Cardiac Examination Techniques
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE)?
Procedure in which probe is inserted down a patient’s throat to image heart structures at varied levels within stomach and esophagus
What temperature should the TEE probe be kept at?
< 40 degrees celsius because excessive heat can cause damage to organs
What are the advantages of a TEE?
Higher resolution imaging
Better visualization of small structures and valves
Evaluation of LAA and atrial thrombus formation
Provides multiplane imaging techniques not possible with TTE
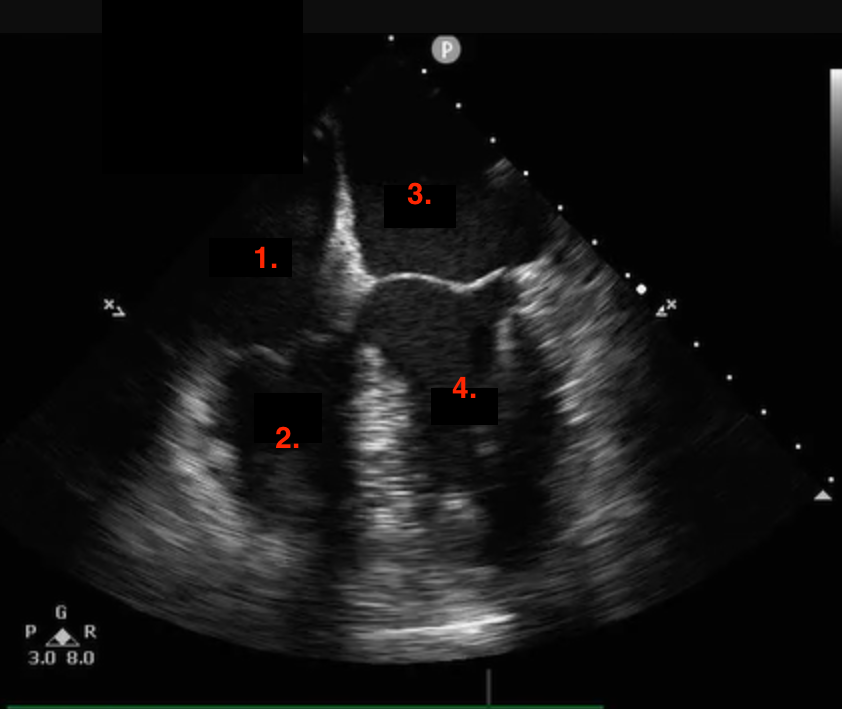
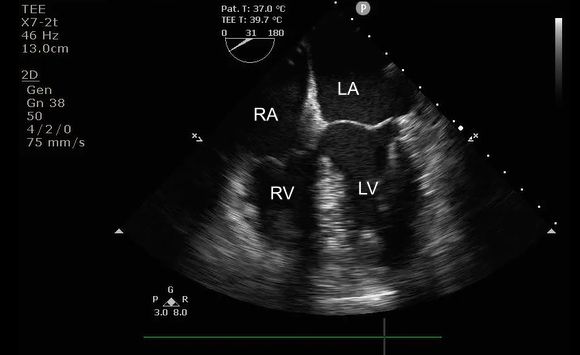
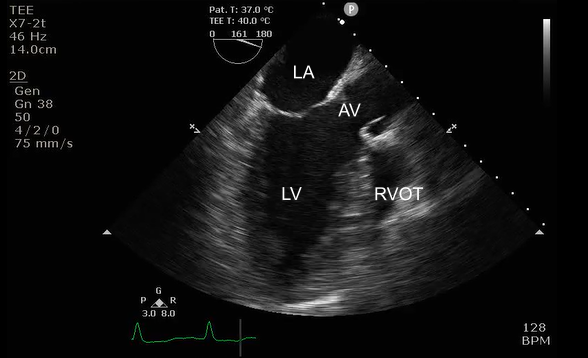
Identify this image.
TEE midesophageal four chamber taken at 0-10 degrees
RA
RV
LA
LV
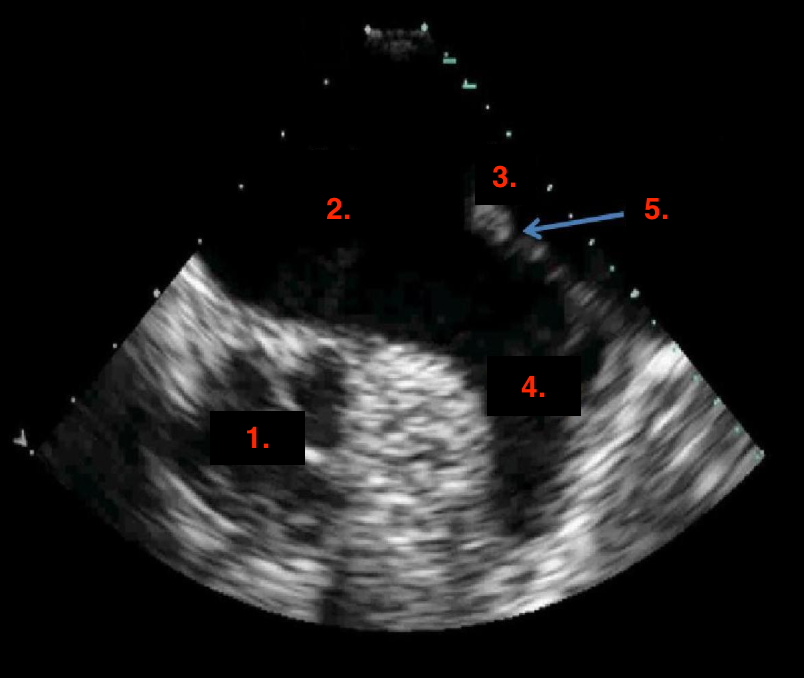
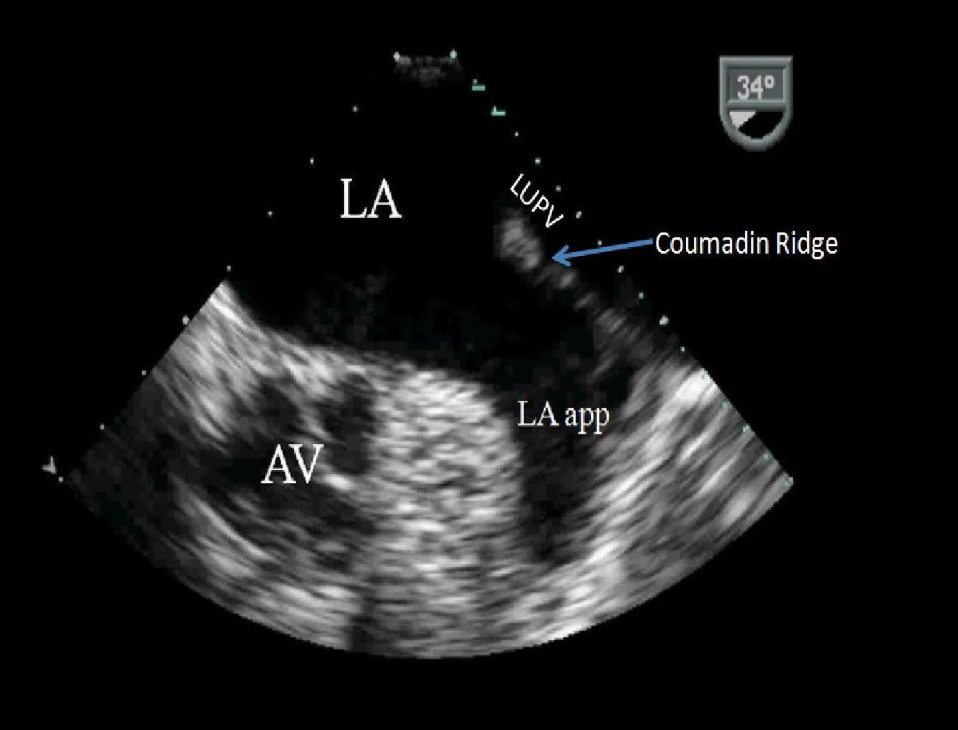
Identify this image.
TEE two chamber taken at 30-60 degrees
AV
LA
Left upper PV
LAA
Coumadin ridge
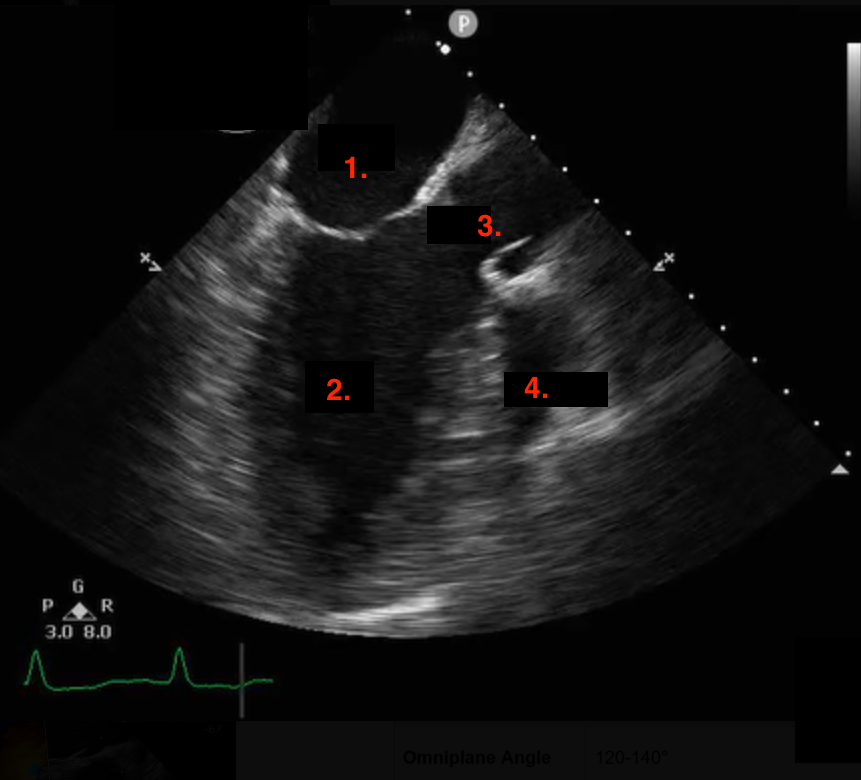
Identify this image.
