PRACTICAL PART - PROPED
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
EXAM, practical part, fra ANKI
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What to do on signalment, General Status, TPR
Signalment:
Name
Age category/species/sex
cattle - weaner, heifer, steer, bull, dairy cow, ox
sheep: lamb, ewe, ram wether (castrated)
goat: kid, goat, billy goat, buck
dog: puppy, bitch, dog, neuter
breed
color pattern
age accurate (by teeth or horns)
weight
Designation (branding), ID number (ear tag, tattoo, chip)
Owner info
Anamnesis: symptoms, nature, development, circumstances, etc.
General status:
Behavior (coma (-2) - dull - bright/alert - excited - restless - mania - frenzy (4)
Posture (reg/irregular)
nutritional state (very poor, poor, average (3), good, excellent, obese
TPR:
Respiration per minute
cattle: 10-30
horse: 8-16
small ru: 12-30
dog: 10-30
Pulse per min.
cattle: 50-70, horse: 32-40, small ru: 70-80/90, dog: 110-130.
Temperature
cattle: 37,5-39
horse: 37,5-38
Small ru: 38,5-40
dog: 37,5-38,5
Hair and skin Examination
A. Hair coat:
Integrity - no alopecia or atrichia
Color, corresponding to breed
surface - shininess, smoothness, soiling (shiny, smooth, clean)
ectoparasites
Individual hair:
elasticity, trichorrhexis (brittleness), trichoptilosis (splitting)
Healthy: coat integrity without changes, color acc. to breed, smooth, shiny, moist, elastic, no trichorrhexis, tricoptilosis and no ectoparasites.
sheep: whole, clean, color acc. to breed, no ectoparasites.
B. Skin examination:
Color
Integrity (can be changed by lesions/injuries)
elasticity (behind scapula or neck, upper eyelid in sheep)
Moisture (sweat and sebaceous gland activity)
sebaceous: oily covering of coat/skin, crust, fatty crust (normal: not oily/greasy)
examined on body (cattle, horse), ears (pigs), paws (dogs/cats). hyperhidrosis - overproduction.
temperature (symmetry on spots on body)
odor
changes in size
pruritus (itchiness)
Detection of efflorescence, ectoparasites, ringworm
Healthy: compact skin integrity, light red/pink color, no swelling, even temperature, normal sweat and sebaceous gland activity, odor typical for species, no pruritus, no efflorescences, ectoparasites and ringworm.
Examination of visible mucous membranes and eye
A) Mucous Membranes - check (1) oral, (2) nasal, (3) conjunctiva, (4) vaginal/preputial
color
smoothness
shininess
moisture
volume
integrity
discharge
efflorescence
Healthy: Pink, smooth, shiny, moist, no swelling, no injury, no discharge (some in bo), no efflorescence.
Inflammation is called; conjunctivitis, rhinitis, stomatitis, vaginitis, posthitis. The mucous membranes are hyperaemic (red).
B) Eyes:
Surrounding area
Hair, swelling, lesions, injury, Parasites, Discharge
Healthy: No alopecia/atrichia, no swelling, no lesions/injuries, no parasites, normal amount of discharge
long-term discharge can lead to hair loss, depigmentation.
Eyelids
Size, position, symmetry, movement
healthy: Normal size, even position, symmetrical, movable
Conjunctiva & Third eyelid:
color, smoothness, shininess, moist, swelling, integrity, discharge, efflorescence.
Healthy: pink, smooth, moist, shiny, no swelling, no injury, no discharge, no efflorescence (third eyelid: normal position and shape).
Eyeball
Size, position, movement, direction of visual axis
Healthy: normophtalmus, normal position, no nystagmus, no strabismus
Sclera
Color, surface, episcleral vessels
Healthy: white, smooth, adequate dilated episcleral vessels
Cornea
Reflectiveness, smoothness, regularity, transparency, bulging, deposited material
healthy: Reflective, smooth, regular, transparent, no keratoglobus/keratoconus, no presence of material
keratitis - inflamed cornea
Iris
color, pigment, shape, pupillary reflex
healthy: color acc. to breed, normal pigmentation, isocoric shape, present pupillary reflex
Lens (examined with opthalmoscope or in daylight)
transparency, change of position
healthy: transparent, normal position
Eye function
wave hand in front of eye, touch cornea (with hair)
healthy: normal function
Examination of Lymphatic system
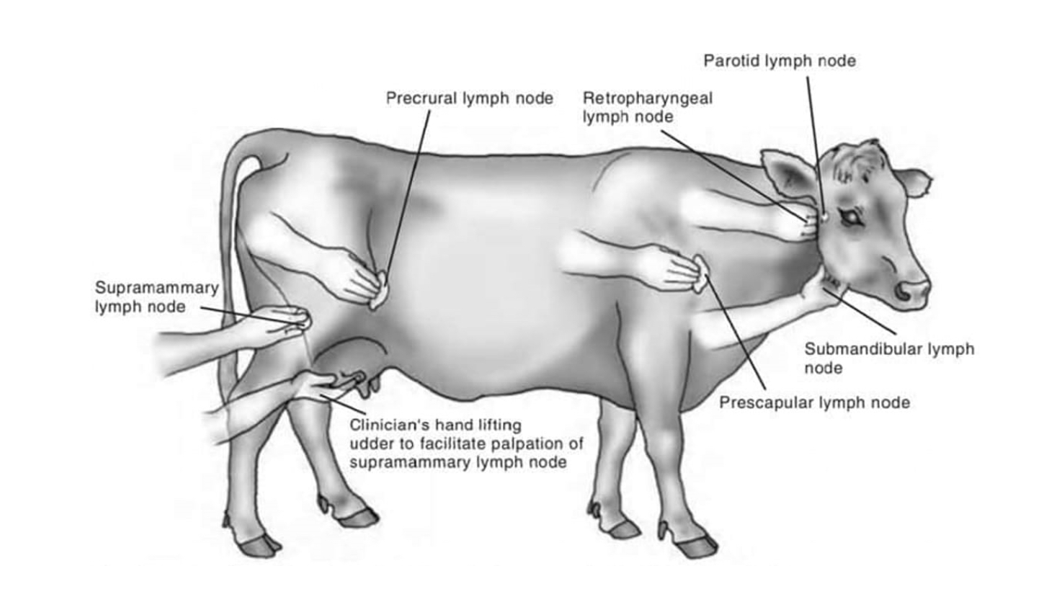
List of Lymph nodes and their shape:
Submandibular - walnut (cattle, dog), raspberry (horse)
Parotid - flat, elongated shape, not palpable (only cattle)
retropharyngeal - not palpable (cattle)
prescapular - fusiform (cattle & small ru)
prefemoral - fusiform (cattle & small ru)
mammary - plum shaped
