Quiz 2 - History of Art and Design
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What was important to the Roman culture at this time?
conquest and administration
militaristic society
used art to tell stories
What was happening socially and politically during Ancient Rome?
military expansion spread into other areas = dominance
conquer lands, spread their language, law and religion
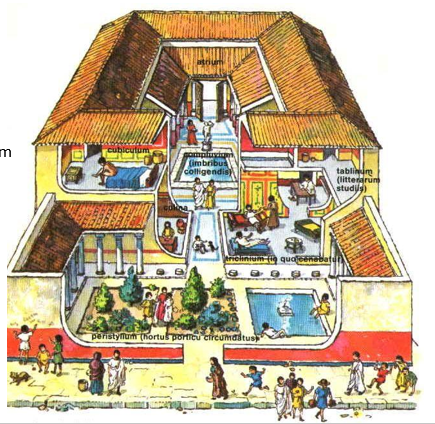
Domus
single homes for the wealthy
entry was through the atrium
there are no exterior windows to allow for privacy from the street
built with stone, plaster and brick

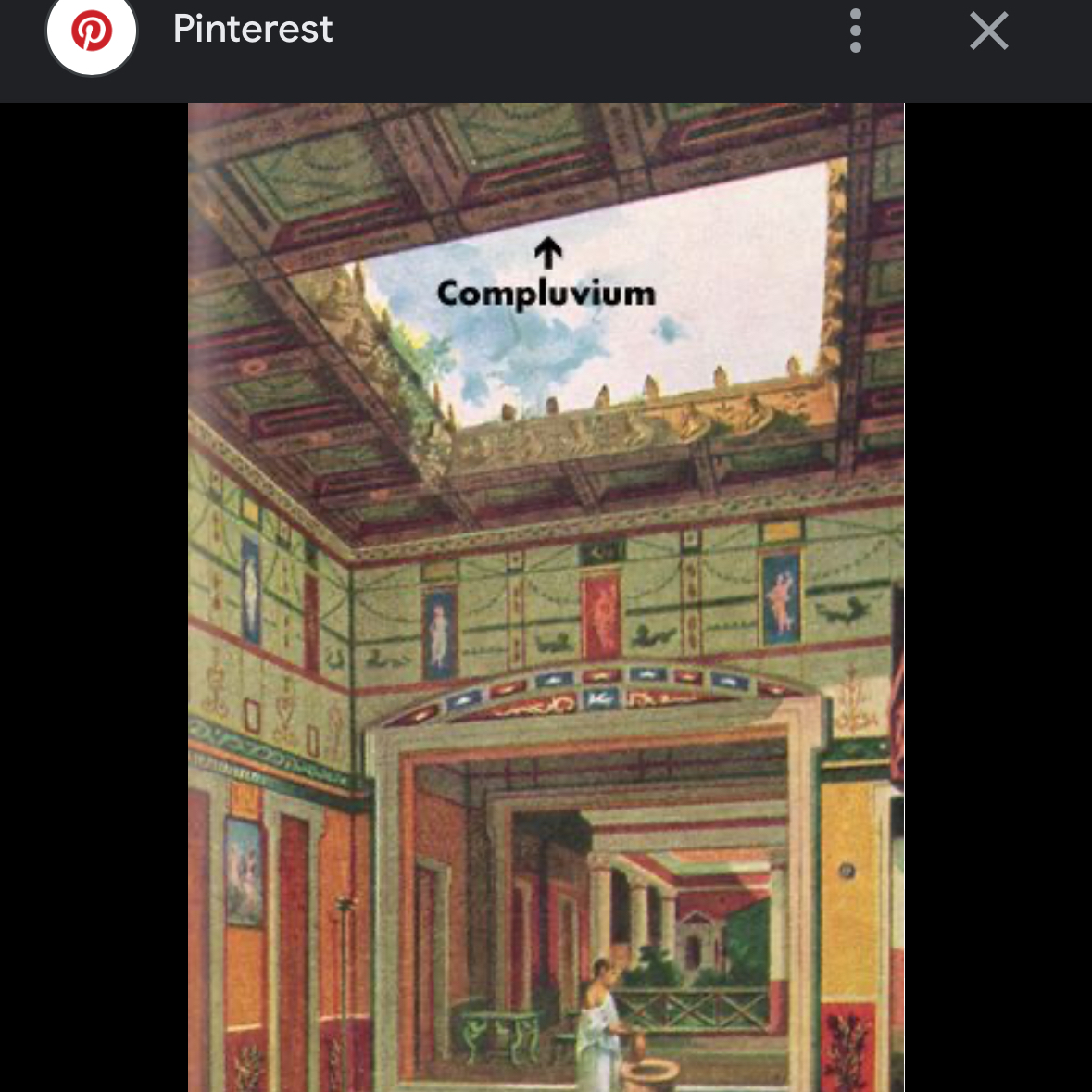
Compluvium
Skylight used to let in light and rainwater
Impulvium
sunken floor basin used to collect rainwater and channel it into cisterns

House of silver wedding
archaeological remains of a roman house in Pompeii
was found buried in ash

Insulae
What were they?
Who lived where?
Rome
typical middle or lower class dwellings
concrete apartment blocks; rarely had interior plumbing
rise as high as five stories
housed up to 50 people
ground floor was shops; wealthiest lived on ground floor
the higher up you lived the poorer you were and the more risks they took with their safety in regards to the building

The Forum
an outdoor public space/market with a temple
open space, square or rectangle bounded on three sides by colonnades with the fourth side being a basilica
center for civil and social activity
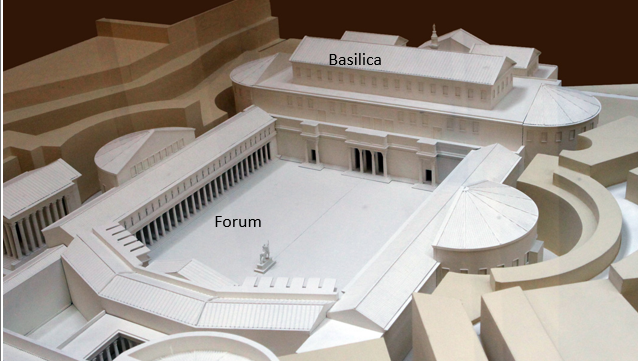
The Basilica
huge roofed building that acted as a municipal hall and law court
divided into three aisles
central main aisle flanked by 2 smaller aisles with rows of colonnades