TEE midesophageal LAX taken at 120-140 degrees
LA
LV
AV
RVOT
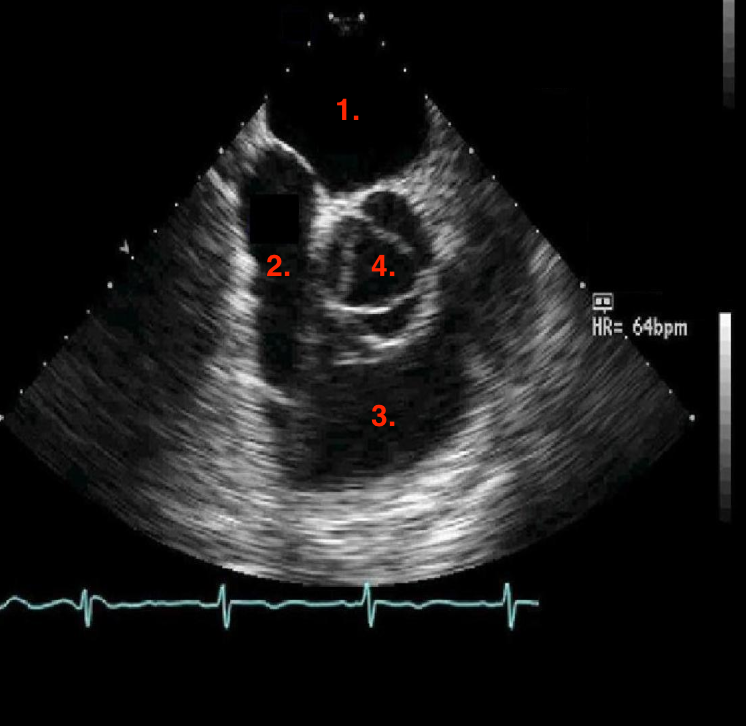
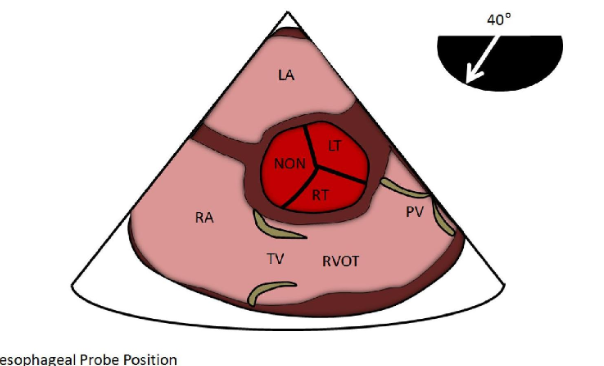
Identify this image.
TEE midesophageal SAX base taken at 40 degrees
LA
RA
RVOT
AV
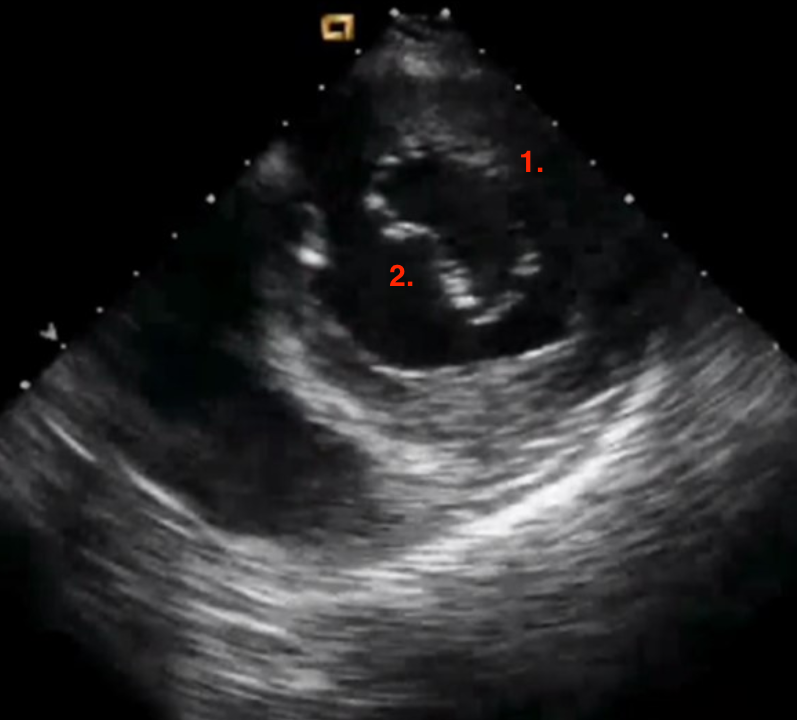
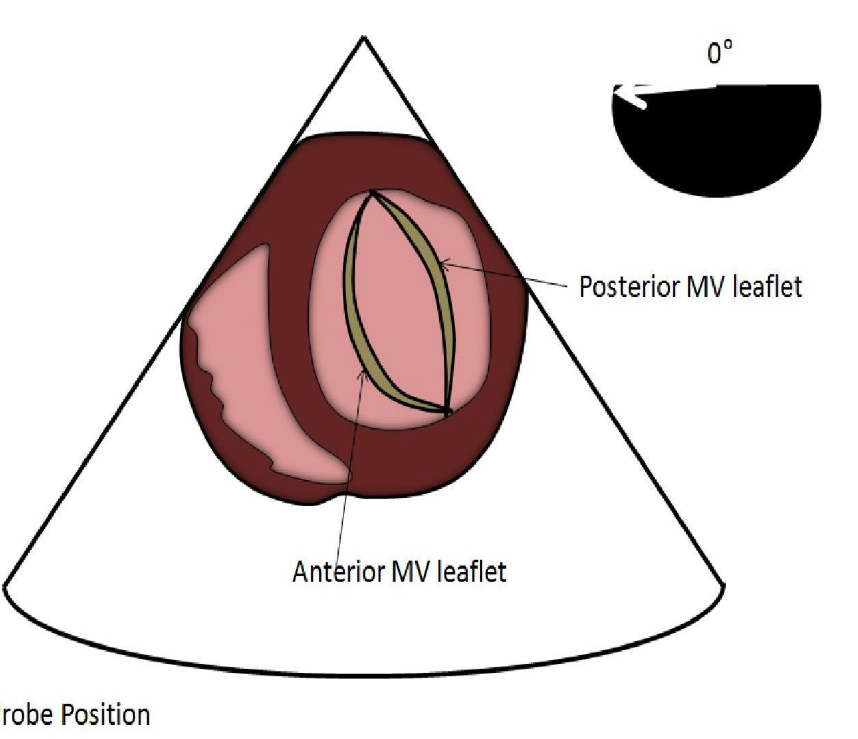
Identify this image.