scrotal - not palpable (cattle, small, ru, dogs and horse)
popliteal - pea-shaped (only in dog)
How to examine:
size, shape, symmetry (hands on each side), tenderness, consistency, surface, structure, adhesion to underlying tissue, temperature
Healthy:
anatomical size, shape according, symmetrical, no tenderness, firm-elastic consistency, normal temperature - same as surrounding parts, normal adhesion - movable against underlying tissue.
How to examine lymphatic vessels:
Inspection and palpation (normally not possible)
Terms:
Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node
lymphangitis = inflammation of lymph vessels
Examination of the cardiovascular system
History, peripheral circulation, heart.
A. Peripheral Circulatory system:
Inspection:
visible Mucous membranes - look for:
pallor (anemia, shock), hyperaemia (engorgement of b.v.), hemorrhages, cyanosis, swelling of conjunctivae, dryness (dehydration, fever).
Skin
color, size, elasticity
B. Arteries:
frequency (normo/tachy/brady), rhythm (reg/irreg.), quality (size, strength, duration)
healthy: Normocardia, Regular pulse, uniform, of adequate strength.
quality:
horse: strong (cardiac function), soft (vascular tone)
Cattle: weak, strong
dog: strong, hard
C. Capillaries:
inspection of episcleral vessels (fullness, color, dilation)
check on eye
healthy: Adequately/moderately filled, in contrast to background
Palpation: CRT on oral mucosa (1-2 sec is normal)
D. Veins:
Fullness of superficial veins (ear/jugular)- venostasis test on jugular vein, visual subcutaneous abdominal
movement of abdominal and jugular vein
healthy: abdominal (full), jugular (empty, negative venostasis test, undulating movement)
negative test: accumulation of blood above pressure point (normal)
E. Heart area:
Dog: 4th or 5th ICS
Horse: 3rd-6th ICS
Cattle/small ru: 3-4th ICS
Inspection: Chest shape, deformities, elbow abduction, chest wall vibrations
Healthy: normal chest shape, no elbow abduction, no vibrations
Palpation: Palpate both sides 3rd-6th ICS
check for tenderness, temperature, tremor
Healthy: Even temp., no tenderness, no tremors
Percussion (left side, dytt foten litt fram):
Size
sensitivity/tender
type of sound alteration
relative dull (ru, su, fe), absolute dull (eq, ca)
healthy: Normal size, no pain, sound typical for species
F. Heart: (located - eq (3-6 ICS left), dog (4-5 ICS left), Bo (3-4 ICS left)
Palpation: frequency, rhythm, presence of fremitus
Healthy: normocardia, regular rhythm, no fremitus
Auscultation sounds:
healthy: Lub-Dub (S1-S2)
S3 in some horse, s4 in large animals detected by phonocardiography
Heart sound - FIRDA:
frequency
intensity
rhythm
demarcation (clarity of onset/offset)
murmur
Healthy: normocardia, intensive, regular rhythm (respiratory sinus arrhythmia in borubon), distinctive terminated sounds, no abnormal sounds.
5. Examination of respiratory system
A. Audovisual examination:
Frequency (inspection/auscultation of trachea or chest)
Cattle: 10-30, horse: 8-16, small ru: 12-30, dog: 10-30
Type of breathing (costoabdominal, abdominal, costal)
Costal - racehorse, dog dominant
abdominal - ru dominant
costoabdominal (mixed) usually
Rhythm (eupnoe = normal/abnormal)
Intensity
depth (normal/dyspnea)
dyspnea: changes in depth, breathing, distressed
symmetry (symmetrical/asymmetrical)
Healthy: Normopnea, costoabdominal (ru more abdominal, car more costal), eupnoea, intensive, normal depth, symmetric, no dyspnea
B. Upper Respiratory System:
Breath from nostrils: Using back of hand → checking:
Intensity, symmetry, volume, odor
Healthy: intensive, symmetrical, normal volume, odor species specific
Nose/Muzzle surroundings:
nose: symmetry, deformation, swelling
Muzzle: moistness, shininess, smoothness, discharge
Healthy: moist, shiny, some/no discharge (bo - normal with serous discharge), smooth, no lesions
symmetrical, no deformities, no swelling of nose
Nostrils:
color, surface, efflorescence, discharge
Healthy: pink, smooth, no efflorescence, some serous discharge
Nasal mucosa
Healthy: pink, smooth, shiny, moist, no swelling, no injuries, some serous discharge, no efflorescence
Nasal and paranasal cavities:
inspection: size, shape, symmetry, injury
palpation: tenderness, consistency
percussion: tenderness, percutoric sound
Healthy: normal size and shape, symmetric, no injury, no pain, hard consistency on palpation, no pain and clear percutoric sound on percussion.
