β-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
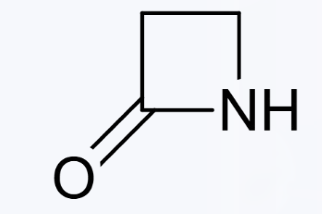
β-Lactam ring structure
β-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS: INTRODUCTION
Antibiotics that possess this ring structure are the dominant class of agents currently used for the chemotherapy of bacterial infections.
Penicillin (Penicillin G or benzylpenicillin)
Phenoxymethyl Penicillin (Penicillin V)
β-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS: INTRODUCTION
-The first antibiotic to be used in therapy is the?
-And a close biosynthetic relative?
-These remain the agents of choice for the treatment of infections caused by most species of Gram-positive bacteria
Cephalosporins
Chemical modifications of naturally occurring penicillin’s
β-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS: INTRODUCTION
-The discovery of a second major group of these β-lactam antibiotics, have provided semisynthetic derivatives that are variously effective against bacterial species known to be resistant to penicillin, in particular, penicillinase producing staphylococci and Gram-negative bacilli.
Inherent or acquired resistance
β-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS: INTRODUCTION
Thus, apart from a few strains that have either______________, almost all bacterial species are sensitive to one or more of the available β-lactam antibiotics.
-A potent and rapid bactericidal action against bacteria in the growth phase
-A very low frequency of toxic and other adverse reactions in the host
β-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS: MECHANISM OF ACTION
-Two properties contribute to the unequaled importance of β-lactam antibiotics in chemotherapy:
Inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis
β-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS: MECHANISM OF ACTION
The uniquely lethal antibacterial action of these agents has been attributed to a selective _____________.
-Inhibition of the transpeptidase enzyme
-inhibiting the biosynthesis of the dipeptidoglycan
β-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS: MECHANISM OF ACTION
-Specifically, the basic mechanism involved in the action of β-lactam antibiotics is inhibition of this enzyme, conversely inhibiting the biosynthesis of this that provides strength and rigidity to the cell wall.
β-lactam thiazolidine Structure
PENICILLIN’S
The structure of the penicillin molecule shows a fused ring system of unusual design, which is the?
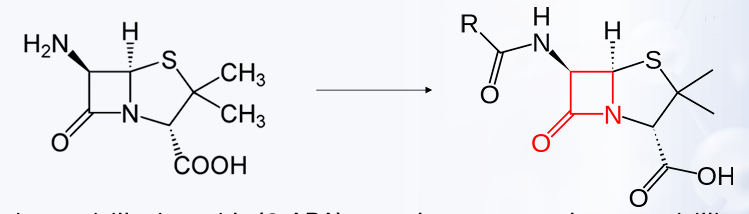
6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA)
PENICILLIN’S
-This can be converted to penicillin’s by acylation of the 6-amino group.
• Hydrolysis of the β-lactam ring in acid
• Hydrolysis of the β-lactam ring via β-lactamase
• Limited spectrum of activity
PENICILLINS: STRUCTURAL MODIFICATIONS
-The structure of penicillin’s can be modified by attaching various moieties to the R-group to address at least one of three problems:
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis
PENICILLINS: ELECTRON-WITHDRAWING GROUPS
Substitution of an electron-withdrawing group in the α-position of benzylpenicillin markedly stabilizes the penicillin to this hydrolysis
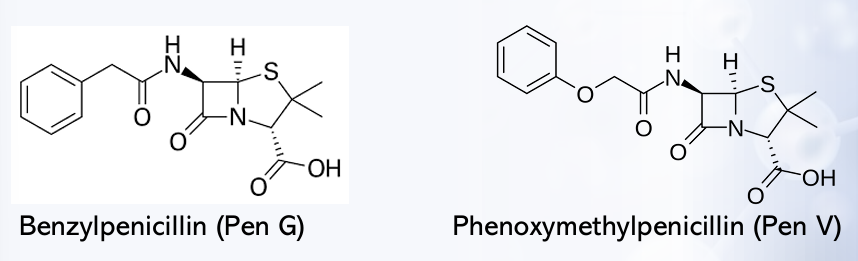
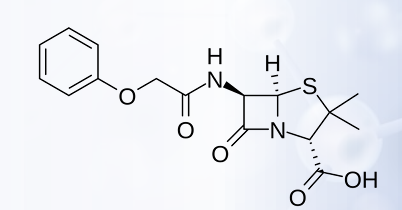
Benzylpenicillin (Pen G)
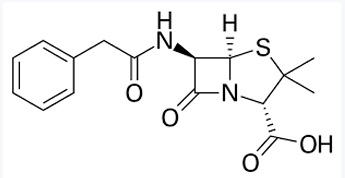
Phenoxymethylpenicillin (Pen V)
Staphylococcus aureus
PENICILLINS: BULKY GROUPS
-The addition of bulky substituents as R-groups to the penicillin structure confers resistance to β-lactamase or penicillinase produced by?
