Copper Chemistry With Pictures 23.24
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
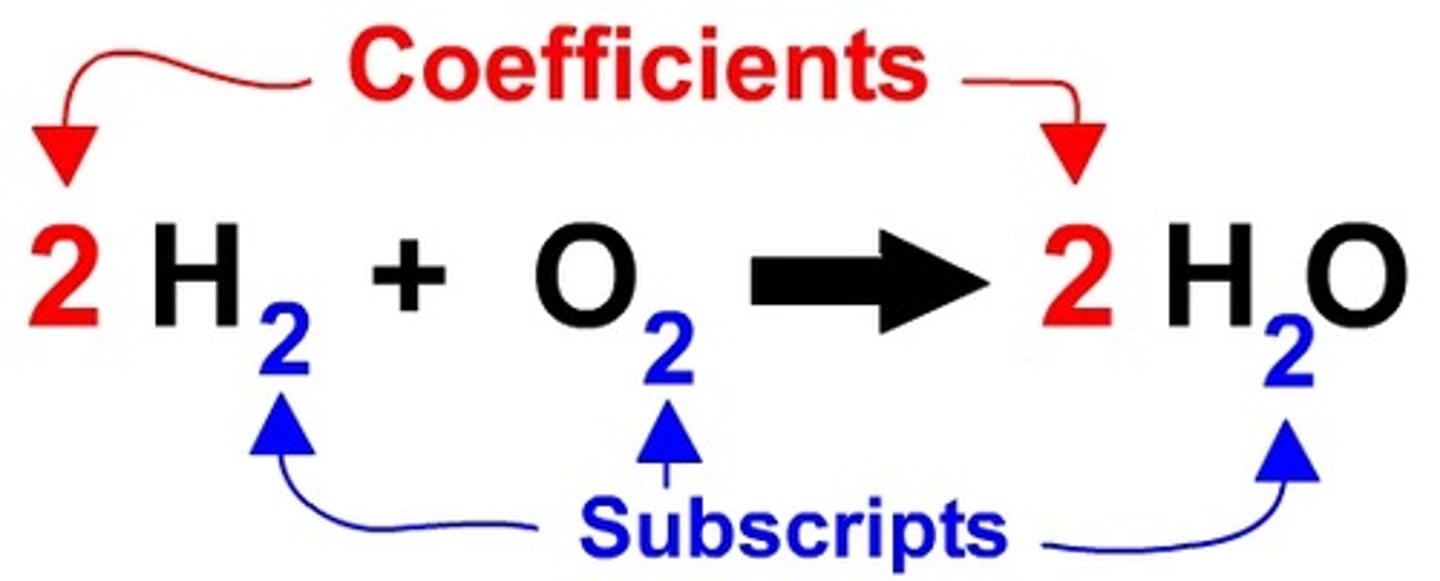
Coefficient
A number placed in front of a chemical formula to indicate how many particles there are. Ex: 2FeO means two particles of FeO and FeO. Used to balance equations to demonstrate the law of conservation of matter
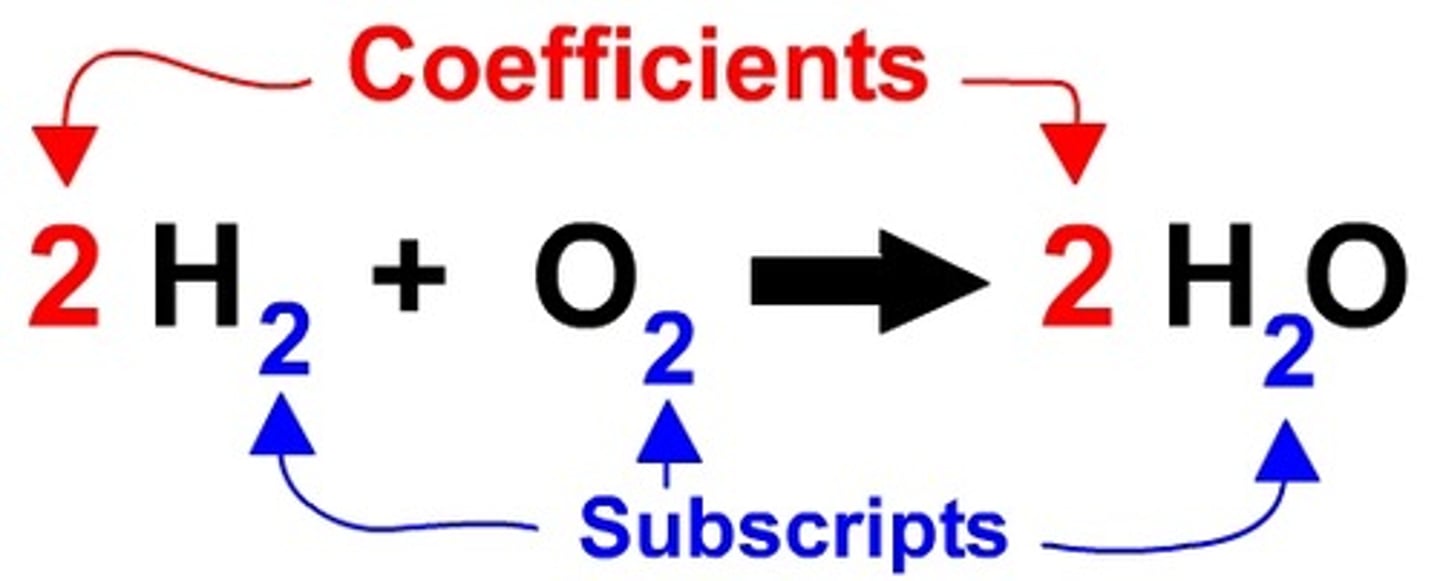
Subscript
The little number to the lower right of a symbol that indicates how many atoms of that symbol are included in that particle. Ex. H₂O the 2 means that there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom bonded together to form a single water molecule. Indicates BONDING
