Bacterial cell biology 2
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
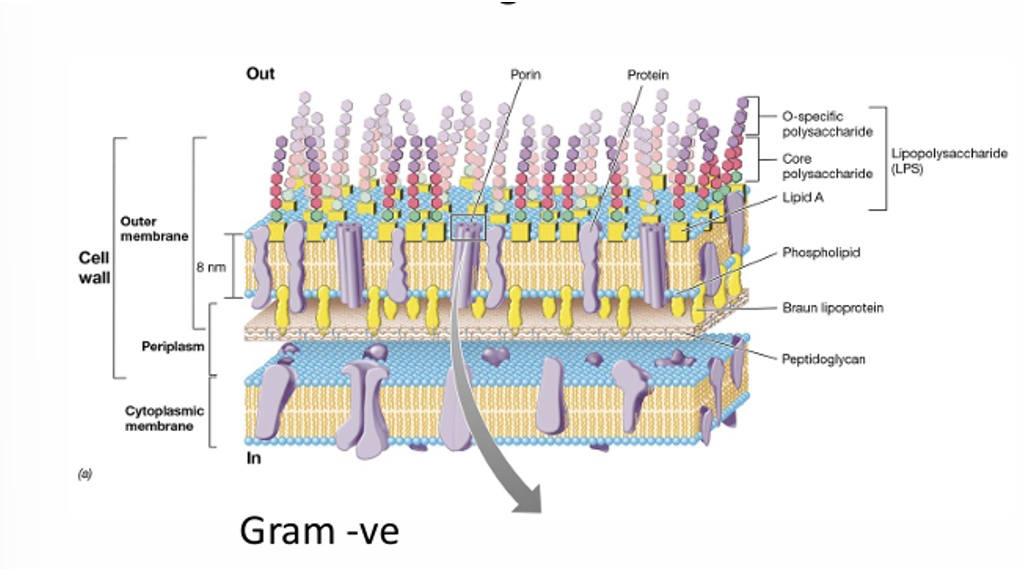
In Gram negative have
2 membranes - inner and outer membrane
between them have small peptilaglycon layer
In gram positive have
1 membrane and pepetilagoliocon layer is attached to membrane
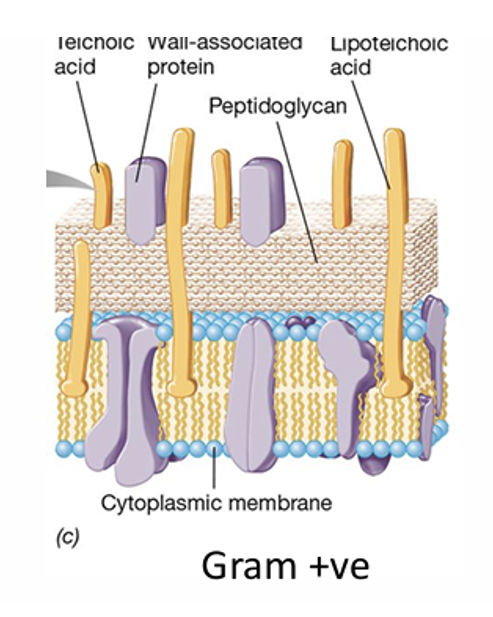
Which bacteria do most antibacterial attack
gram positive and only 1 membrane (more difficult with gram - as 2 membranes)
what can bacteria have on outside
capsules (structred) - pollysacharde proetin layer on outside
slime capsule (loose and deformed)
What is the function of these
Virulence factors - protect them against host immune system
Aid attachment to solid surfaces
Biofilm formation
Prevent dehydration/desiccation
Cell appendages
Fibreae
Pili
Flagella
(things that extend out of cell)
Function of Fimbrae
short
lots of them
help its stick to surfaces
no active function
Function of Pili
longer than fibrae
few per cell
present in all gram - some gram +
they allowing:
Function of secretion systems (bring things form inside to outside)
Cell movement - twitching motility
Important for genetic exchange (e.g horizontal gene transfer)
Secretion systems in Gram -
Different types of secretion systems
Molecules that bring things form inside of cell to other side of cell membrane
Powered by ATP
Type 4 secretion system well studied: transports enzymes, toxins, proteins and DNA
Type 4 pilus extends form type 4 secreation system involved in ; conjunction, transformation and electron transduction
3 mechanism of horizontal gene transfer
Conjugation
Transformation
Transduction
Conjugation
How genetic info is transferred
Plasmid with resistant gene replicate and passes through pilus secretion system to another cell
Trasfoemtaion
Pick up DNA form environment
Pilus extends to environment picking up DNA fragments from dead cells or secreted cells
enter through pilus and gen encouperated in to genome
Transduction
Happens through virus - Bacteriphage
once infect cells with there DNA can either :
Cause cell to burst and release more viruses - LYSIS
Or can hide in genome for a while and then cause the cell to burst
type 4 secretion system can be used in different ways to attack other cells:
secreate things to attack other cells
inject things to harm cells
move into cells and then produce toxins
what are PHBs and PHAs
PHBs are polymers, different types called PHAs
made in carbon rich environment
get broken down when in environment lacks carbon or they need it
Phosphate
bacteria store phosphate
Phosphate used to make nucleic acids, bi-layer…
stored as inoragnic PI to be used in times or need
Sulfur
can be generated in bacteria through reduction of things like H2S in fermentation
this releases electrons to be used in metabolism or CO2 fixation
Sulfur element stored in periplasam of cells to protect them