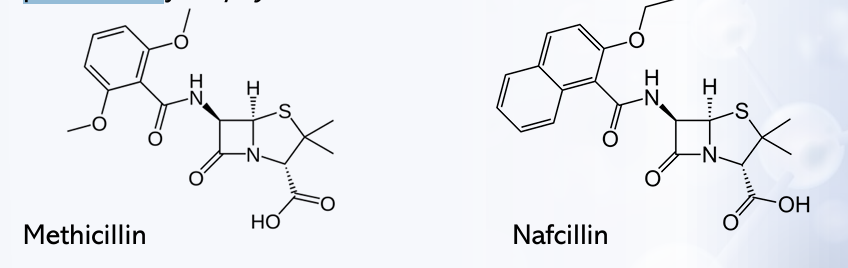
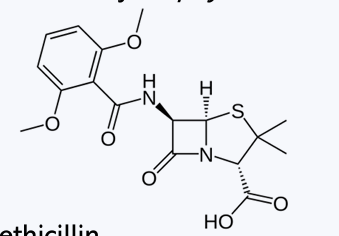
Methicillin
Nafcillin
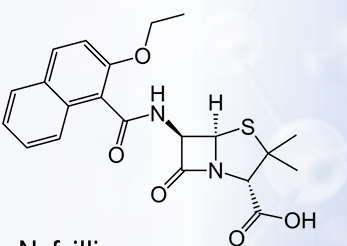
Non-β-lactamase-producing bacteria
PENICILLIN’S: BULKY GROUPS
Increasing the bulkiness of the acyl group is not without its price, however, because all of the clinically available penicillinase-resistant penicillin’s are significantly less active than either penicillin G or penicillin V against most this bacteria normally sensitive to the penicillin’s.
Amino
Carboxyl
Urea
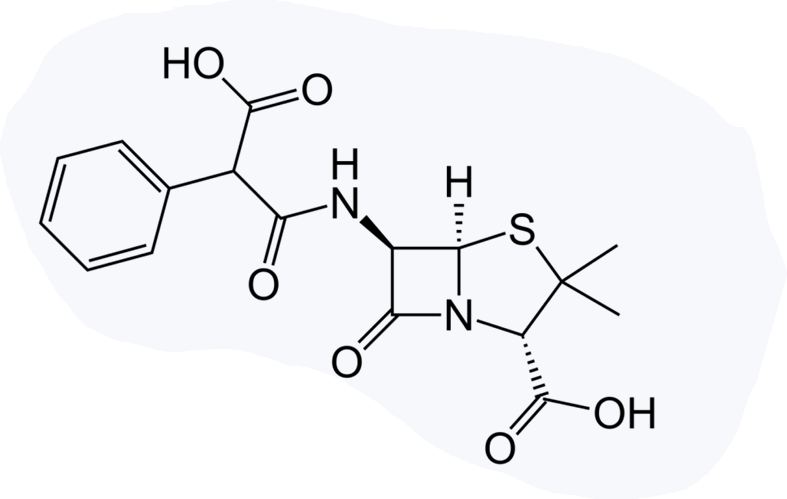
PENICILLIN’S: POLAR GROUPS
-Another highly significant advance arising from the preparation of semisynthetic penicillin’s was the discovery that the introduction of an ionized or polar group (examples are?) into the α-position of the side chain benzyl carbon atom of penicillin G confers activity against Gram-negative bacilli.
Organisms resistant to ampicillin
PENICILLINS: POLAR GROUPS
Incorporation of an acidic substituent at the α-benzyl carbon atom of penicillin G also imparts clinical effectiveness against Gram-negative bacilli and, furthermore, extends the spectrum of activity to include?