Tapping on sinuses - maxillary (cranially ventrally) and frontal (bw. eyes)
Guttural pouches: inspection + palpation in eq
Pharynx and Larynx:
Inspection: size, shape, symmetry
palpation: consistency, tenderness
healthy: normal shape and size, symmetric, elastic consistency (pharynx), firm-elastic (larynx), no pain
Trachea:
inspection: size, shape
palpation: tenderness, consistency
auscultation: breathing sounds
special: bronchoscopy, transtracheal lavage
Healthy: normal shape and size, no pain, firm-elastic consistency, louder inspiration.
Lower Respiratory Tract:
Topography:
cow/dog: right side: 11 ICS-9ICS-olecranon. Left side: 12 ICS - 9 ICS - olecranon.
Horse: 16ICS-11ICS-olecranon
dog:
Inspection of thorax:
Size
symmetry
local changes
breathing movements
type of breathing
movement of ICS
Healthy: symmetrical walls, balanced ICS, size appropriate to species
Palpation of thorax (fist or fingers in ICS):
temperature, tenderness, consistency, tremor, pain, crepitation, reaction of animal
Healthy: even temp., no pain, elastic, no tremor, no crepitation
Auscultation of breath sounds (listen to 2-3 cycles at each):
Nasal cavity, larynx, trachea (turbulent sound)
bronchioles - thoracic (quiet, laminar sound)
Frequency, intensity, duration, abnormal sounds
Healthy of thorax: laminar air flow without any abnormalities.
Percussion: In ICS, from top to bottom or side to side, 2 taps each place
size, percutoric sound, tenderness
healthy: normal size, resonant percutoric sound, no pain
Examination of GIT
Diet: Appearance, color, odor, consistency, quantity, composition, structure, frequency of feeding, time
Appetite - good/inappetence/anorexia
Feed intake - movement of lips, jaw, mandible
Salivation - normo/hyper/oligosialia (cattle secrete 12L per kg dry feed/day)
Fluid intake, rumination, eructation, regurgitation + vomiting.
Healthy: normal diet, appetite, feed-intake, saliva, fluid-intake.
physiological, chewing, swallowing.
Head - inspect & palpate
normal: no swelling or injury
Oral cavity and pharynx
odor of oral cavity (normal according to diet)
Then we inspect:
tone of jaw muscles, Mucous membranes, teeth, tongue (color, movement, pain, consistency, covering, injuries)
Healthy:
normotonous (of muscles)
pink, smooth, shiny, moist, no swelling, no injuries, no discharge and no efflorescence (of MM)
teeth acc. to species and age, white, no/some tartar.
Tongue is pink, movable, painless, firm-elastic, uncovered, no injuries/lesions
Pharynx: size, shape, changes/swelling, tenderness (look externally)
healthy: normal size and shape, no swelling, no pain
Esophagus:
inspection: swallowing, bolus movement, gas released observed in left jug. groove
palpation: tenderness and consistency (not palpable)
Abdomen:
inspection: from behind in large animals, from above in small
size and symmetry
monogastric (symmetrical) while polygastric - ru (asymmetrical) - apple shape left, pear shape right.
palpation: fullness, tenderness, tension (eq + ca normally tense during palpation)
Percussion: pain, location and extent, percutoric sound
Auscultation: peristalsis
Rumen - q7.
normal: normal fullness and contour, doughy consistency, no tenderness, damped percutoric sound, normal frequency
intensity and duration of rumen contractions: Cattle + goat: 7-14, sheep: 6-16 per 5 min.
Reticulum - Q9.
normal: no tenderness, dull percutoric sound, normal frequency (5-7 per 5 min), quality of reticular contractions, no foreign bodies.
Omasum (right: 7-9th ICS)
palpate for tenderness, percussion - damped sound, auscultate in 10th ICS for quiet sounds of leaves motility (7-8 times/5min). Puncture fluid evaluation for assessing motility - 9th ICS.
Normal: no pain, damped percutoric sound, quiet leave sounds in auscultation.
Abomasum (11-12th ICS right side)
inspection: size
palpation: behind costal arch, right side - pain and consistency
auscultation - should be quiet normally
If abomasal displacement is suspected → perform auscultation with percussion and swinging auscultation
percutoric auscultation: stethoscope in 11th or 12th ICS, with fingers tapping around. → for hearing metallic percussion sound (bad) → perform swinging
normal: normal size, no pain, elastic consistency, quiet auscultation sound
Stomach (Only palpation in su and car)
inspection: size
palpation: size, elastic consistency, tenderness, foreign bodies
normal: normal size, elastic, no tenderness or foreign bodies.