TEE transgastric SAX basal taken at 0 degrees
Posterior MV leaflet
Anterior MV leaflet
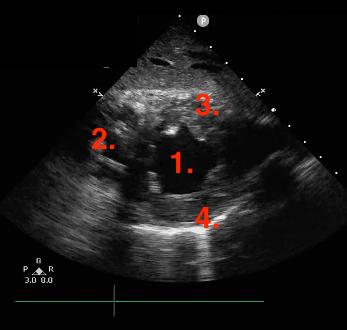
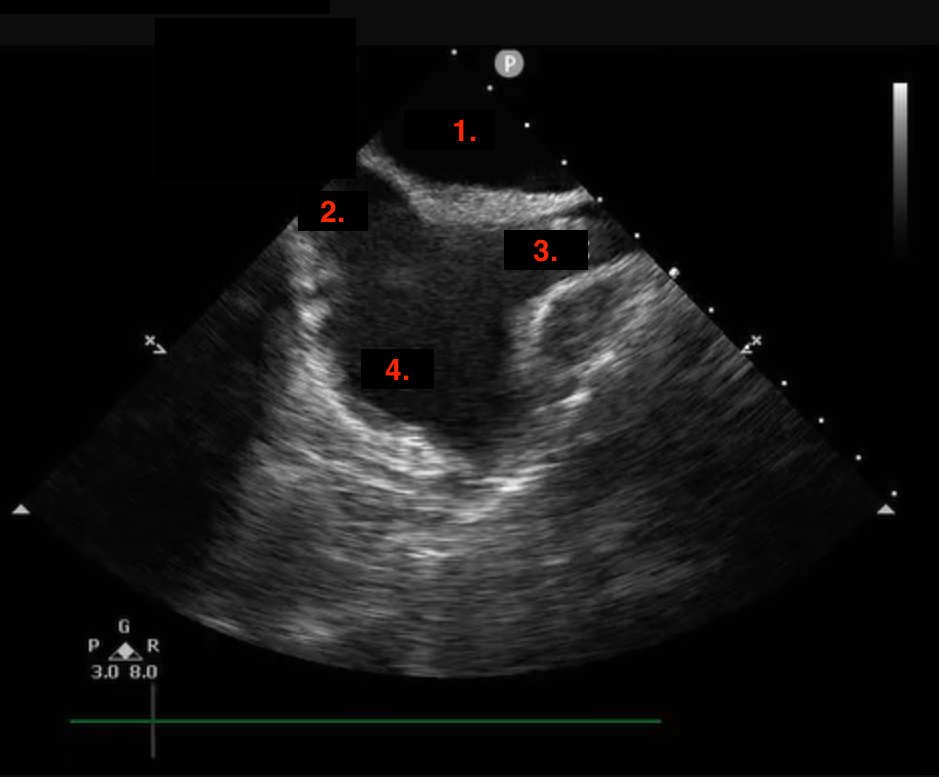
Identify this image.
TEE transgastric SAX mid LV taken at 0 degrees
LV
RV
Inferior
Anterior
Identify this image.
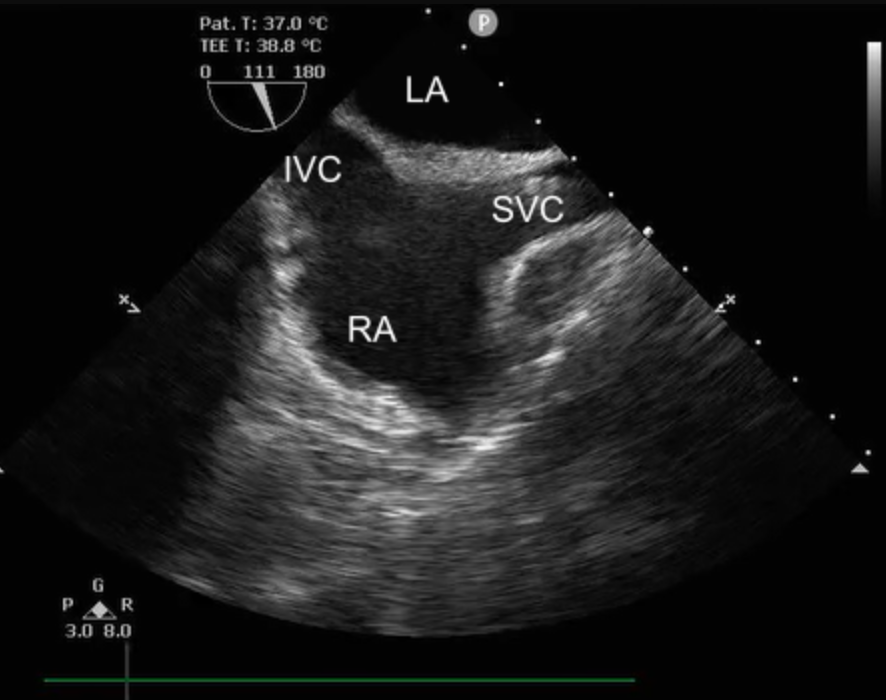
TEE bicaval taken at 90-110 degrees
LA
IVC
SVC
RA
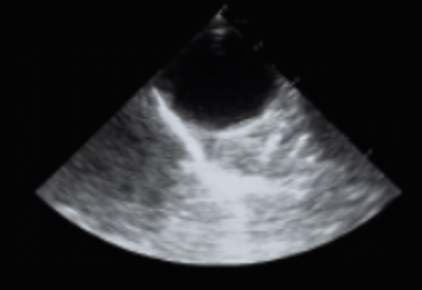
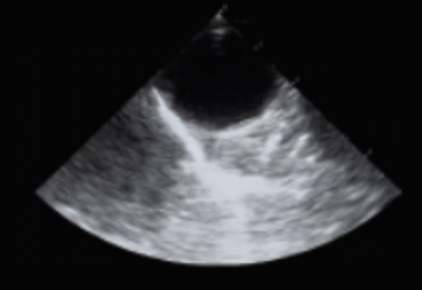
Identify this image.