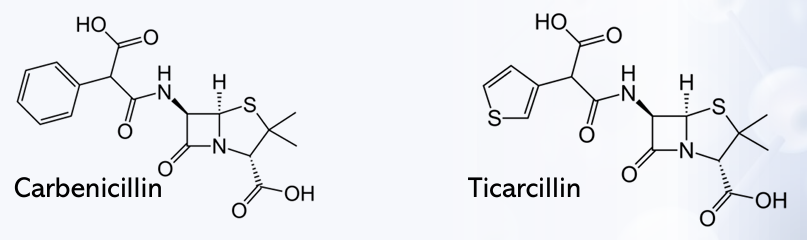
Carbenicillin
Ticarcillin
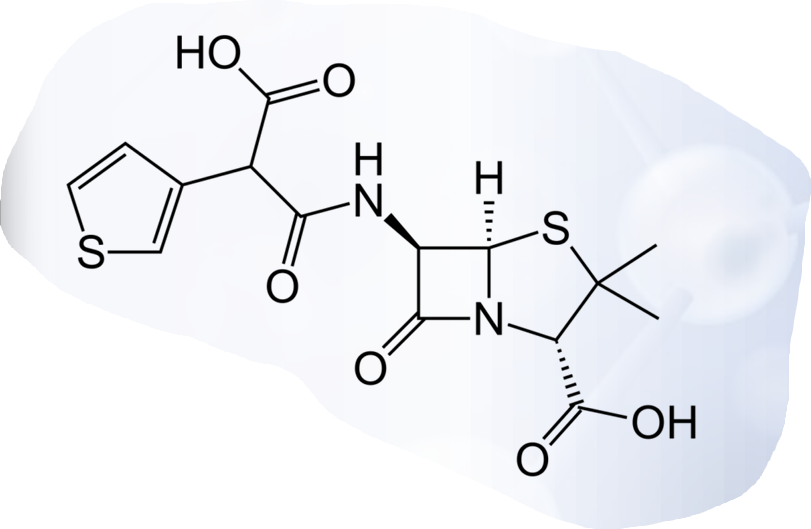
It is less potent due to poorer penetration caused by higher ionization.
PENICILLINS: POLAR GROUPS
How does carbenicillin compare to penicillin G or ampicillin against Gram-positive bacteria?
Better penetration through Gram-negative bacteria's porin channels.
PENICILLINS: POLAR GROUPS
What advantage does carbenicillin's increased polarity provide?
They exhibit greater activity.
PENICILLINS: POLAR GROUPS
How do α-acylureidopenicillins compare to carbenicillin against Gram-negative bacilli?
Carbenicillin
PENICILLINS: POLAR GROUPS
What is the antibacterial spectrum of acylureidopenicillins similar to?
Kelebsiella spp
Enterobacter spp
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
PENICILLINS: POLAR GROUPS
Against which bacteria are acylureidopenicillins superior to carbenicillin?
Azlocillin
Mezlocillin
Piperacillin
PENICILLIN’S: POLAR GROUPS
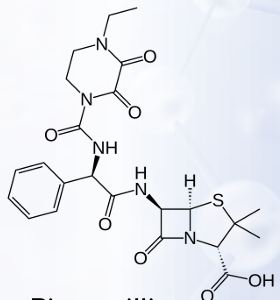
Enumerate the α-acylureido-substituted Penicillins:
Azlocillin
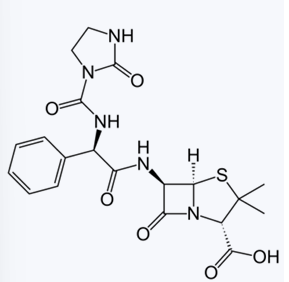
Mezlocillin
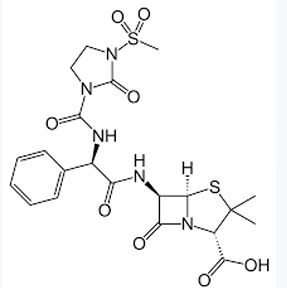
Piperacillin
Oxacillin
Cloxacillin
Dicloxacillin
Flucloxacillin
PENECILLINS: ISOXAZOYL PENICILLINS
Enumerate the Isoxazoyl Penicillins
Acid-resistant
PENECILLINS: ISOXAZOYL PENICILLINS
-Electron-withdrawing group
Penicillinase-resistant
PENECILLINS: ISOXAZOYL PENICILLINS
-Bulky group
Oxacillin
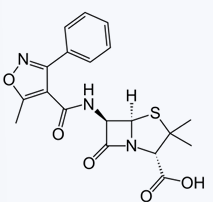
Cloxacillin
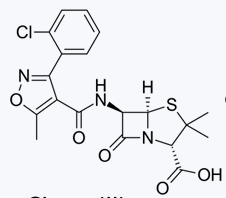
Dicloxacillin
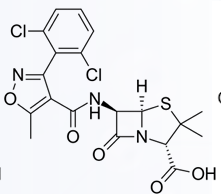
Flucloxacillin
Ampicillin
Amoxicillin
PENICILLINS: AMINO PENICILLINS
Enumerate the amino penicillins
Ampicillin
