Biology Semester 1
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
hydroxyl
OH - alcohol - alcoholic beverages
carbonyl
COH - aldehyde/ketone - end/middle - sugars, ketose, and aldose`\
carboxyl
COOH - carboxylic acid/organiz acid - acetic acid (vinegar)
sulfhydryl
SH - thiol - cross links stabilize protein structure (hair)
amino
NH2 - amine - glycine/amino acids
methyl
CH3 - methylated compound - affects expression of genes/sex hormones
phosphate
OPO32- - organic phosphate - DNA backbone/chemical reactions
polymerization
process by which cells make polymers and enzymes
structural isomer
different arrangement of atoms
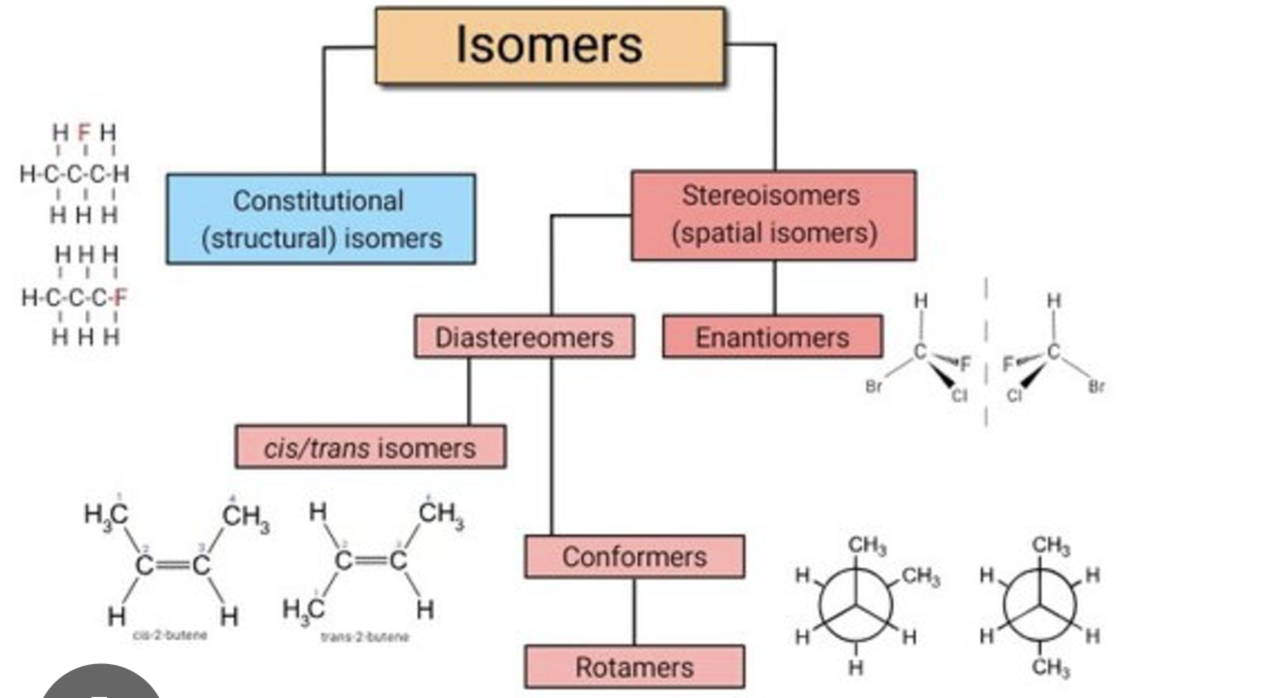
cis-trans (geometric) isomer
different spatial arrangement because the double bond is inflexible - functional groups in different orientations
enantiomer
mirror image because of asymmetric carbon
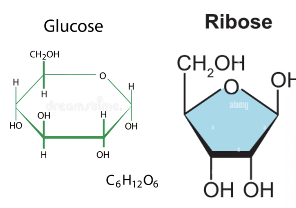
carbohydrates
CHO - 2:0 H to O ratio
ribose, glucose
lipids
CHO; insoluble in water, fats solid + oils solid at room temp
sterouds, waxes, fatty acids, triglycerides, oleic acid, testosterone
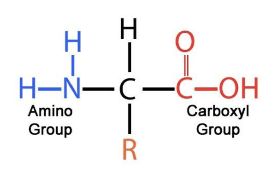
proteins (amino acid chains)
CHON(S); amino acid chains
amine group, carboxyl group, hydrogen atom, r group
nucleic acids
CHONP; nucleotide chains - RNA, DNA
metabolism
sum of all reactions that occur in an organism
metabolic pahtways
chain reactions and cycles
anabolism
make big from small - synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules
needs energy (atp)
condensation rxns and dehydration sysnthesis
ex: protein synthesis w/ ribosomes, dna synth during replication, photosynth, formation of macromlc from monomers
