Ella's Quiz 1: Alginate & Gypsum
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from halec_serlin on quizlet | has alginate AND gypsum
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
impressions are ____ and casts are _____
impressions are NEGATIVE
casts are POSITIVE
we classify impression materials based on 3 things:
USAGE/clinical app (ie low/high accuracy)
physical state after setting (ie elastic/ nonelastic)
setting RXN (chemical irreversible, reversible)
preliminary impressions vs definitive impressions (usage or clinical application)
preliminary are low accuracy
definitive are high accuracy
non-elastic vs elastic (physical state after setting): when do you use these impression materials?
non elastic are for edentulous (NO teeth) mouths
elastic is for both edentulous and dentulous mouths
reversible vs irreversible (setting reaction)
reversible (thermally softened and hardened)
irreversible (chemical reaction)
2 types of impression trays
stock (metal)
custom (plastic)
perioral vs intraoral tissue management
perioral: lips and cheeks
intraoral: hard/soft tissues AND gingiva
which tray uses adhesive and which doesn't
NO adhesive: metal
GENERALLY YES adhesive: plastic, custom trays (fabricated on a cast)
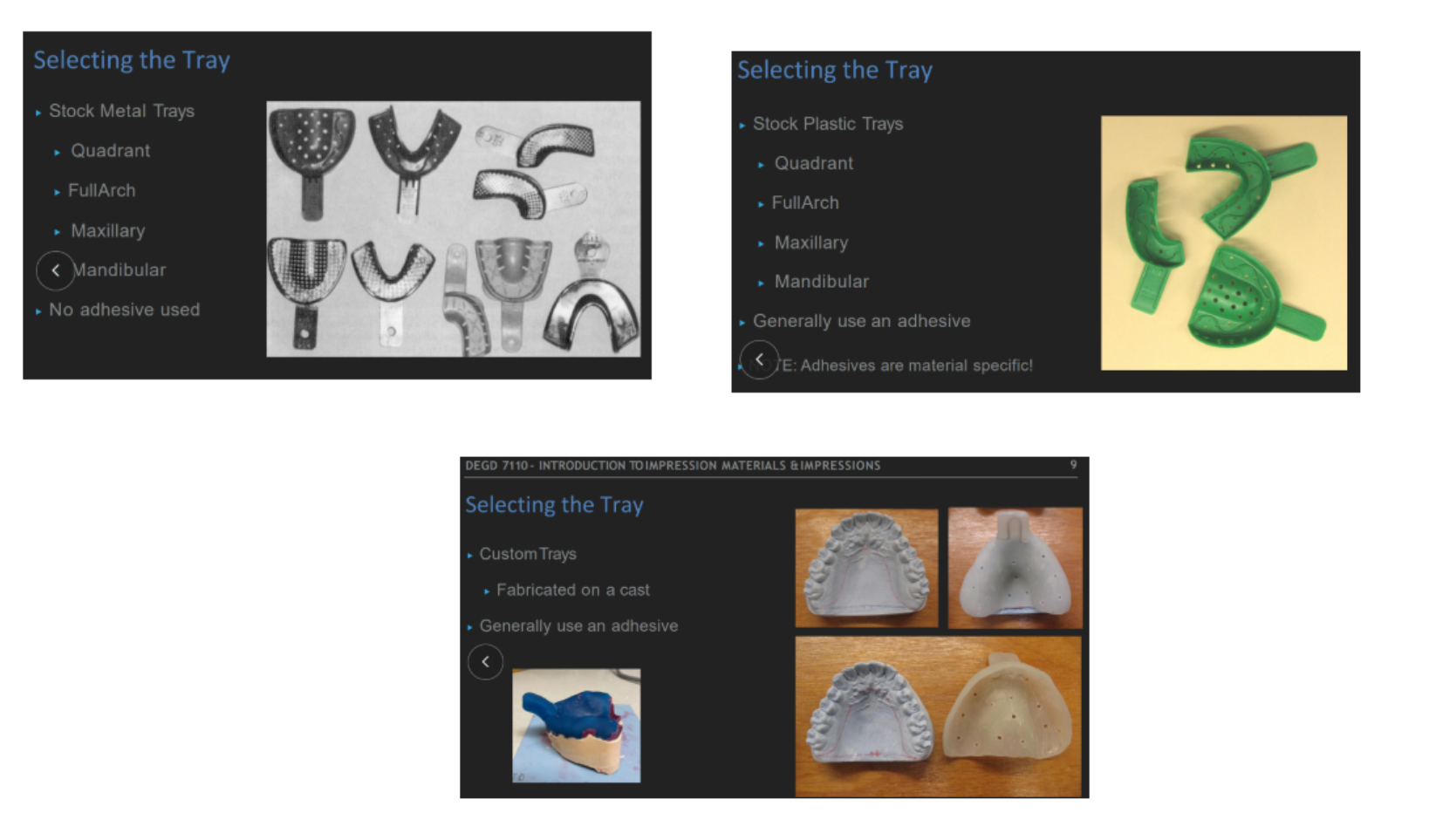
what is the purpose of perforations and ridges in the tray
provide retention of impression material so that it doesn’t separate & distort
adhesives are…
material specific
3 types of manipulation of impression materials
hand mixing
static mixing
dynamic mechanical mixing (what dr. michelle uses)

setting reaction starts when
mixing starts
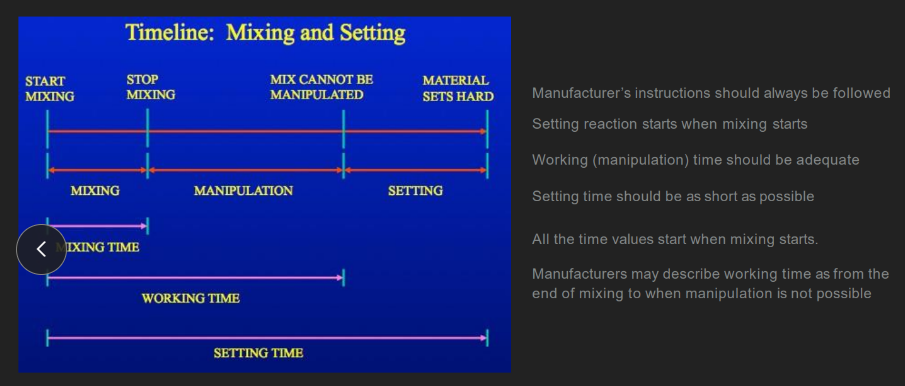
wtf is “working time” according to manufacturers? vs general public