TEE Midesophageal descending thoracic aorta SAX taken at 0 degrees
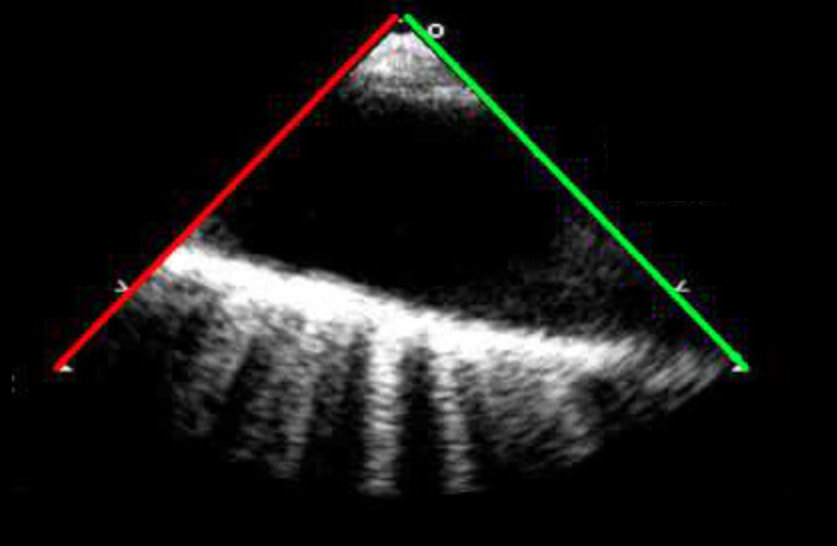
Identify this image.
TEE Midesophageal descending thoracic aorta LAX taken at 90-100 degrees
What is POCUS?
Point of care ultrasound used to evaluate effusion, wall motion abnormalities, and EF with a limited exam
What are the indications for a stress echocardiogram?
CAD screening
Assess systolic function
Evaluate MI improvement
Evaluate hemodynamic effects of valvular disease
Assess diastolic dysfunction in those with dyspnea
What are contraindications for a stress echocardiogram?
Unstable angina
Acute MI
Severe ventricular arrhythmias
Resting BP > 200/100
SYMPTOMATIC severe AV stenosis
Severe LVOT gradient at rest with HOCM
ST elevation in resting EKG
What is the Bruce protocol?
Standardized treadmill test used to assess LV function and wall motion changes
What is the protocol for an exercise stress echocardiogram?
Nurse or physiologist will obtain resting EKG and BP
Obtain resting images: A4C, A2C, A3C, PLAX, PSAX
Patient will begin treadmill test with speed and incline increasing every 3 minutes (Bruce protocol)
Nurse or physiologist will obtain BP every two minutes
Patient exercises until symptoms occur or target HR is reached
Obtain post images in 60 seconds or less AT SAME DEPTH AS RESTING: A4C, A2C, A3C, PLAX, PSAX
What are the results of a normal exercise stress echocardiogram?
BP increases during exercise and returns to normal after cessation
No EKG changes or symptoms (ST remains normal, no AFIB or SVT)
Increased EDV and EF
Decreased ESV
Hyperkinesis
Increased velocity of contraction
What is a pharmacologic stress echocardiogram?
Usage of dobutamine or atropine to simulate exercise in patients unable to perform exercise
What is the protocol for a pharmacologic stress echocardiogram?
Nurse or physiologist will obtain resting EKG and BP
Obtain resting images: A4C, A2C, A3C, PLAX, PSAX
Gradual intravenous infusion of dobutamine for up to 15 minutes
Obtain low-dose, pre-peak, and peak stress images during infusion
Obtain recovery images 5 minutes post-infusion
* Atropine may be administered to increase heart rate in those who cannot reach target HR with Dobutamine alone
What are the results of a normal pharmacological stress echocardiogram?
BP increases during infusion and returns to normal after cessation
No EKG changes or symptoms (ST remains normal, no AFIB or SVT)
Increased EF
Decreased EDV and ESV
Hyperkinesis
Increased velocity of contraction
What is speckle tracking?
Test that evaluated for early LV systolic dysfunction
What is global longitudinal strain (GLS)?
Test used to evaluate maximal deformation of LV myocardium at peak systole
What is the normal value for global longitudinal strain (GLS)?
-17 to -26%
Expressed as negative because it describes amount of shortening
GLS values close to 0 indicated severe LV dysfunction
Who is recommended for strain imaging?