catabolism
make small from large - breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules
hydrolysis releases energy (atp)
ex: dugestion, cell resp, macromolecule to monomer
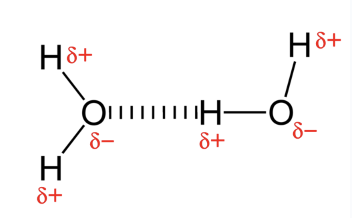
hydrogen bonds
unique bc of polar covalent bonds within water mlc
H bonds are weak but abundant in water
cohesion
hydrogen bonds, 2 water mlc
transport of water undertension in xylem
use of water surfaces bc of surface tension
adhesion
materials that are polar and charged
capillary action in soil and plant cell walls
keep cell walls moist and water droplets
specific heat capacity of water
very high; hear needed to raise water temp is a lot → water temp suitable for living things
water - latent heat of vaporization
heat needed to go from liquid to vapor → creates a coolant effect in evaporation and makes for a good coolant
boiling point of water
high boiling point
water vs methane (methanogenic proaryotes in swamps)
sweat cooling: the heat needed to evaporate water in sweat is taen from skin tissue
water as a solvent
water = medium for metabolism and transport in animals (cytoplasm)
hydrophilic mlc dissolve in water (H bonds with polar mlc)
enzyes catalyze in aq solution
fuctions of some molecules depend on them being hydrophobic and insoluble
physical properties of water
buiyancy, viscosity, thermal conductivity, specific heat capacity
transport in blood plasma
NaCl - dissolve, carried in blood plasma
amino acid: soluble enough to carry in blood plasma (varies by R)
glcose: dissolve, carried in blood plasma
oxygen: nonpolar but dissolves bc small, hemoglobin in RBC