Intestines - topography:
cow: right side (SI ventrally, cecum dorsally)
Horse:
right: cecum caudally, large colon cranially
left: small colon and flexura pelvina of large colon
car: SI right side, LI left side
Intestines - palpation, percussion, auscultation:
palpation: tenderness + tension (rigid in eq + ca)
percussion: tenderness, percutoric sound
bo: tympanic, subtympanic dorsally, dampened ventrally
eq: completely damped
ca: tympanic
Auscultation:
eq: clear loud sound. SI = splashing, bubbling. LI = roaring
ru, dog, pig: quiet auscultatory sound
Defecation: posture and frequency (eq - 8-20, bo-12-24, ca-1-3 a day)
Feces: color (herb - green/brown, ca - brown), consistency (solid, pasty, porridge, watery, mucous), surface (mucoid in horse), odor, comminution degree in herb (high), abnormal content, microscopy.
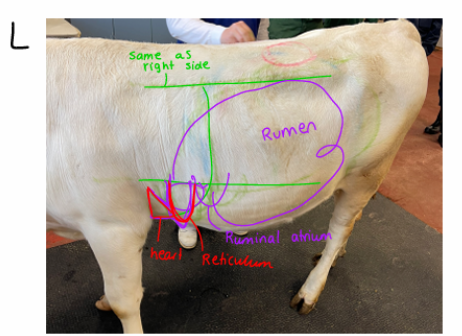
Examination of the rumen in cow
Location of rumen: whole left side of abominal cavity
inspection: fullness and contour evaluation by scoring system: 1 (deeply hollow) → 5 (heavily filled rumen)
normal: 3
Palpation: fist in left flank hollow
frequency, intensity, consistency, pain
normal: doughy consistency, no pain
Percussion: combined with palpation
fullness, tenderness
layering: content - consistency - percutoric sound
gas - elastic - tympanic
roughage - doughy - relatively damped
fluid - elastic - absolute damped
sediment - elastic - dull
Auscultation:
rumen contractions per 5 min: frequency, rhythm, duration - normal
cattle and goat: 7-14/5min
sheep: 6-16/5 min
Examination of the rumen fluid in the cow
Collection: 3-4h after feeding by oral passage of metallic Thygesen/esophageal tube, collection by syringe, attach it to the tube → aspirate → into warmed double jacket container.
Filtrate rumen fluid through cotton for sensory examination. Centrifuge for chemical examination.
Examine within 1-2 hours after collection, including sensory, chemical and microscopic.
Sensory examination
color: various mix of green/brown
pathologic color: milk grey (grain overfeeding), darker green (ruminal stasis), grey with clots of milk (abomasal reflux calves).
consistency: watery, slightly viscous
odor: aromatic, non-repellent
Microscopical:
One drop of the fluid onto slide → 10x
density, motility of protozoa, proportions (L, M, S)
Chemical:
pH: 5,5-7
over 7 - during starvation, inactive microflora, urea poisoning, alkalosis etc.
below 6 - overfeeding of easily digestible carbs.
total acidity: 17-29 titration units
volatile FA: 80-120
Cl conc: < 25 mmol/L
lactic acid: 0.3 - 3.3 mmol/L
Examination of reticulum in the cow
Location: behind olecranon, left side, 6-8th rib
Palpation: not-palpable, but in area of xiphoid cartilage, laterally behind diaphragm in lower third of chest.
fist pressure on both sides → evaluate pain
Percussion: below lung field - 6-8th rib
diagnostic value in foreign body disease
normal: dull sound - resonant in lung field
painful and box sound in case of reticuloperitonitis
Auscultation: 10cm behind elbow both sides, behind 7th rib
Check: number and quality of reticulum contractions: 5-7/5min
biphasic contraction: one leading to rumen and one gives fluid to omasum
weak crushing/swishing sound
Test for foreign bodies in reticulum:
Principle: cause or increase pain
back grip: grab skin fold over withers. Inspiration = inflamed area moves = animal shows pain or interrupts expiration
normal breathing = no pain
pole tests: 2 people place metal pole on ventral part of
abdomen. From sternum to udder. Lift pole then suddenly lower. 3rd person observe signs of pain.
Pressure on reticulum: press with fist with support of knee.
Percussion: percutoric sound and no pain (pain + box sound = traumatic peritonitis)
downhill or circlic movement: animal refuses to move down slope or in a circle = pain. Little diag. value.
ferroscopy: detect metal object by ferrite magnet being swallowed.
Other: zone test (low diag. value, create small skin fold in painful area), Ultrasound
Positive test: grunting, teeth grinding, interruption of expiration, sweating, incr. movement of an animal or kicking towards the painful area.
Inflammatory pain (traumatic reticuloperitonitis), injury pain (penetrating foreign bodies)

Examination of Liver
Topography:
Bo: 11-12 th ICS right side
Eq: not in contact with wall
sRU: right side, same as cattle, might extend beyond costal arch
Ca: right side: 10-13th rib, left side.: 10-12th rib (palpate laying on back)
Inspection:
Looking at sclera, skin mucous membranes (jaundice)
Neurological signs - depression, coma
Nutritional state - anorexia, weakness, poor nutrition, colic (abdominal pain - kicking)
edema formation (fall in plasma protein)
ascites - accumulation of fluid, abdominocentesis.
hemoglobinuria
Feces change (steatorrhea, diarrhea)
Palpation (not in horse):
size, position, pain, consistency (firm-elastic)
non-palpable in healthy cows - palpable in very thin cows or in case of enlarged liver
Percussion:
ru: 11-12th ICS
ca: 10-13th ICS
dull percutoric sound, size, tenderness
Special examination:
biopsy (horse: 12-14th ICS, cattle: 10th ICS)
USG, MRI, CT, laproscopy
Lab methods: biochemical (conc. of bilirubin, hepatic enzymes)
Liver enzymes increases:
ALT (alanine transaminase - liver necrosis)
AST (aspartate aminotransferase - liver damage)
LDH (lactate dehydrogenase
ALP (alkaline phosphatase - cholestasis)
GMD (glutamic dehydrogenase - liver damage)
Icterus:
pre-hepatic - hemolytic
hepatic - liver damage
obstructive - problem with bile system
spleen: not extending costal arch, located on left side - normal. can examine by special - like USG or x-ray.