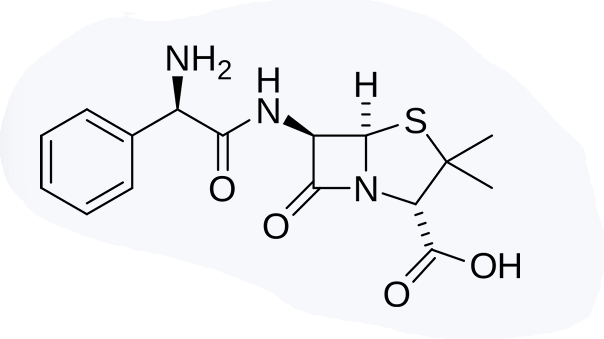
Amoxicillin
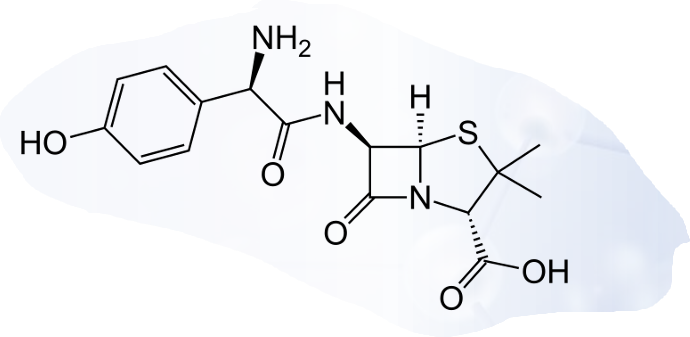
acid-resistant
PENICILLINS: AMINO PENICILLINS
-electron-withdrawing group
extended spectrum
PENICILLINS: AMINO PENICILLINS
-polar group (amino)
Clavulanic Acid
β-LACTAMASE INHIBITORS
-The discovery of this naturally occurring, mechanism-based inhibitor, causes potent and progressive inactivation of β-lactamases has created renewed interest in β-lactam combination therapy
Sulbactam
Tazobactam
β-LACTAMASE INHIBITORS
After the interest of clavulanic acid has led to the design and synthesis of additional mechanism-based β-lactamase inhibitors, such as?
Suicide substrates
β-LACTAMASE INHIBITORS
The design and synthesis of additional mechanism-based β-lactamase inhibitors, such as sulbactam and tazobactam are also substrates for the enzymes that they inactivate, they are sometimes referred to as?
Clavulanic Acid
β-LACTAMASE INHIBITORS
• Isolated from Streptomyces clavuligeris
• A potent inhibitor of S. aureus β-lactamase and plasmid-mediated β-lactamases elaborated by Gram-negative bacilli
• Combined with amoxicillin in various formulations as co-amoxiclav (Augmentin®)
• Effective against β-lactamase–producing strains of S. aureus, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, Enterobacter, H. influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Haemophilus ducreyi, which are resistant to amoxicillin alone
Streptomyces clavuligeris
Clavulanic acid is isolated from this bacteria
S. aureus β-lactamase
Plasmid-mediated β-lactamase
This is a potent inhibitor of these enzymes of clavulanic acid elaborated by Gram-negative bacilli
Co-amoxiclav (Augmentin®)
Clavulanic acid is combined with amoxicillin in various formulations as?
