titre large
NaOH decreases
Why was the aqueous layer was the lower of the 2 layers
More dense
Why was the ether layer washed with deionised water
some of sodium benzoate dissolves in water
Explain why the addition of HCl results in precipitation of benzoin acid
benzoate ion is protonated by HCl
Benzoic acid is less soluble than Na salt
Explain why the front windows of the fume cupboard must be below the safety line even with the exhaust fan switched on
safety line exhaust system is not strong enough to draw in the fumes
Toxic fumes will escape
Outline the procedure that the student could use, including a diagram and the measurements needed.
add HCL and immediately stopper the flask
Record the volume of gas
Collect gas at regular intervals
Describe what happens to the melting temperature of the paracetamol is not pure
melting temperature lower
Melting temperature over a range of temperatures
Give a reason why using a burette than a measuring cylinder will not improve the accuracy of experiment
Describe changes to the method and how the data is used that would improve the accuracy of the determination of the temperature of the temperature change in experiment 2. Your description should involve the use of a clock and plotting a graph
measure temp of HCl
Every 30 seconds 2 ½ mins
Add Na2SO3 at 3 mins
Stir and measure temp every 30 secs for another 5 mins
Plot graph of temperature against the join 2 sets of points
With 2 best fit straight lines
Determine max temp change
Identify the 2 changes that must be made to be apparatus before heating the pear-shaped flask giving a reason for each change
Replace a thermometer at the top to act as a seal prevent vapour from escaping
Water in and out to keep condenser full better cooling
Give 3 reasons for difference in combustion values
energy lost to the surroundings
Incomplete combustion
Evaporation of methanol/water
Value for the enthalpy change of combustion of methanol from this experiment would differ a
.
Student planned to obtain any dissolved magnesium carbonate by evaporating the filtrate and then weighing the residue
MgCO3 may decompose
Residue would contain XS Na2CO3
Explain how if at all very slight solubility of magnesium carbonate I’m water would affect the value of ax
X would increase
Moles of MgCO3 would decrease
Explain how the student could ensure that the hydrated salt was fully decomposed
heat to a constant mass
Identify 2 modifications to the method that would enable the student to lower the percentage uncertainty in measurement of the mass of solid residue
increase the mass
Use a balance with more decimal places
Explain one procedural error which could have resulted in student 2 obtaining a molar mass greater
bung not replaced quickly
Some of CO2 escaped
Give one reason why the mass of the carbonate measured by student 3 has a greater uncertainty than that mesured of student 1
Used a smaller mass
Larger percentage error
student B’s mistake would affect the titre
number of NaOH as diluted
Moles decrease
Titre would decrease
Explain how if at all student c’s use of a wet conical flask affects the value of titre
titre would be unchanged
Number of moles of NaOH would be the same