manu: end of mixing to when manipulation is IMPOSSIBLE
general public: ALL of mixing time + ALL manipulation time
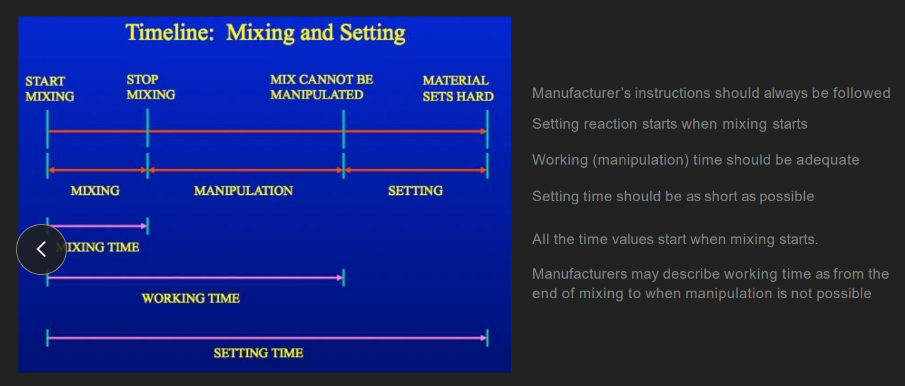
wtf is the “manipulation” period?
when you STOP mixing … until the material HARDENS and you can’t move it anymore
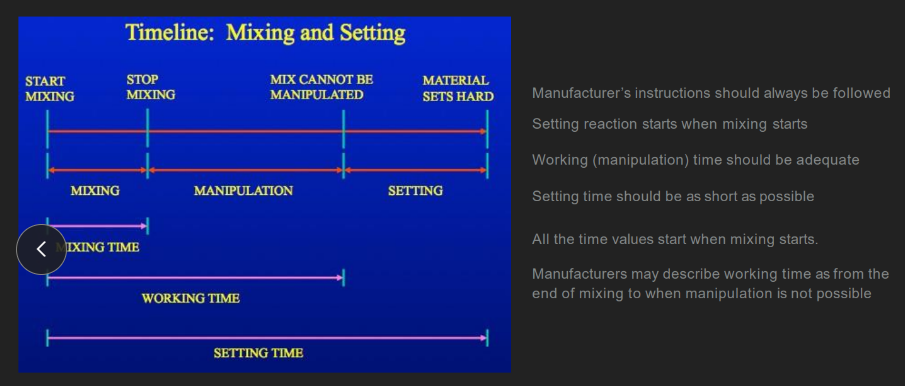
setting time should be
ASAP (as short as possible)
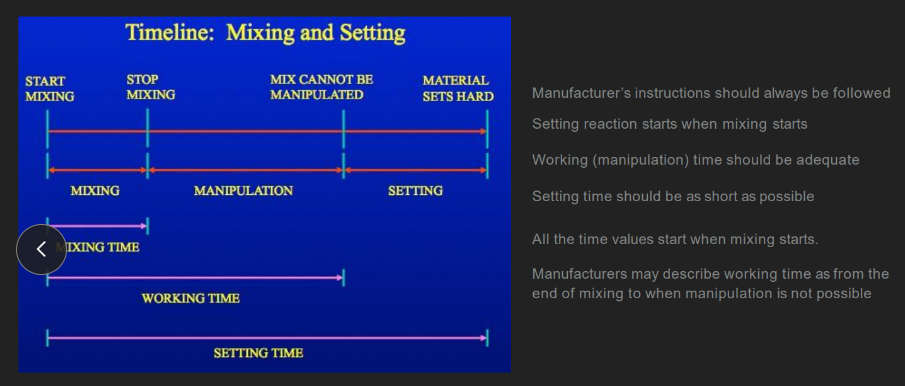
all the time values (mixing, working, setting) start when…
mixing starts
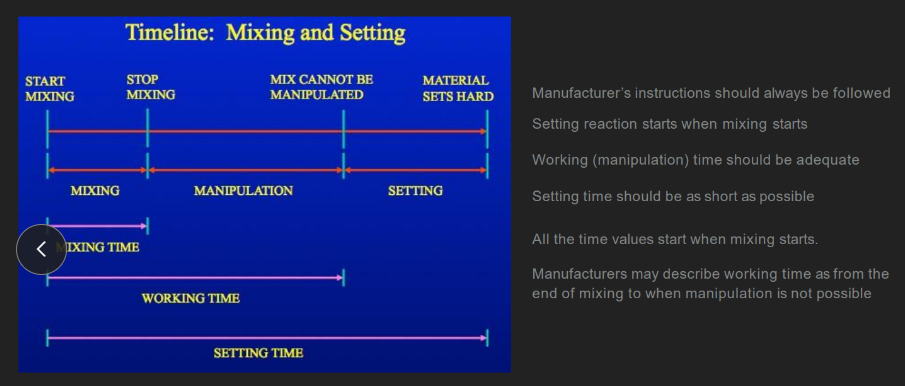
“setting” time value =
mixing + manipulation + setting
(aka, from when you FIRST mix the materials together UNTIL the impression sets HARD)
general requirements of impression materials
adequate shelf life
easy to manipulate and handle
non toxic and non allergenic
adequate working time and short setting time
elastic and strong to resist tearing
dimensionally stable for long periods of time
compatible with model and die materials
disinfection without distortion or loss of details

viscoelastic behavior means
material should returns to its original dimensions ASAP after removing from mouth
the should be no permanent deformation
(ie, you pull out the impression and accidentally bang it against the crown of the tooth… now there’s a PERMANENT dent despite the material already having “set” Be FR)
examples of REVERSIBLE and IRREVERSIBLE hydrocolloids
reversible: agar
(literally think jello. it’ll turn to liquid at high temps)
irreversible: alginate
wtf is a “hydrocolloid”
water soluble polymers (make a gel when mixed with water)
ie alginate and agar
alginate is less ____ and not as ______
so, we only use it…
accurate
dimensionally stable over a period of time
only used for prelim impressions! ie diagnostic casts for TREATment planning, patient education, making custom impression trays!!
