PNB 2265 PRACTICAL 2
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
199 Terms
general functions of the lymphatic system
maintain fluid balance, transport fat, participate in immune response
components of lymphatic system
lymph vessels, lymph nodes
primary lymphoid organ
thymus
cortex of thymus
appear as darker regions
cortex of the thymus contains
T cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, epithelial cells
medulla of thymus contains
more mature T cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, Hassall’s corpuscles
lighter region of the thymus
lighter regions
filters blood and site of initiation of immune response
spleen
red pulp
spleen: site of storage of RBCs and filters them
white pulp
spleen: clusters of T cells, B cells, and macrophages
T lymphocytes in immune response
responsible for cell mediated immunity; directly targeting and eliminating infected or cancerous cells
B lymphocytes
humoral immunity, producing antibodies to neutralize pathogens
direct ELIZA
uses single antibody directly conjugated to an anzyme
indirect ELIZA
uses two antibodies;
primary antibody binds the antigen
secondary antibody binds the primary antibody and it conjugated to the enzyme
steps to ELISA
coat plate with antiobdy
block any remaining binding sites
add a sample
wash
add a secondary antiobdy with an enzyme
wash again
add a substrate that reacts with the enzyme to produce a color change which is then measured
how to interpret results for ELISA
compare absorbance readings of the samples to a standard curve, which plots known concentrations of the target antigen against their corresponding absorbance values
principles of spirometry and how integration of the flow signal gives a volume