Patients at risk of chemotherapy-related LV systolic dysfunction
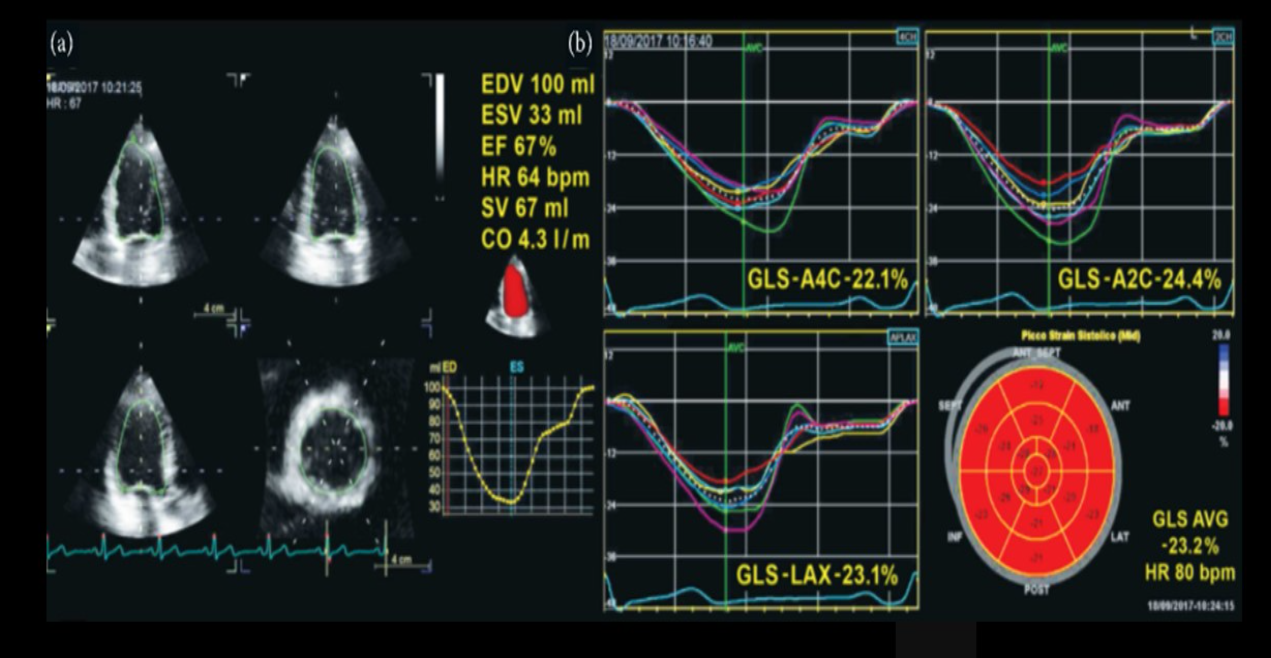
Identify this image.
Normal GLS
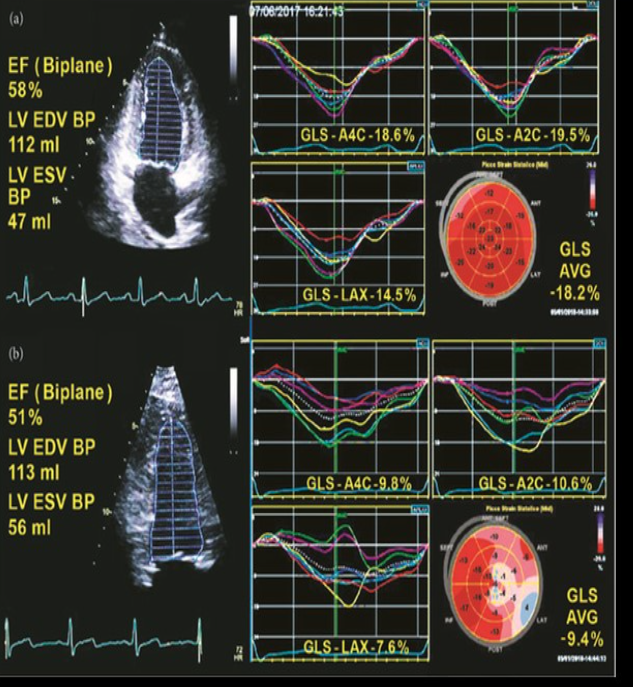
Identify this image.
Abnormal GLS
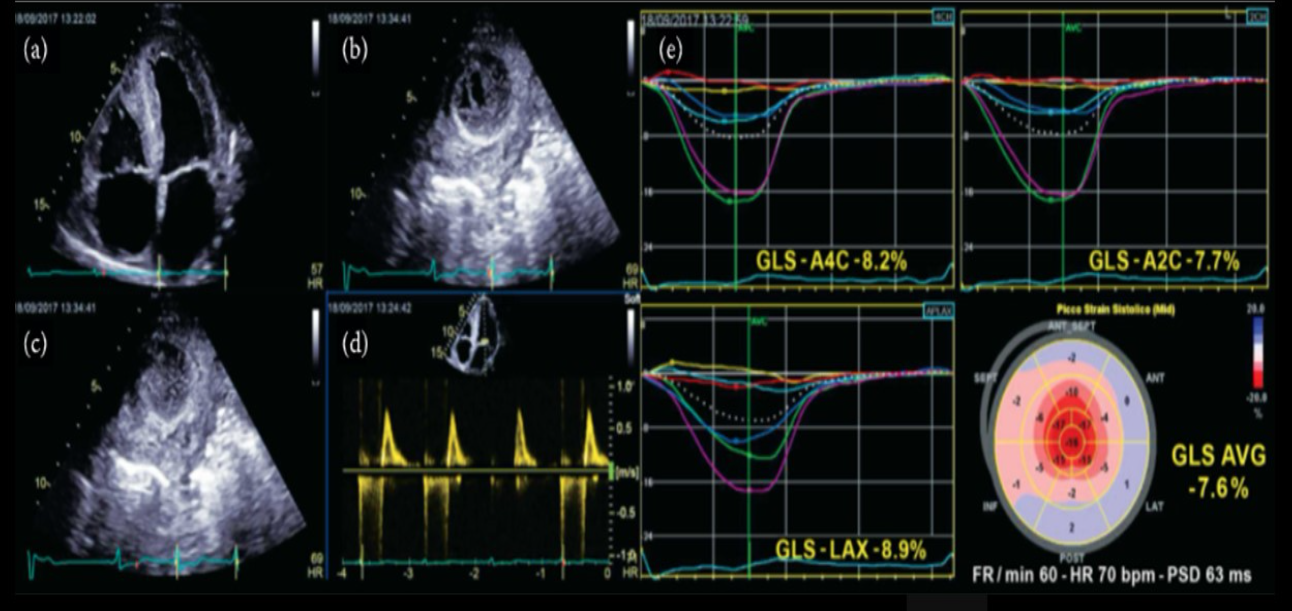
Identify this image.