what accuracy is needed for alginate
75 um (micrometers) for primary impressions and 25 um for definitive
good alginate impressions….
do NOT change in shape/dimension btw mouth removal and stone model pouring
imbibition is…
SWELLING: absorption of water from the environment
syneresis is…
SHRINKAGE: loss of water
(opposite of inbibition)
broadly speaking, besides with WATER specifically (syneresis), what IS shrinkage?
ANY volatile byproduct that evaporates
pros and cons of alginate?
pros: hydrophillic, cheap
cons: obvi not as accurate
poor tear strength
need to pour IMMEDIATELY bc it shrinks after 10-15 mins!
musod alginate: mix time, work time, initial set time, set time
60 sec, 2 min 15, 2 min 30, 3 min 30 sec
after taking alginate how quickly do you need to pour it
10-15 min (cannot repour the same alginate)
warm water vs cold water on alginate setting
warm: faster
cold: slower
can the mix be lumpy for alginate and how much adhesive would you use on a stock plastic tray
no lumps, and minimal amount
before making an impression, the adhesive should be…
THIN and fully dry.
where does alginate waste go
trash
what does it mean if an impression is “not retained”?
and is this okay for pouring it up?
not retained = impression literally peeling off the tray
HELL NO you can’t pour it up
when can you practice with alginate?
in class on the BENCHTOPS
NOT on any humans- needs to be supervised by faculty.
gypsum is
calcium sulfate dihydrate (CasSO4)
use of gypsum in dentistry: what’s the DIAGNOSTIC casts used for VS DEFINITIVE?
diagnostic:
evaluate pt’s articulation & dentition
plan & track treatment
pt education
definitive:
INDIRECTLY making dental restorations.