used to measure the amount of volume or flow of air that can be inhaled and exhaled
FEV1
forced expiratory volume in first second
FVC
force vital capacity
equation for spirometry
FEV1/ FVC
respiratory acidosis
when the body retains excessive carbon dioxide, leading to a decrease in blood pH (more acidic)
respiratory alkalosis
when the body eliminates too much carbon dioxide, resulting in an increase in blood pH
cause of MI
blockage of blood flow to the heart muscle
treatments of MI
restoring blood flow to the heart and preventing further damage; angioplasty/stenting
cirrhosis causes
chronic hepatitis; excessive alcohol use; fatty liver disease
cirrhosis symptoms
weakness; fatigue; abdominal pain; nausea
cirrhosis treatment
preventing further liver damage; liver transplant; medication
angina pectoris causes
reduced blood flow to the heart muscle- lack of oxygen
angina pectoris symptoms
pain in arms, neck, jaw, shortness of breath, fatigue
angina pectoris treatment
medications (beta blockers), calcium channel blockers, aspirin
gallstones causes
high cholesterol, imbalance in bile composition
gallstones symptoms
nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, jaundice
pulmonary fibrosis
environmental exposure; medications
pulmonary fibrosis symptoms
shortness of breath, dry cough, fatigue
pulmonary fibrosis treatment
medications, oxygen therapy
Myasthenia gravis causes
body’s immune system mistakenly attacking the neuromuscular junction
Myasthenia gravis symptoms
weakness of the eye muscles, drooping eyelids, double vision, changes in facial expression
Myasthenia gravis treatment
medication, surgery, or combination of therapies
diabetes inspidus causes