Molecule
A group of nonmetal atoms bonded together by covalent bonds to form a covalent particle. It is the smallest piece of a covalent substance that retains all the properties of that substance. (H₂ and CO₂ for example)
Formula Unit
A group of ions bonded together by ionic bonds to form an ionic compound. This is the smallest piece of an ionic compound that retains all the properties of that compound. They are composed of metal and nonmetal atoms.
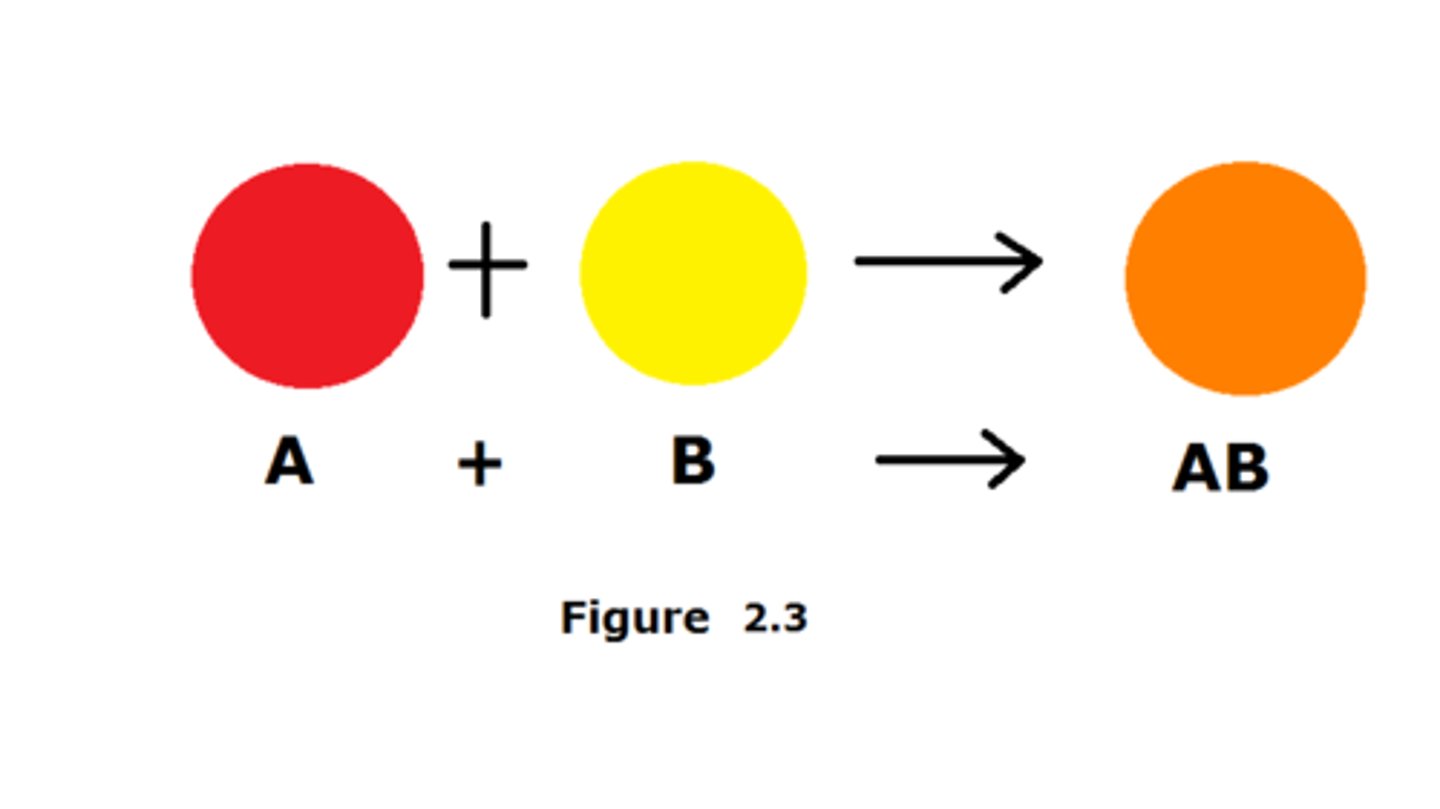
Synthesis Reaction
A chemical reaction where two or more reactants combine chemically to form one new product.