fats: nonpolar/insoluble, carried by lipoprotein complexes
cholesterol: hydrophobic, carried in lipoprotein phospholipid monolayer (hydrophilic region phases outwards)
hemoglobin
binding sites for oxygen - increases capacity
catbohydrates
macromolecules produced by condensation rxns that link monomers to forn a polymer
monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
pentoses
fructose, ribose (dna backbone)
hexoses
glucose, galactose (milk)
disaccharide
maltose, sucrose (table sugar), lactose
disaccharide
maltose, sucrose (table sugar), lactose
polysaccharide
energy storage compound - starch, glycogen, cellulose
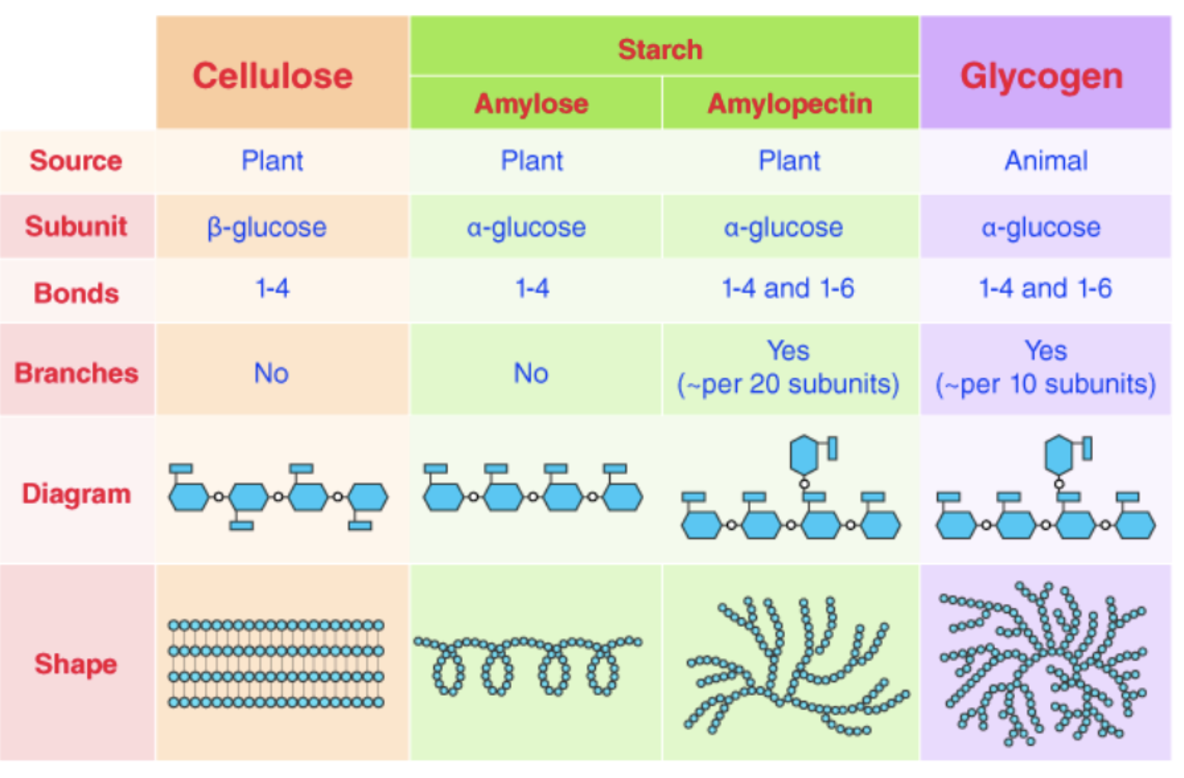
starch
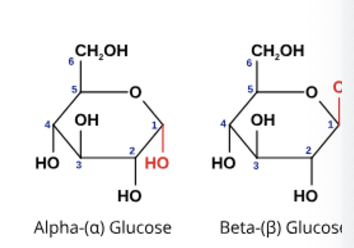
in plants; alpha glucose molecules, only made by plant cells
amylose
unbranched, forms a helix (all oriented in the same direction)
think bc ose sounds circular
amylopectin
branched; globular shape
does not affect osmotic balance
temporary store in lead cells + energy storage
glycogen
in animals and fungi
branched (compact molecule)
does not affect osmotic balance - used in cells where large stores of dissolved glucose would cause osmotic problems
glycoproteins in cell-cell recognition (ABO antigens)
cellulose
structure related to function as a structural polysaccharide in plants
alternating orientation of beta glucose monomers = straight chains that can be grouped in bundles and cross-linked with H bonds
cross links: cellulose microfibrils
high tensile strength - prevents plant cells from bursting
vertebrates cannot digest cellulose. grazing animals have host bacteria in their guts that have enzymes to break down cellulose
MEMORIZE THIS CHART!!