problems with ADH secretion that help the kidneys regulate fluid balance
diabetes inspidus symptoms
excessive thirst and frequent urination
diabetes inspidus treatment
desmorpressin is used to replace ADh
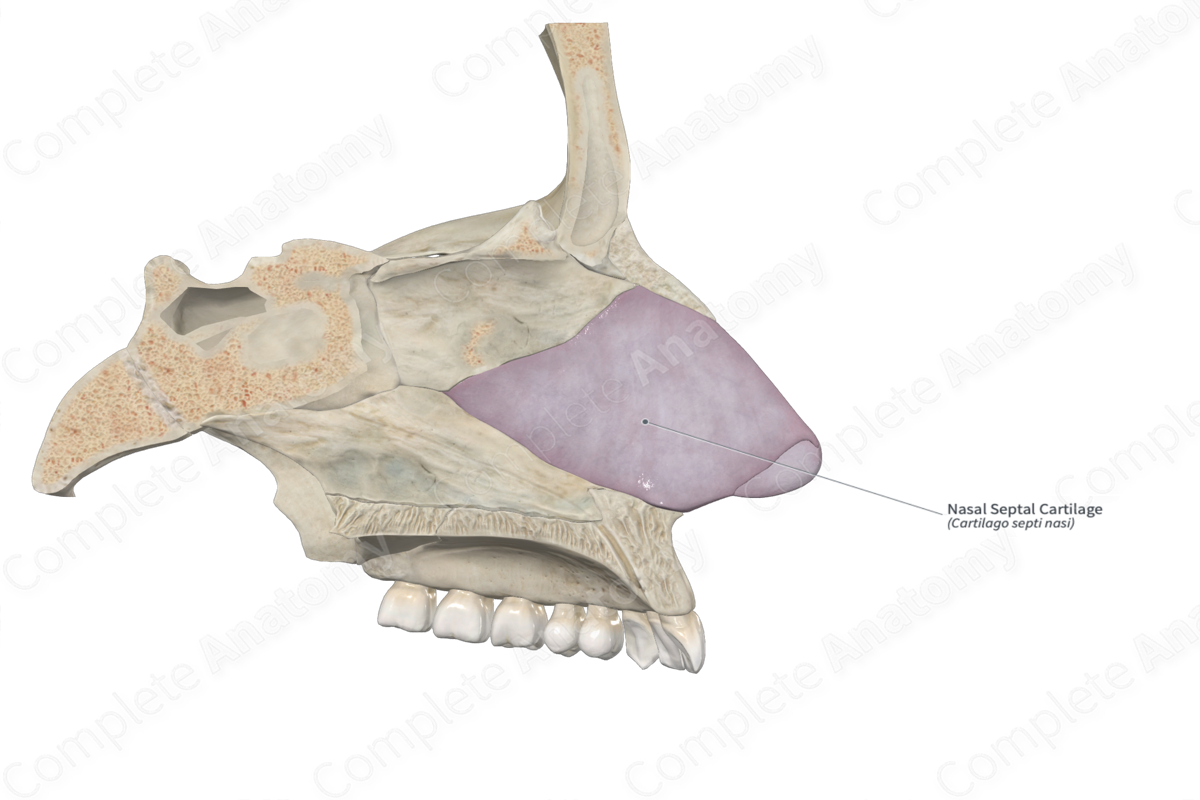
nasal septum (vomer/ cartilage)

pharynx
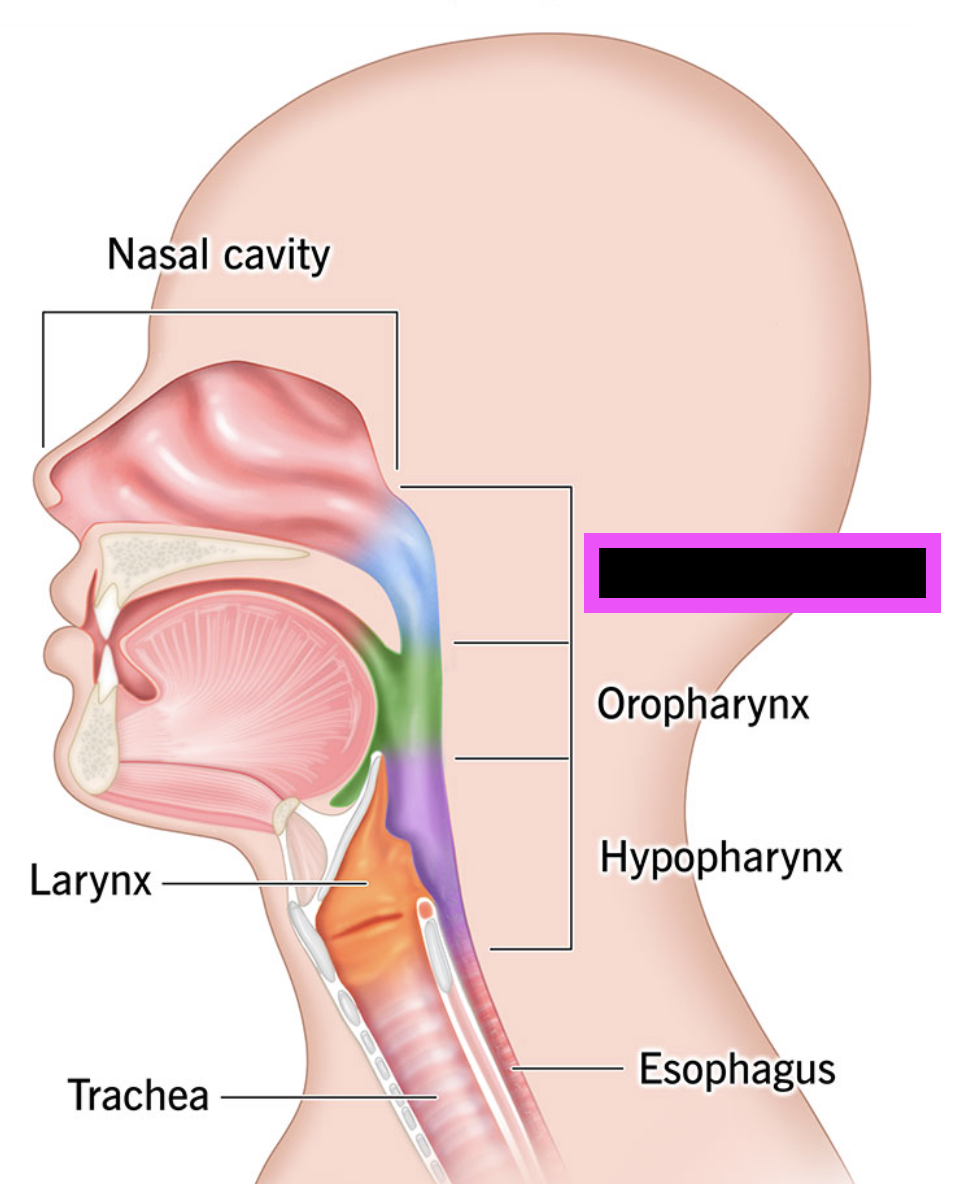
nasopharynx
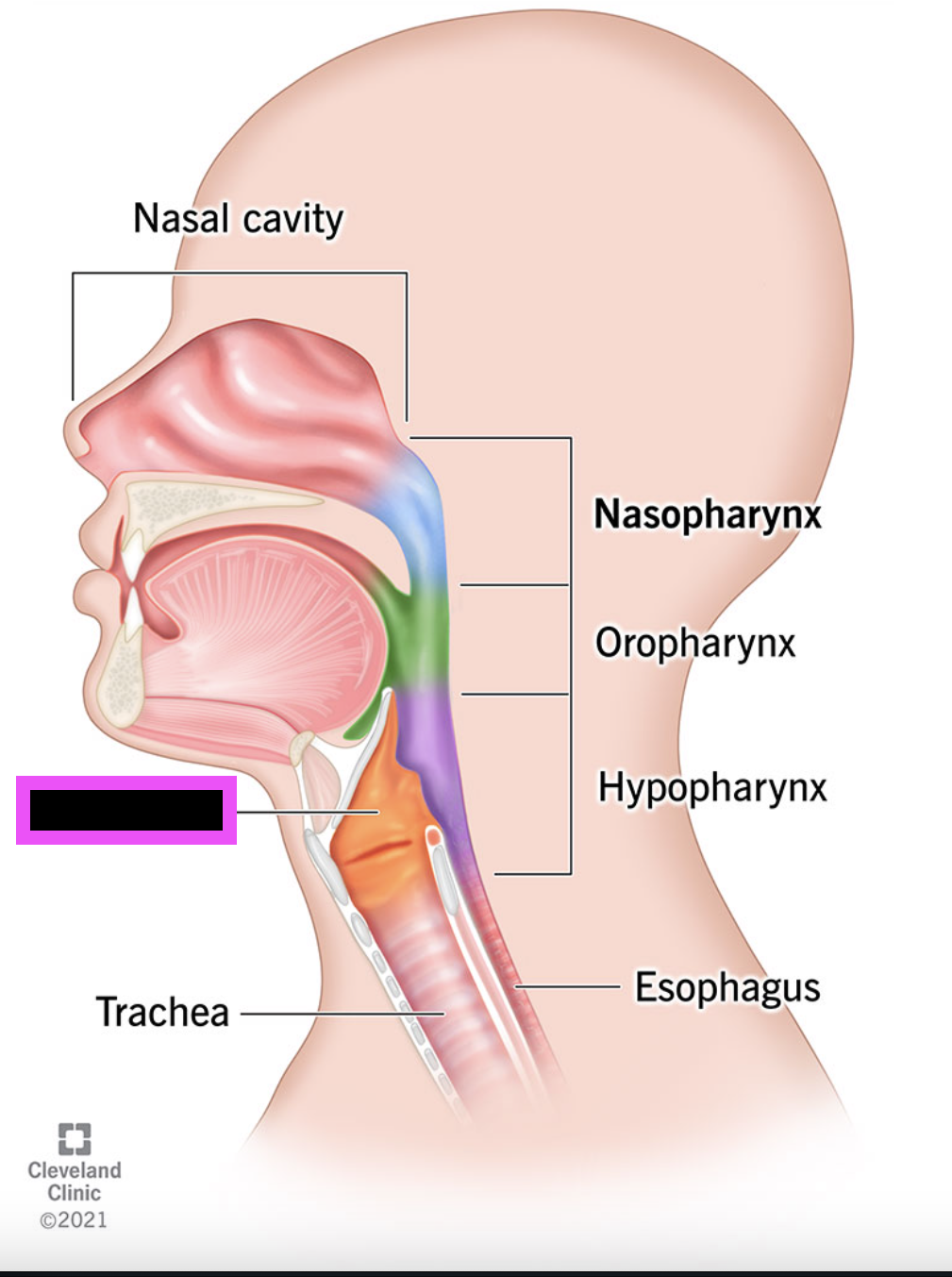
larynx
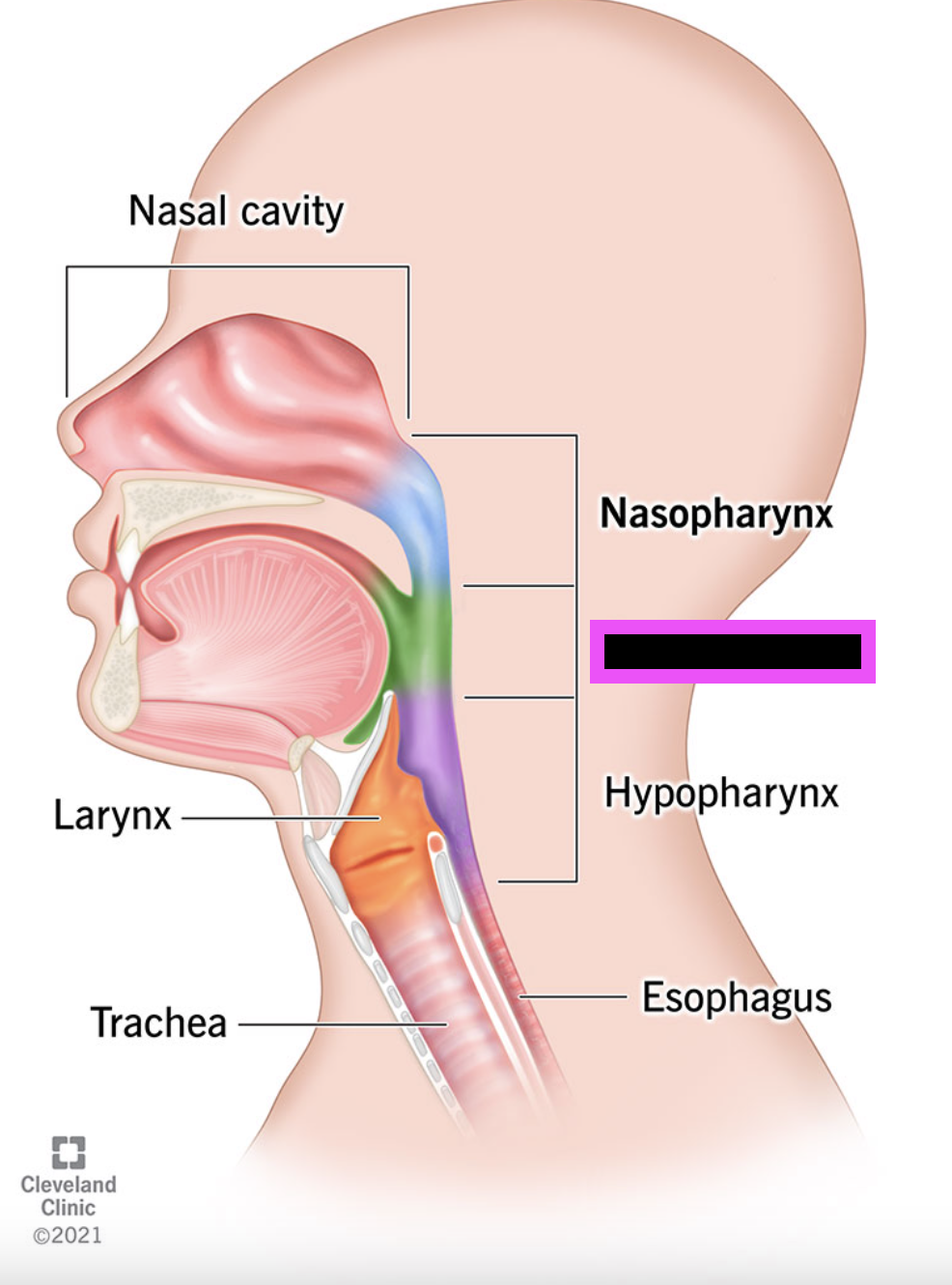
oropharynx
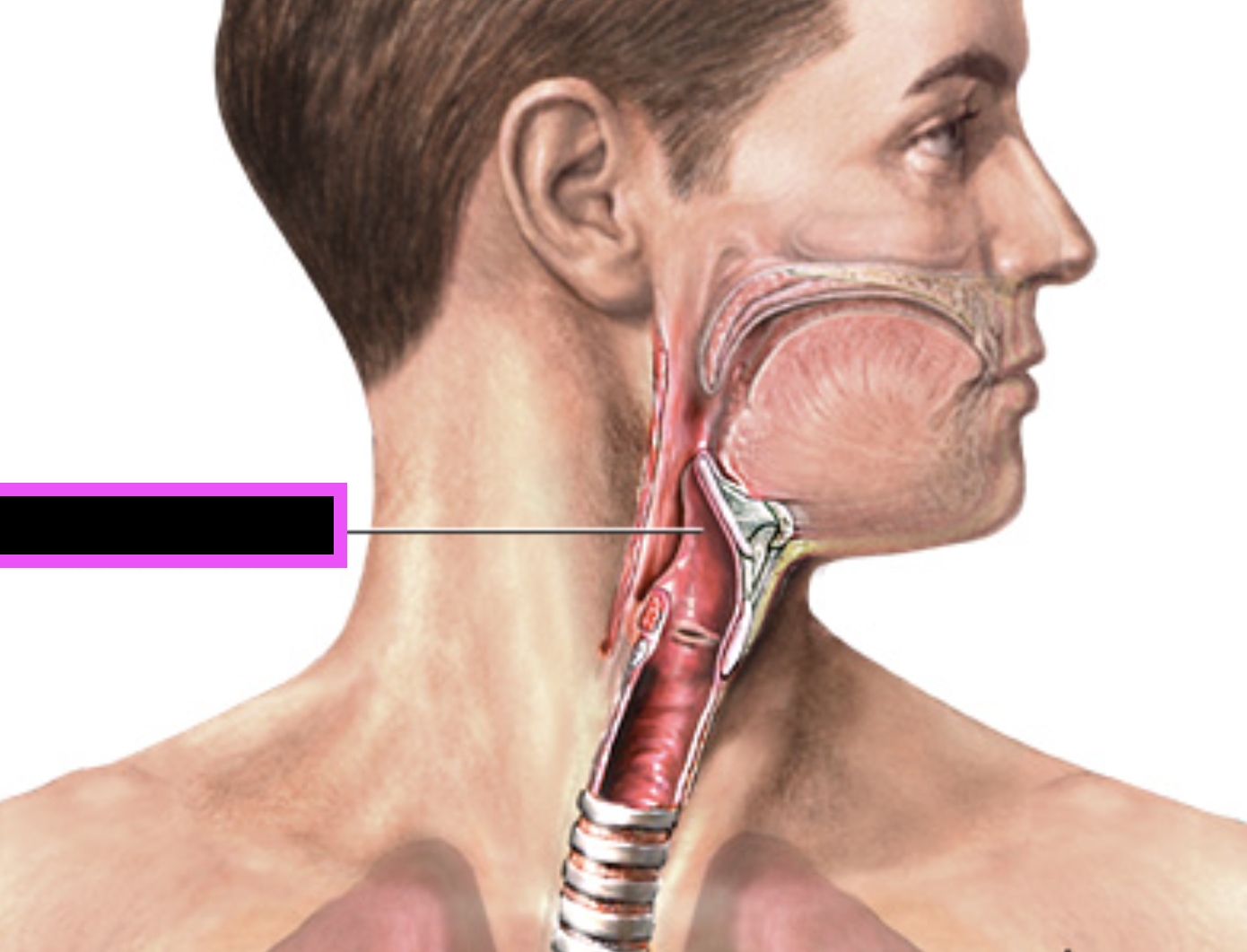
epiglottis
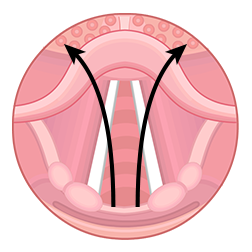
glottis
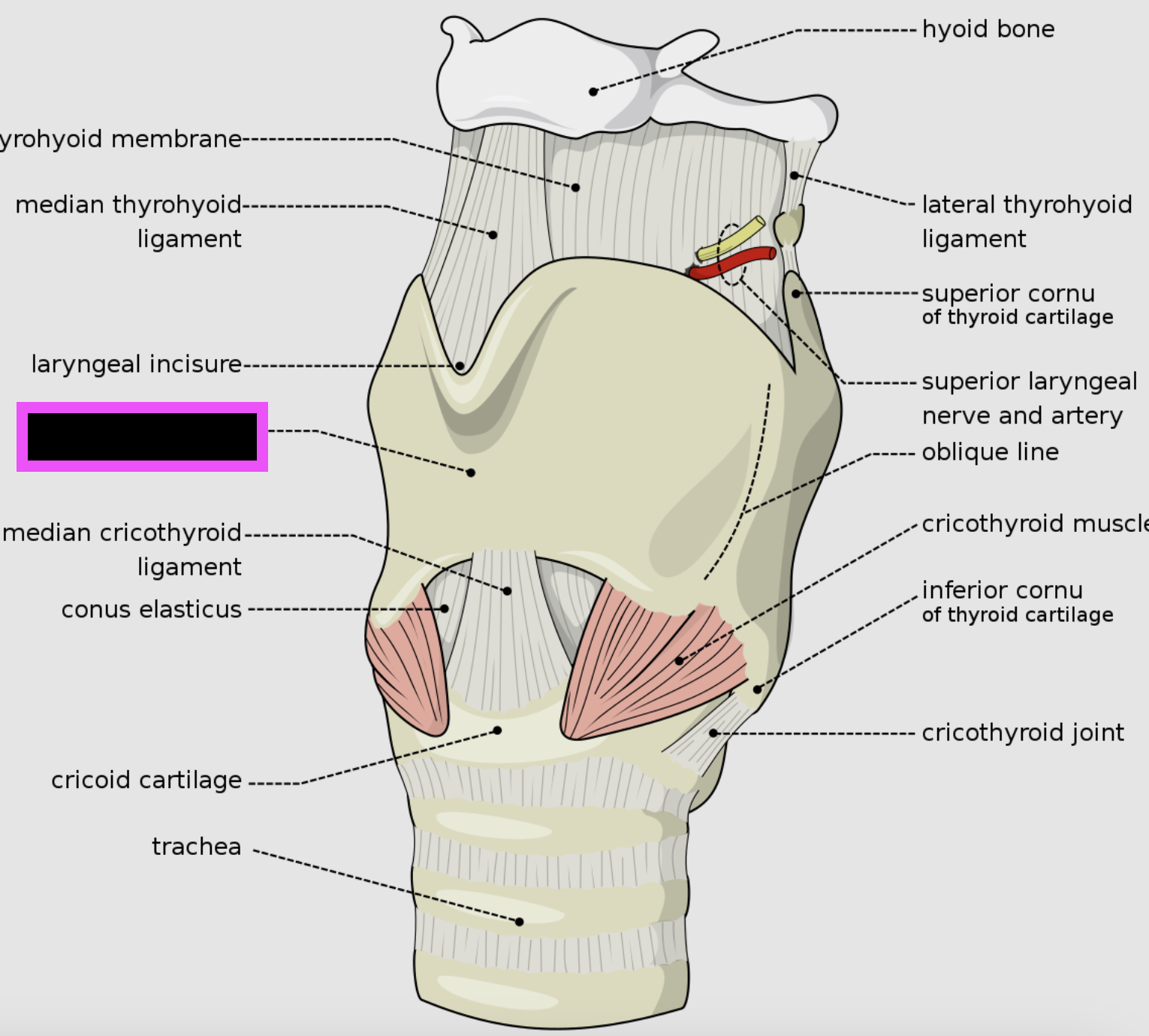
thyroid cartilage
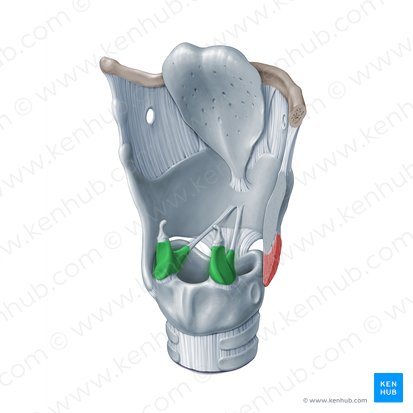
arytenoid cartilage
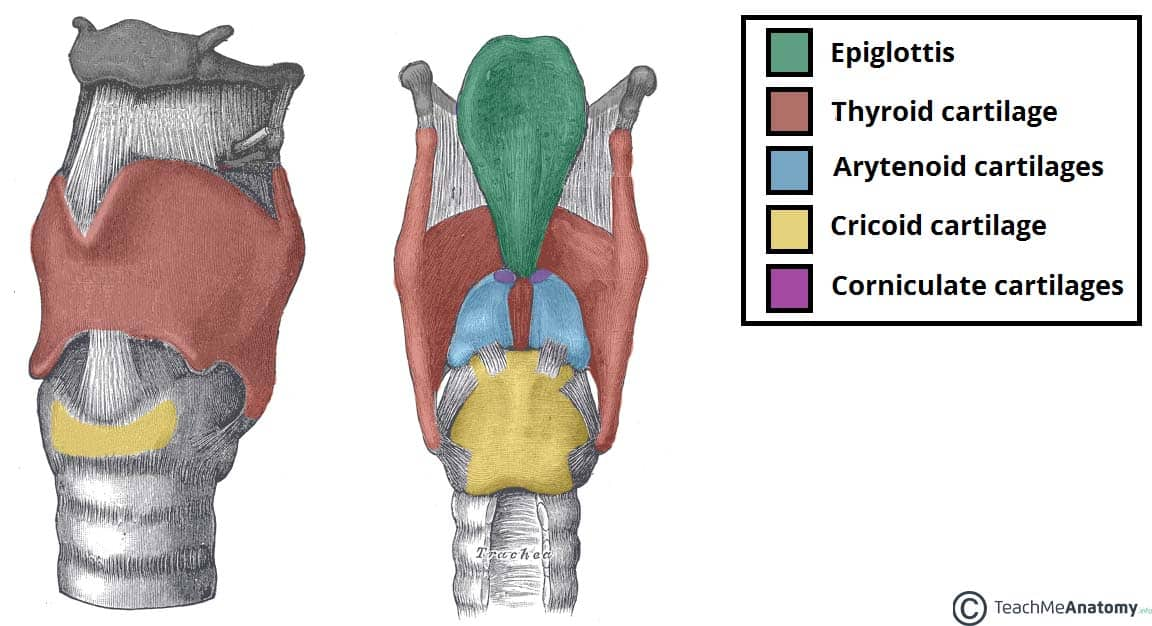
study this
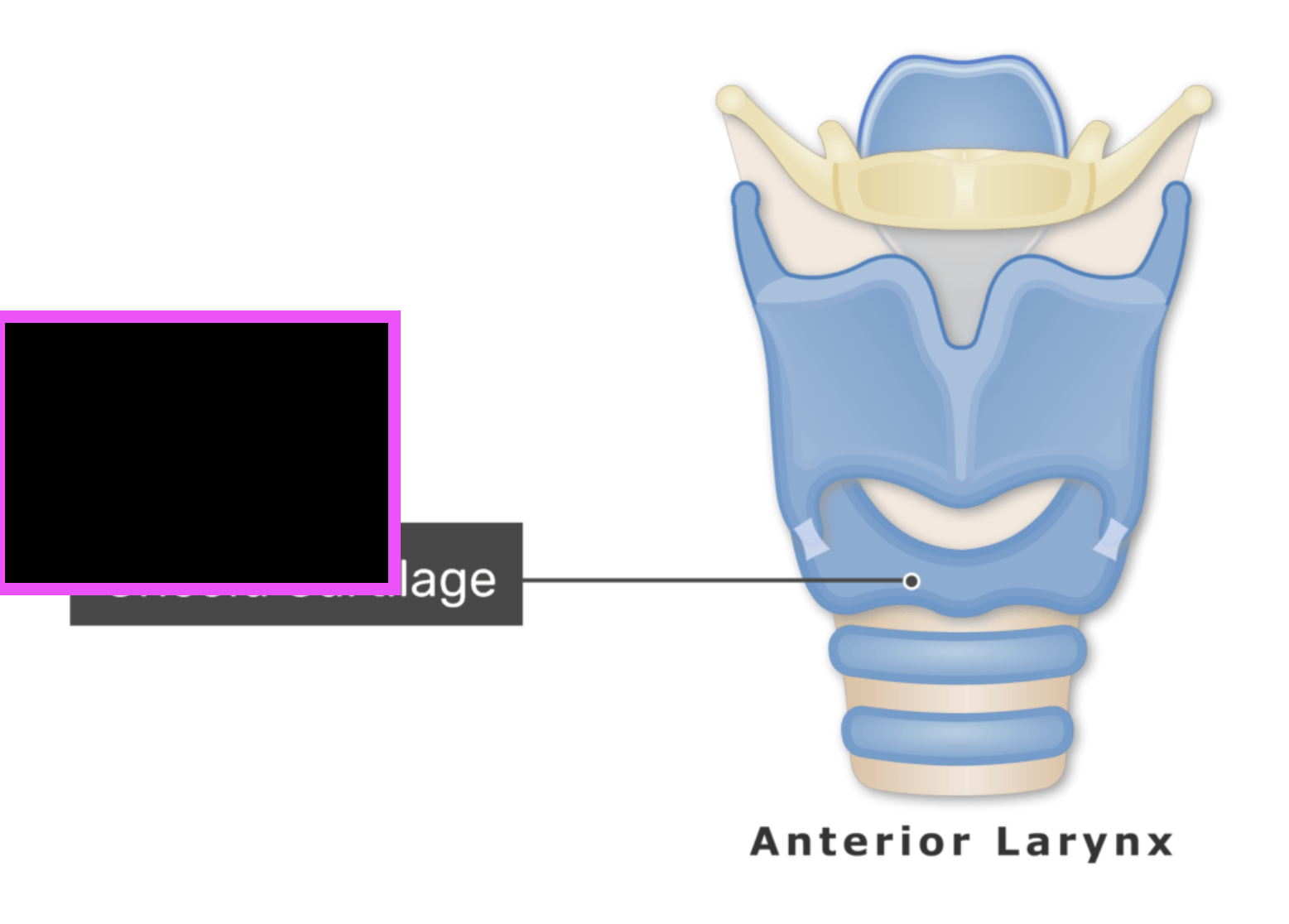
circoid cartilage
hyoid bone
trachea
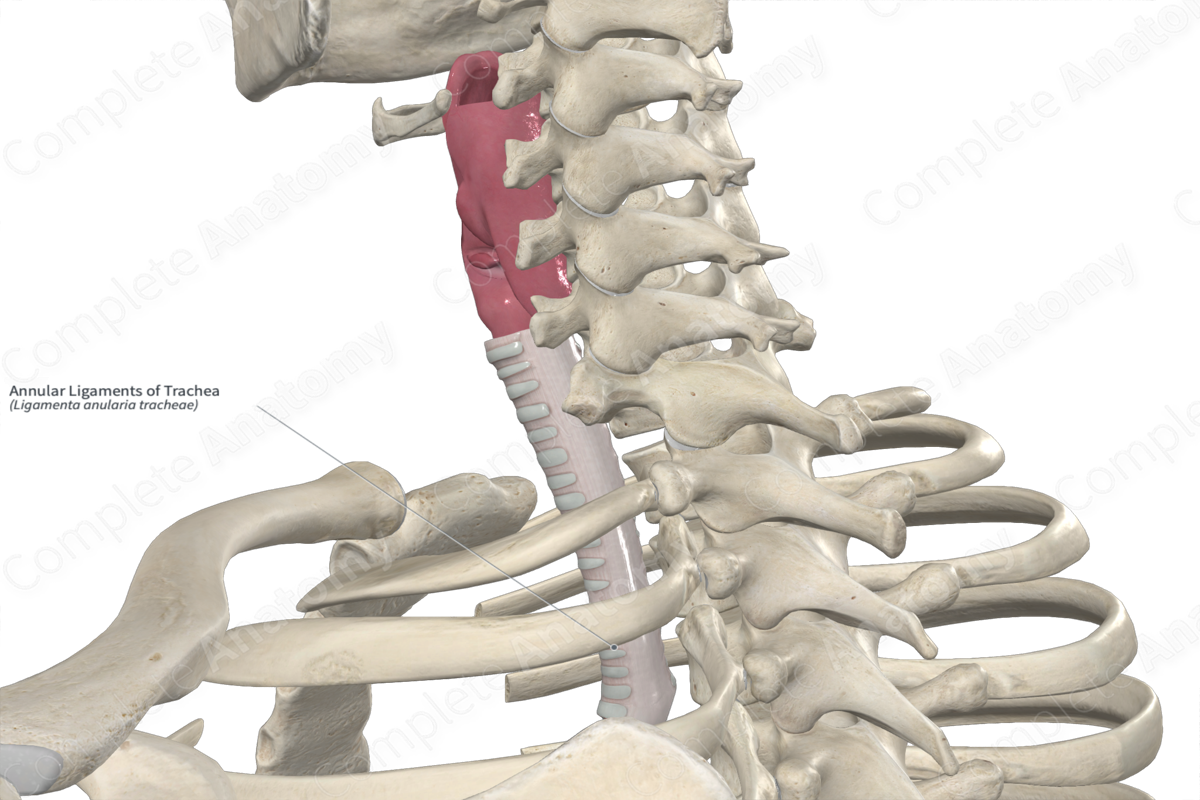
annular ligaments