Basilica Ulpia
Where is it located?
What did it contain?
located at the end of the forum
3 aisles:
main central
two smaller ones
the apses contained statues of gods or thrones emperors
also contained libraries
interior was marble and bronze

The colosseum
referred to as an amphitheater
used for sports events
constructed of concrete and stone with an exterior covered in travertine marble
held 50,000-80,000 spectators and would host 100 days worth of events
consists of rows of arcades and has superposed classical orders: Tuscan, ionic and Corinthian
the corridors employ vaults: barrel and groin


The Pantheon
What was it dedicated to?
What was special about it architecturally?
Was the first building of its kind to have a concrete dome
Temple dedicated to 5 planetary Gods
Jupiter
Mars
Mercury
Saturn
Venus
Comprised of portico and rotunda
Domed space has illumination from the oculus

Trajan’s column
125’ high
marble: originally painted
interior spiral staircase
continuous storyline by showing a story from bottom of column to top
tells us about the life of romans a the time

Public Baths
places for bathing, socializing and swimming
men and women bathed at different times or areas

Young Flavian Woman
Marble
25”
Bust: Funerary Art
Carved in idealized beauty
showed the movement away from realism to idealism in art

Material?
What did this pose symbolize?
What was this statue used for?
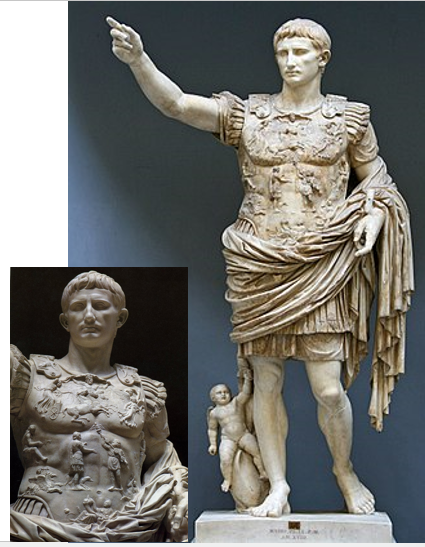
Augustus of Prima Porta
Early 1st century of A.D
Marble
6’8” high
had mother earth with a cornucopia on his breastplate
symbolized plenty of food and rome’s dominion over earth
Arm stretched out in peace to show he us humble
strong example of art used as propaganda
Augustus lived a hedonistic life

What is it?
Style?
Features?
Soothsayers: Villa of Cicero
1st style: Roman mosaic
Hellenistic
Small coloured stones and tiles with grout
facial features are exaggerated
found in homes and public buildings

Villa of Mysteries
What is it?
Where is it?
Pompeii
2nd style fresco
narrative fresco mural that wraps around the room
background is known as ‘Pompeian Red’
Ritual involving the God Bacchus and a wedding scene
No shadows. Images are flat and lack perspective depth.

what is this
Early 4th Style fresco
‘Still Life’: Herculaneum
depicts volume and light within the painting. Tries to get a sense of round and attention to detail
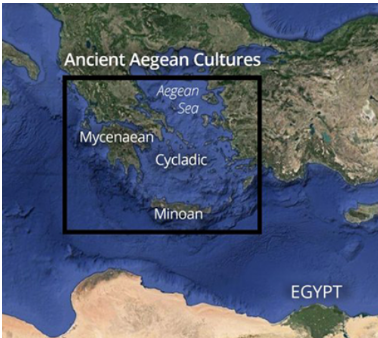
Aegean - Cycladic Civilization, Minoan Civilization, Mycenaean Civilization
Where were they located? (where did they live?)
What was their culture like?
What are frescos? They were discovered underneath what?
Cite two main influences of Minoan-Mycenae culture on the Greeks or Romans.
Civilizations of Greece around the Aegean Sea.
The Cycladic Islands
The Minoans of Crete
The Mycenaeans of the mainland of Greece
Greeks used art to idealize - A renaissance (rebirth) in government, philosophy, art, literature, drama, mathematics, astronomy, and science occurred.
Frescos are the art of painting on plastered walls. They were hidden within the city of Pompeii
Religion and Mythological beliefs & Art and Architecture
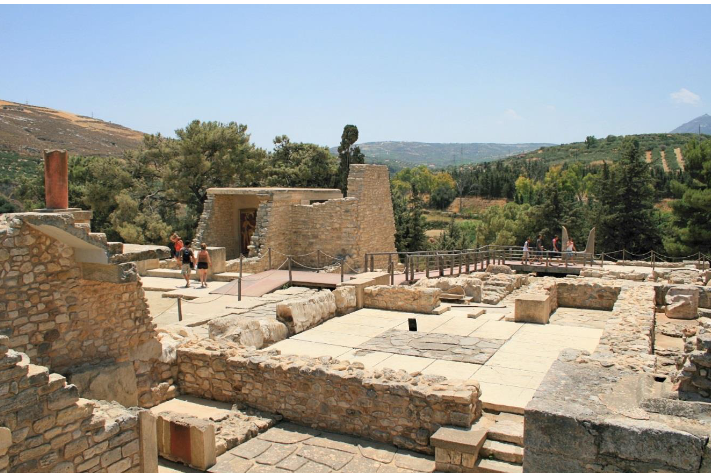

Palace of Minos (Knossos)
State elements of its structure + architecture
Red columns
The structure was made of a combination of stone masonry, rubble, plaster and wood.
Artwork on the interior walls (frescos)
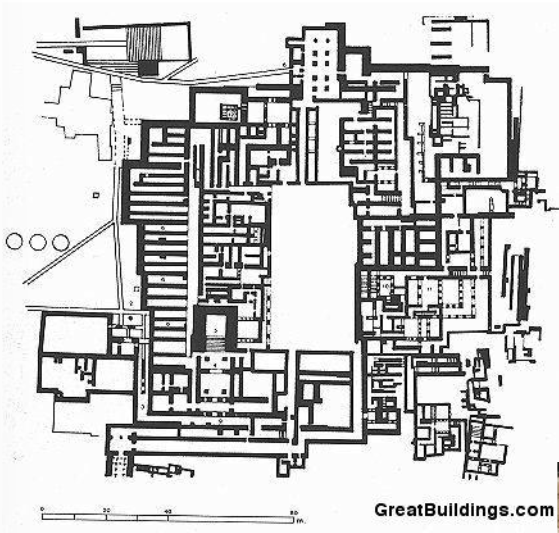
What is this?
Palace of Minos (Knossos)