functions of lipids
long term energy storage (triglyc)
hormonal roles (steroids
insulation (thermal - triglyc and electrical - sphingolipids)
protection of internal organs
structural components (plips and cholestrol)
types of lipids
tryglycerides (long term energy), phospholipids (structure), wax (protection against water loss), cartenoids (absorb light), glycolipids (cell receptor), steroids (hormones)
hydrophobic fat
dissolve in nonpolar; fats, oils, waxes, and steroids
triglyceride
forms from one glycerol and 3 fatty acids
phospholipid
forms from 2 fatty acids and 1 phosphate group (head and 2 tails)
fat structure
ester bonds; four fused rings in sterouds
sat vs monosat vs polyunsat fatty acid
number of double carbons affects melting point
diff types of fatty acids in oils and fats used tfor energy storage in plants and endotherms respectively
sat (oils, palmitic acid), polyunsat (cis-linolenic acid), monounsat cis (palmitoleix acid), trans fat and saturated (CHD correlation)
Depiction - sat vs monosat vs polyunsat fatty acid
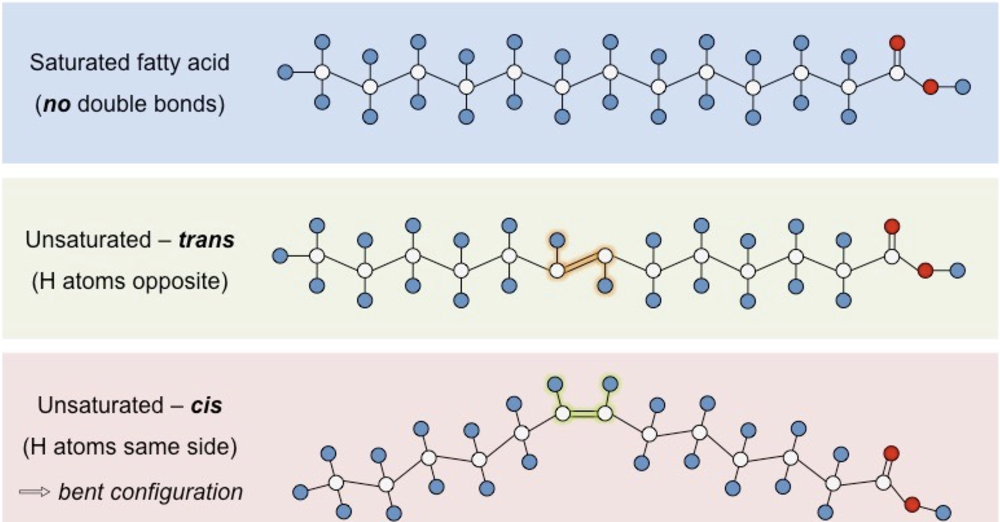
cis isomers
very common in nature
h atoms on the same side of the 2 C atoms
double ond —> bend in chain —> loosely paced
have melting points — usually liquid @ room temp
trans-isomers
rare in nature - usually artificially produced for margarine from veg oils
h atoms on dif sides of the 2 C atoms
double bond = no bend → closely packed
solid @ room temp
triglycerides in adipose tissue
for energy storage and thermal insulation
amphipathic
phospholipid bilayer - having both hydrophibic and phillic parts
ostradiol and testosterone
both can pass through the plip bilayer - tetracyclic skeleton - 4 ringsb
bmi calculation
(mass in Kg)/(height in m)²
other lipid info
the amount of energy released in cell resp per gram of lipid is double that for carbs and proteins
lipids add 1/6 as much to body mass as carbs
fats stored as droplets but carbs are stored with water
lipids have a higher hydrogen to oxygen ratio (are more reduced and release more energy
polypeptide
amino acid chain linked by peptide bond through condensation (amine and carboxyl group)
on ribosome during translation
oligopeptide: chains of <20 amino acis
aino acid
20 dif diverse ones; hydrophillic/hydrophobic or acid/base; evolved from one single species with 20 a
amino acids + genes
amino acid sequence is coded by genes
20^n possible sequences
3 bases of a gene = 1 amino acid
