Interim fixed restorations
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From Maddie
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What does an interim/provisional restoration enhance?
Esthetics, stabilization and function
What is a interim/provisional restoration?
A dental prosthesis placed for a limited time which will be replaced with a definitive dental prosthesis
Provisional prostheses are used to assist in determination of what
Therapeutic effectiveness of a specific treatment plan or
Form and function of the planned definitive prosthesis
Requirements of a provisional restoration
Biologic factor
Mechanical factor
Esthetic factor
Biologic requirements of a provisional restoration
Protect pulp
Maintain periodontal health
Provide occlusal compatibility
Protect against fracture
biologic requirements of a provisional restoration: protect pulp
Must seal and insulate the prepared tooth surface from the oral environment to prevent sensitivity and further irritation of the pulp.
Can lead to irreversible pulpitis
Leakage of the provisional restorations can cause _________
irreversible pulpitis --> need for a root canal
Biologic requirements of a provisional restoration: maintain periodontal health
Must have good marginal fit, proper contours, and smooth surfaces to facilitate plaque removal
Inadequate contacts of provisional restorations may cause _________ and ________
Supra-eruption
Horizontal movement
mechanical factors of provisional prosthesis
Resist functional loads
Resist displacement
Resist removal forces
The greatest stresses in an interim fixed restoration occur during ______
mastication
How to reduce the risk of fracture with a provisional (interim) restoration
- connector size (overcontouring of interproximal contacts) of provisional restorations is often increased in comparison with the definitive restoration, but not at the expense of cleans ability
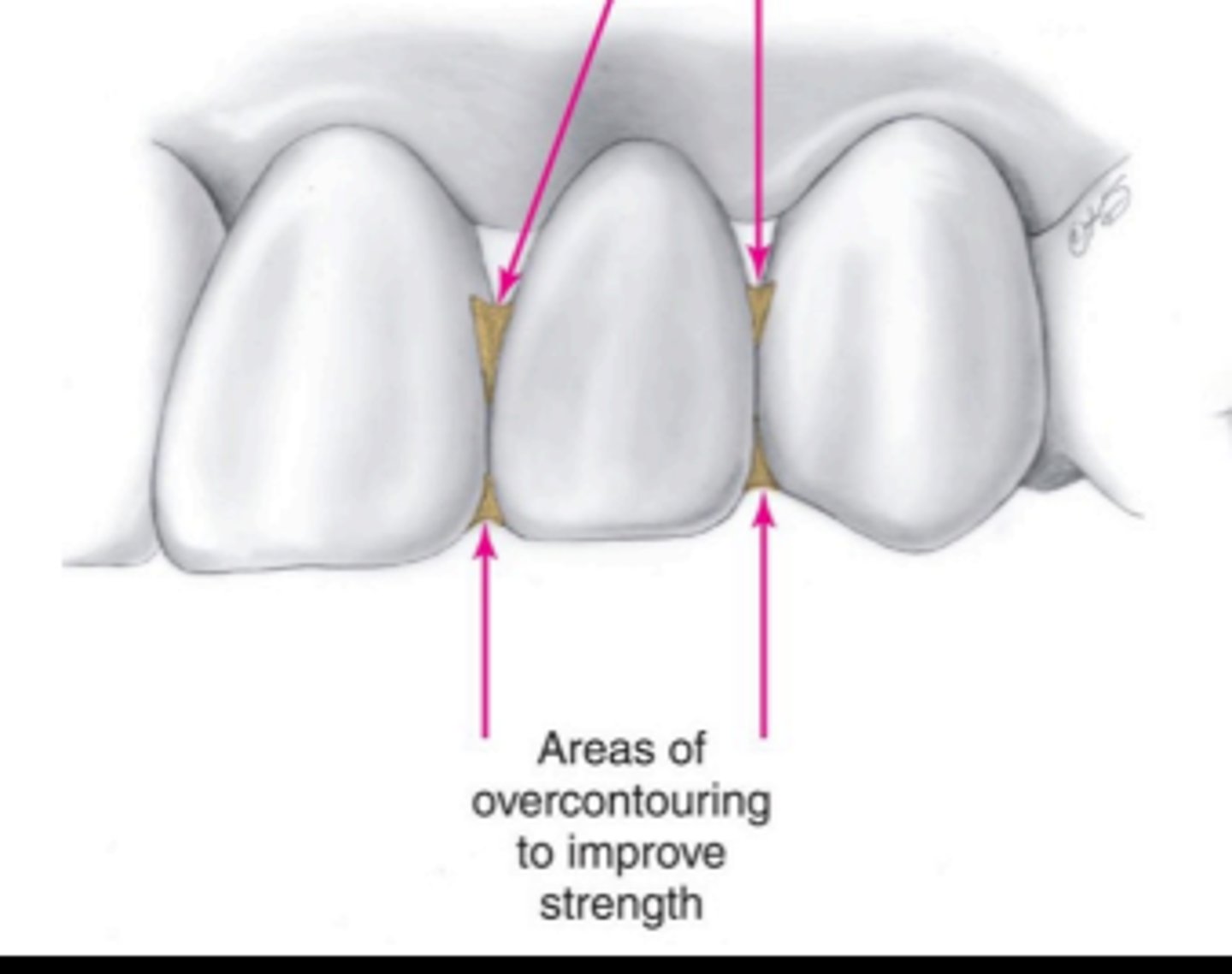
when overcontouring, to avoid jeopardizing periodontal health, the _______ should be opened to provide good access for plaque control.