Examination of the urinary system
Topography:
Anamnesis: info about water intake, urinary behavior, changes in volume and quality of urine.
Inspection:
Posture
Frequency
changes in amount and quality
free of pain/dysuria
Normal: normal posture, frequency + volume of urination.
Palpation:
rectal examination in large animals, external in small
size, pain/tenderness, consistency (firm elastic), surface (smooth)
Percussion (ONLY CATTLE)
right kidney, size and pain
dull sound without enlargement and pain.
Special examination: X-ray, USG, renal function test
biopsy (bovine, left behind costal arch 5-10cm below 1st lumbar).
Ureters: normally not palpable, can feel rectally if ureteritis.
Urinary bladder palpation: rectal examination in large, through abd. wall in small
size - according to fullness
adhesions - no
consistency - elastic
pain/tenderness
presence of foreign bodies
(normal size, elastic, no pain, no foreign)
special: USG, Cystoscopy-color, bladder mucosa, x-ray
inflammation = cystitis.
Urethra:
Females: Inspect vaginal cavity - orificium urethrae with vaginal speculum, digital palpation/urethroscopy - size, shape, injuries, lesions and foreign objects
males: urehtroscopy, palpation of penis, perineal area - consistency (elastic), pain
Examination of the urine
1) Urine collection:
Horse & cattle: spontaneous, catheterisation and induced urination (stroking vulva/perineum (cow/mare), stroking preputial sac (bull), glove in front of nostrils/mouth in small ru for 30-60s).
Dog: spontaneous, catheterisation & cystocentesis
2) Sensory urinalysis:
colour - yellow (urochrome)
transparency - transparent, cloudy in horse
consistency - water, viscous in horse
odour - pleasant in herbivores (aromatic odor of urine of ruminants), unpleasant in carnivores, fruity smell = ketosis
abnormal content
specific gravity: 1.010-1.065
3) Chemical Urinalysis: (By pH strip and PHAN papers)
pH: ru and eq: 7-8, car: 5-7
proteins-low to none
enzymes - none
glucose - none
ketones - minimal
bile pigments - bilirubin and urobilinogen
4) Microscopic Urinalysis:
Organic sediment: cells, bacteria
Inorganic sediments: crystals
Cattle & horse: calcium carbonate, calcium oxalate, calcium sulphate and others are found.
Dog: phosphates, urates, cysteine, oxalates are found.
Calcium oxalate = antifreeze poisoning
ammonium biurate = liver failure
cysteine uroliths = congenital, tubular defect
Examination of locomotor system
1) Posture: Seen from cranial, caudal, lateral position
Regular/irregular
Stiffness: muscle disorders
Kneeling: pain in distal parts of limbs (fracture. laminitis)
Crossing of legs: fractures of claws (ru, pig)
Dog sitting position: acute gastric dilatation in horse, achilles/hamstring tendon rupture, nutritional muscular dystrophy, paraparesis
2) Position
Normal: Animal is able to stand up without assistance
Test with external stimuli
cattle: hindlimbs first, horse: forelimbs first
3) Movement/Locomotion “Rabbits run fast downhill”
make animal walk - evaluate rate, range, force, and direction (normal: even length + direction of steps)
Locomotor scoring system:
Normal gait
mild lameness (stand with flat back, arched when walking)
moderate lameness (stand and walk with arched back)
lameness (shifting weight from affected leg)
severe lameness (cannot walk on affected legs)
4) Muscles
Inspection: size and shape - normothrophy and symmetrical
Palpation: muscle tone, pain, temperature
normotonus, no pain, even temperature
5) Bones
Inspection: shape and contour - normal shape and contour
Palpation: consistency, sensitivity, crepitation
hard consistency, no pain and no crepitation
6) Joints
Inspection: size and shape, extent of bending and flexing
normal size and shape, regular flexing and bending
Palpation: temperature, pain, consistency
even temp., no pain, consistency
special examination: x-ray, examination of puncture fluid (collection of synovial fluid, normal: clear, colorless (yellowish opalescence), no smell, coagulates in 48h)
7) Foot examination
Inspection: normal size, shape
palpation: no tenderness
percussion
pressure test or probe
Examination of the nervous system
A. Skull and Spine
Inspection:
changes on Skull cover: volume, loss of substance, integrity, pain, flexibility of bone base
normal: normal size, shape and position, stiffness, no loss of substance, normal integrity, no pain
changes of spine and neck: Lordosis (inward curvature), scoliosis, kyphosis, Opisthotonus (head + neck arched backwards)
generally: size, shape, position, stiffness
Palpation: tenderness, consistency
Percussion: tenderness
B. Sensorium
Consciousness: bright/alert
deviations: depression or excitation
C. Sensitivity
Superficial
a) pricking skin along whole body
b) Pinch interdigital skin/skin above hooves
In ru: interdigital spaces with hoof testing pliers or blunt end of percutoric hammer. (Normal: present)
Deep
a) Bending head and neck to one side
b) crossing legs
small animals:
Wheel barrowing (forelimbs)
Hopping (forelimbs)
Proprioceptive positioning (all limbs)
Extensor postural thrust (hindlimbs)
Placing (forelimbs)
Sensory
a) Eye - vision loss = amaurosis
b) hearing - anacusia (no hearing)
c) smell - anosmia (no smell)
Described: normal, exaggerated, diminished or absent.