What is this place?
Palace of Minos (Knossos)

What is this?
Palace of Minos (Knossos)
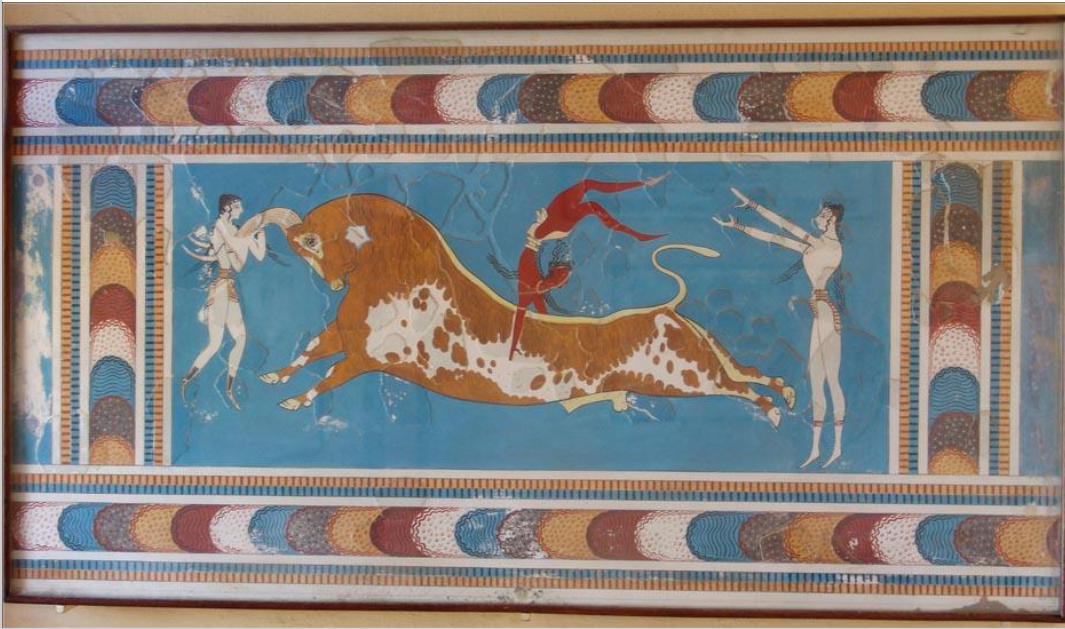

What is this and what’s its story? What is the meaning of it?
The bull-leaping fresco
It is a restored fresco on the walls of the Minoan palace at Knossos in Crete. It shows a bull-leaping scene.
It is significant to Minoan culture as it underlies man’s somewhat mastery of nature. This is reaffirmed each time human triumphs over animal.
What were Megarons
Ancient Greece/Classical architecture
Their temple plans were derived from the ‘megarons’ found in Mycenaean palaces - their temple plans were derived from the ‘megarons’ found in Mycenaean palaces.

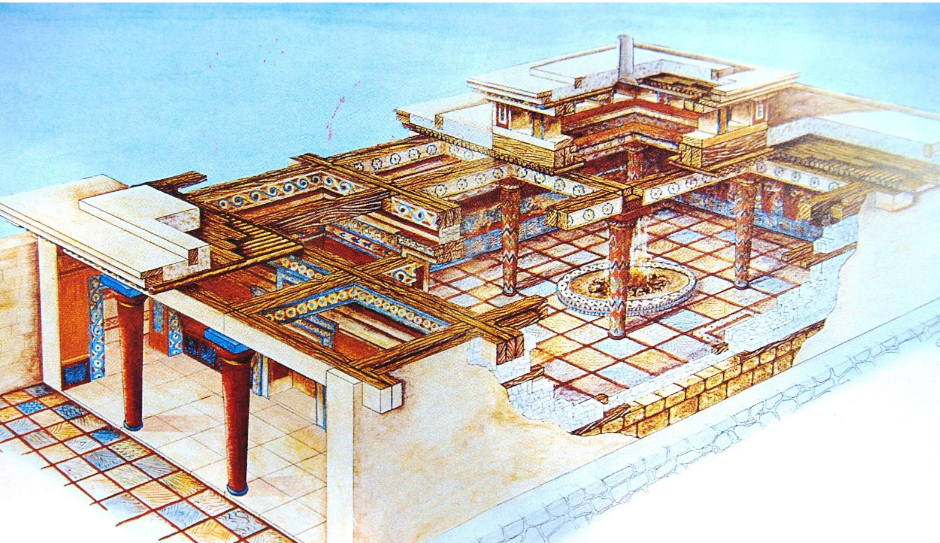
What is this an example of?
A Megaron - these were how their temples were planned out.
It was the great hall in Mycenean and ancient Greek palace complexes. Architecturally, it was a rectangular hall that was surrounded by four columns, fronted by an open, two-columned portico, and had a central, open hearth that vented through an oculus in the roof
What are tholos and what are their purpose?
It is a round structure with a circular wall and a roof, usually built up on steps and often with a ring of columns supporting a domed roof.
They were used as large ceremonial tombs.
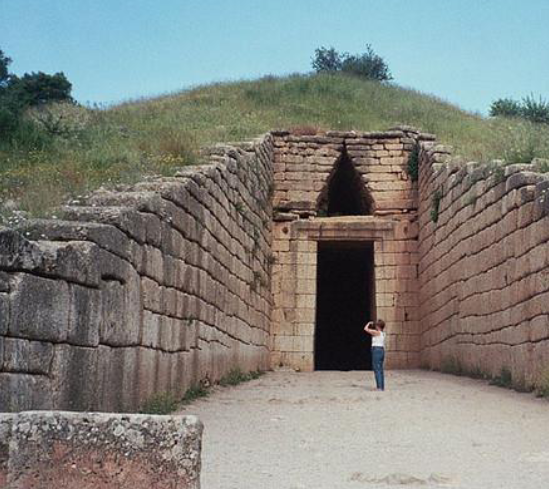
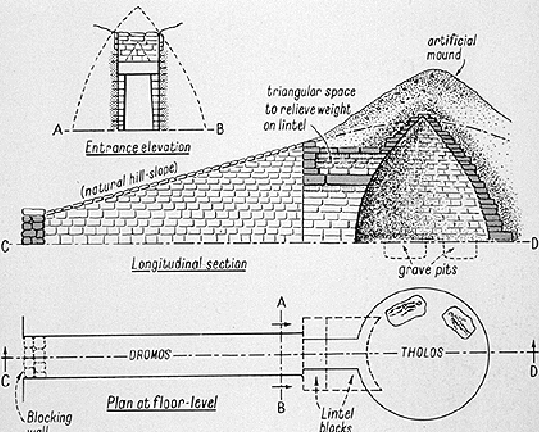