gingiva embrasures
what type of restorations can be used to reinforce the interim restorations of a bridge
Fiber-reinforced, laboratory-processed resin, heat-processed polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA),
CAD/CAM milled or three-dimensional (3D)-printed PMMA,
Reinforcing metal mesh
Cast metal reinforced interim restorations
Indications for reinforced interim restorations
A long-span posterior fixed partial denture
Prolonged treatment time
Patient's inability to avoid excessive forces on the prosthesis
Above-average masticatory muscle strength
History of frequent breakage
How is Displacement of an interim best prevented
- through proper tooth preparation
- closely adapted internal surface of provisional restorations
Provisional restorations are used as a guide to achieve optimum _____ in the definitive restorations
esthetics
Ideal properties of Interim Materials
Convenient handling
Biocompatibility
Ease of contouring and polishing
Adequate strength and abrasion resistance
Good appearance
Good acceptability to patient (nonirritating, odorless)
Ease of adding or repairing
Chemical compatibility with interim luting agents
what characteristic are included in convenient handling of an interim
- adequate working time
- easy modeling
- rapid setting time
Biocompatibility of an interim restoration
Nontoxic
Nonallergenic
Nonexothermic
Appearance of interim material
Translucent
Color controllable
Color stable
Material options of a provisional restoration
Poly-methyl methacrylate resin
Poly-ethyl methacrylate resin
Bis-acryl (bis-GMA) resin
Light-polymerized resin
Brand names of Poly-methyl methacrylate resin (PMMA)
• Alike (GC)
• Jet (Lang)
• Temporay Bridge (Dentsply
Because monomers may be unpleasant or even harmful biologically what reaction is desirable for provisional material
-what material does this describe?
- the chemical conversion of monomer to a biologically inert polymer
- Poly-methyl methacrylate resin(PMMA)
-Poly-ethyl methacrylate resin
what changes are seen in the polymerization process of a the chemical conversion of a monomer to a biologically inert polymer
-chemical
-mechanical
-dimensional
-thermal changes
which Poly-methyl methacrylate resin generates the most heat
methyl methacrylate (Jet)
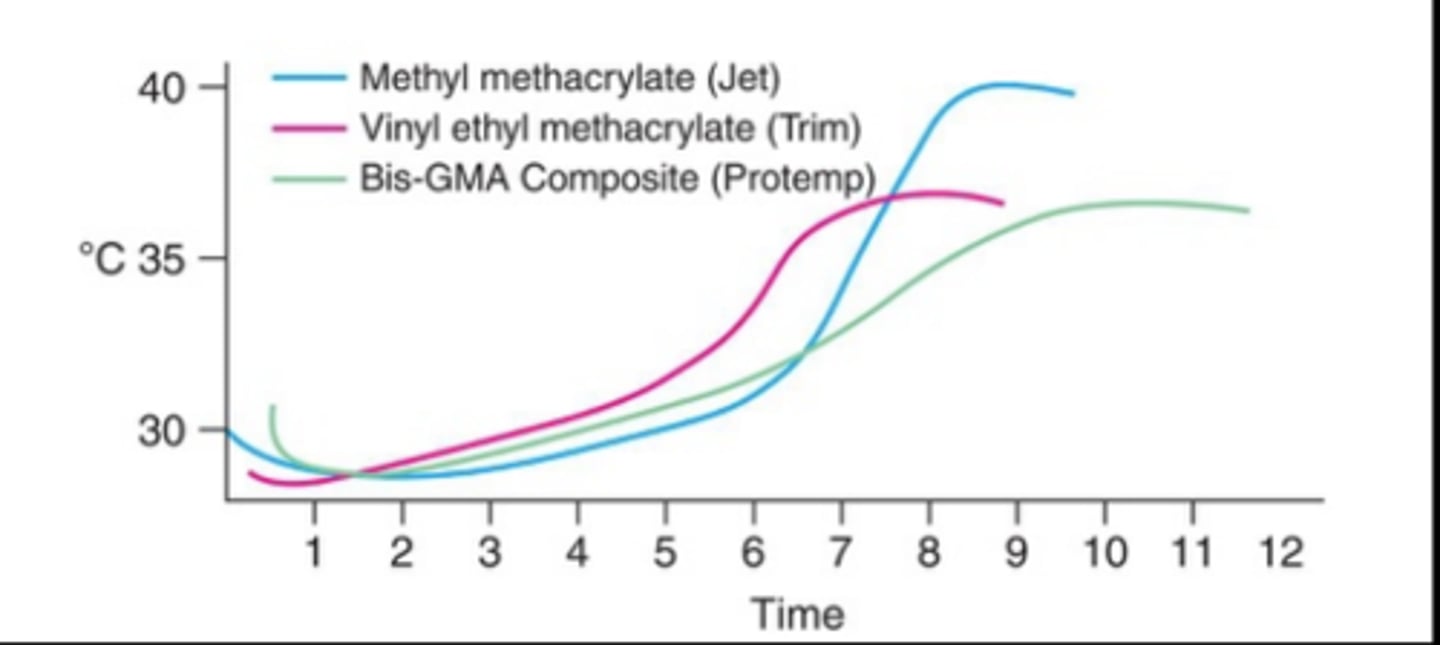
which temp material generates the least heat
protemp - Bis-GMA composite
how much shrinkage is seen with Poly-methyl methacrylate resin
15% --> open margins
Disadvantages of Poly-methyl methacrylate resin
Exothermic heat
Shrinkage
Discoloration
Odor
Advantages of Poly-methyl methacrylate resin
Flexibility
Easy of adding & repairing
Good marginal adaptation
Easy of contouring & polishing
Adequate strength