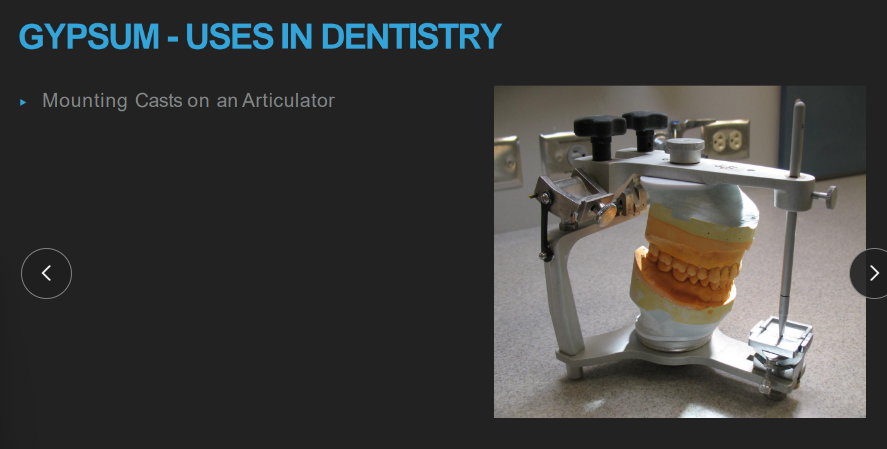
wtf does gypsum have to do with articulators
MOUNT stone casts ON an articulator
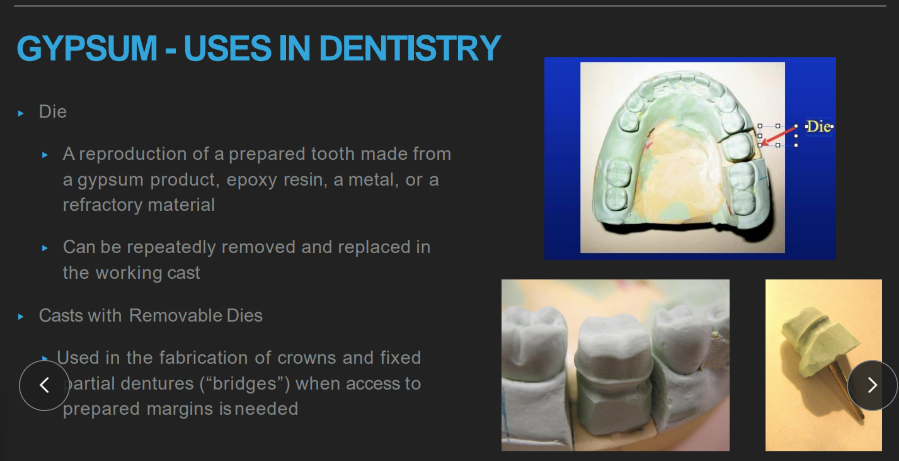
wtf does gypsum have to do with “die”?
to make a tooth from a cast removable!! can slide in and out
(helpful for bridges and crowns where u want to access the margin)
cast (verb):
reproducing a shape/surface by pouring up a NEGATIVE impression
what’s a MODEL in dentistry? example of a model?
a POSITIVE likeness of an object
a cast is a MODEL!
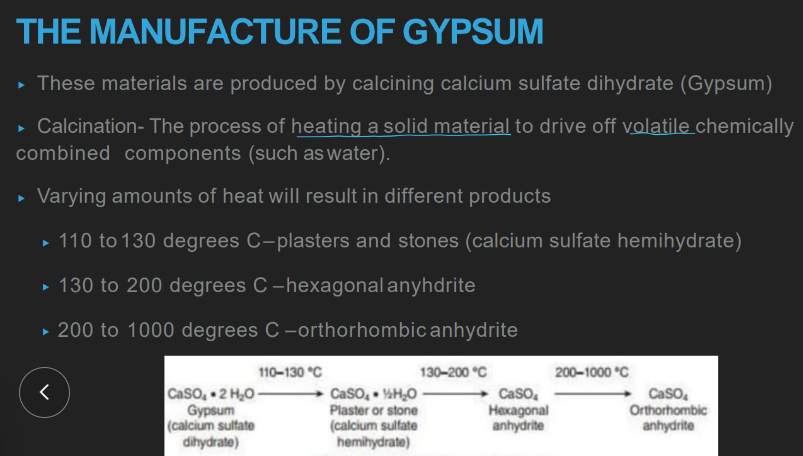
wtf is calcination?
heating a solid material to evaporate off volatile, chemically combined components (water & CO2)
how tf is gypsum made from CaSO4 as opposed to OTHER products?