Carbon materials
some bacteria store carbonate material through Biominerlization
Cyanobacteria provide ballast to keep it stay deep in water column - weighs it down
Magnetosomes:
in bacteria can form tiny magnets
build magnetic particles enclosed in membrane
MF line is aligned with going deeper or shallower into the water
Gas vesicles
Provide cyanobacteria the ability to float
How are gas vesciles formed
formed form 2 proteins GvpA and GvpC
GvpA is small hydrophobic proetin, rib like structures, keeps gas in and water out
GvpC cross links GvpA , increases strength of vesicles
what are bacterial micro compartments (BMCs or MPSs)
proetin enclosed structures that allow metabolic reactions to occur that would have been otherwise toxic to the cell
Examples of BMCs
Carboxysomes → allow photosynthesis within them , stores RuBisCo and concentrated carbon dioxide for photosynthesis (anabolic)
Metabolosomes → allows for higher concentrations of toxic molecules
EUT: ethanolamine utilisation → ethanolamine comes from the breakdown of cellular membranes so allows bacteria to use ethanolamine as energy and as a nitrogen resource
what is bet hedging behaviour
decision needs to be made, certain cells do one thing and other cells do another and there is an overall advantage to the population
Most common way cells can divide
Binary Fission
get elongation then formation of septum and closes off 2 membranes
What is generation time
the time required for a population of microbial cells to double
Other types of ways that cells can divide
Budding division: a cell division process whereby new cell material is produced from a single point instead of along the entire cell

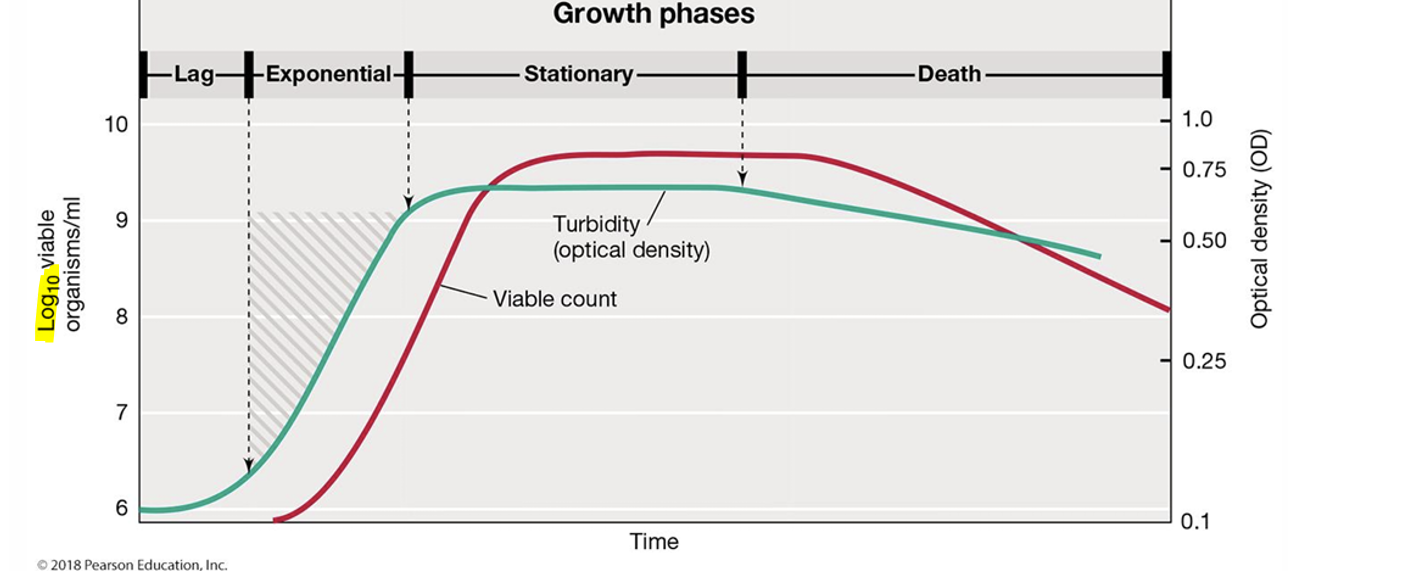
Growth phases
Lag phase
Exponential growth phase
Stationary phase
Death
Endosporulation
examples are C . Difficile and Anthrax
Common in soil
spore are heat resistant,thick-walled, differentiated structure produced by certain gram-positive bacteria
It is a survival strategy if run out of things then become a spore then later regrow again from that spore
Spores are easily dispersed by wind, water, animal gut (faeces)
Process of Sporulation
Cell forms ahrd tough later with DNA still intact
Cell now refered ot as mother cell
DNA condenses and lines up in middle of cell
DNA divides and mother cell invaginates to form Forespore
Mother cell then enguls spore so now has 2 membranes
Then form active spore - resistant to envornmental conditions
enzymes break down mother cell and spore released
What activates spore activation
spore heated for few minutes
what is Dipicolinic acid
makes sure DNA is dehydrated and protected
it is a substance unique to endospores that confers heat resistance on these structures
How many genes are spore specific
200 genes
when in favourable area
germination happens and forms cell again