D. Reflexes - cranial nerves (10)
menace - vision
palpebral - medial canthus of eye
mandibular touch
vibrissae - touch upper lip
auricular - touch ear
corneal - touch cornea with hair
pupillary - by light
oculocephalic - move head to one side, move quick to other side (nystagmus)
Gag - touch larynx
tongue movement and symmetry
F. Reflexes - spinal cutaneous nerves:
Panniculus - examined by irritating skin by sharp object along spine and hips
withdrawal - interdigital pinch/hoof (positive - withdrawal of foot)
anal/perineal reflex - touch around anus
G. Reflexes - Spinal limb (ONLY CAR!)
Front limb:
Triceps - tap tendon over olecranon
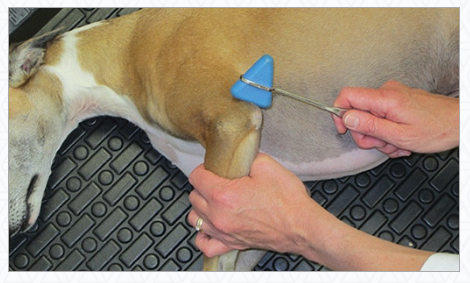
extensor carpi radialis - tap dorsolateral on leg
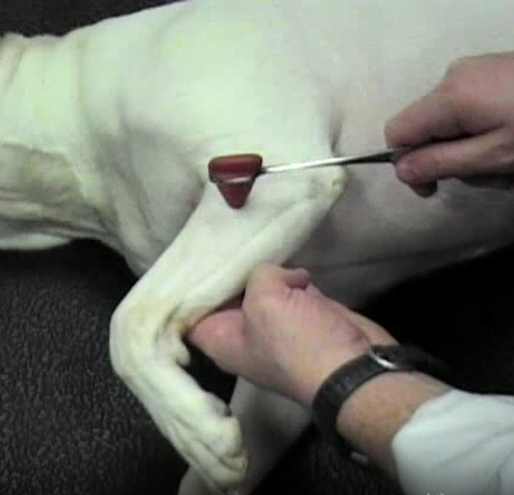
flexor - stretch limb maximally and release → flex
Hind limb:
patellar - tap patellar ligament
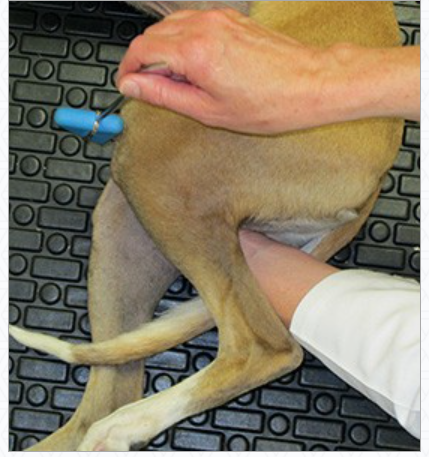
cranialis tibialis - dorsolateral part of leg
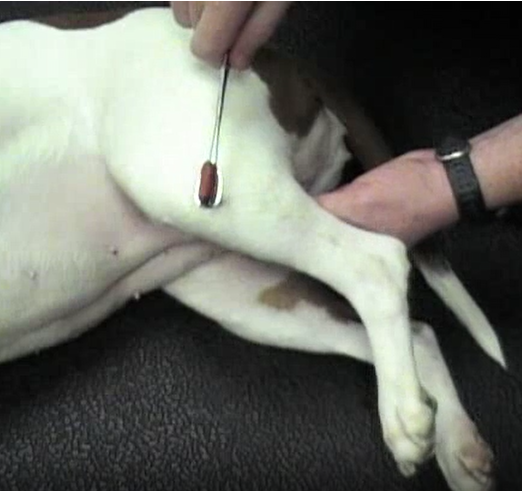
flexor - stretch limb max. and release → flex
H. Motor disturbances: no qualitative (ataxia) or quantitative (paralysis, spasms, tremors, nystagmus, or forced movement), disturbances present.