heat at a CERTAIN temp to evaporate off a CERTAIN am of water
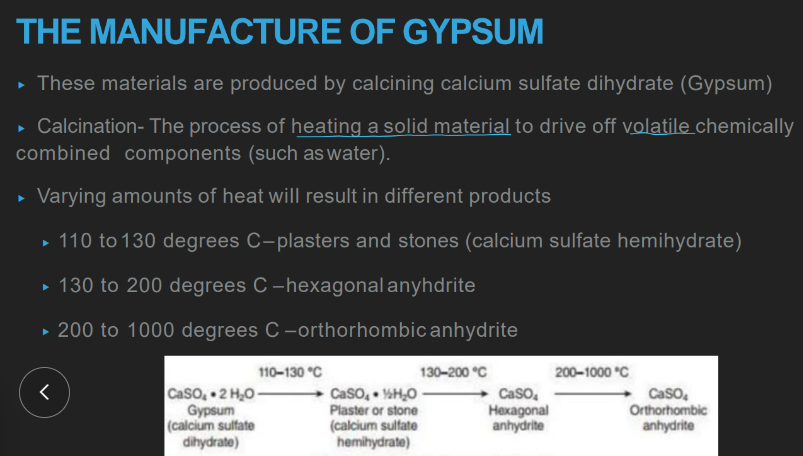
plaster and stones: temp of heating
aka?
110-130 C
“calcium sulfate hemihydrate”
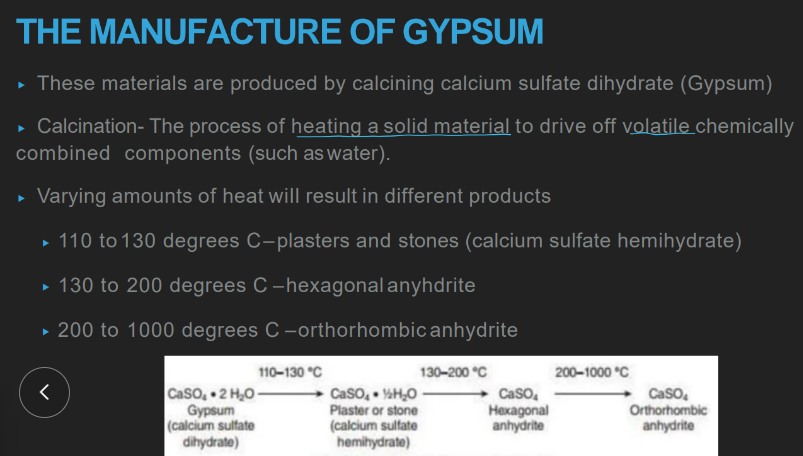
hexagonal anhydrite: temp of heating
130-200 C
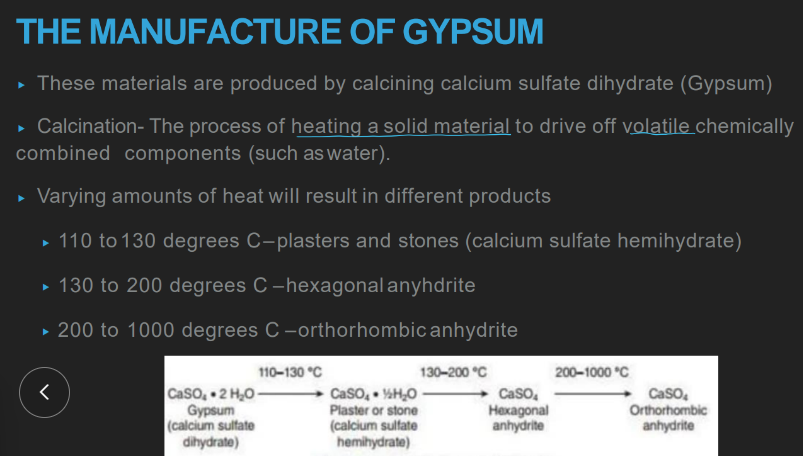
orthothrombic anhydrite: temp of heating
200-1000 C
as gypsum material sets…
exothermic rxn converts HEMIhydrtate to DIhydrate

using few crystals from past gypsum reaction makes what?
why tf would you ever do this?