dna in the nucleus, polypeptide made in the cytoplasm on ribosomes (mRNA)
collagen
structural protein in tendon, liganment, skin, blood vessel walls - high tensile strength - limited stretching
protein denaturation
change in conformation of a protein by heat or pH extremes
conformations stabilized by R groups interactions are weak
usually permanent e.g. hydrophobic r group exposed to water
heat causes vibrations and break bonds
pH changes R group charge — ionnic bonds break and new ones form
conformations of proteins
fibrous (collagen) = elongated
elongated
globular = helical/sheet like —polypeptides fold up as they are made
r groups sabilize structure
hydrophobic/hydrophillic amino acid on surface determines solubility
fibrous proteins
long, narrow, structural, usually insoluble, repetetive sequence, less sensitive to pH and heat
collagen, myosin, fibrin, actin
globular proteins
spherical, functional (catalytic, transport etc), soluble, irregular sequence, sensitive to pH change
catalase, hemoglob, insulin
muscle contraction
actin + myosin = locomotion, transport
tensile strengthning
fibrous protein = tensil strength — collagen = rope like mesh with skin and blood vessel fibers
histones
proteins that help chromosomes condense during mitosis
spider silk
extensible and veyry resistant to breaking
proteome
all of the proteins made by a cell, tissue, or organism
genome: al of the genes of a cell, tissue, or organism
gel electrophoresis: separates protein mixtures
vairiable bc diff cells in an organism make dif proteins
primary structure
sequance of amino acids in a polypeptide (count starts @ amino end)
PEPTIDE BONDS

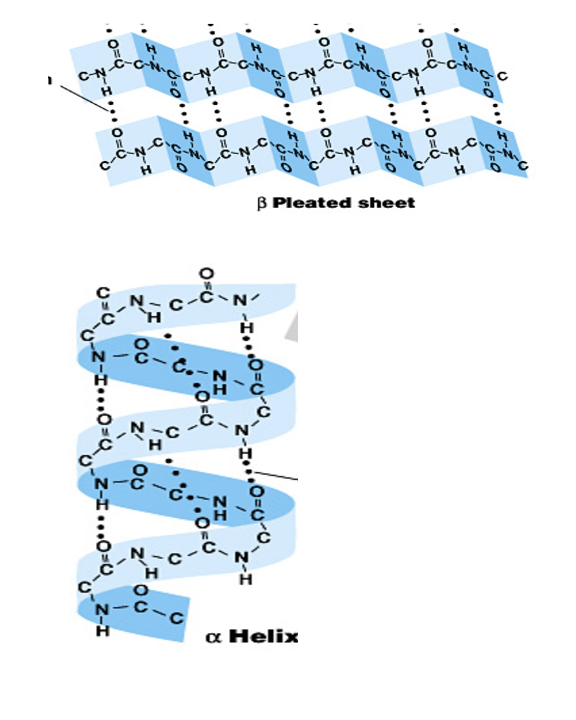
secondary structure
alpha helices/beta pleated sheets stabilized by hydrogen bonds
HB between carboxyl and amine groups
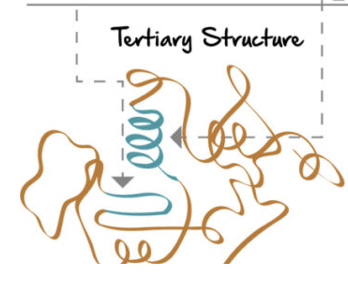
tertiary structure
further folding stabilized by R group interactions
+ r groups interact with -r groups, polar interactions
hydrophbic oriented towards the center
disulphide bridge: cysteine r-groups
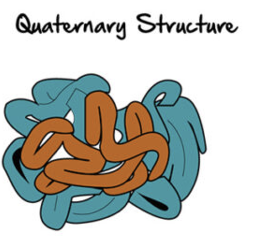
quaternary structure
exits in proteins withmore than one polypeptide chain
enzymes
globular protein that speeds up chemical reactions
enzyme substrate specificity
collusion
substrate mlc and active site coming together
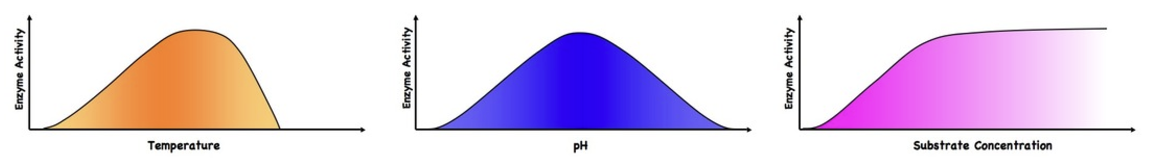
temperature
increase in temp = more colluision s—> denaturation becuse bonds break (pH = ionic)
pH & enzymes
pH differences have a bell curve effect on enzyme activity