Abnormal GLS due to amyloidosis (“cherry on top” or bullseye)
What is an agitated saline ultrasound enhancing agent (UEA)?
Agitated salt solution that creates bubbles for PFO or ASD detection
How is a bubble study performed?
IV established for injection of saline
Obtain A4C without bubbles
Obtain A4C with bubble at rest, with a cough, and with valsalva or abdominal compression
What are the results of a positive bubble study?
Bubbles on left side in 1-3 beats indicates PFO or ASD
Bubbles in left side in 4-8 beats indicates pulmonary AVM
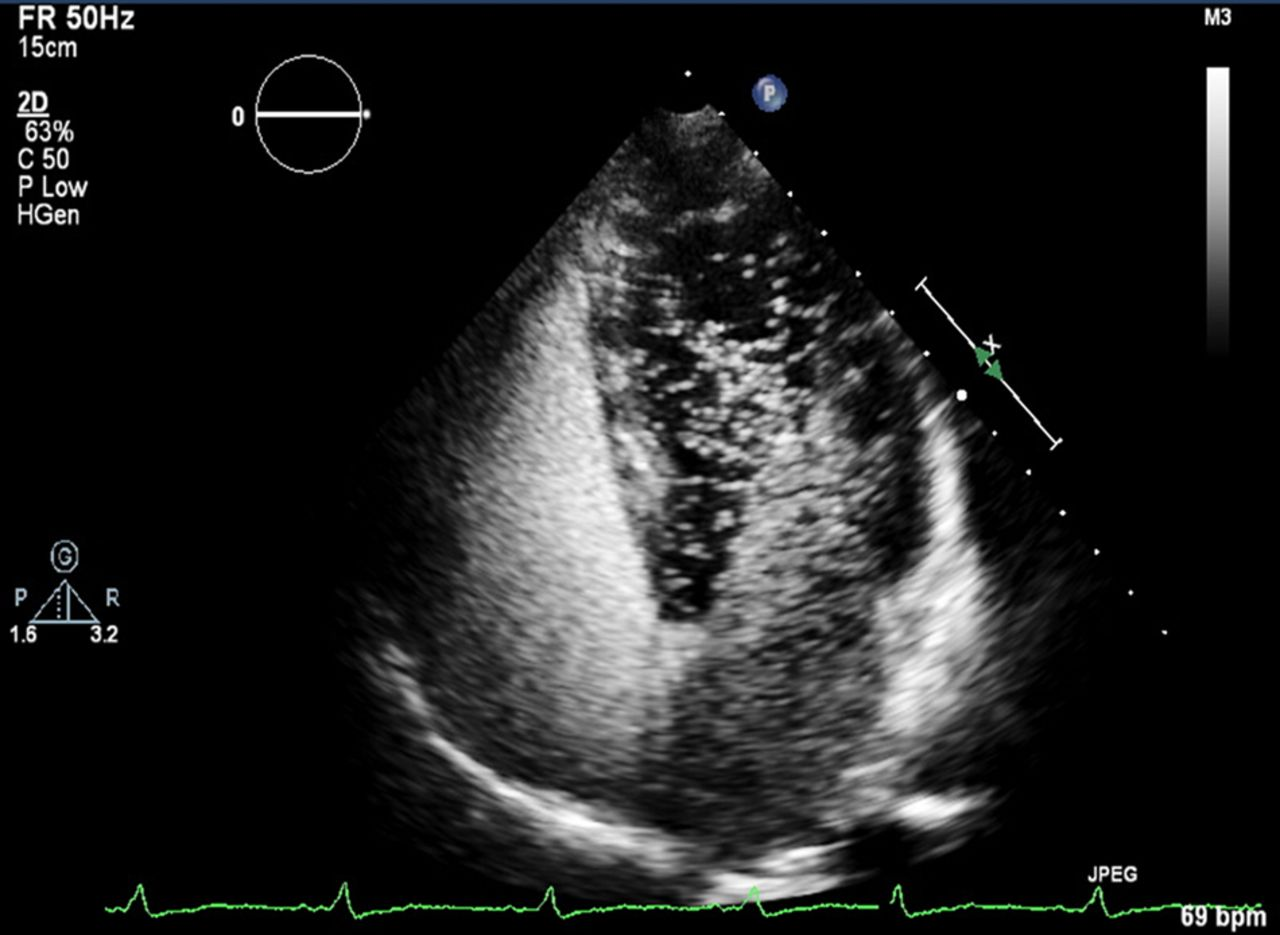
Identify this image.
Positive bubble study
What is a perfluorocarbon ultrasound enhancing agent (UEA)?
FDA-approved contrast agent such as Definity, Sonovue, Lumason, or Optison used for evaluation of LV function or detection of LV thrombus, aneurysm, or mass
How is a contrast echocardiogram performed?
IV established for injection of contrast
Reduce output power and overall gain
Reduce MI < 0.3 to prevent bursting microbubbles
Place focal zone at MV annulus
Obtain images with contrast: A4C, A2C, A3C, PLAX, PSAX
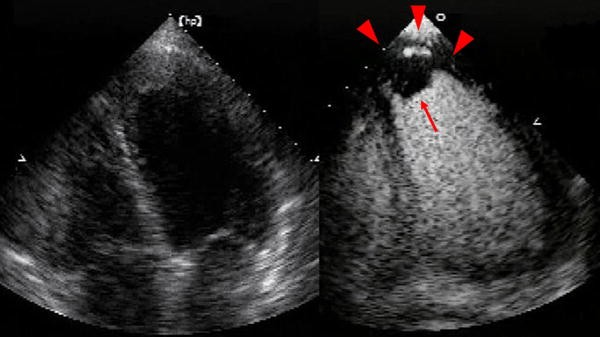
Identify this image.