slurry water
can use to ACCELERATE the setting rxn

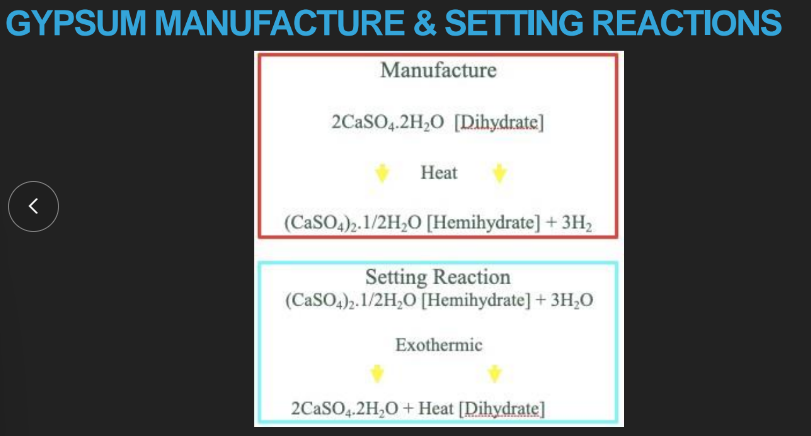
manufacturing VERSUS actually setting gypsum… describe the rxns
manufacture: dihydrate + heat → hemihydrate + H2 gas
set: H2O+ hemihydrate → dihydrate + heat
beta hemihydrate compared to alpha ?
(water, strength, shape)
what types of gypsum powder is it, and what’s it used for ?
gypsum powder that’s IRREGULAR shaped, spongey, requires HELLA water to react
type 1 & 2 used for impression & model plaster)

alpha hemihydrate compared to beta?
what’s it used for?
REGULAR shape, dense, needs less water (no duh- it’s a STONE)
type 3,4,5 - dental stone, high strength dental stone, high strength and high expansion dental stone

what is modified alpha hemihydrate with shorter and thicker crystals, uses even less water, and has a higher strength stone
Die stones
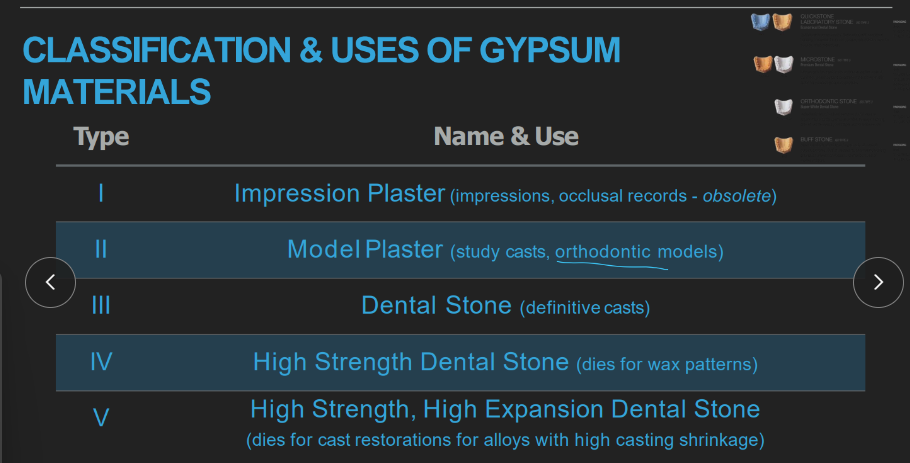
lowest to highest strength of type 1-5 gypsum products? what hemihydrates are they made from?
beta (1-2): impression plaster, model plaster
alpha (3,4,5): plain dental stone, high strength dental stone, high strength and high expansion dental stone
4, 9, 20.7, 34.5, 48.3 strength at 1 HOUR (MPa)
over time, the compressive strength of gypsum products…
INCREASES.
longer it’s allowed to dry, the STRONGER it becomes!
dental gypsum PROS
(time, expansion, strength)
ADEQUATE working time + HELLA short setting time (+ doesn’t expand a ton AFTER setting!)
hella strong, resistant to abrasion
the longer you mix gypsum…
the SHORTER the working time!
(literally eating up working time)
if you don’t use enough water for gypsum?
DECREASE in strength, hardness, abrasion resistance
wtf is the W:P ratio?
water (mL) : 100 g powder
a W:P ratio of 0.4 means…
40 mL water / 100 g powder
most widely accepted mechanism describing setting process of gypsum?
what does it mean?
supersaturated solution precipitation SSP
hemihydrate dissolves → dihydrate PRECIPITATE
gypsum: what defines the INITIAL setting time vs FINAL setting time?
initial: when the mix cannot be penetrated by light gillmore needle pressure
final is barely perceptible mark left by heavy gillmore needle pressure
time to mix mechanical vs hand?
what supplies do you use for these?
mechanical is 20-30 sec; vacuum mixer
hand is 60 sec; mixing bowl & stone spatula

rate of gypsum dihydrate crystal formation INCREASES with:
hemihydrate solubility
number of nuclei
accelerators (aka catalysts)
increased water to powder ratio (more water) does what to
working and setting times
strength and hardness
expansion
increased working and setting times
decreased strength and hardness
decreased setting expansion
chemical accelerants are
potassium sulfate (K2SO4)
sodium chloride (NaCl)
sodium sulfate (Na2SO4)
borax at LOW concentrations (at HIGH concentrations it is retards)
what happens during HYGROSCOPIC setting expansion of gypsum?