examination of the mammary gland
Anatomy of Mammary gland
Cattle: 4 glands, one lactiferous duct per
Horse: 2 glands, 2 lactiferous ducts per
Anamnesis:
Previous lactation (milk yield, prev. disease)
stage of lactation (1st, 2nd, 3rd, dry-period)
Zoo hygienic conditions
Previous and current problems in the herd
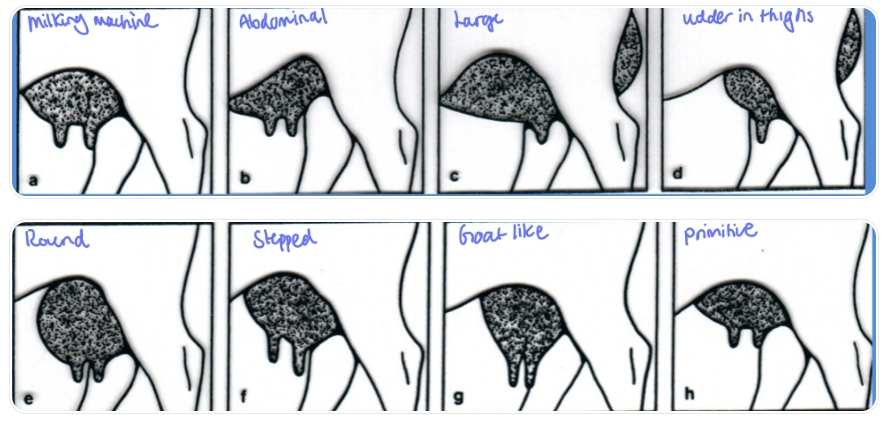
A. Inspection udder:
Shape: key shaped optimal
abdominal, large, caudal, round, stepped, goat-like, primitive
Size: medium and large optimal (L, M, S)
Symmetry: fore-hind asymmetry, right-left symmetry - right is smaller (seen from behind in healthy), left-right symmetry - left is smaller.
Skin: Color, soiling, hair, temperature, efflorescence, injuries, ectoparasities
normal: pink, unsoiled, reasonable hair, even temp., no efflorescence, injuries or ectoparasites
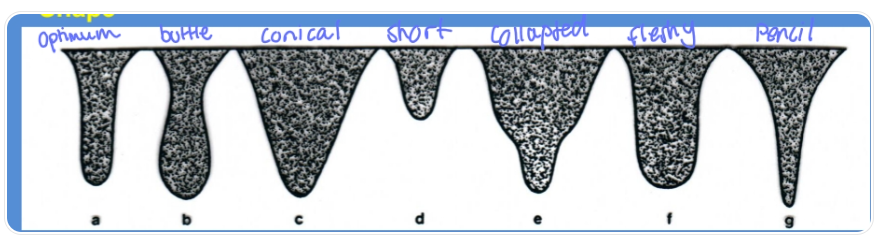
B. Inspection of teats:
shape: cylindrical optimal
other: Bottle-like, pencil-like, conical, short, collapsed, fleshy
Size: 8-10cm
surface: smooth
number: according to species
supernumerary teat: cranial, accessory, intermediate
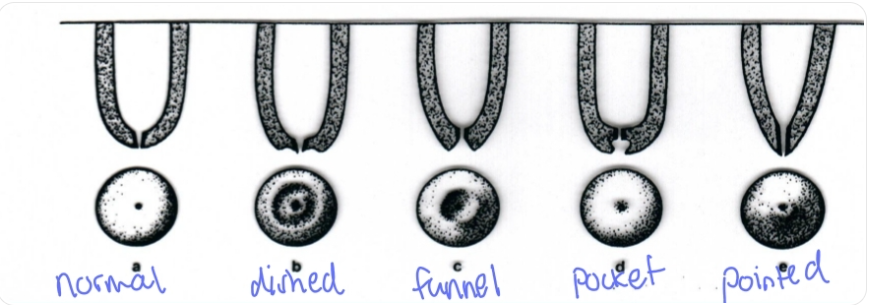
Teat end: normal with rounded tip
other: dished teat with flat tip, funner or crater, shaped, pocket, pointed
Dripping from teats, hygiene under udder, behavior of animal
C. Palpation of Udder: Palpate after milking from right side, palpate symmetrically with both hands
Parenchyma (normal case): structure (fine-grained), consistency (soft-elastic), no pain, temperature the same as environment
if mastitis: structure is non-palpable, firm consistency.
D. Palpation of teats and lnn.
Teats and cisterns are painless, elastic, sphincter is firm-elastic
Lymph nodes: no enlarged, plum-shaped, symmetrical, firm-elastic, homogenous, smooth, painless
E. Examination of secretions
1)Sensory:
Volume, color (white, milky, colostrum = yellow), consistency (water/milky), odor (typical), abnormal contents (blood, flakes, fibrin, pus, blood clots, serous secretion).
2)California Test:
1ml sample + 1 ml test, coagulation/gelification occurs if positive. (incr. somatic cells, red color).