S. aureus
E. coli
K. pneumoniae
Enterobacter
H. influenzae
Moraxella catarrhalis
Haemophilus ducreyi
Clavulanic acid is effective against β-lactamase-producing strains of? (which are resistant to amoxicillin alone)
Sulbactam
β-LACTAMASE INHIBITORS
• Has weak intrinsic antibacterial activity but potentiates the activity of ampicillin and carbenicillin against β-lactamase–producing S. aureus and members of the Enterobacteriaceae family
• Combined with ampicillin as sterile powder for injection (Unasyn®)
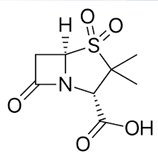
Ampicillin (Unasyn®)
Sulbactam is combined with this aminopenicillin as sterile powder for injection
Tazobactam
β-LACTAMASE INHIBITORS
• Available in fixed-dose, injectable combinations with piperacillin consisting of an 8:1 ratio of piperacillin to tazobactam by weight (Zosyn®, Piptaz®)
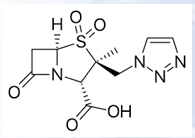
Avibactam
β-LACTAMASE INHIBITORS
• Available in combination with ceftazidime (Avycaz®)
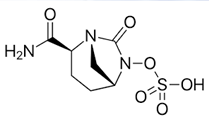
Thienamycin
CARBAPENEMS: 1ST GENERATION
• First isolated and Identified from fermentation of cultures of Streptomyces cattleya
• Highly active against most aerobic and anaerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, and B. fragilis
• Resistant to inactivation by most β-lactamases elaborated by Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria and, therefore, is effective against many strains resistant to penicillins and cephalosporins
Streptomyces cattleya
The thienamycin if first isolated and identifies from fermentation of cultures of?
S. aureus
P. aeruginosa
B. fragilis
Thienamycin highly active against most aerobic and anaerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including?
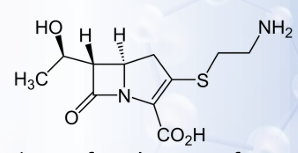
Imipenem
This carbapenems is a β-lactam antibiotic
Cilastatin
This carbapenems is a dihydropeptidase-I inhibitor
Imipenem-Cilastatin
CARBAPENEMS: 1ST GENERATION
The combination provides a chemically and enzymatically stable form of thienamycin that has clinically useful pharmacokinetic properties (Primaxin®)
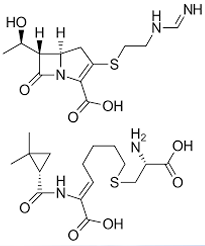
Meropenem
CARBAPENEMS: 2ND GENERATION
• Approved for the treatment of infections caused by multiply resistant bacteria and for empirical therapy for serious infections, such as bacterial meningitis, septicemia, pneumonia, and peritonitis
• Exhibits greater potency against Gram-negative and anaerobic bacteria than does imipenem, but it is slightly less active against most Gram-positive species
• Not hydrolyzed by DHP-I and is resistant to most β-lactamases but is not effective vs. MRSA
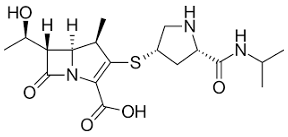
Biapenem
CARBAPENEMS: 2ND GENERATION
• Has broad-spectrum antibacterial activity that includes most aerobic Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria and anaerobes
• Stable to DHP-I and resistant to most β-lactamase
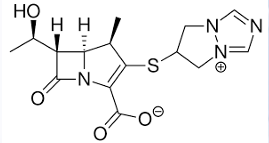
Cephalosporium spp.
CEPHALOSPORINS: HISTORY
The cephalosporins are β-lactam antibiotics isolated from this species or prepared semisynthetically.
Semisynthetic Cephalosporin
CEPHALOSPORINS: HISTORY
Most of the antibiotics cephalosporin introduced since 1965 have been?
Cephalosporium acremonium
CEPHALOSPORINS: HISTORY
Interest in Cephalosporium fungi began in 1945 with Giuseppe Brotzu’s discovery that cultures of this fungi obtained from cephalosporins inhibited the growth of a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram negative bacteria.
D-(4-amino-4 carboxybutyl)penicillanic acid
CEPHALOSPORINS: HISTORY
The structure of penicillin N was discovered to be?
-Salmonella spp.
-Penicillin G
CEPHALOSPORINS: HISTORY
-The structure of penicillin N was discovered to be D-(4-amino-4 carboxybutyl)penicillanic acid.
-The amino acid side chain confers more activity against Gram-negative bacteria, particularly __________., but less activity against Gram-positive organisms than ___________.
-It has been used successfully in clinical trials for the treatment of typhoid fever but was never released as an approved drug.
Dihydrothiazine Ring
CEPHALOSPORINS: HISTORY
Cephalosporin C, isolated in 1948, turned out to be a close congener of penicillin N, containing this ring instead of the thiazolidine ring of the penicillins.