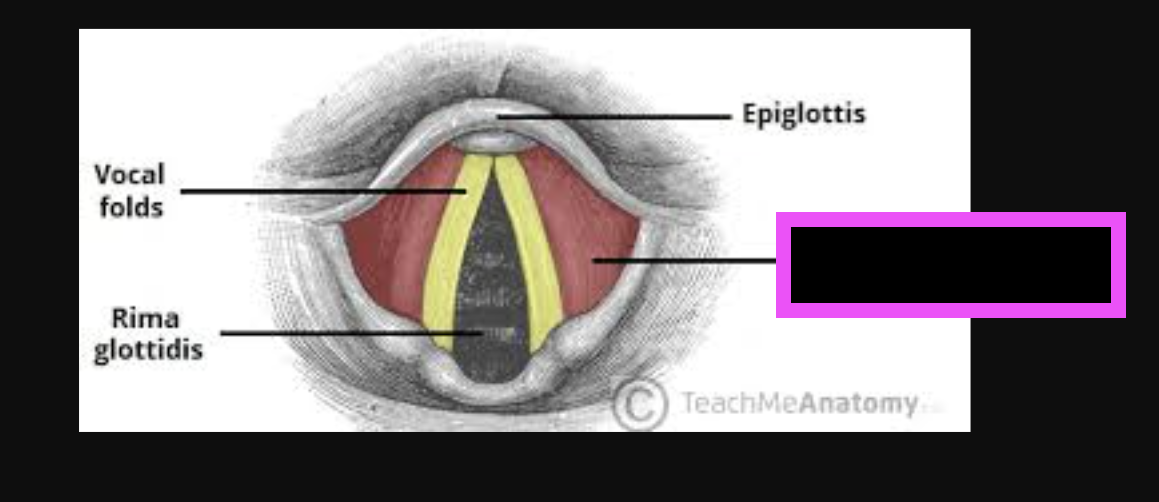
vestibular folds (false vocal cords)
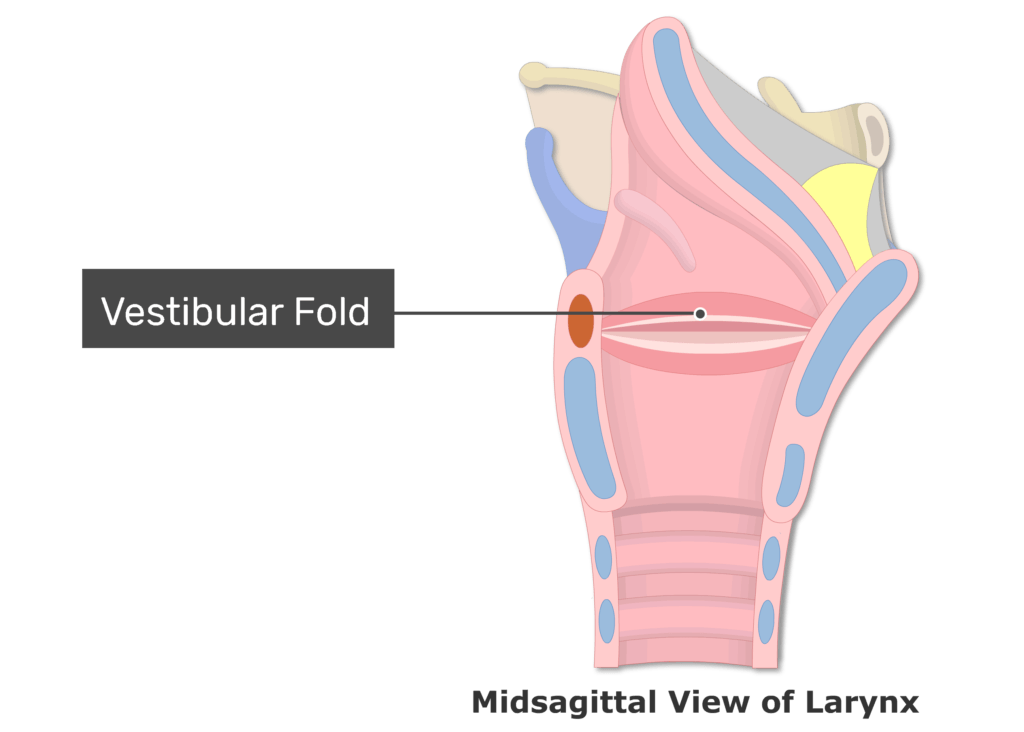
vestibular fold (false vocal cords)
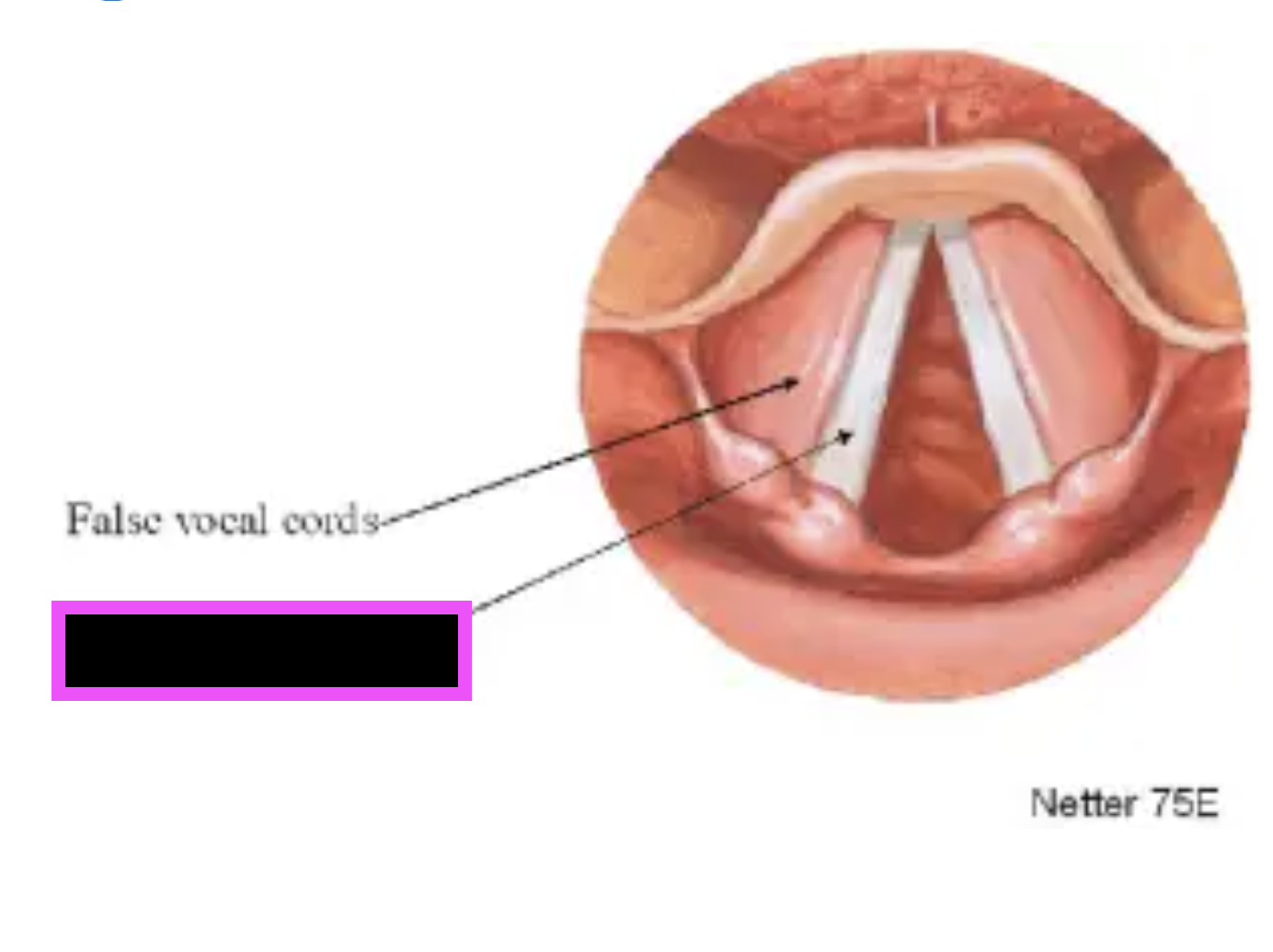
vocal folds (true vocal cords)
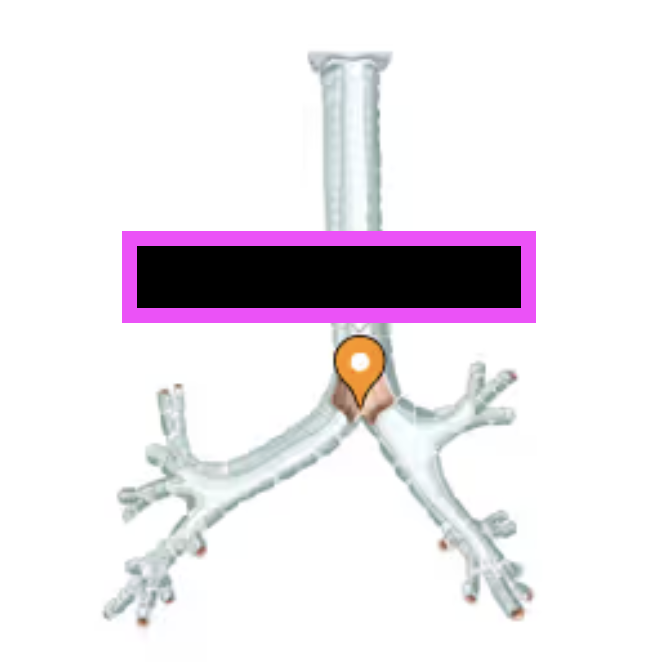
(internal ridge where the trachea branches into left and right bronchi)
carina
right lung lobes
3: superior, midle, inferior
left lung lobes
2 lobes: superior and inferior
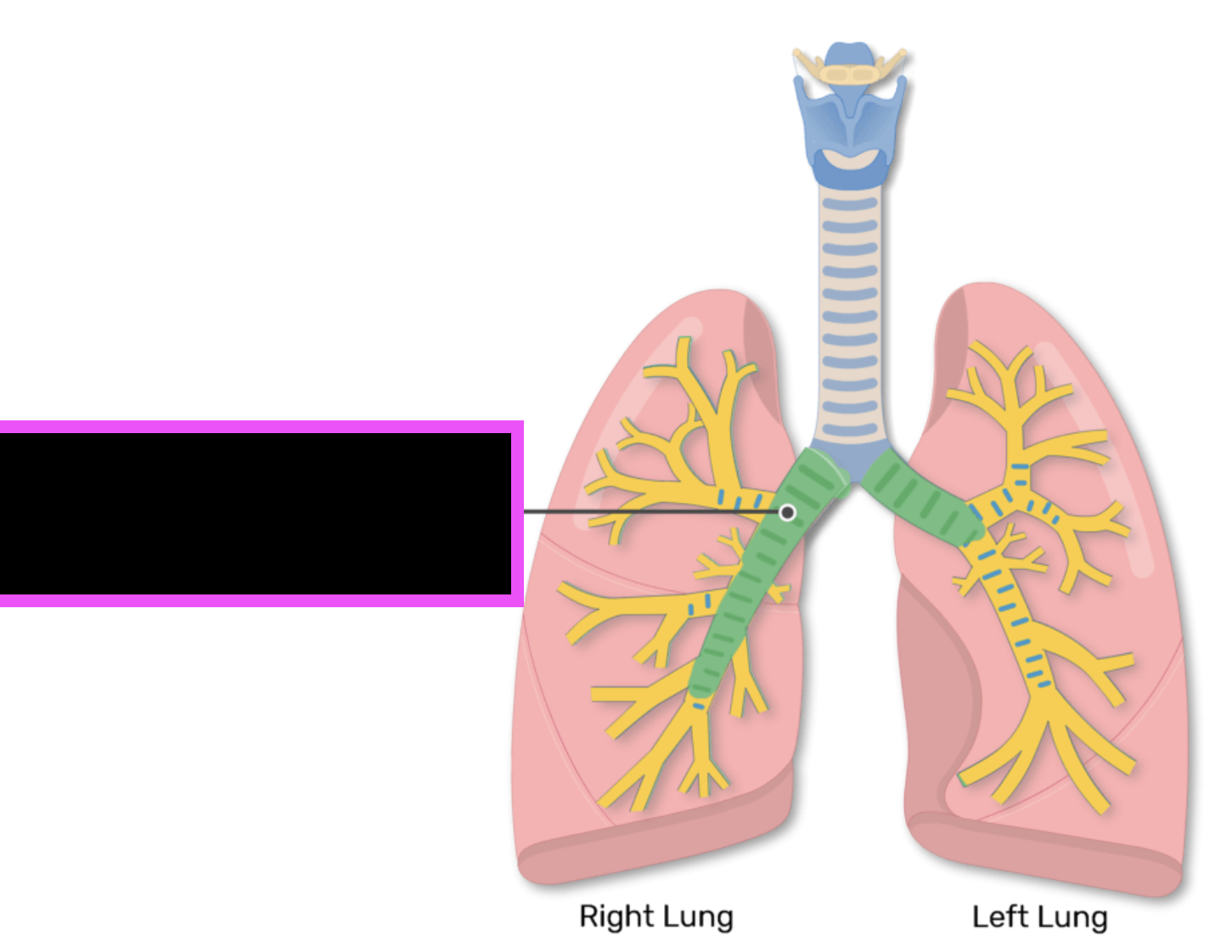
R and L primary bronchi
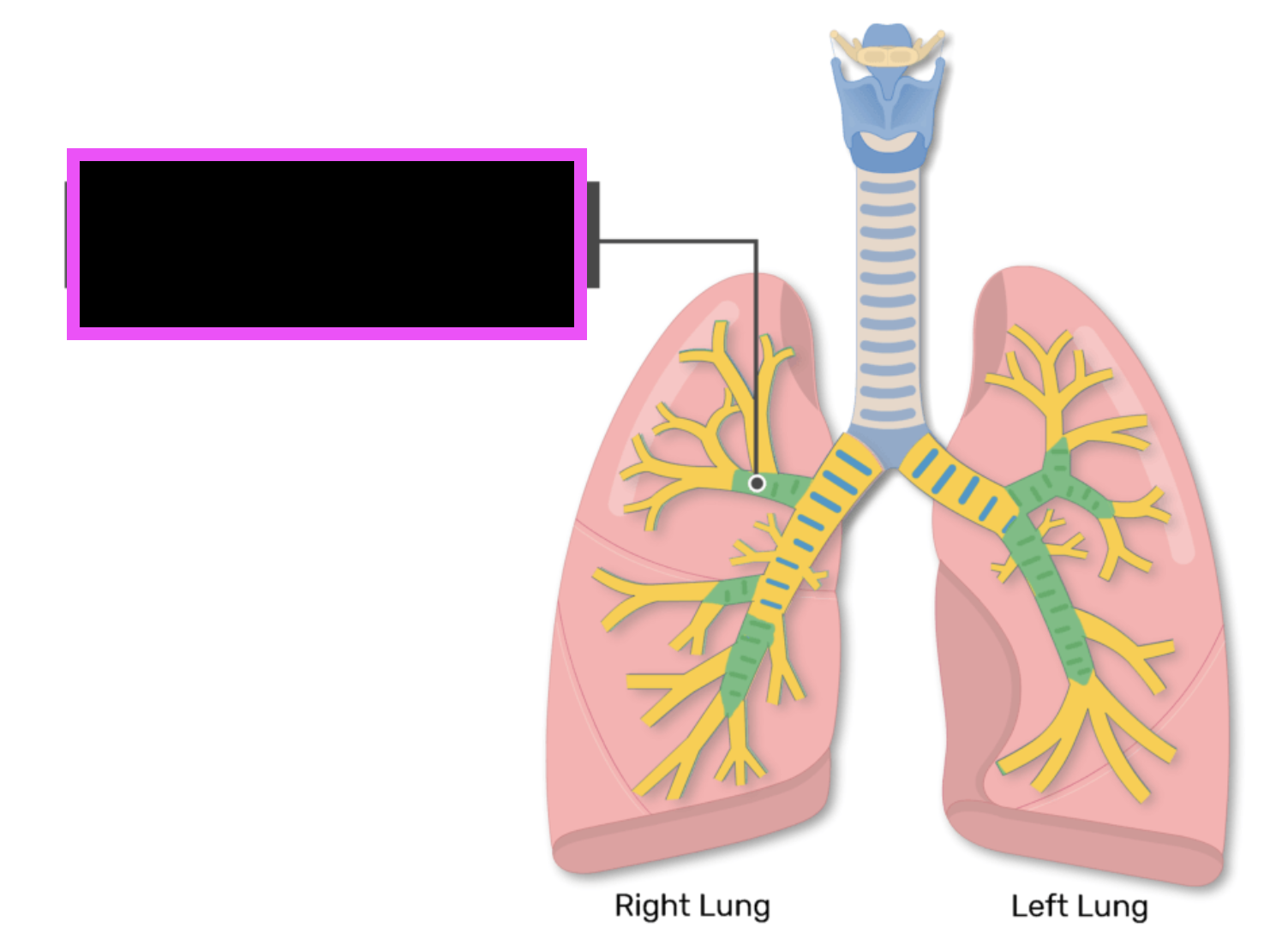
secondary bronchi
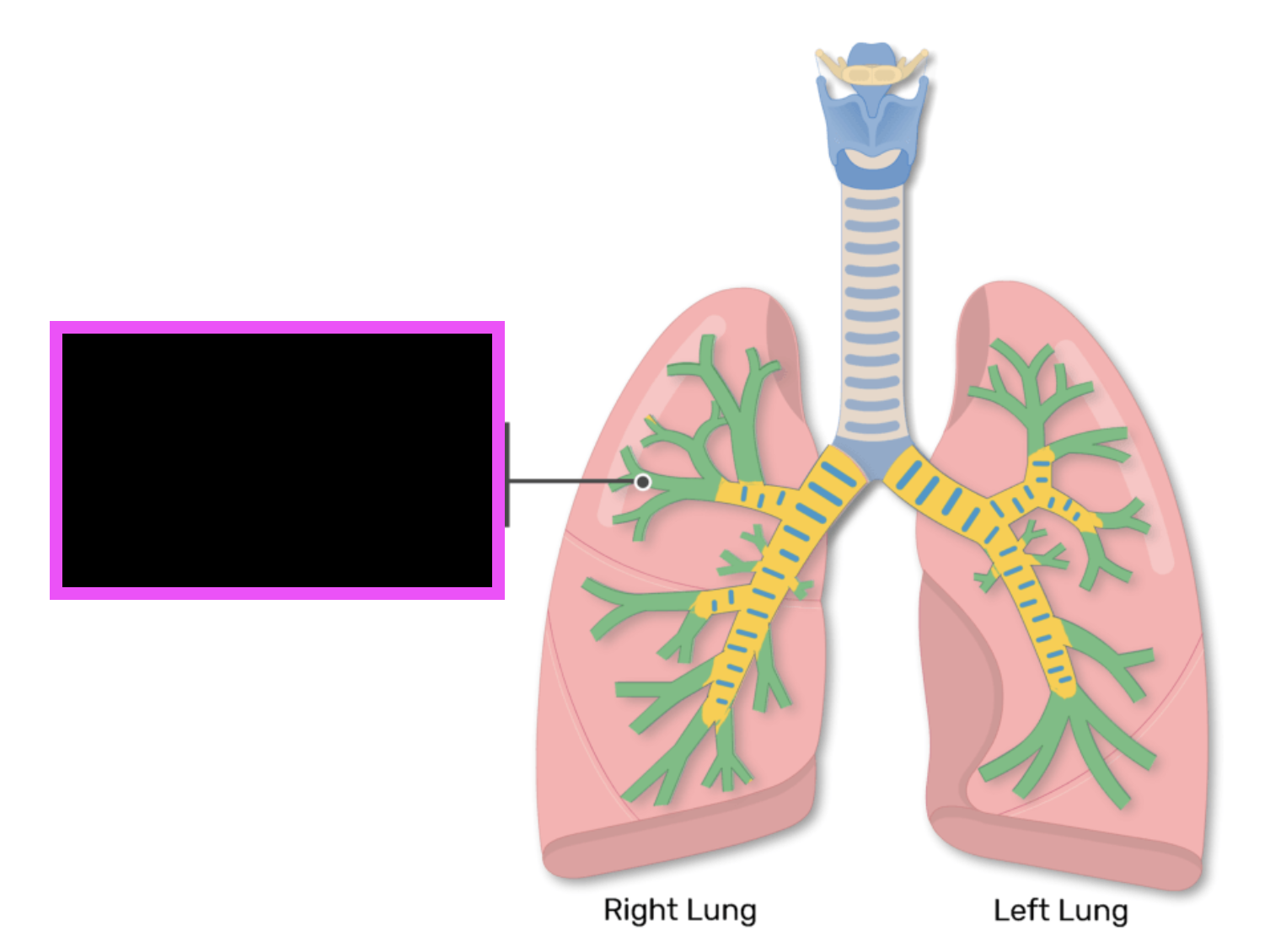
tertiary (segmental) bronchi (10 per lung)
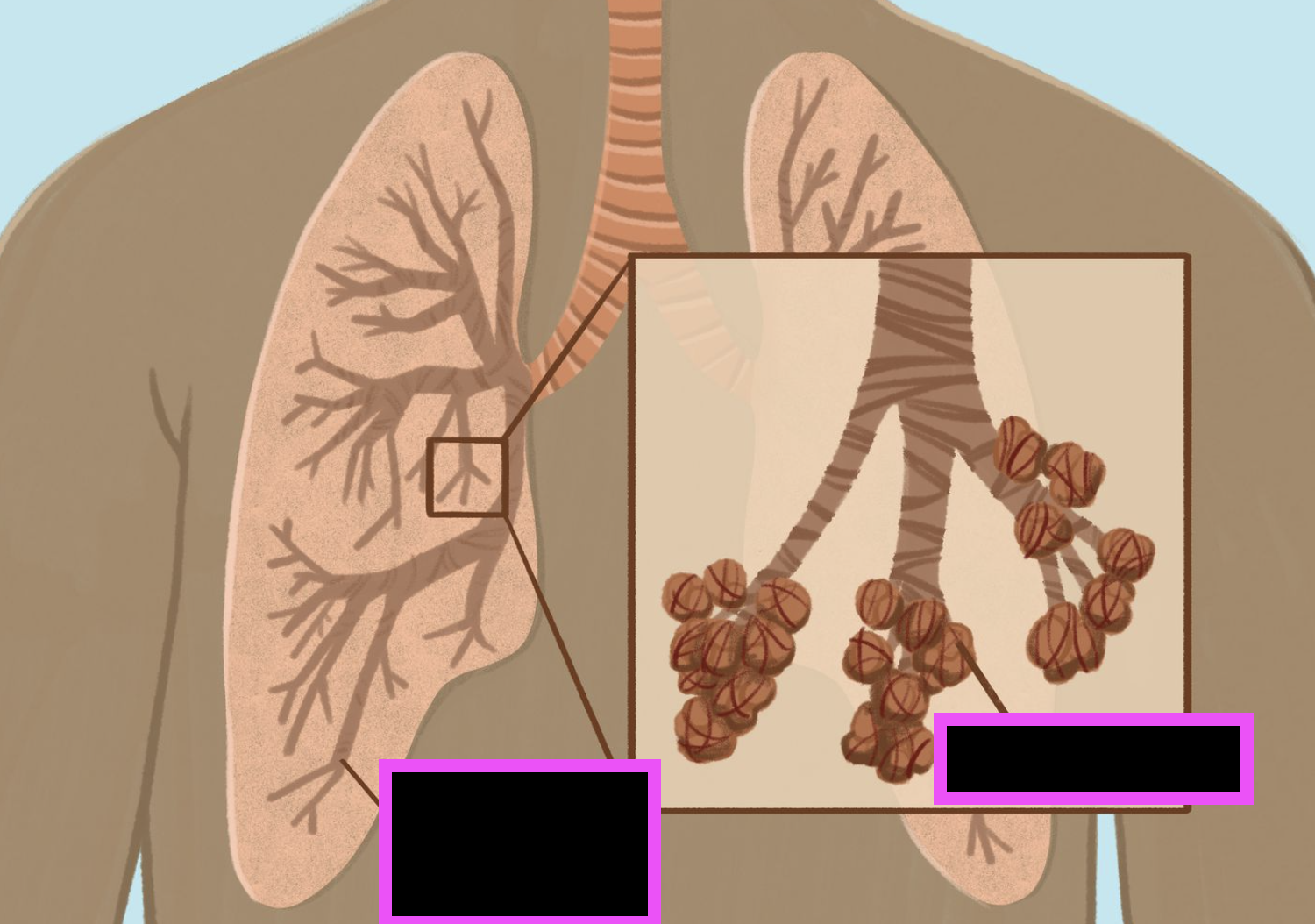
bronchioles
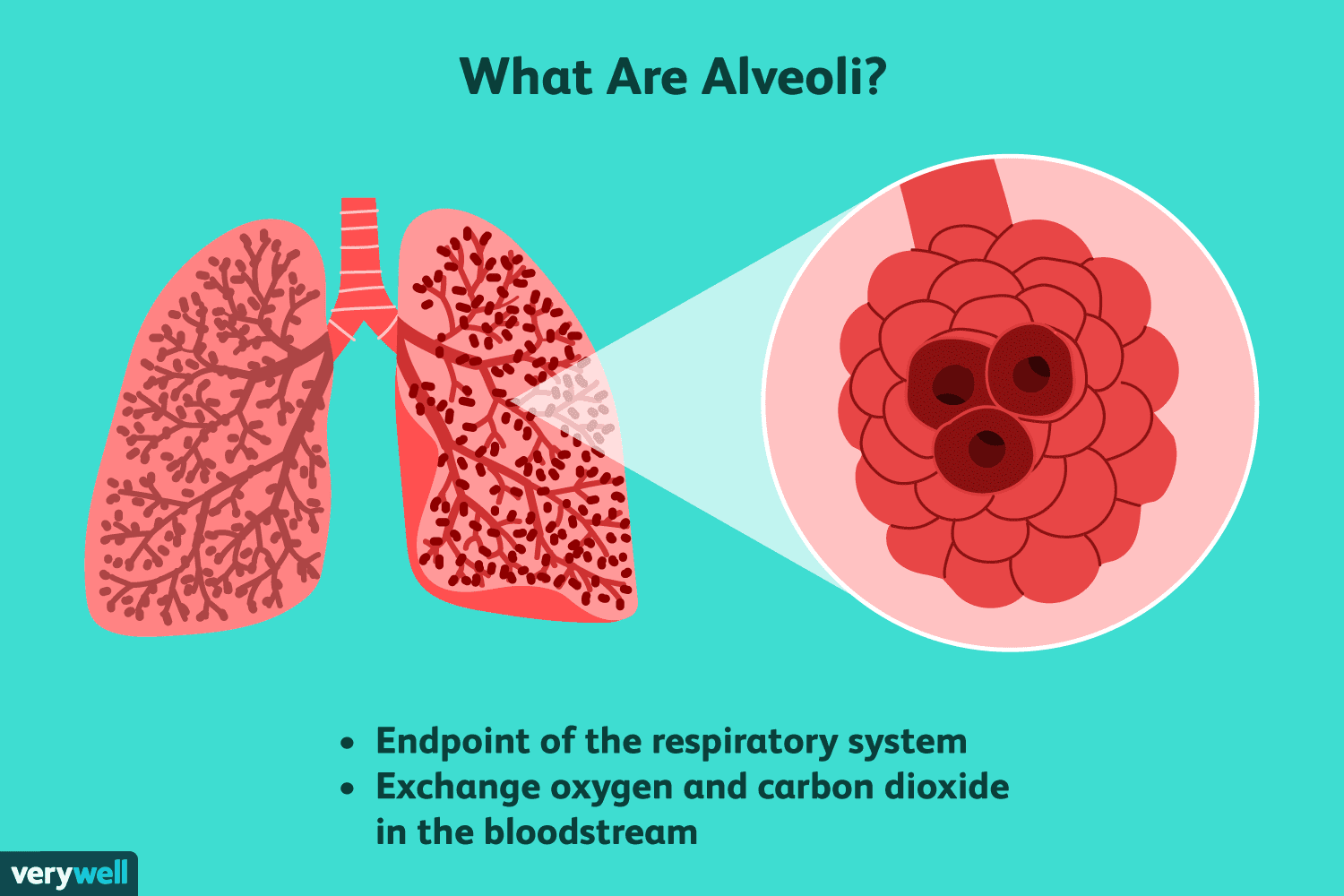
alveoli
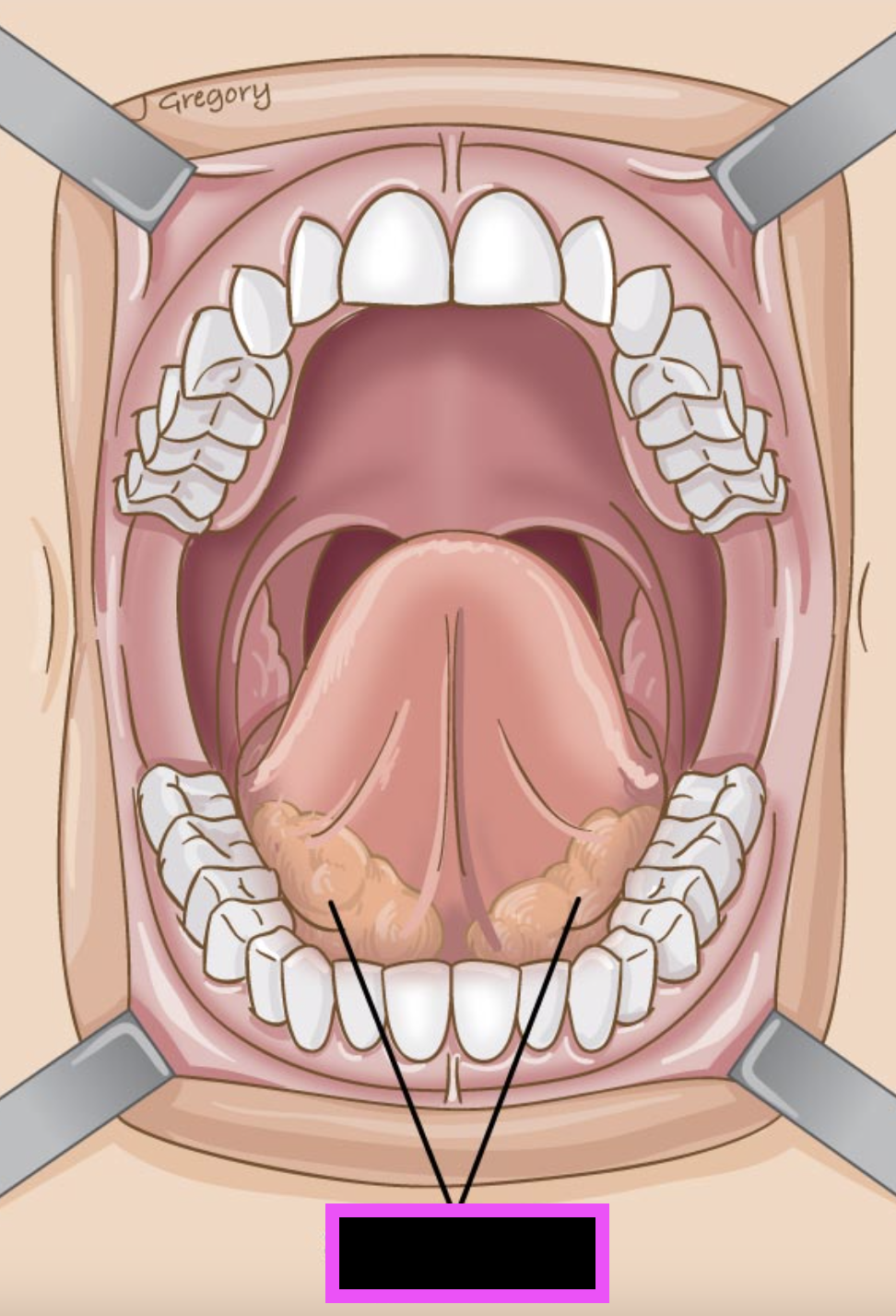
sublingual salivary glands (smallest)
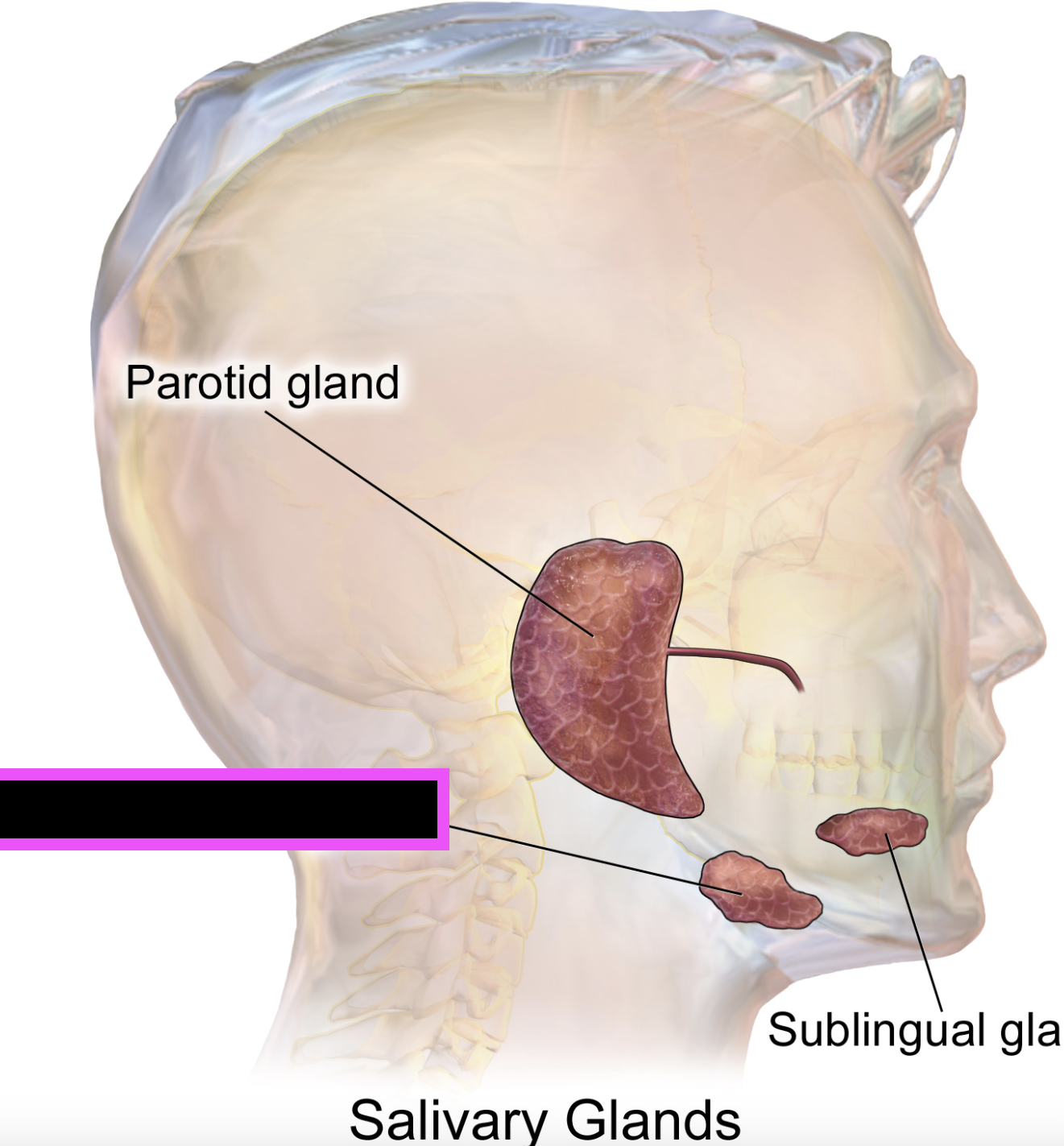