Plastic paddle: A right front, B right hind, C left front, D left hind
3)Chemical:
pH (6-4-6.8)
Cl conc. < 1.5g/L (incr. in mastitis)
Fat: circa 3.5%
lactose: circa 4%
Proteins: casein - 2.7%, globulins 0.1%
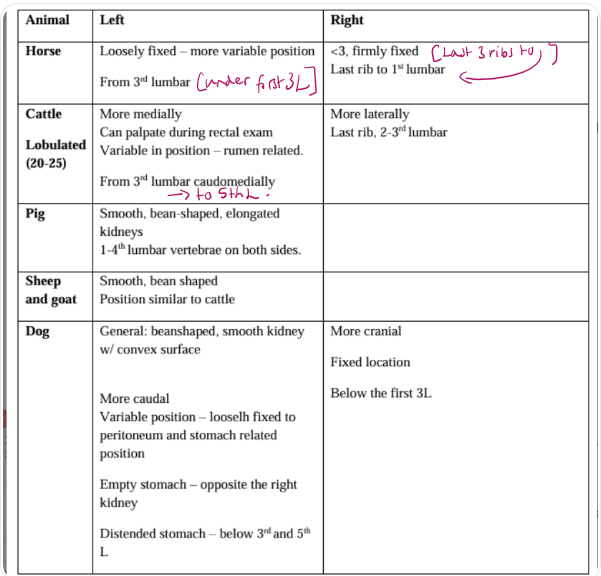
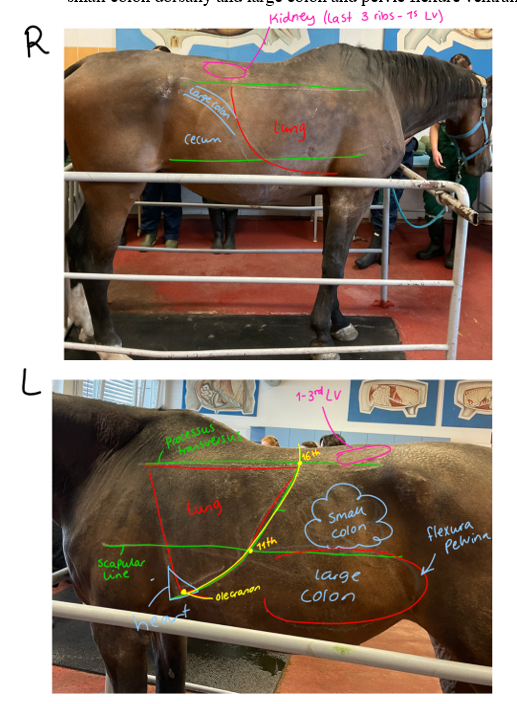
Topography of the horse
Lung field: dorsal line, 16 ICS - 11th ICS - olecranon
Kidneys:
Right: heart-shaped, firmly attached. Last 3 ribs → L1
Left: L1 → L3, looser attached
Heart:
Right: 3-4 ICS
Left: 3-5 ICS
Liver and intestines:
Right side: cecum caudally, large colon cranially, in front of cecum
left side: small colon dorsally, flexura pelvina of large colon ventrally
Liver: in concavity of diaphragm
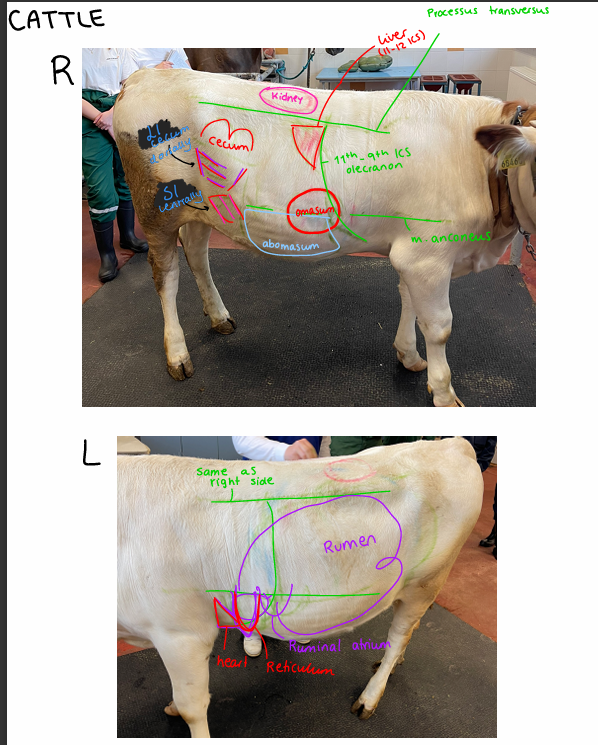
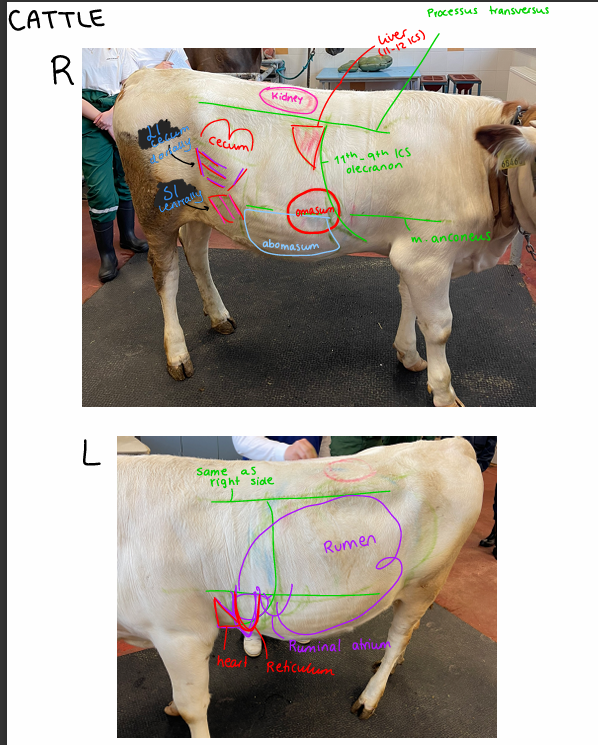
Topography of the cattle
Lungs:
right side: dorsal line, 11th ICS - 9th ICS - olecranon
Left side: dorsal line, 12th ICS - 9th ICS - olecranon
Kidney:
Right: last rib → L2/L3
Left: depends on rumen content, from L3/L4
Heart:
3-4th ICS left side
Liver:
11th-12 ICS right side
Stomach:
Right side:
Abomasum: 11th-12th ICS (immediately behind costal arch ventrally)
Omasum: 7-9 ics (15 cm diameter)
Left side:
rumen: all over
reticulum: 6-8 ICS
Intestines:
Small intestine: ventrally
cecum between SI and Colon (right side)
colon: dorsally