happens when gypsum SETS while completely dumped in water
2x normal setting expansion amount
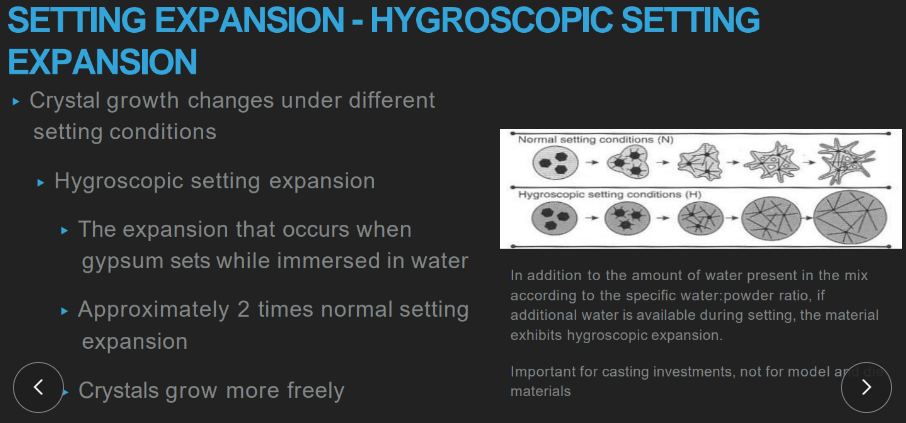
increased setting expansion results from ________ water to powder ratio and ________ mixing times
lower w:p
longer mixing
what happens during gypsum setting expansion?
initial contraction
expansion
smaller contraction
wet strength (green strength) vs dry strength
what are they? how do they compare?
wet strength: strength when water in excess
dry strength: strength when all excess water used and 2-3 times that of wet strength
increase W:P ratio _____ strength? because…
decreases
FEWER am of crystals per UNIT volume of gypsum-water
aka more DILUTE slurry
effect of mixing on strength…
longer mixing time INCREASES strength
… until OVERMIXING which decreases strength :(
there are additives to gypsum which can…
STRENGTHEN the final product
for clinical care cases, the preferred method of mixing is ?
mechanical/ vacuum mixing
(demonstration videos are on D2L and should be watched before class)
HOW do you hand mix gypsum?
thorough mix for 1 min
bowl on VIBRATION table to minimize incorporated air
(reduces air by HIGH frequency, LOW amplitude vibration)
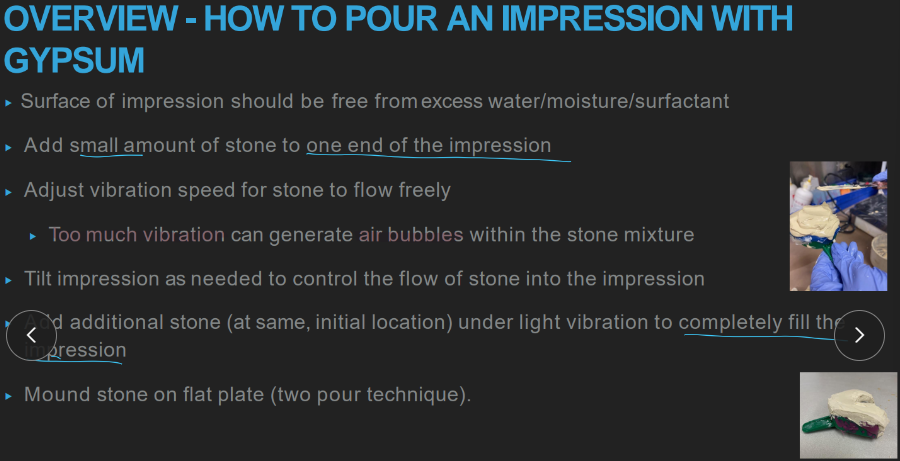
HOW do you pour a gypsum impression?
add stone to one end, while impression ON LIGHT vibration
tilt impression to fill with material
continue adding to SAME spot and tilting :)
what typically causes BAD gypsum casts?
saliva/ blood contamination

how do we prevent BAD gypsum casts?
hardening chemicals in the alginate impression material
treat impression
RINSE impression of ALL saliva and blood

has FDA approved disinfecting agent in the gypsum itself? where do we use disinfectant?