submandibular gland
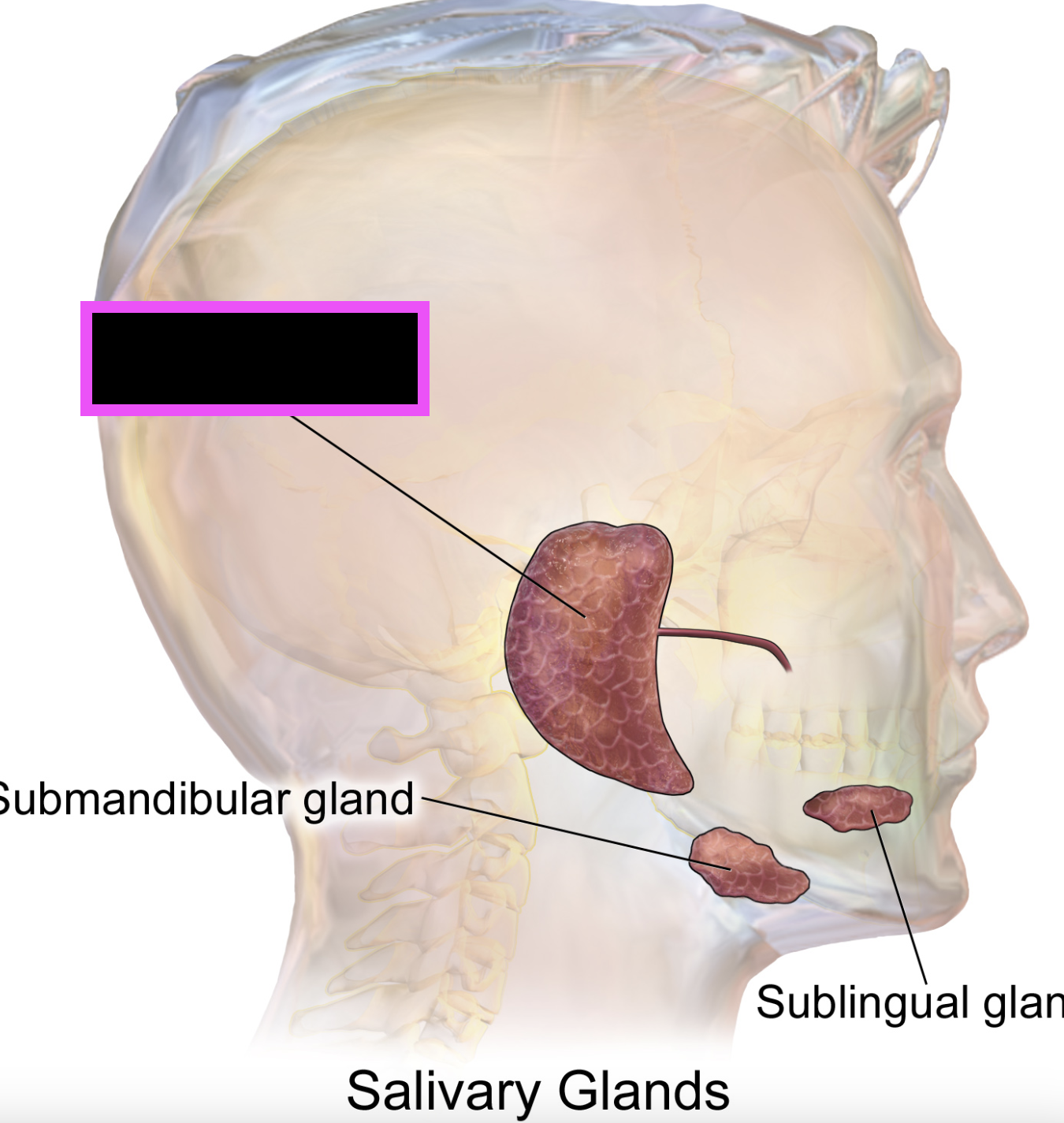
parotid gland
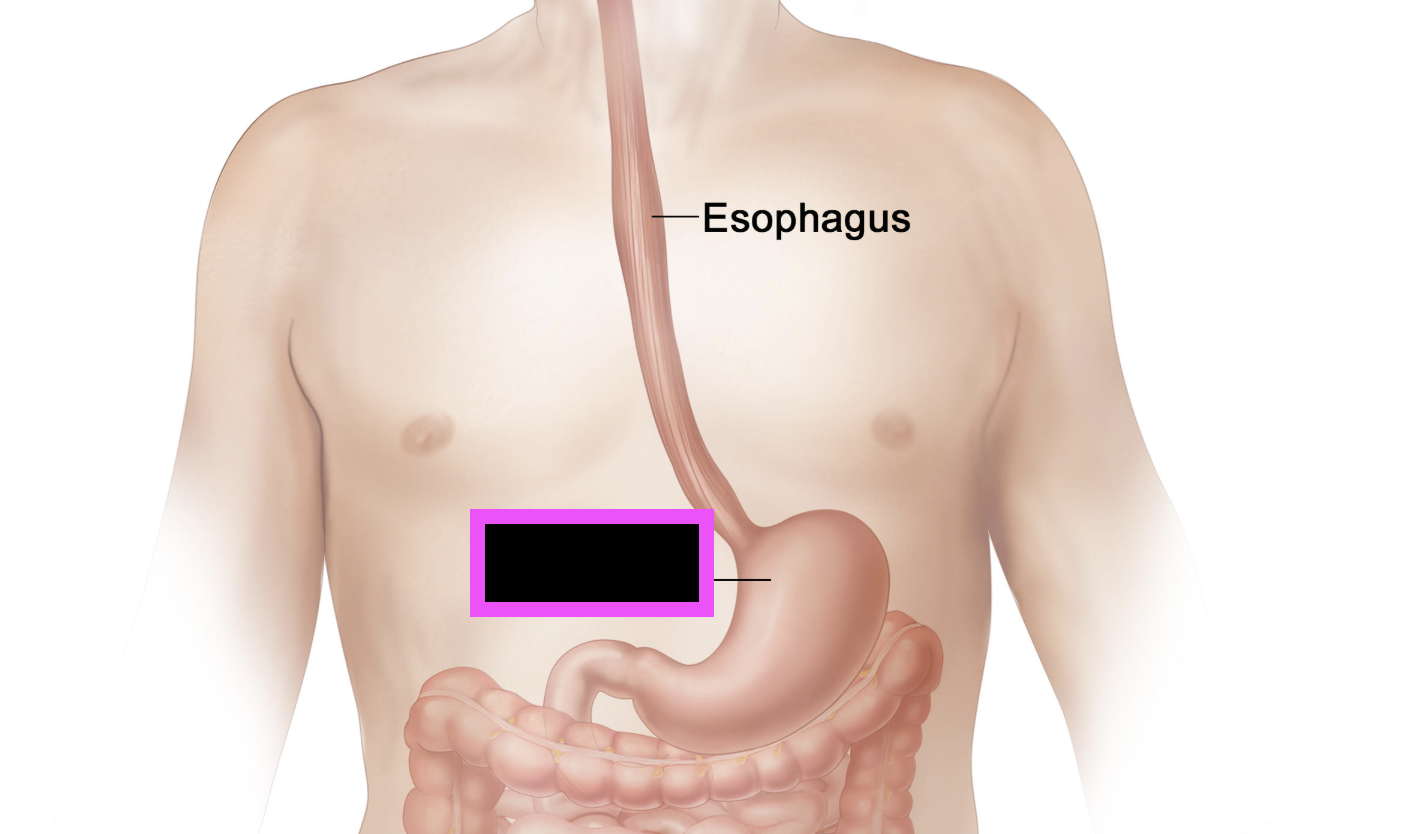
stomach
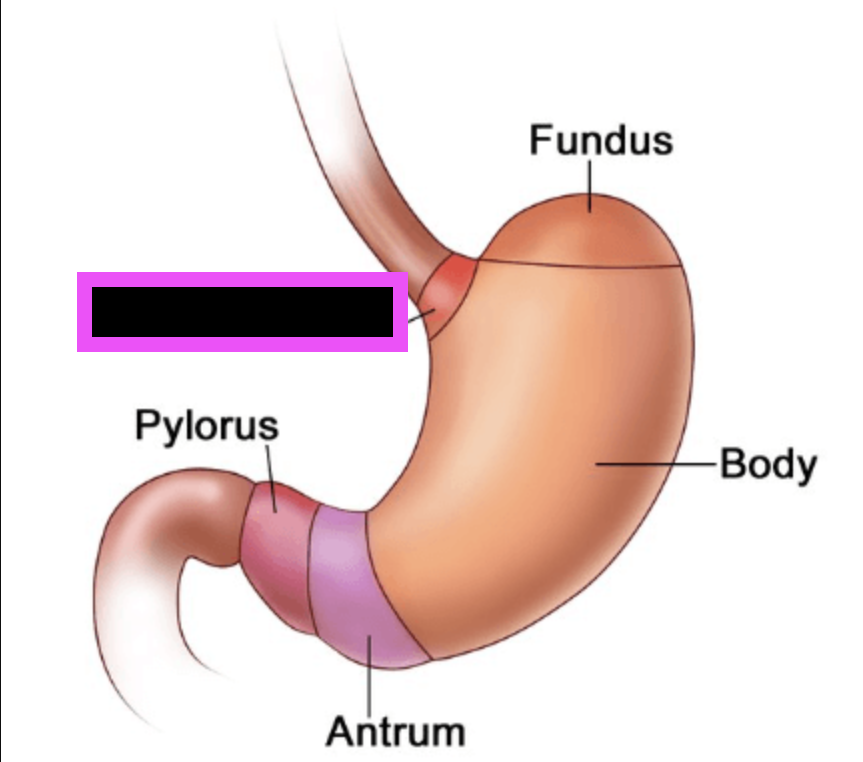
cardiac portion of stomach
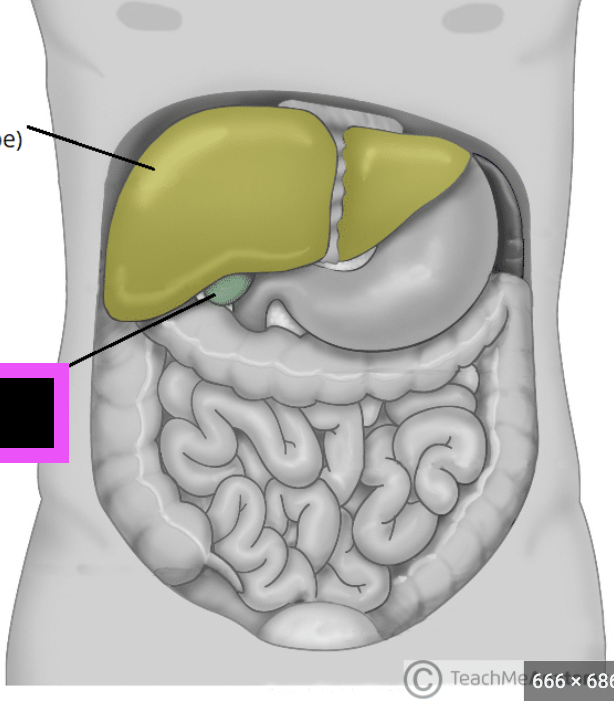
gallbladder
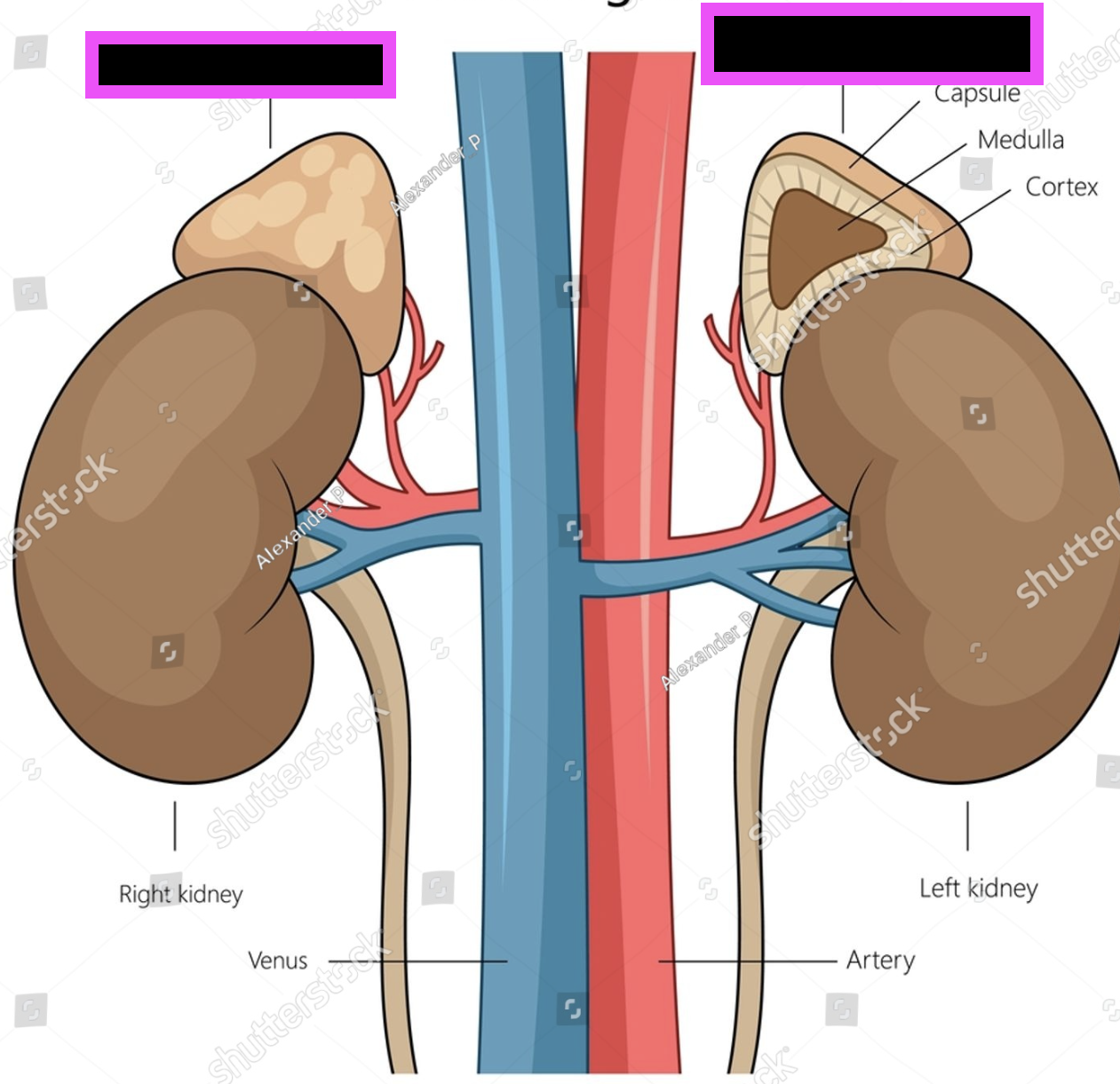
adrenal gland
kidney
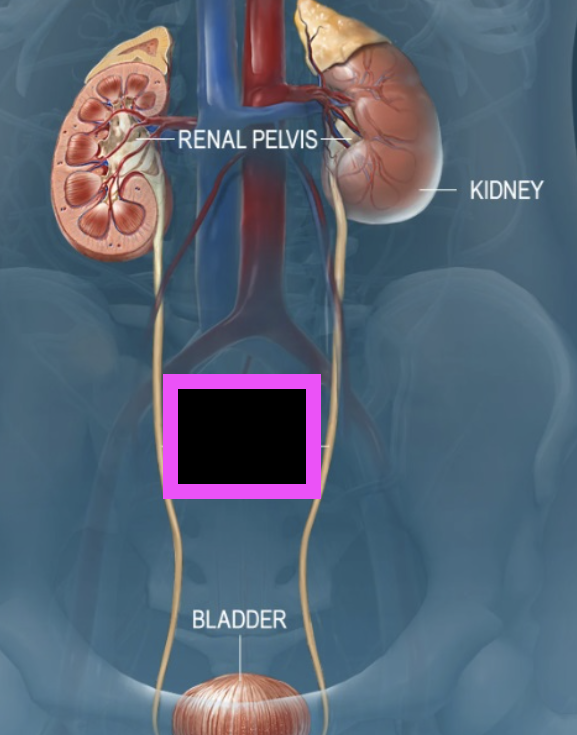
ureter
urinary bladder
urethra
where urine is carried to outside the body
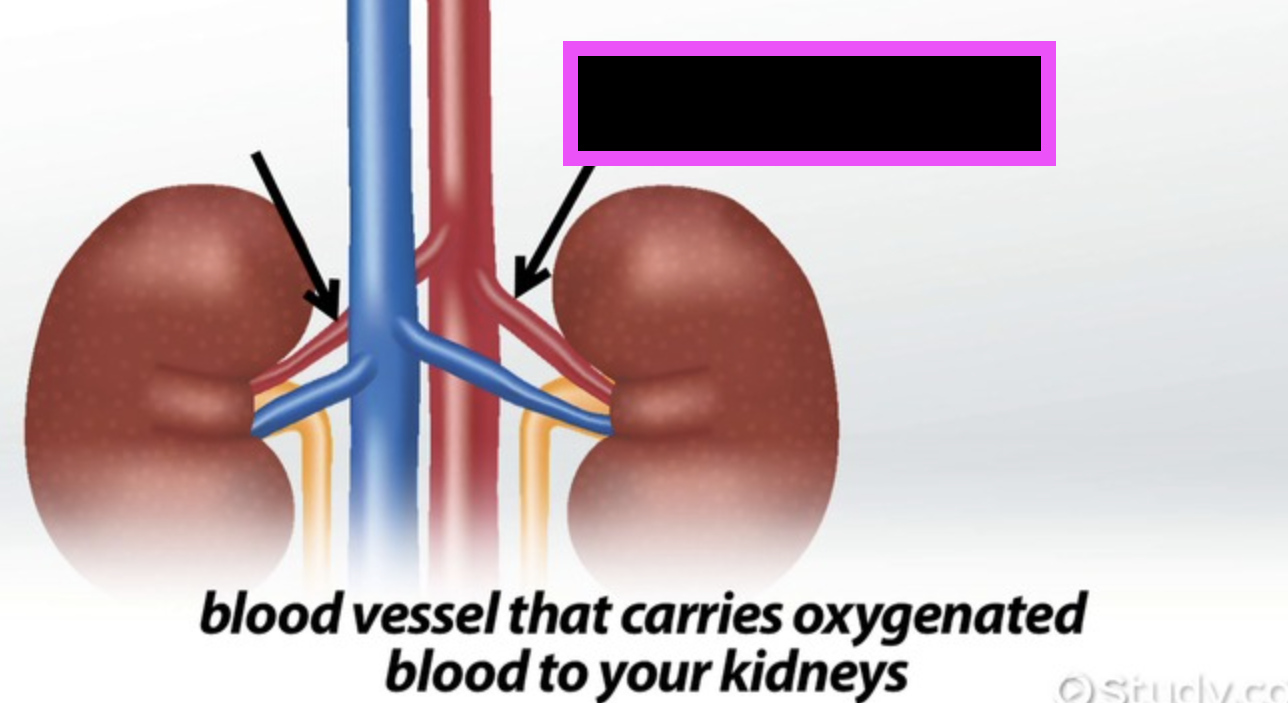
renal artery
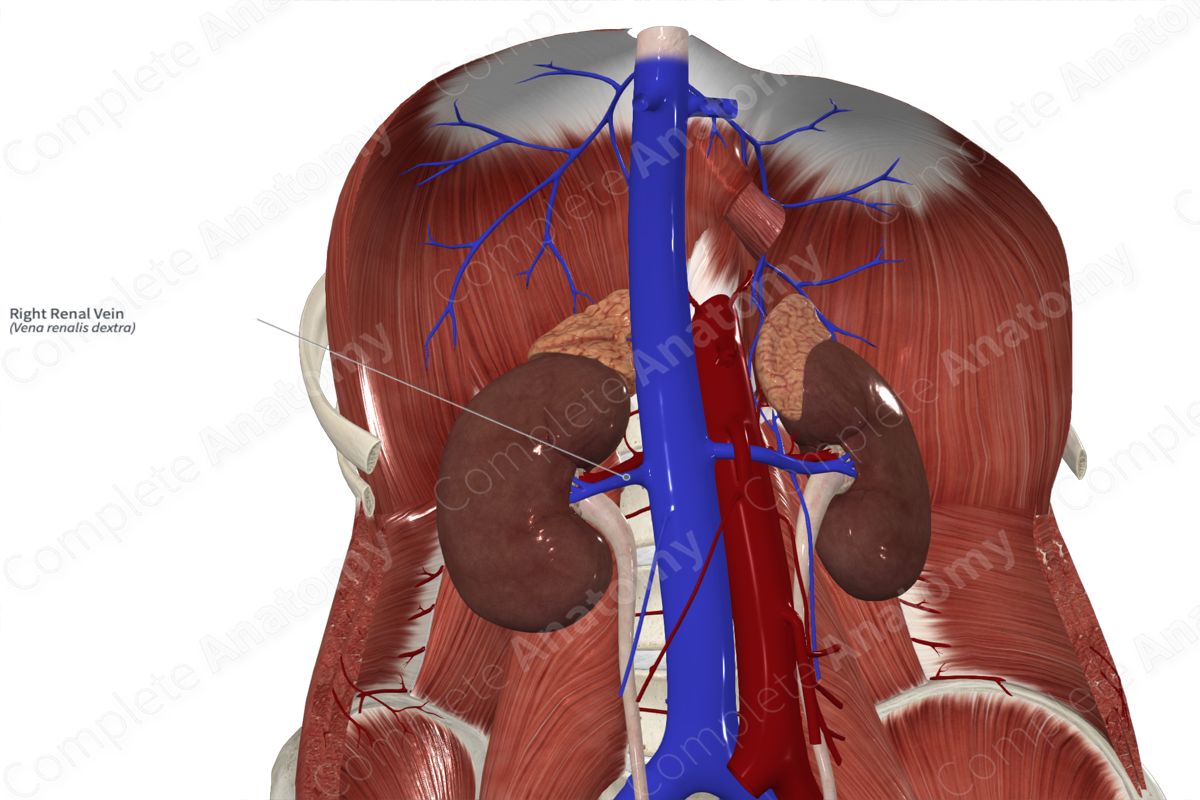
renal vein
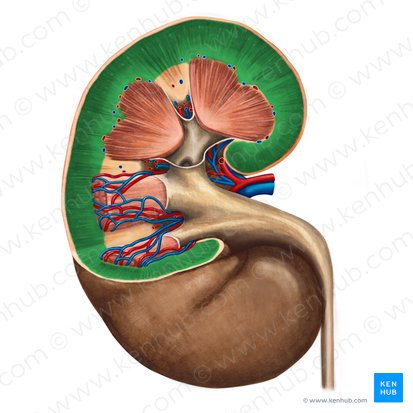
green
cortex of kidney
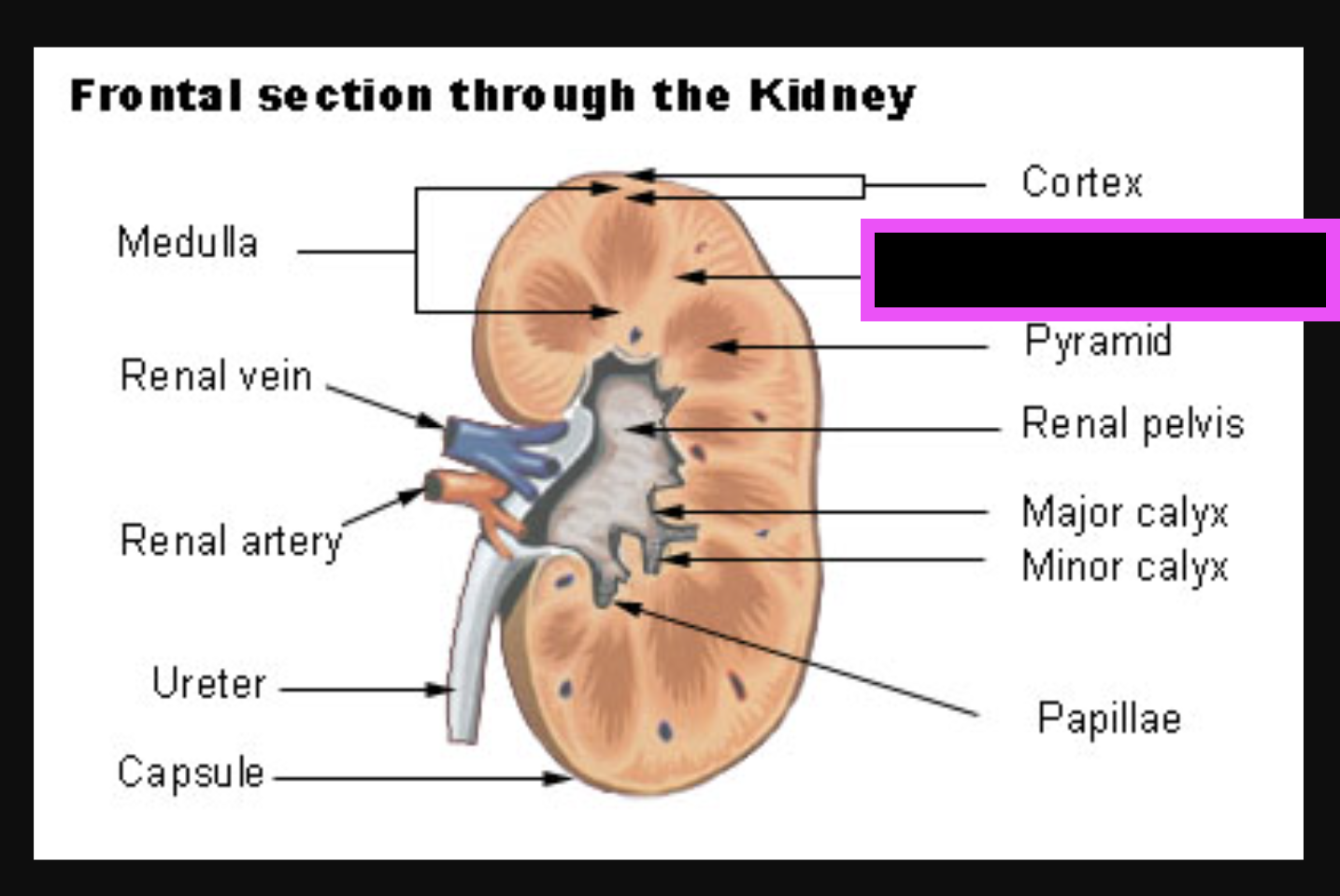
renal columns of kidney
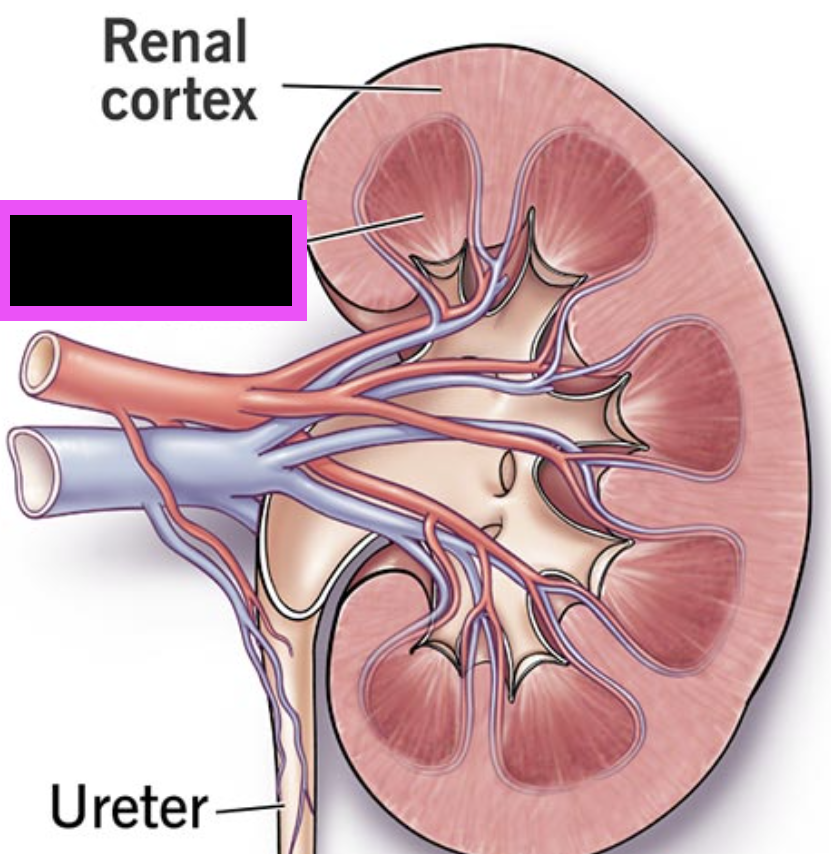
medulla in kidneys
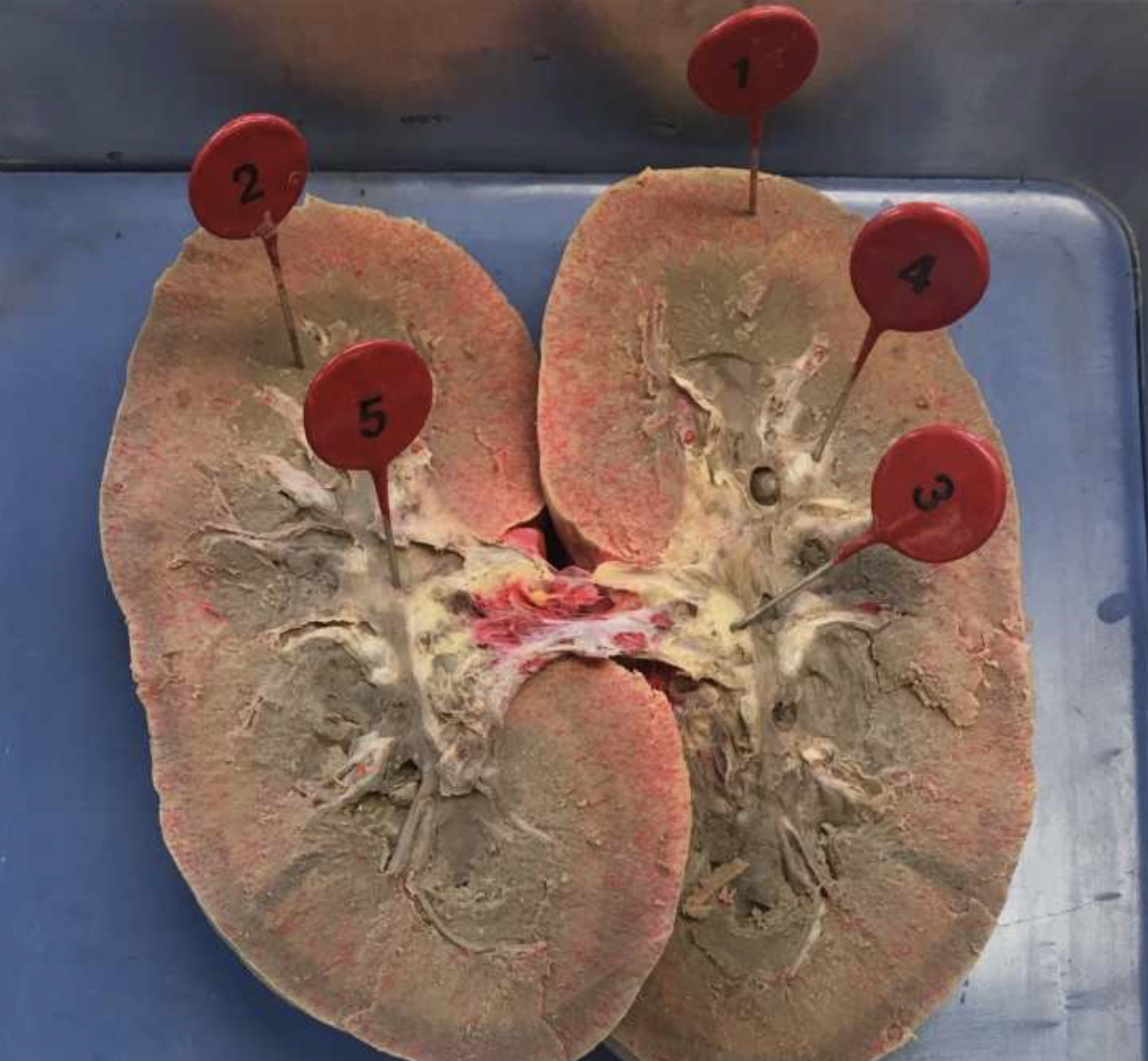
1
renal cortex
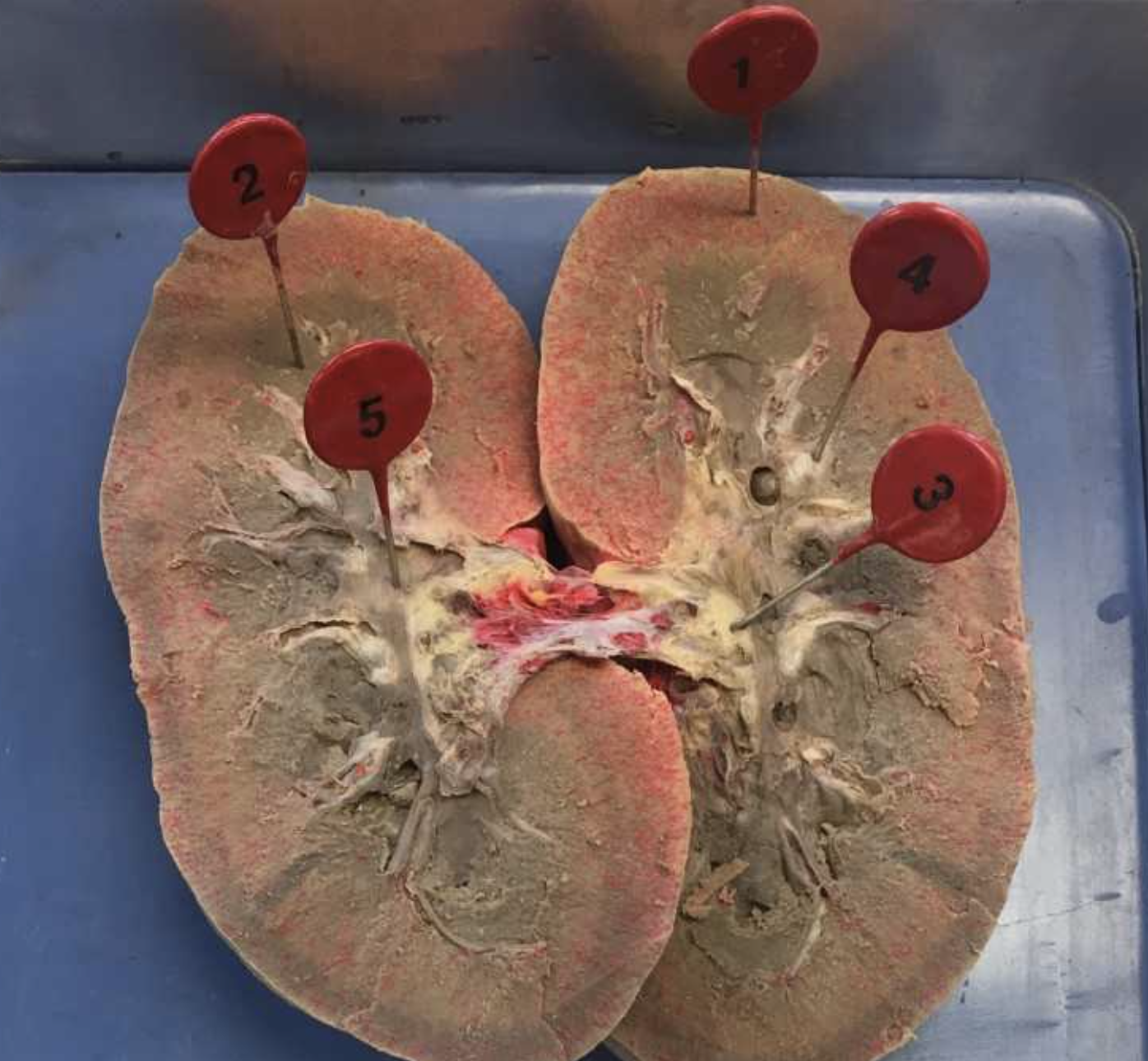
2
renal pyramids
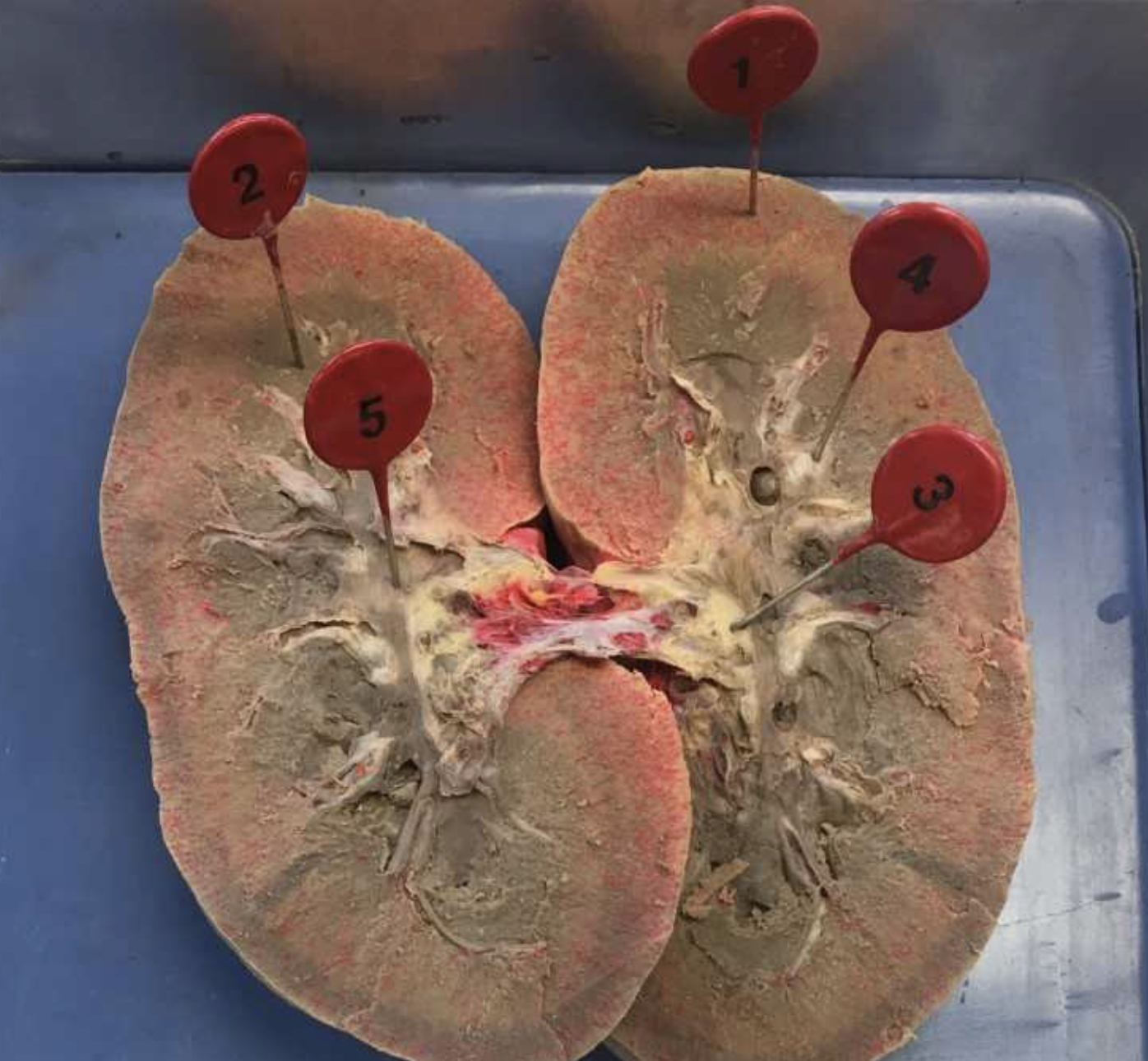