induced fit model
enzyme can change shape to fit the substrate
competitive inhibition
often irreversible if binding has covaleent bondsno
non-competitive inhibition
changes shape of enzyme; reversible inhibition part of metaolism
binds @ allosteric site
feedback inhibition
pathway turned off by its end effect
enzyme factors graphs
immobilized enzymes
attachment of enzymes to another material/into aggregations to restrict enzyme movement via glass surface, alginate gel, bodn with enzyme aggregate
cell theory
all things are composed of cells
cell = smallest unit of life
cells only come from prior cellsc
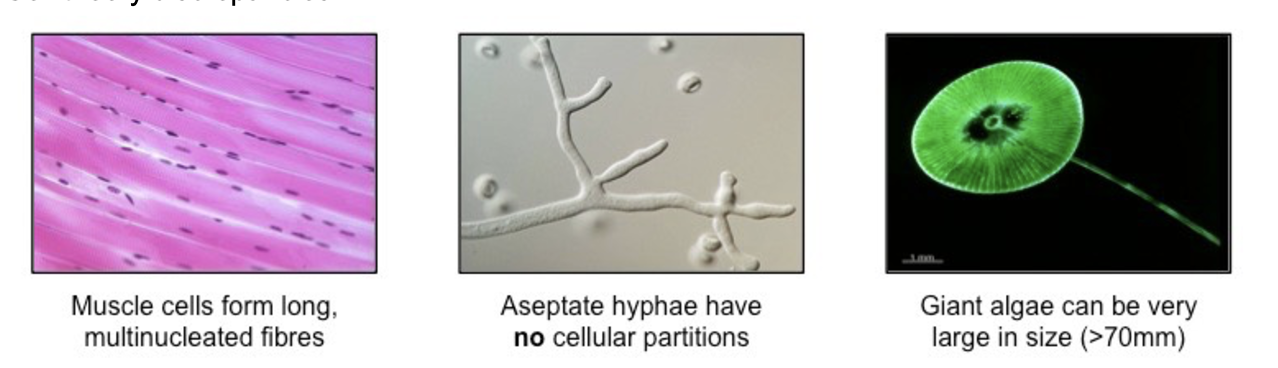
cell theory discrepancies
striated muscle fibers: not an autonomous unit
aseptate fungal hyphae: not discrete cells
giant algae: not microscopic cells (unicellular algae may grow very large)
light microscopes
lenses bend light and magnify; chemical stain/fluorescent labeling
magnification = image size/actual size (according to scale bar)
unicellular organisms
nutrition, metabolism, growth, response, excretion, homeostasis, reproduction
paramecium
Scenedesmus
Chlamydomonas
sa to volume ratio
specialized: villi or microvilli (alveoli in lungs)
cell division
efficiency, growth, cell differentiation, development of embryos, replace dead/damaged/infected cells, asexual reproduction
prophase
DNA supercoils, nuclear membrane breaks down, centrosomes move to opposite polesm
metaphase
fibers attatch to centromeres, contraction of fiber = chromatids line up
anaphase
sister chromatids are separated
telophase
chromosomes deconsdense, nuclear membranes reform
cytokinesis
division of cell cytoplasm
animal vs plant cytokinesis
animal: ring of contractile protein produces a cleaage furrow
plant: vesicles from golgi move to the center of the cell , fuse as tubular structures
tubular structures merge to form 2 layers of p membrane
cell plate develops until it connects with membrane
vesicles deposit pectins, lumen, etc → forms middle lamella
diploid cells
somatic cells; temporarily 4n before cell replication
gametes (sex cells) are haploid
humans have 23 sets = 46 chromosomes
gap 1
increase volume of cytoplasm, organelles produced, proteins synthesized
needs external stimulus
restriction point (point of no return)
gap 0
resting phase where cell has left the cycle and stopped dividing
G0 = nonregrowing state (quiescence)
synthesis phase
dna replicated; checkpoint before s phase (cell size + dna damage)