LV thrombus detected with contrast
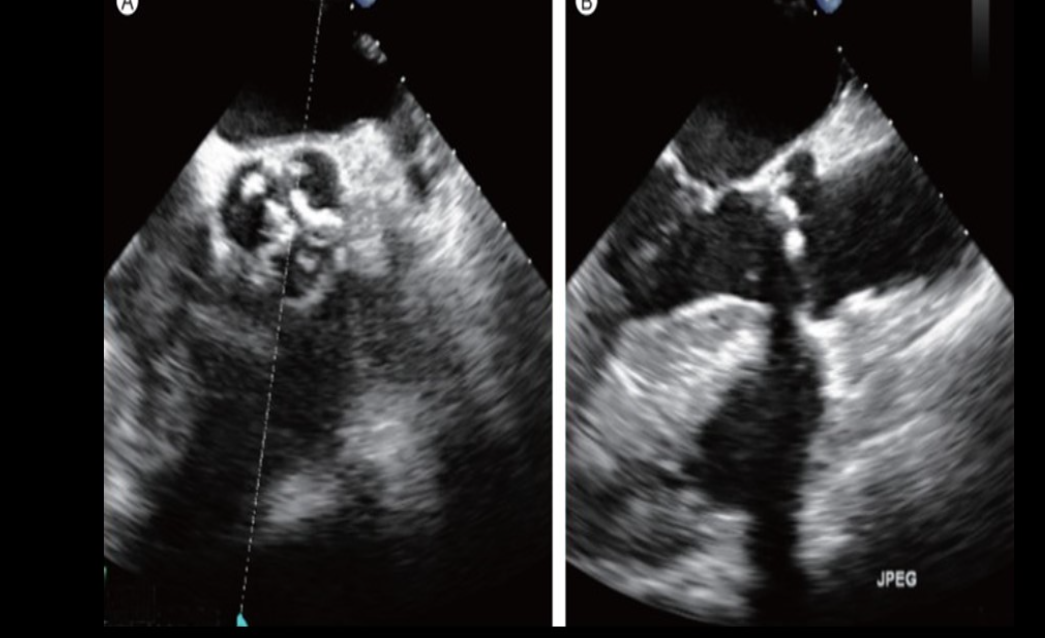
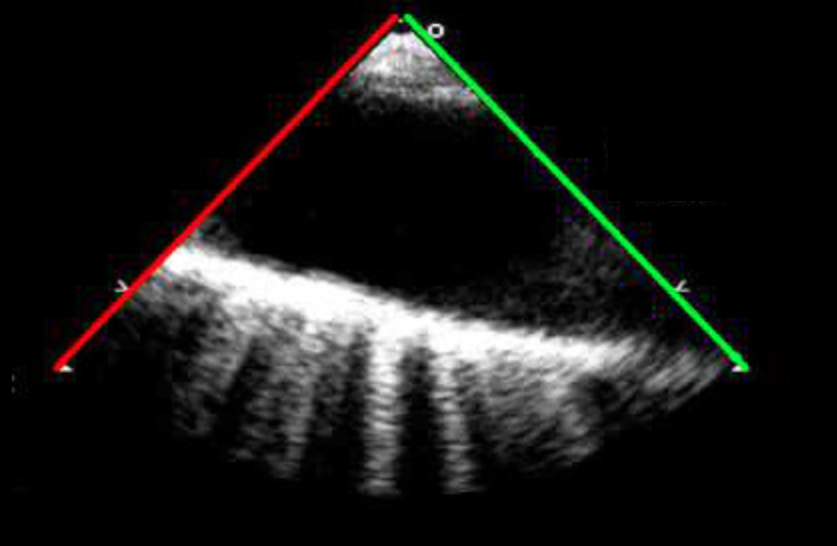
Identify this image.
Biplane imaging
What is a cardiac catheterization or coronary angiography?
Procedure performed by inserting catheter into brachial or superficial femoral artery to assess coronary arteries for blockages
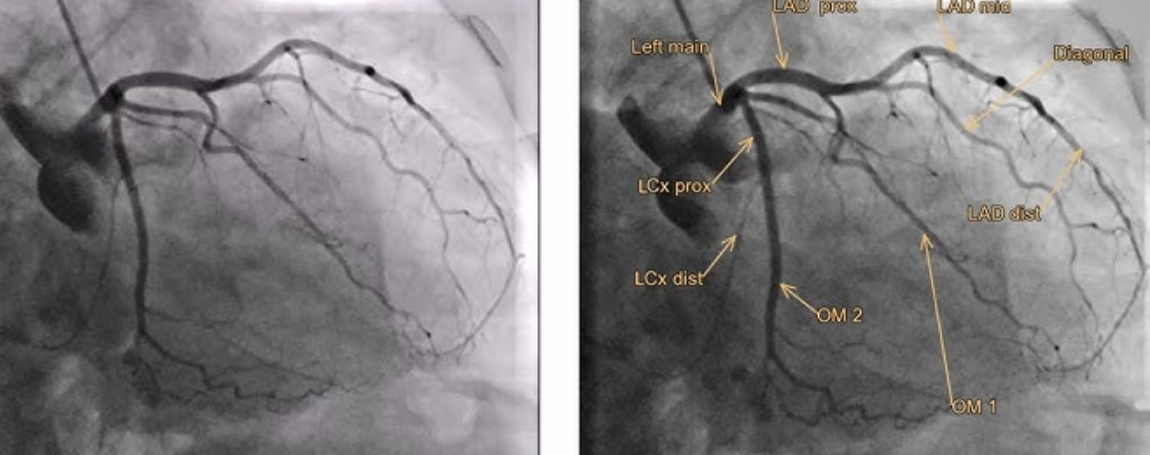
Identify this image.
Cardiac catheterization or coronary angiography