What is this and whats its purpose
It is a round structure with a circular wall and a roof, usually built up on steps and often with a ring of columns supporting a domed roof.
They were used as large ceremonial tombs.
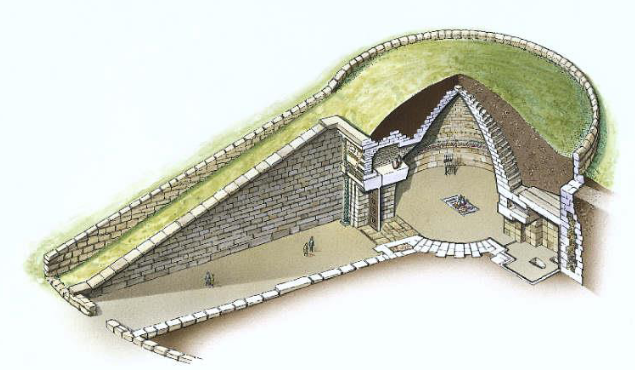
Ancient Greece
What was important to the Greek culture at this time? (what was valued)
What was happening socially and politically?
Athletic skill was admired and the Greeks began the Olympics in 4 year segments. The Olympics were so important - all wars on Greek territory were halted so competitors could travel safely.
Democracy was established - Independent city-states were created with the requirement that male citizens had to participate in their government. Even though slaves were still kept and women weren’t allowed to be involved in politics - the basis of democracy was established within the Greek city-state. - their influence extended to Ancient Rome
What are Amphoras?
Means grave marker
Upon death, the dead were buried intact with a grave marker (memorial) rather than preserved (Egyptian).
These decorated vases were placed on grave sites as a mark of elite status.
What were the 7 styles of Ancient Greece?
Geometric Style
Orientalizing Style
Archaic Style
Late Archaic Style
Classical
Late Classical Style
Hellenistic Style
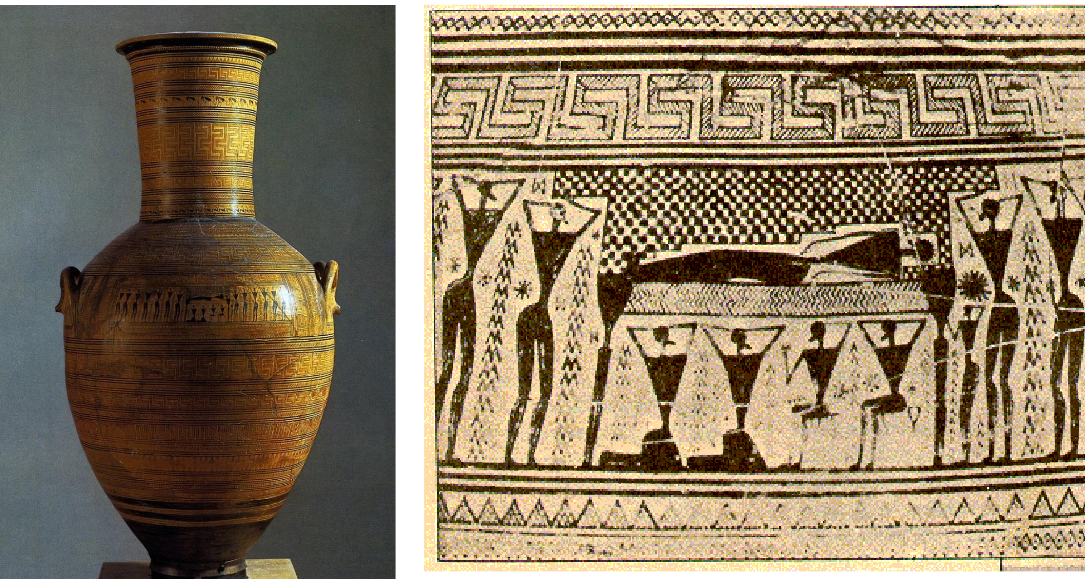