3
renal pelvis
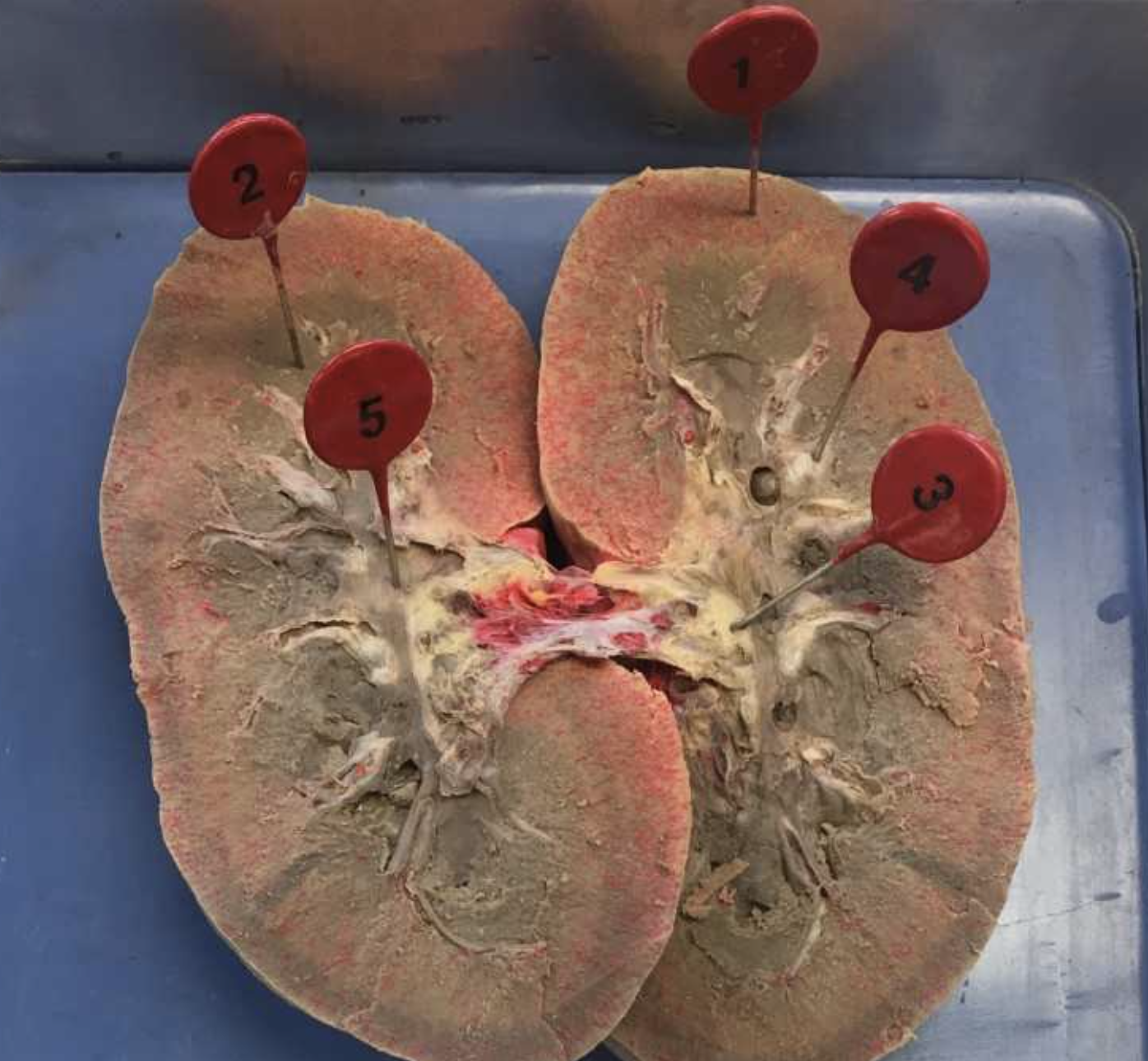
4
minor calyx
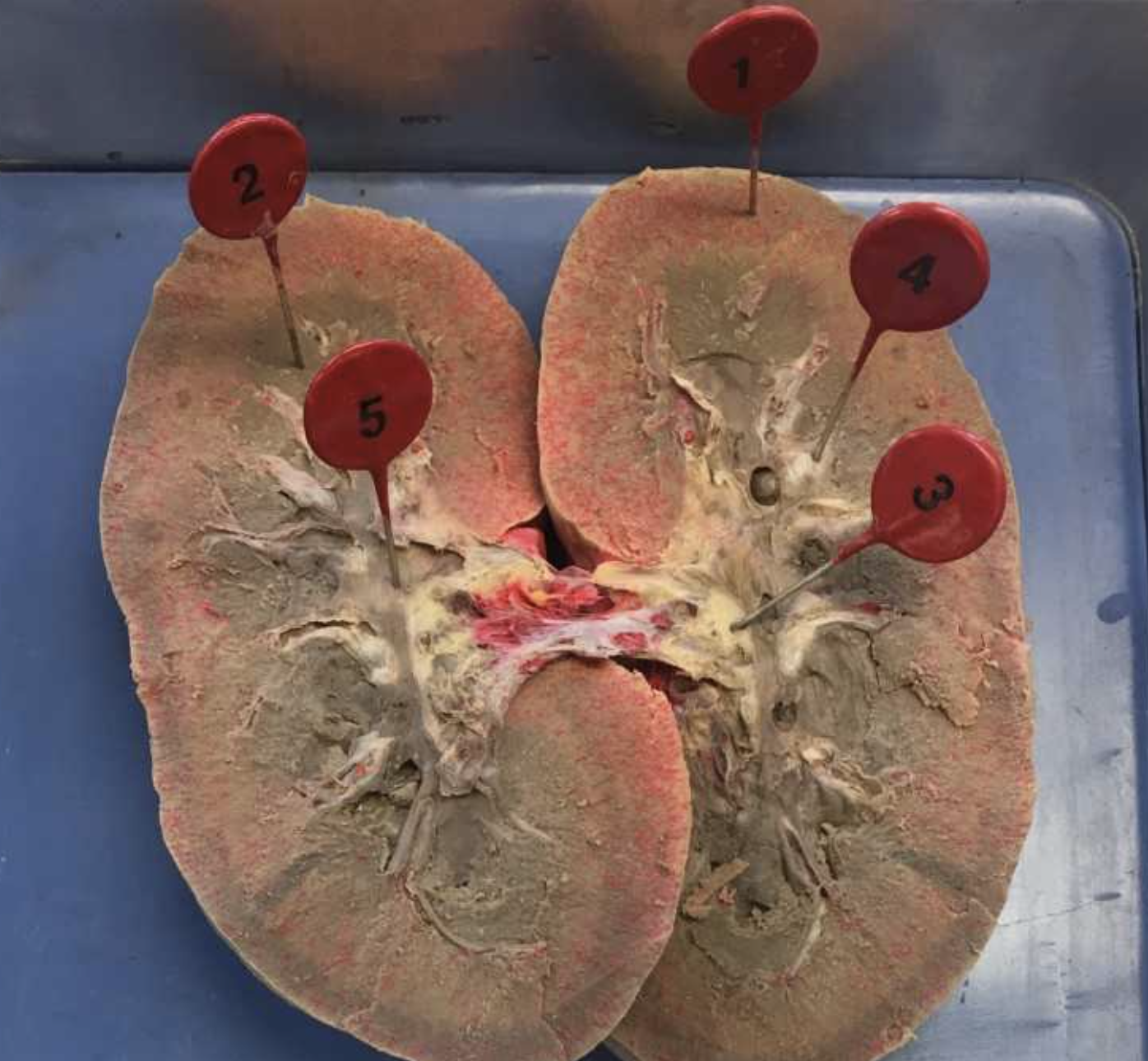
5
major calyx
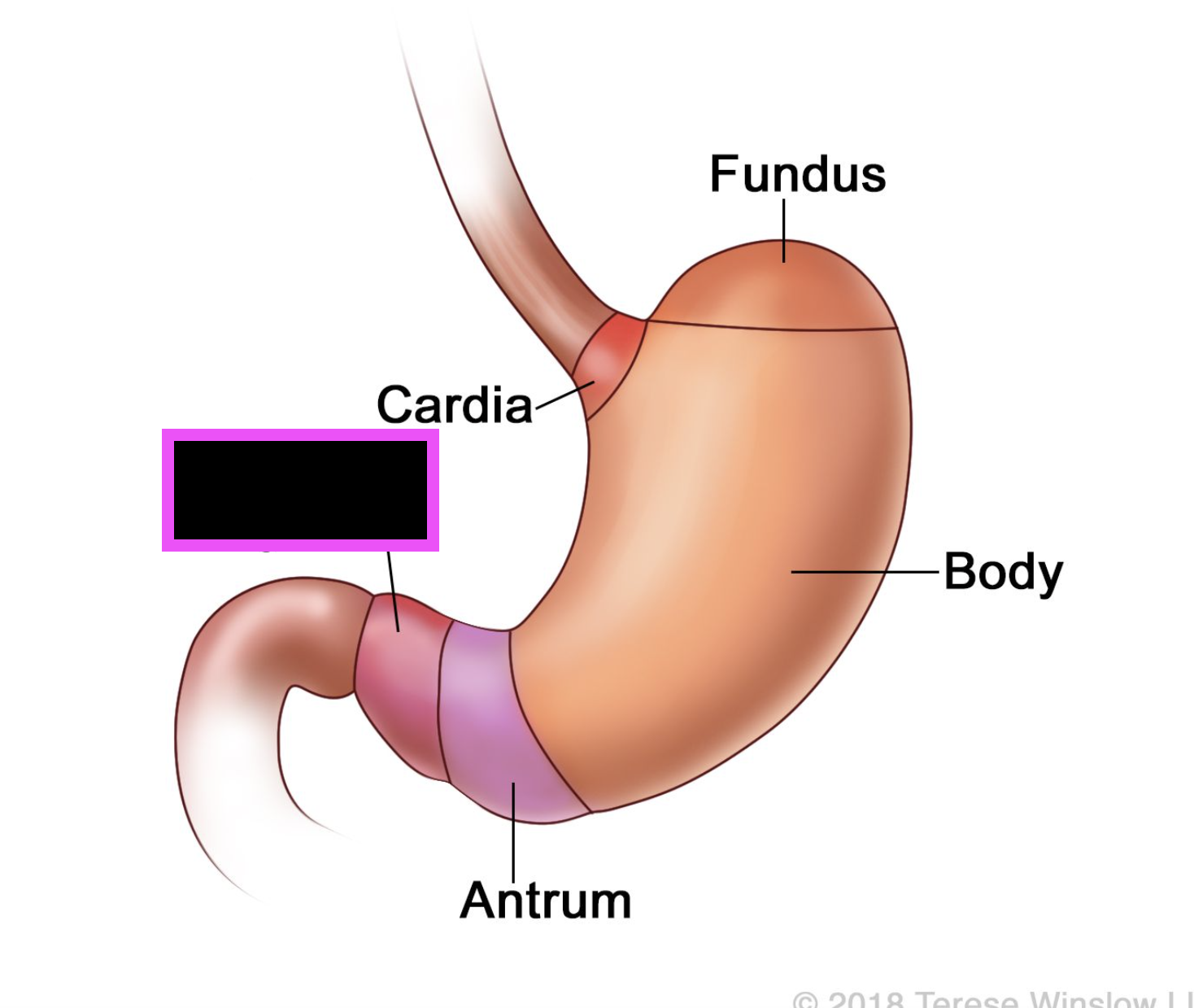
pylorus
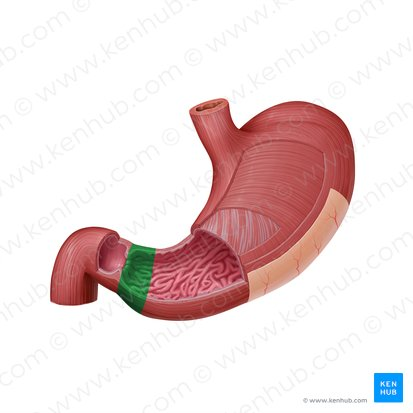
pyloric sphincter
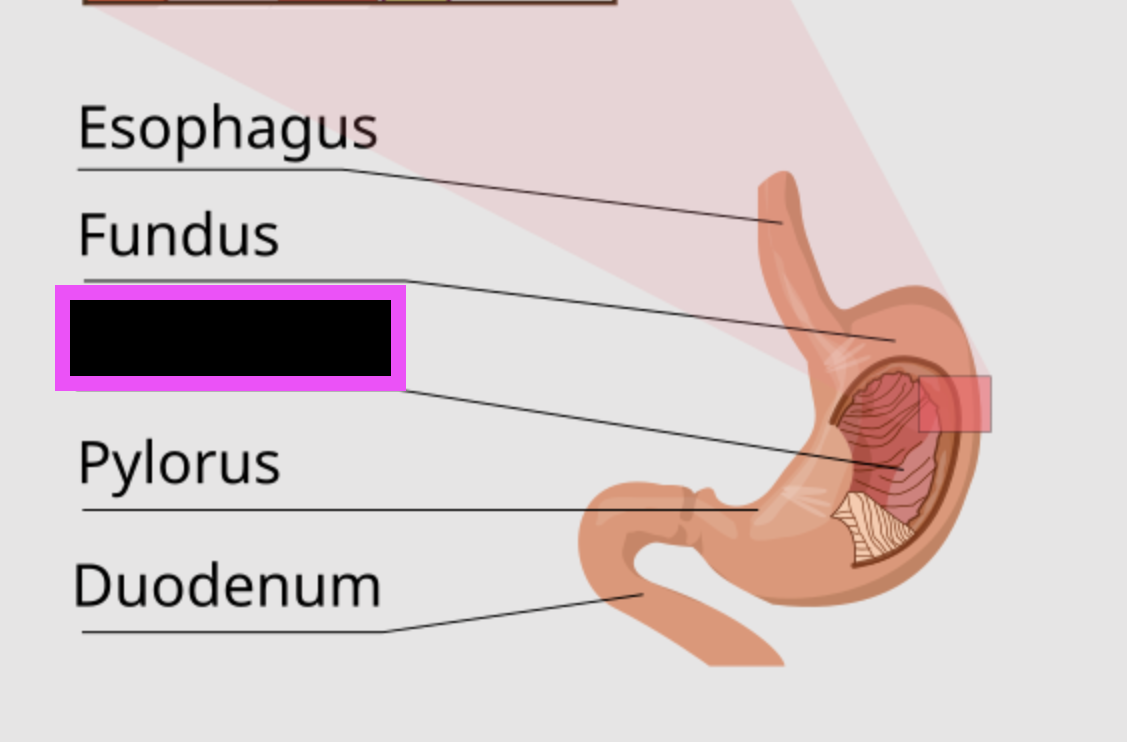
rugae
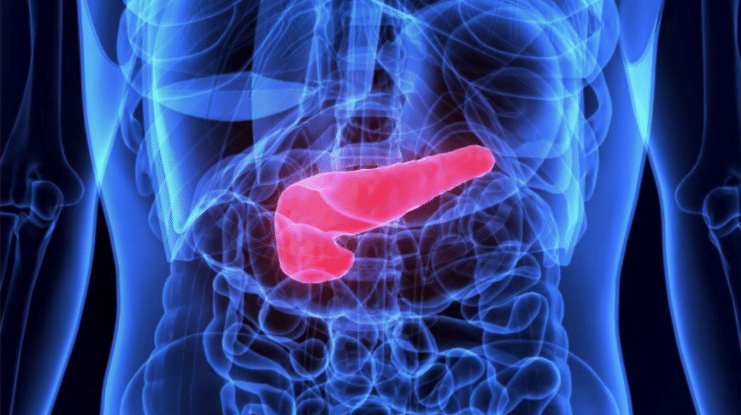
pancreas
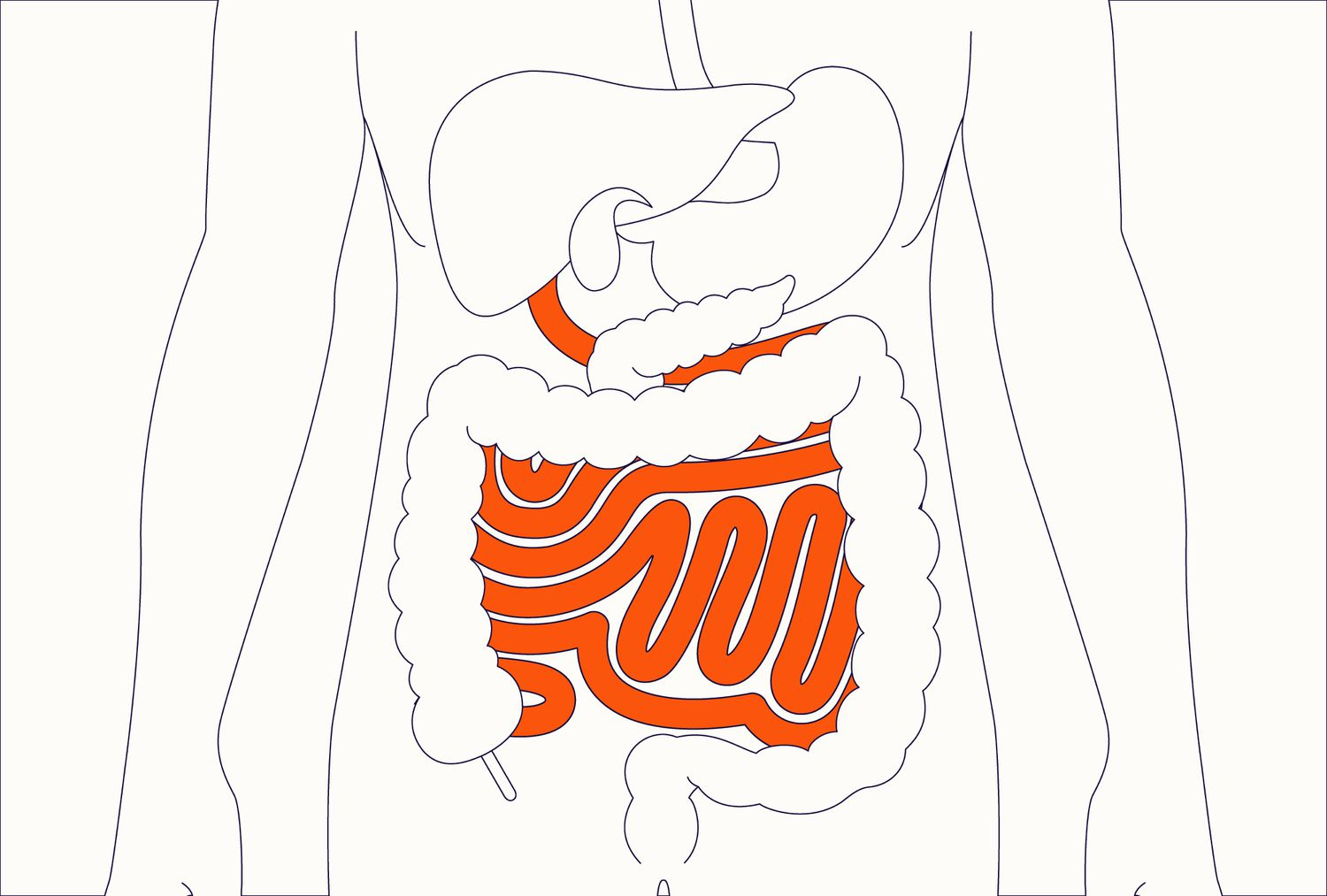
small intestine
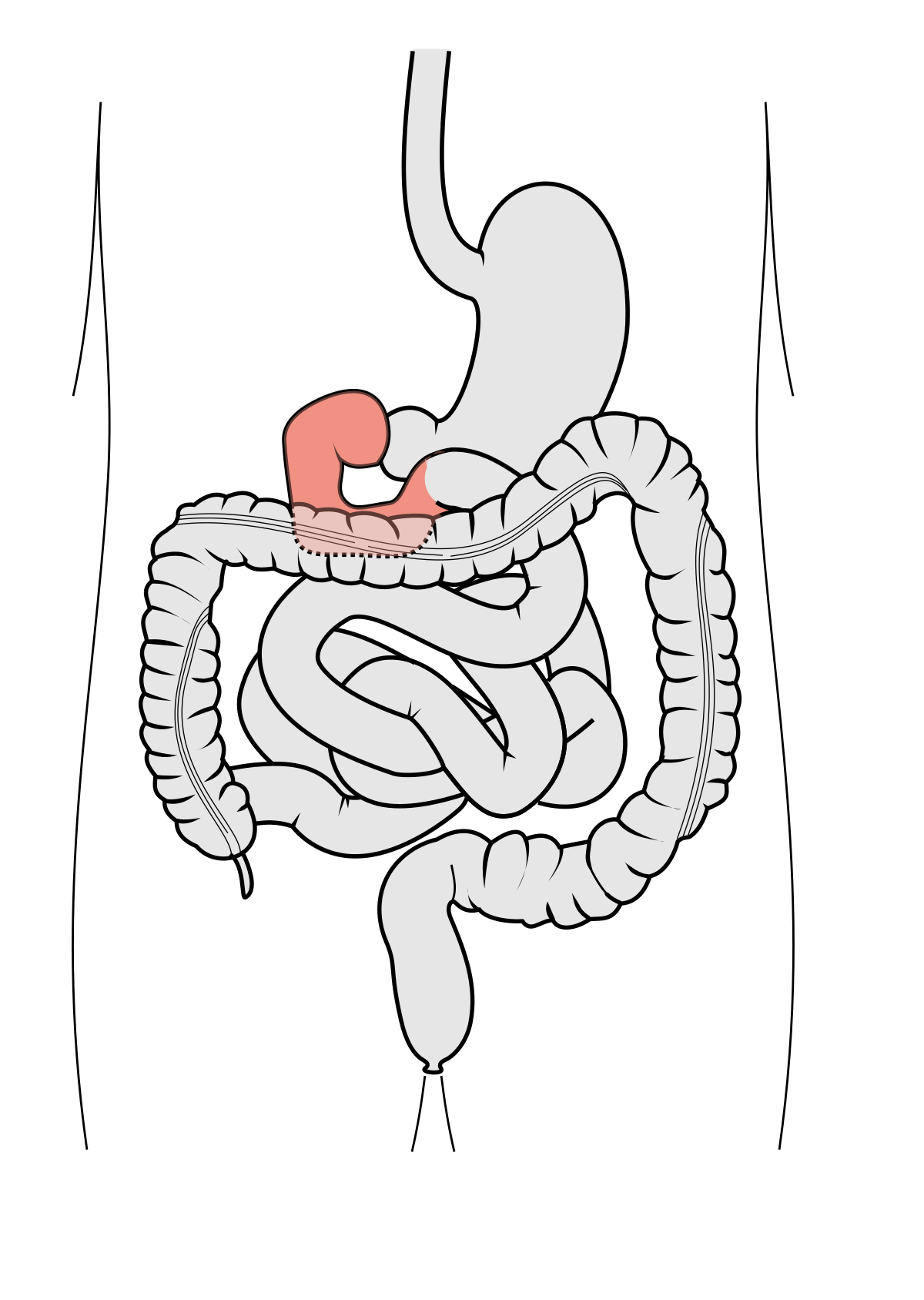
duodenum
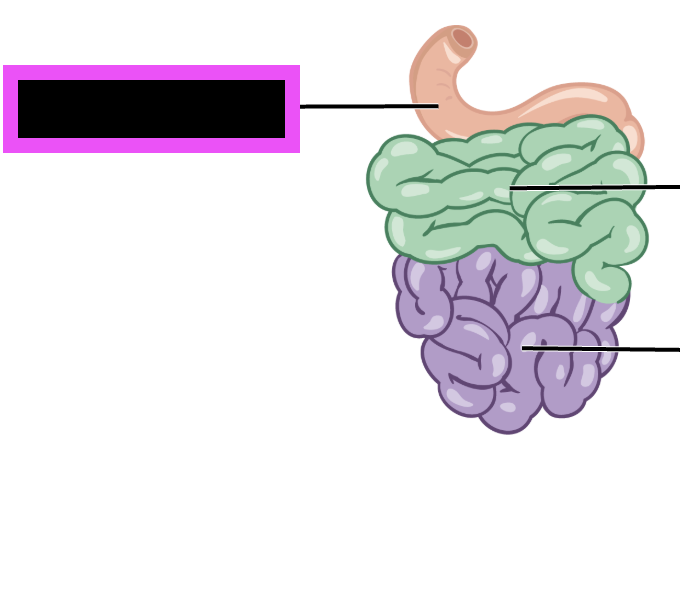
(part of small intestine)
duodenum
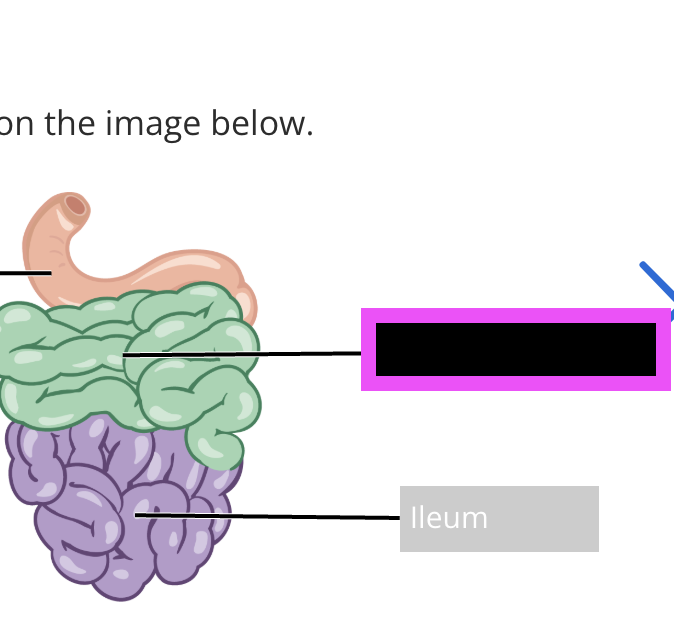
(part of small intestine)
jejunum
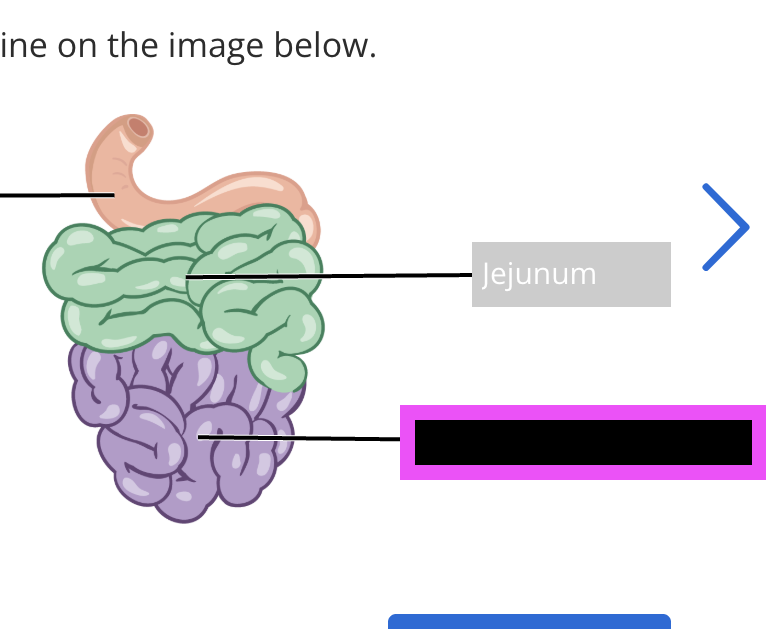
ileum
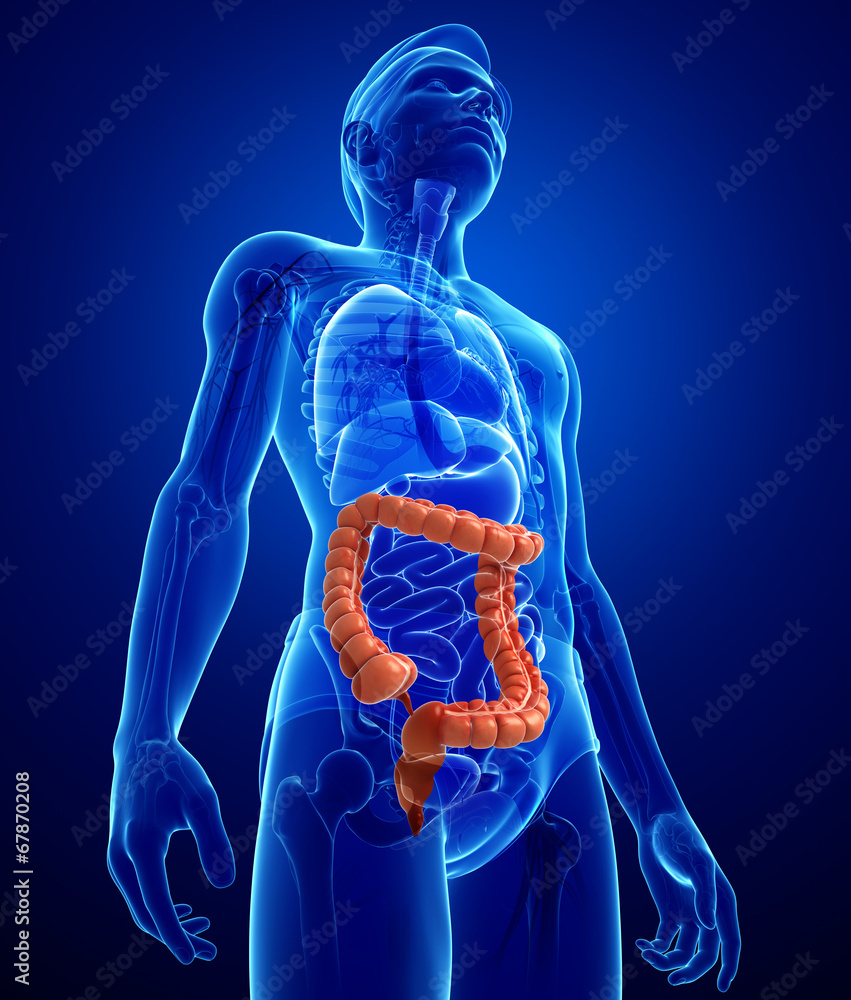
large intestine
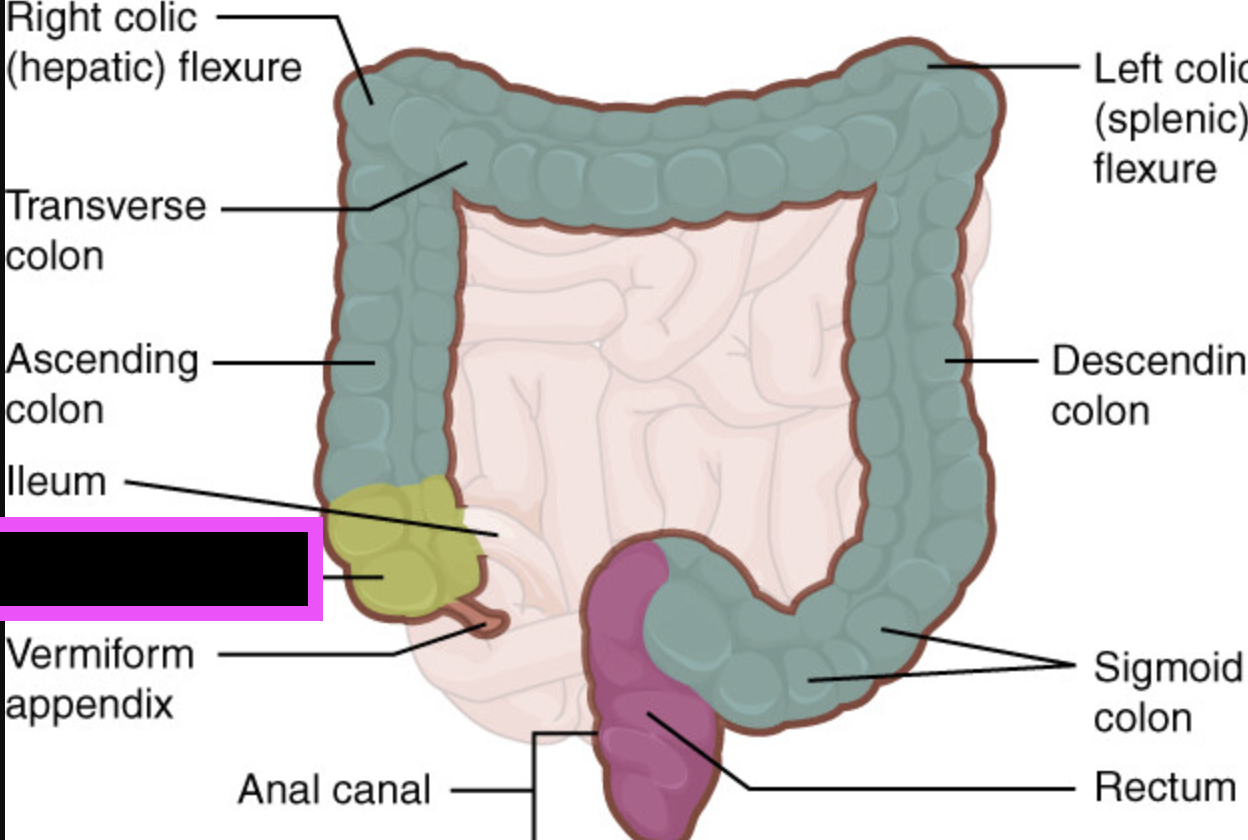
cecum
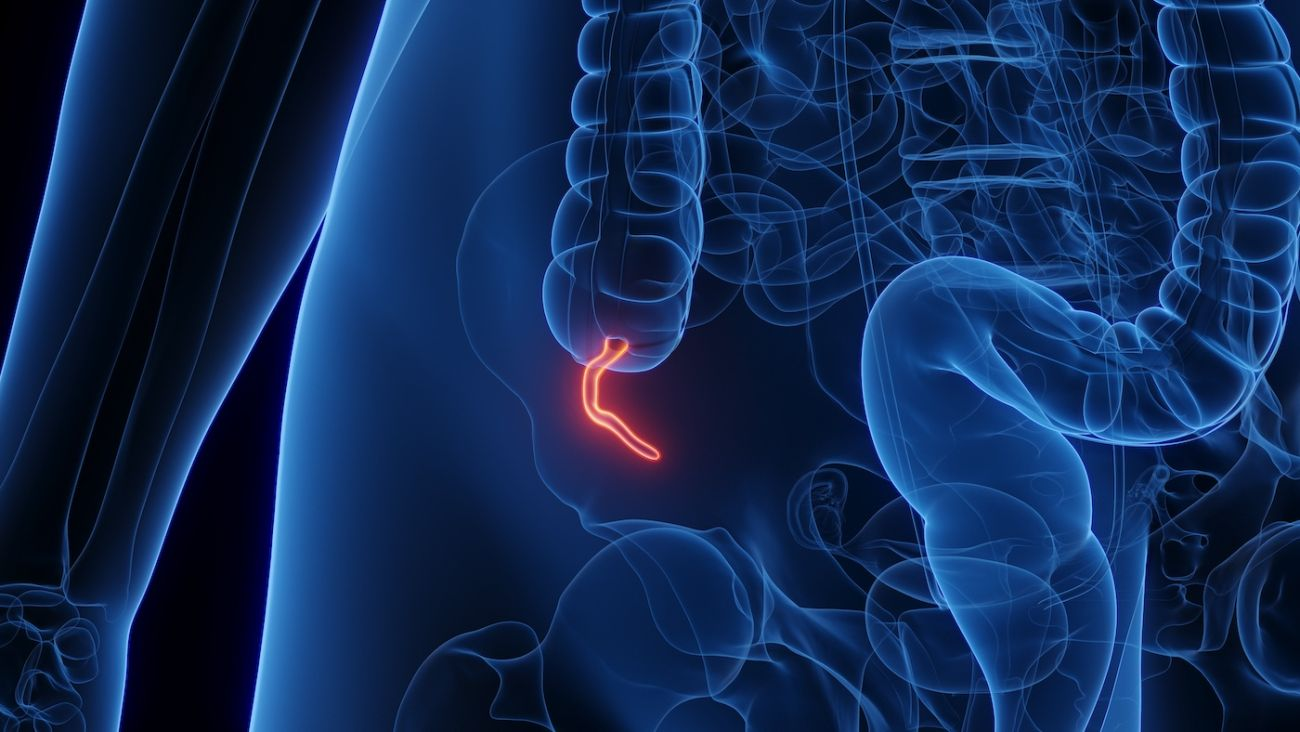
appendix
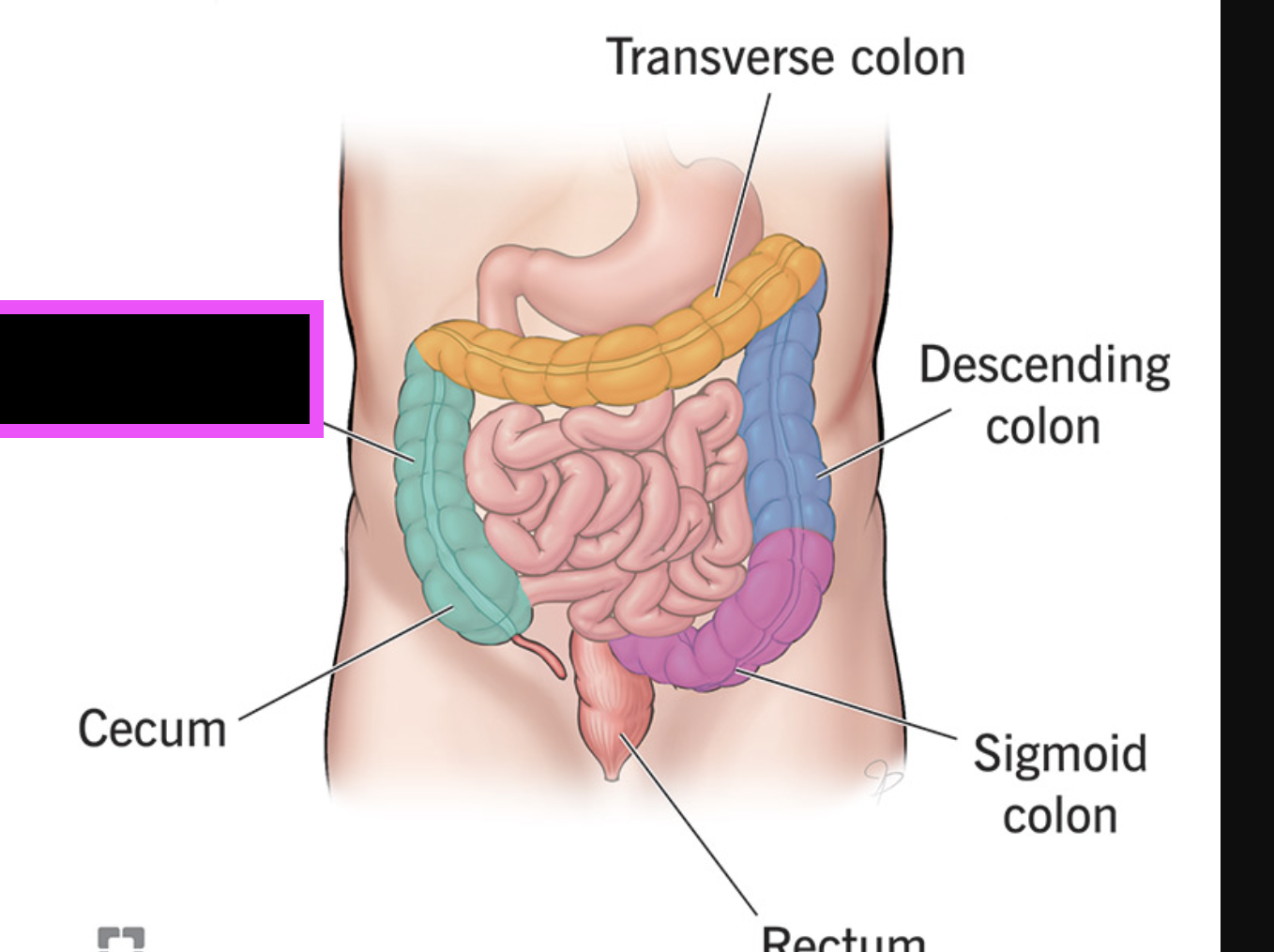
ascending colon