Adequate esthetics
Indications of using Poly-methyl methacrylate resin
Long-span prostheses
Multi-abutment prostheses
Long-term Provisionals
brand names of Poly-ethyl methacrylate resin (PEMA)
Snap (Parkell)
Trim (Bosworth)
Advantages of Poly-ethyl methacrylate resin
Less shrinkage
Mild heat generate
Disadvantages of Poly-ethyl methacrylate resin (PEMA)
Less strength
Color stability
Difficult to add on
When using autopolymerizing PMMA or Poly-ethyl methacrylate, contact of free monomer with the tooth preparation or gingiva can cause what?
damage or allergic reactions
Brand names of Bis-acryl (bis-GMA) resin
Protemp (3M)
Luxatemp (DMG)
Integrity (Dentsply)
Advantages of Bis-acryl (bis-GMA) resin
Convenient handling
Low exothermic heat
Dimensional stability
Color stability
Strength
Good finishing quality
Disadvantages of Bis-acryl (bis-GMA) resin
Brittle
Less flexibility
Difficult to add & repair
Cost
Brand names of Light-polymerized resin
• Unifast LC (GC)
• Sinfony (3M)
Advantages of Light-polymerized resin
Flexible working time
No exothermic heat
Dimensional stability
Color stability
Strength
Optimal esthetic outcome
disadvantages of Light-polymerized resin
Brittle
No flexibility
Potential to lock on
Difficult to add & repair
Multiple laboratory procedures
Techniques of provisional restorations
Direct technique
Indirect technique
Indirect-direct (combination) technique
Digital technique
Advantages of direct technique: interim
Quick
Easy
No laboratory work needed
Disadvantages of direct technique: interim
Free monomer (PMMA)
Heat production (PMMA)
Marginal inaccuracy
Steps of a direct technique for an interim restoration
External surface form (ESF)
Load the provisional restorative material into the ESF
Trim and contour the provisional restorations
Finish and polish the provisional restorations
Indirect technique requires that a template be formed into ____ corresponding parts? what are these parts?
Two
External surface form
Preparation surface form
what is an external surface form
defines the external contour of the crown or FPD
what is a preparation surface form
reproduce the prepared tooth surfaces and the edentulous ridge areas, when presented (used with indirect technique)
Steps of the indirect technique
Full contour wax up
Matrix formation
Impression of the prepared teeth & pour a working model
Load the matrix with provisional material
Contour the provisional
Finish & polish the provisional
Steps of combination techniques
Full contour wax-up
Duplicate the wax-up model and modify the cervical contour
Matrix formation
Load the matrix with provisional material & trim the tissue surface form
Reline the provisional shell with PMMA
Finish, polish & characterize the provisionals