What is this and what is the detail showing? What is the style?
Geometric amphora
Geometric Style
5’ 1” high
Terracotta painted with dark glaze
Thus amphora was a grave marker and shows a scene of ‘prothesis’: lying-in-state- of the dead.
The deceased is lying on a horizontal bier, held up and flanked by mourners. The figures are geometric in shape: triangular torsos and round heads.
Each geometric pattern is framed by circular horizontal borders with two rows of animals proceeding around the neck of the vessel.
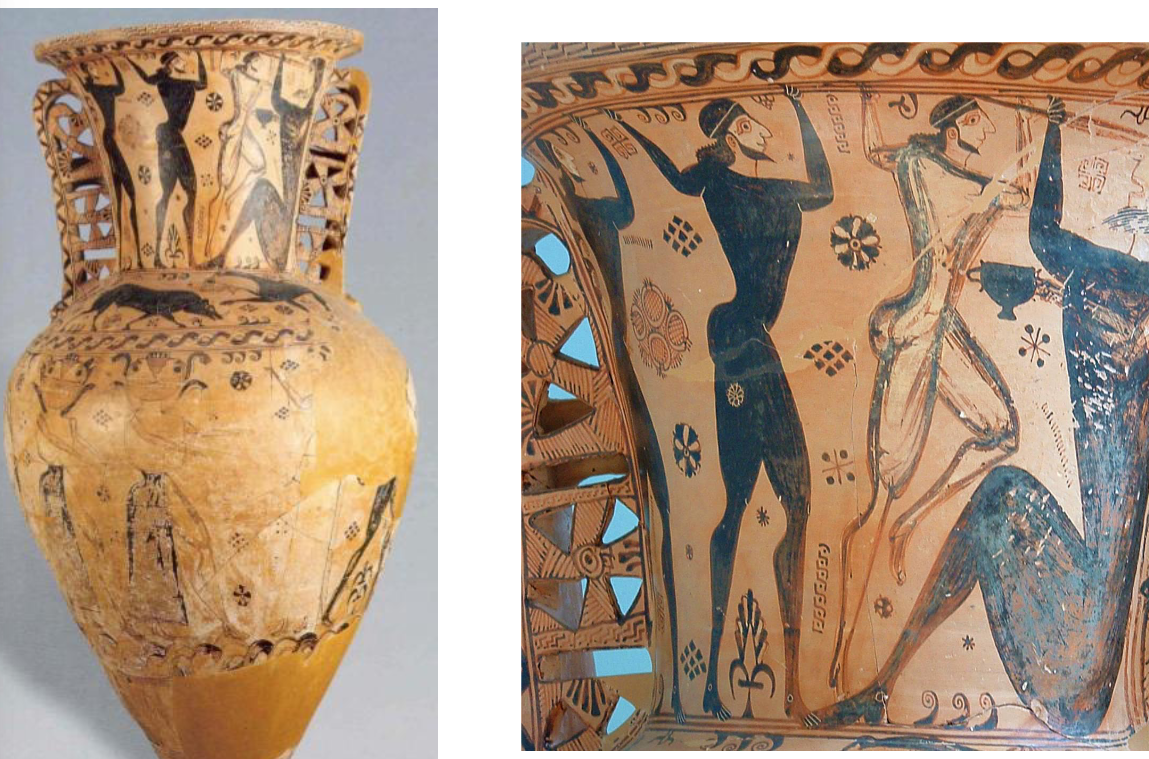

What is this and what is the detail showing? What is the style?
Orientalizing Style Amphora
Orientalizing Style
4’ 8” high
Terracotta
Polyphemos Painter amphora
This scene shows Odysseus driving a spear through Cyclops Polyphemus' eye after he ate some of the sailors.
Influences from the Near East and Egypt started to influence Greek art. Shapes became larger and curvier than the geometric style. Geometric patterns become borders.

What is this and what is it showing? What is the style?
Archaic Style Amphora
Archaic Style
24” high
Terracotta with ‘black figure’ painting
Signed by Exekias (potter & painter)
‘Achilles and Ajax Playing a Board Game’
Patterns become a boarding device - Narrative themes become central.
Dominance is shown in the figure on the left (Achilles) suggesting he’ll win the game. Ajax has removed his helmet, he’s leaning over the board with his head lower.

What is this and what is it showing? What is the style?
Late Archaic to Classical Style Amphora
21’ high
Niobid Painter: red-figure painting
‘Death of the Children of Niobe’
The red-painting techniques allowed for greater detail in the figures
Niobe was a human woman who boasted she was greater than the Goddess Leto because she had fourteen children. Apollo and Artemis reacted to this boast from a mortal woman and killed all of her children with arrows
Two of the fallen children are seen on the foreground in front of the narrative.
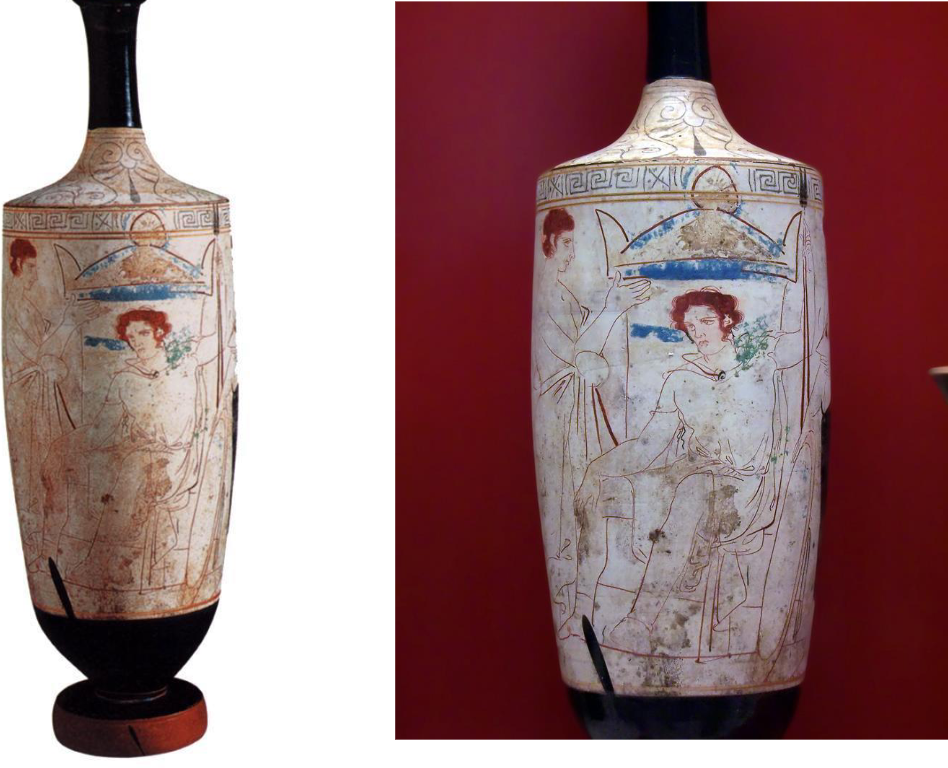