NO
use on the FINISHED teeth models- SHOULD NOT affect detailing.
not safe to store or heat casts above
130 C
what dissolves gypsum?
water
what gypsum are we going to be using?
properties? (w:p, expansion, compressive strength)
Buffstone (whip mix)
30ml/100g
.15% expansion
compressive strength wet (1 hour) 28 MPa and dry (48 hours) 56 MPa
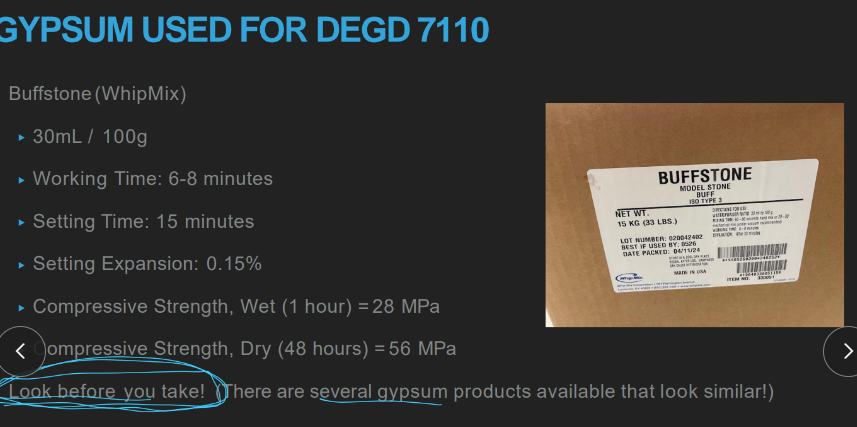
what’s the working and setting time of OUR gypsum?
6-8 mins
15 mins
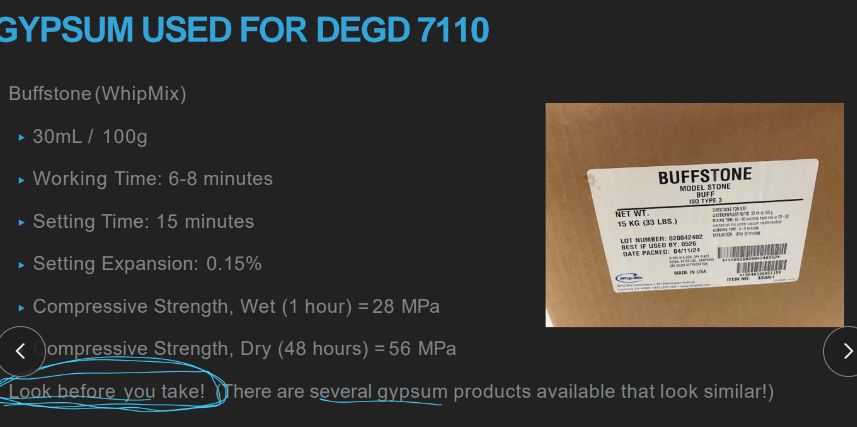
how much does OUR gypsum expand?
0.15%
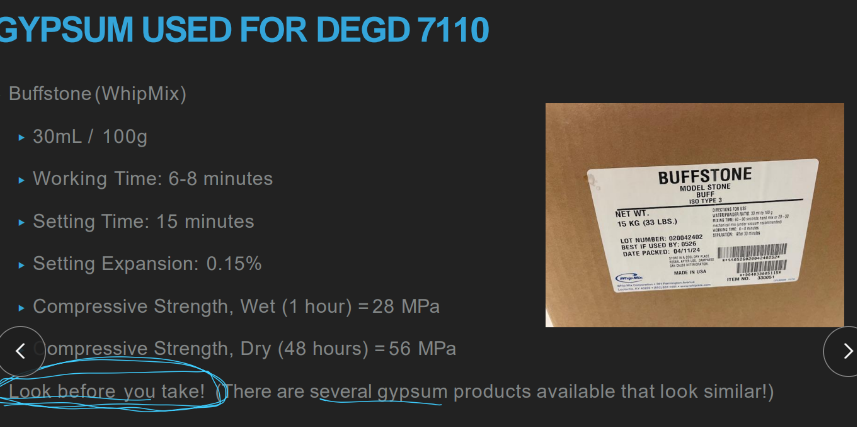
what’s the compressive strengths of our gypsum?
wet (1 hr) = 28 MPa
dry (48 hrs) = 56 MPa
wtf is a “gypsum based investment”?
“refractory” material: gypsum mixed with silica
used to make a MOLD for metal casting process
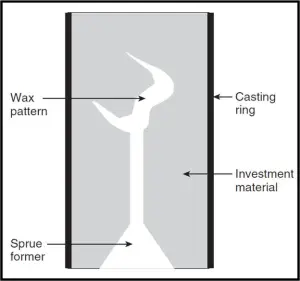
normal setting expansion is defined as…
expansion when gypsum or gypsum bonded investment SETS in ambient air
wtf is “plaster of paris”
dental PLASTER
aka BETA calcium sulfate hemihydrate (CaSO4 × ½ H2O)