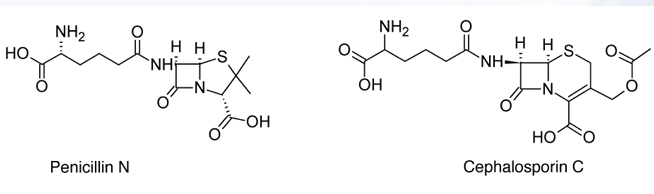
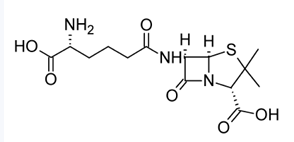
Pencillin N
Cephalosporin C
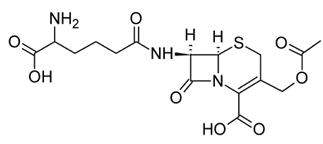
It had weaker antibacterial potency than penicillin N and other penicillins.
CEPHALOSPORINS: HISTORY
Why was early interest in cephalosporin C low?
It was resistant to penicillinase from S. aureus.
CEPHALOSPORINS: HISTORY
What advantage did cephalosporin C have despite its lower potency?
CEPHALOSPORINS: HISTORY
The discovery that the α-aminoadipoyl side chain could be removed to efficiently produce ____________, however, prompted investigations that led to semisynthetic cephalosporins of medicinal value.
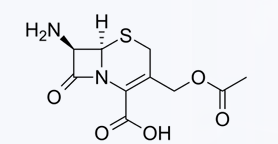
• increased acid stability
• improved pharmacokinetic properties, particularly better oral absorption
• broadened antimicrobial spectrum
• increased activity against resistant microorganisms
• decreased allergenicity
• increased tolerance after parenteral administration
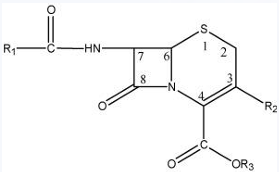
CEPHALOSPORINS: STRUCTURE-ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIP
In the preparation of semisynthetic cephalosporins, the following improvements are sought:
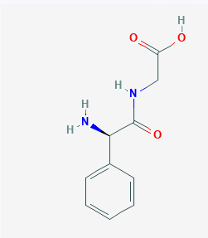
Phenylglycyl
CEPHALOSPORINS: STRUCTURE-ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIP
The oral activity conferred by the this substituent is attributed to increased acid stability of the lactam ring.
Esterification of the 3-carboxylic acid group
CEPHALOSPORIN: STRUCTURE-ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIP
-Oral activity can also be conferred in certain cephalosporins by esterification of this acid group to form acid-stable, lipophilic esters that undergo hydrolysis in the plasma.
-The introduction of polar substituents in the aminoacyl moiety of cephalosporins appears to confer stability to β-lactamase.
Both are broad-spectrum antibiotics.
CEPHALOSPORIN: SPECTRUM OF ACTIVITY
How do cephalosporins compare to ampicillin in spectrum?
They are more resistant to β-lactamases, especially from Gram-positive bacteria.
CEPHALOSPORIN: SPECTRUM OF ACTIVITY
What advantage do cephalosporins have over ampicillin?
Against non-β-lactamase-producing Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
CEPHALOSPORIN: SPECTRUM OF ACTIVITY
When is ampicillin more effective than cephalosporins?
Klebsiella
CEPHALOSPORIN: SPECTRUM OF ACTIVITY
Cephalosporins, among β-lactam antibiotics, exhibit uniquely potent activity against most species of?
Cefoperazone
Moxalactam
Cefotaxime
Ceftizoxime
Ceftriaxone
Ceftazidime
These drugs of cephalosporins have useful antipseudomonal activity
S. aureus
Bacillus subtilis
CEPHALOSPORINS: β-LACTAMASE RESISTANCE
Cephalosporins are significantly less sensitive than all but the β-lactamase–resistant penicillin’s to hydrolysis by the enzymes from?
Cephalothin
Cefoxitin
CEPHALOSPORINS: β-LACTAMASE RESISTANCE
Despite natural resistance to staphylococcal β-lactamase, the different cephalosporins exhibit considerable variation in rates of hydrolysis by the enzyme.