What is this? What is the style? What’s different about it from previous artwork?
Classical to Hellenistic Style
19” high
Terracotta: white-ground
Reed painter
‘Warrior by the Grave’
Greek art begins to get more realistic and natural looking.
Foreshortening is introduced and the bodied get more expressive.
This is a grave dedication. The mourner is sitting by the grave, he’s bending from the waist and his head is angled showing contemplation.
Note: look at the face - its three-quarter profile. (different from the side profile from Egyptian art)

What is this? The style? Style choices?
Statue of Kouros
Ancient Greece/Archaic
76”
Marble
Kouros: youth or boy of rank
These were either grace markers or individuals being honored in religious ceremonies
Stylistic links to Egypt evident in stance

What is this? The style? Observations about her?
Statue of Peplos Kore
Ancient Greece/Archaic
4’ high
Marble
Kore = girl
There are traces of paint on her rove which indicates the statues were painted. She may have been a depiction of the Goddess Athena.
Named for peplos: a woolen dress
Note her face: the lips are curved in a smile and her cheekbones are indicating it through the lift of the facial muscle.

What is this? Style? Observations?
The Kritios Boy
Early Classical Style
34” high
Marble
This is a radical departure from sculpture before its creation and occurs around the time the Athenians were fighting with the Persians (King Darius I invasion then his son Xerxes’ invasion).
After the final defeat of the Persians in 480 B.C.,
sculpture becomes less stylized. The smile is gone and comes neutral in expression. The torso shifts and there’s movement in the head: contrapposto pose (weight on one foot).
Natural representation of the human body
Softer and not exaggerated
Artists thought sculptures like this lacked interest
Note: the ‘acorn’ hair - helps identify early Classical style.
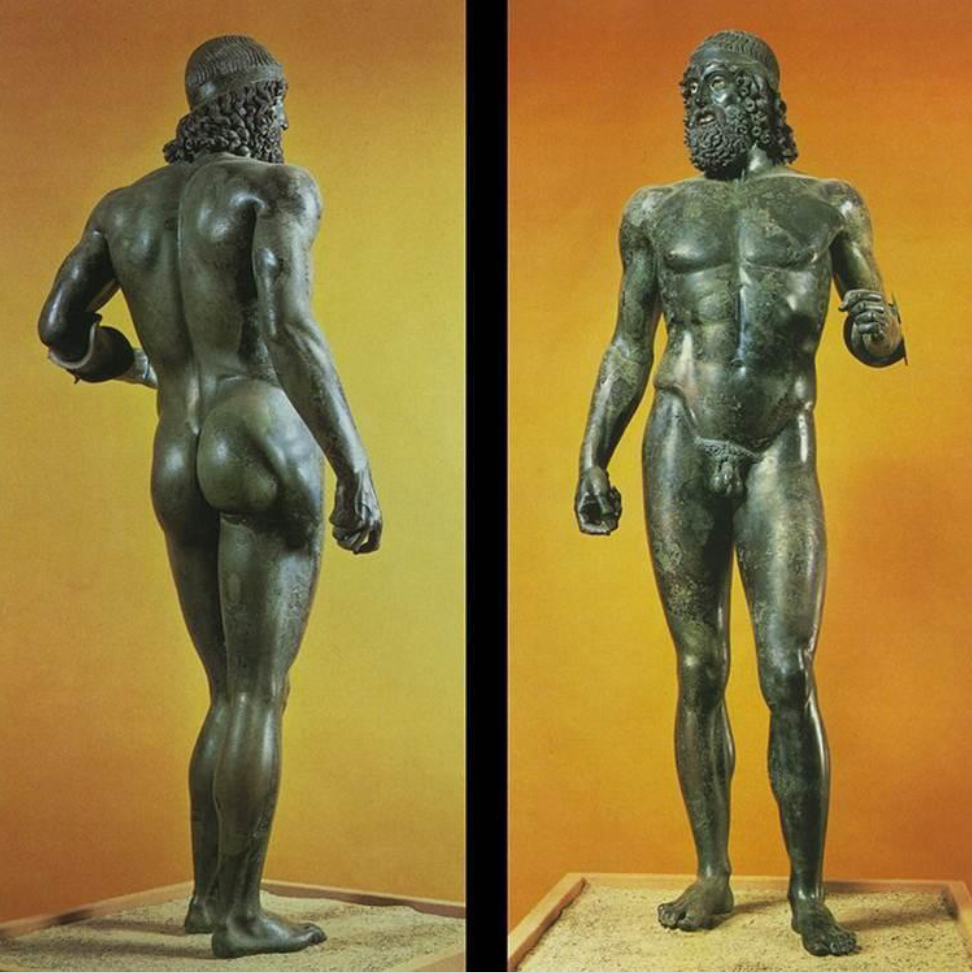

What is this? What is the style? What is different about this style.
Warriors from Riace
Early Classical/Classical Style
6’ 6” high
Bronze with bone, glass paste, and copper inlay
The hair and dome-shaped head reference early Classical Style, the dynamic form and more natural appearance are indicative of Classical style.
Note: A shift away from ‘naturalism’ to exaggerated muscles and lines within the form
Exaggerated features of the human body
Unrealistic representation of the body
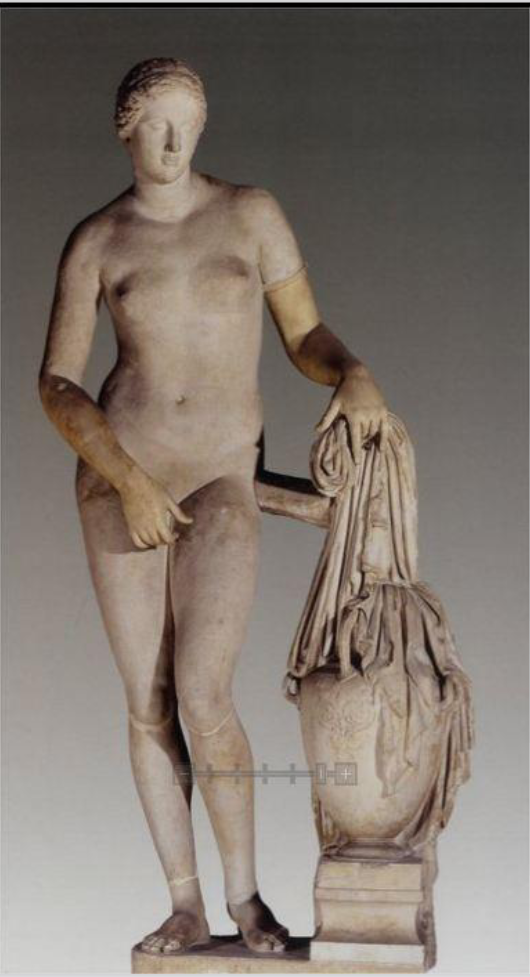

What is this? Style? List observations about the sculpture.
Aphrodite of Knidos
6’ 9” high
Marble
Praxiteles: Late Classical Style
Roman copy of the original
S-curve known in his work
She’s fleshy in her body and face.
It was a commissioned piece by the city of Kos located on the Island of Kos. It was rejected because of its portrayal of a nude female - this was shocking.
She is reaching for her drapery indicating modest, but the position of her hand draws the viewer's attention.
Praxiteles’ female nudes became part of the canon of art.
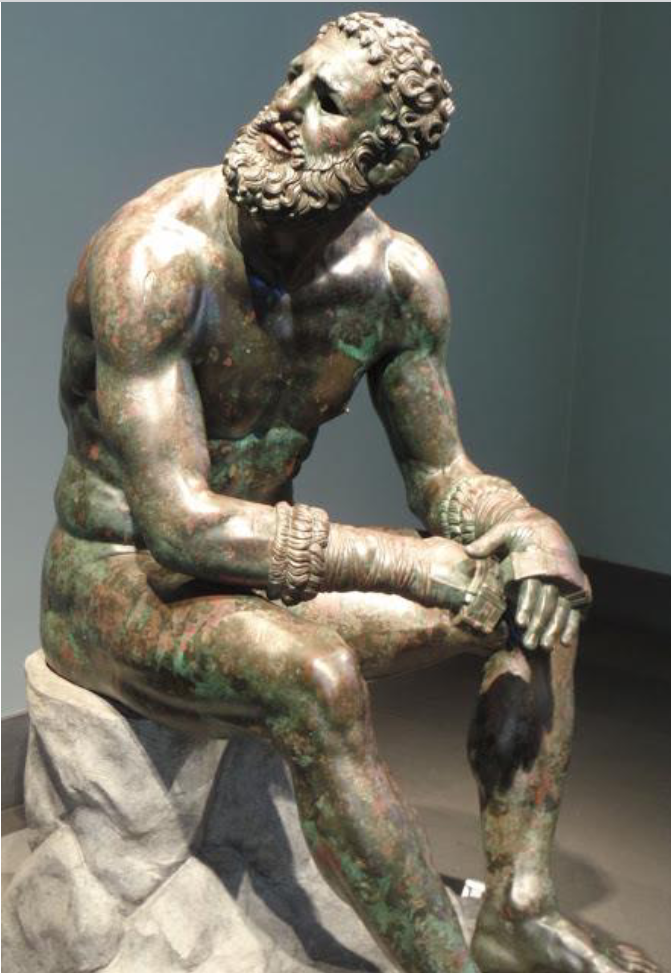

Who is this? Style (period)? Why was this sculpture different from previous ones?
Boxer
Hellenistic Period
4’ high
Bronze
This sculpture is highly realistic in its portrayal. Rather than idealizing the fighter as he would have been in previous periods, he shows cuts and scars on his face and torso. This was highlighted by the sculptor with the use of red/orange copper inlay.
His flesh is sagging in the middle showing his age.
His face is full of expression of weariness: his nose is broken, his ears are damaged (cauliflower ear)
On his hands are leather knuckle straps that were commonly worn when boxing and would have inflicted serious damage on their opponent.
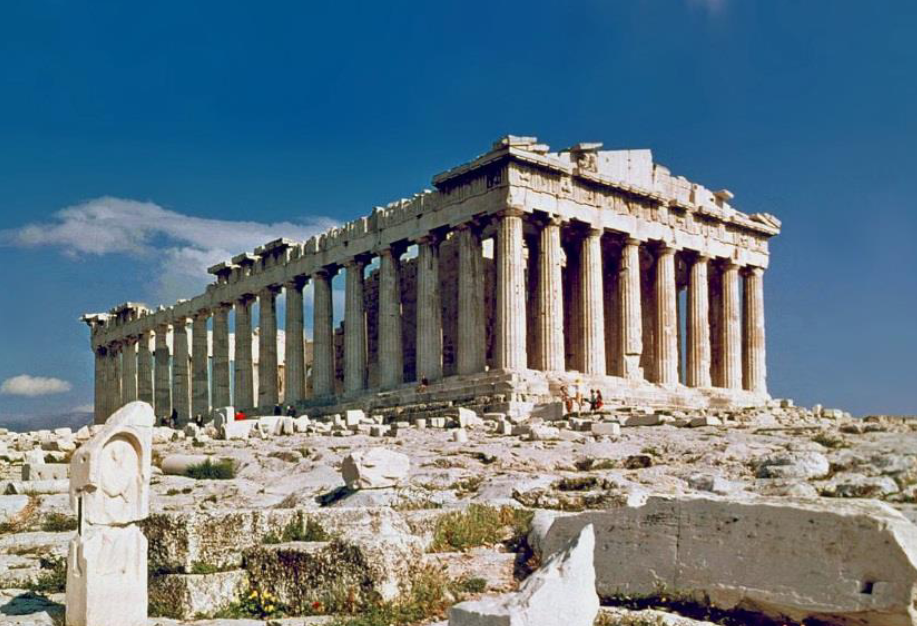