Most resistant to β-lactamase:
Cephaloridine
Cefazolin
CEPHALOSPORINS: β-LACTAMASE RESISTANCE
Despite natural resistance to staphylococcal β-lactamase, the different cephalosporins exhibit considerable variation in rates of hydrolysis by the enzyme.
Least resistant to β-lactamase:
Allergic
Hypersensitivity Reactions
CEPHALOSPORINS: ADVERSE REACTIONS AND DRUG INTERACTIONS
What are the most common adverse effect of cephalosporins?
They range from mild rashes to life-threatening anaphylaxis.
CEPHALOSPORINS: ADVERSE REACTIONS AND DRUG INTERACTIONS
How severe can cephalosporin allergic reactions be?
They are believed to be less frequent than penicillin reactions.
CEPHALOSPORINS: ADVERSE REACTIONS AND DRUG INTERACTIONS
How does the frequency of allergic reactions to cephalosporins compare to penicillins?
True, but the incidence is considered very low.
CEPHALOSPORINS: ADVERSE REACTIONS AND DRUG INTERACTIONS
TRUE OR FALSE
Is there cross-sensitivity between penicillins and cephalosporins?
Cefamandole
Cefotetan
Cefmetazole
Moxalactam
Cefoperazone
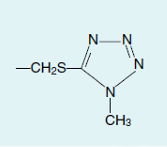
CEPHALOSPORINS: ADVERSE REACTIONS AND DRUG INTERACTIONS
Cephalosporins containing an N-methyl-5-thiotetrazole (MTT) moiety at the 3-position (for example?) have been implicated in a higher incidence of hypoprothrombinemia than cephalosporins lacking the MTT group
It restores prothrombin time to normal.
CEPHALOSPORINS: ADVERSE REACTIONS AND DRUG INTERACTIONS
How does vitamin K affect patients on MTT-containing cephalosporins?
Weekly vitamin K prophylaxis.
CEPHALOSPORINS: ADVERSE REACTIONS AND DRUG INTERACTIONS
What is recommended for high-risk patients undergoing therapy with these cephalosporins?
Possible drug synergism.
CEPHALOSPORINS: ADVERSE REACTIONS AND DRUG INTERACTIONS
Why should MTT-containing cephalosporins not be given with oral anticoagulants or heparin?
Accumulation of acetaldehyde due to inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase.
CEPHALOSPORINS: ADVERSE REACTIONS AND DRUG INTERACTIONS
What causes disulfiram-like reactions with MTT-containing cephalosporins?
If they consume alcohol before, during, or shortly after therapy.
CEPHALOSPORINS: ADVERSE REACTIONS AND DRUG INTERACTIONS
When can disulfiram-like reactions occur in patients taking these cephalosporins?
By generation (first to fifth) based on discovery and antimicrobial properties
CEPHALOSPORIN: CLASSIFICATION
How are cephalosporins classified?
Broader Gram-negative coverage, reduced Gram-positive activity, and increased β-lactamase resistance.
CEPHALOSPORIN: CLASSIFICATION
How does antibacterial activity change from first to fourth generation?
They vary in plasma protein binding and half-life.
CEPHALOSPORIN: CLASSIFICATION
How do individual cephalosporins differ pharmacokinetically?
Monobactam antibiotics
MONOBACTAMS
The development of this useful antibiotics began with the independent isolation of sulfazecin and other monocyclic β-lactam antibiotics from saprophytic soil bacteria.
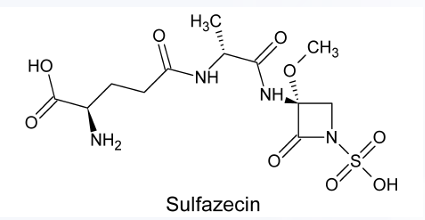
Sulfazecin
MONOBACTAMS
This monobactam drug was found to be weakly active as an antibacterial agent but highly resistant to β-lactamases
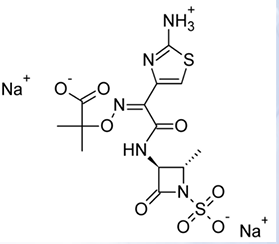
Aztreonam
MONOBACTAMS
• Has high affinity to PBP 3 of Gram-negative bacteria
• Inactive against Gram-positive bacteria and anaerobes
• β-Lactamase resistance is like that of ceftazidime
• The 4-methyl group increases stability to β-lactamases and activity against Gram-negative bacteria at the same time; unfortunately, potency against Gram-positive bacteria decreases