What is this?
Style?
Architectural elements?
Location?
Why was it influential?
And who was it built for?
The Greek Parthenon
Classical Style Architecture
Located in Athens, Greece
This temple was dedicated to the Goddess Athena: Goddess of wisdom, the arts, and war.
It’s one of the most influential buildings in the world because of its proportions:
Its architecture, columns, and states employ the Golden Theory.
All heights and widths were built in the ‘Classical Proportions’ (the Golden Mean)
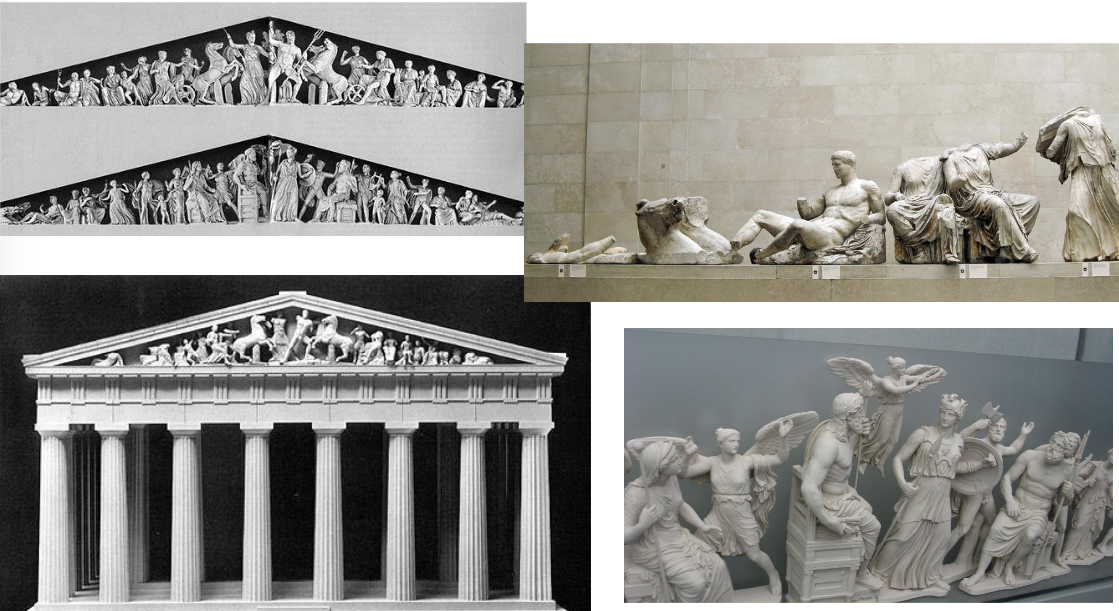


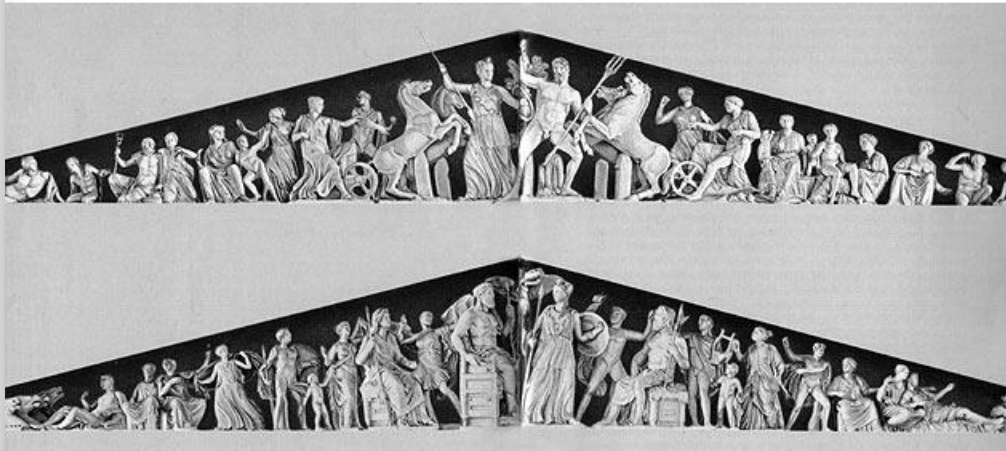
Pediments
Where on the building are these? What are the two stories they’re telling?
These depicted mythological events from the life of the Goddess Athena:
On the West side, she’s contesting Poseidon (God of the sea) for the patronage of the city (Athens).
On the east side, it shows her birth and the rest of the Gods receiving the news: Zeus, her father, is located in the middle.

Doric Metopes
What do the North, South, East, and West show
What are the four battles they’re telling?
They show mythological battles that were won: the victory of the Greeks over the Persians.
North: the Trojan war
East: the Olympians overthrowing the Titans
South: the battle between Lapiths (Greek tribesmen) and Centaurs
West: The Greeks vs the Amazons
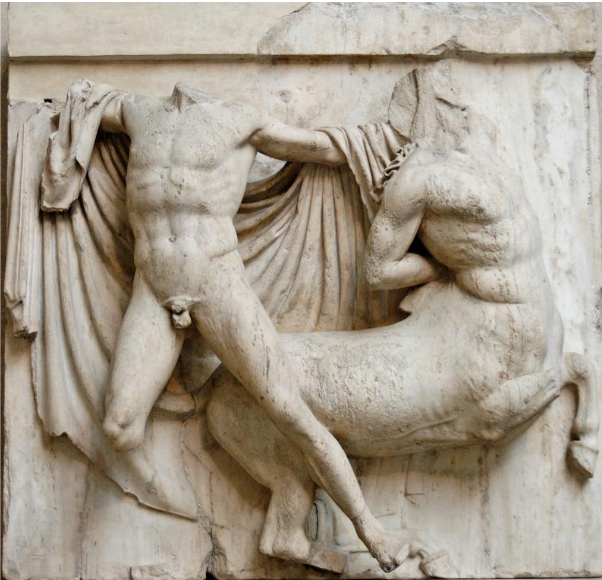

What is this? Style? What does it show
Classical style
The Greek Parthenon
4’ 5” high
Marble
High relief sculpture
Metope shows a battle scene of Lapiths (Greek tribesmen) battling Centaurs (half man, half horse)
There were 14 scenes on the east/west side, 32 on the north/south sides. Most are scenes of single combat, the south side was the most intact.
Traces of paint on the remaining sculptures indicate they would

What is this? Style? What does it show?
East Pediment Sculptures:
Classical style
Ascending height from 5’ to 11’
From left to right: Apollo rising, Dionysos, Demeter, and Persephone, Iris.