Ex. 2Cu + O₂ → 2CuO
Copper + Oxygen → Copper Oxide
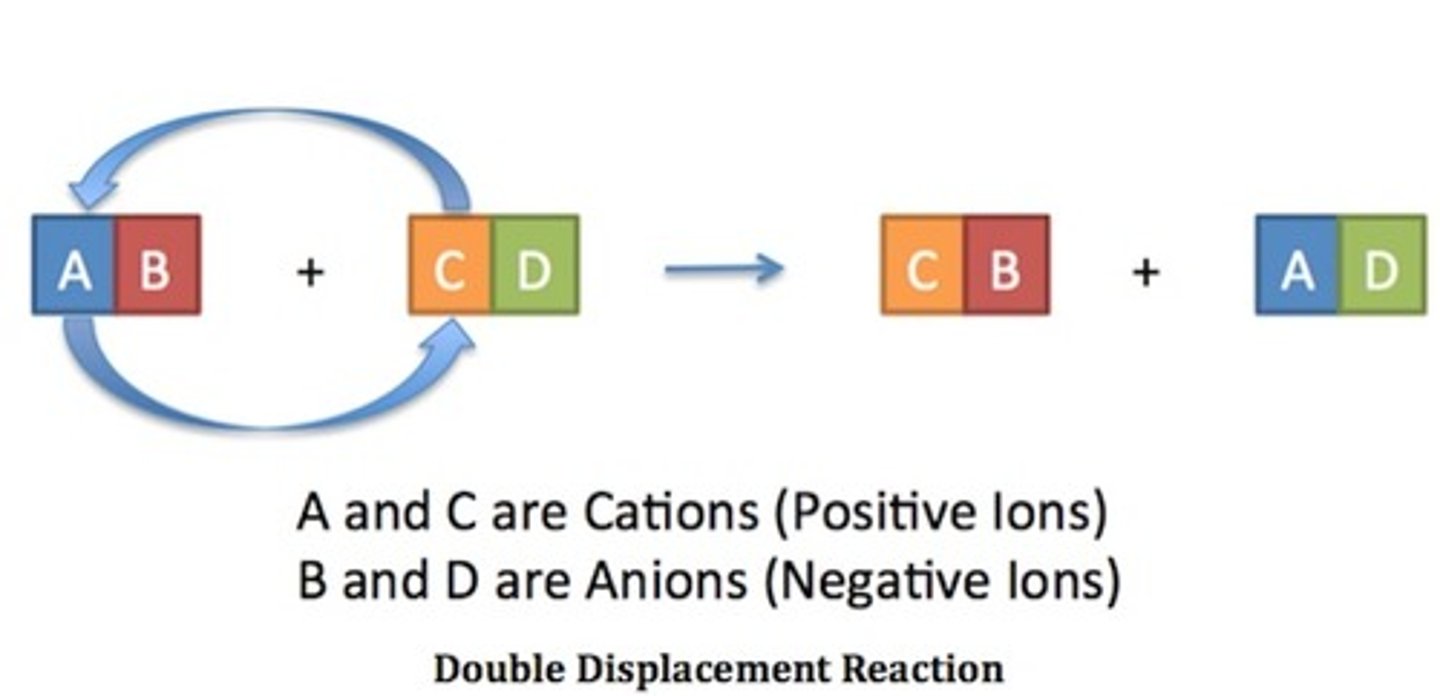
Double Replacement Reaction
A chemical reaction where two compound reactants break apart to recombine chemically and form two new compound products. Each reactant is formed from a metal bonded (ionically) with a nonmetal. To form the products the metals switch places. (*Note, in this special case, Hydrogen (H) is acting like a metallic element but still makes a covalent bond with chlorine!)
CuO(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CuCl₂(aq) + H₂O(l)
Copper Oxide + Hydrochloric Acid → Copper Chloride + Water
Combustion Reaction
A rapid reaction between oxygen and a hydrocarbon fuel that produces carbon dioxide, water, and thermal energy.
An example of the base of an unbalanced combustion reaction is:
CxHy + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
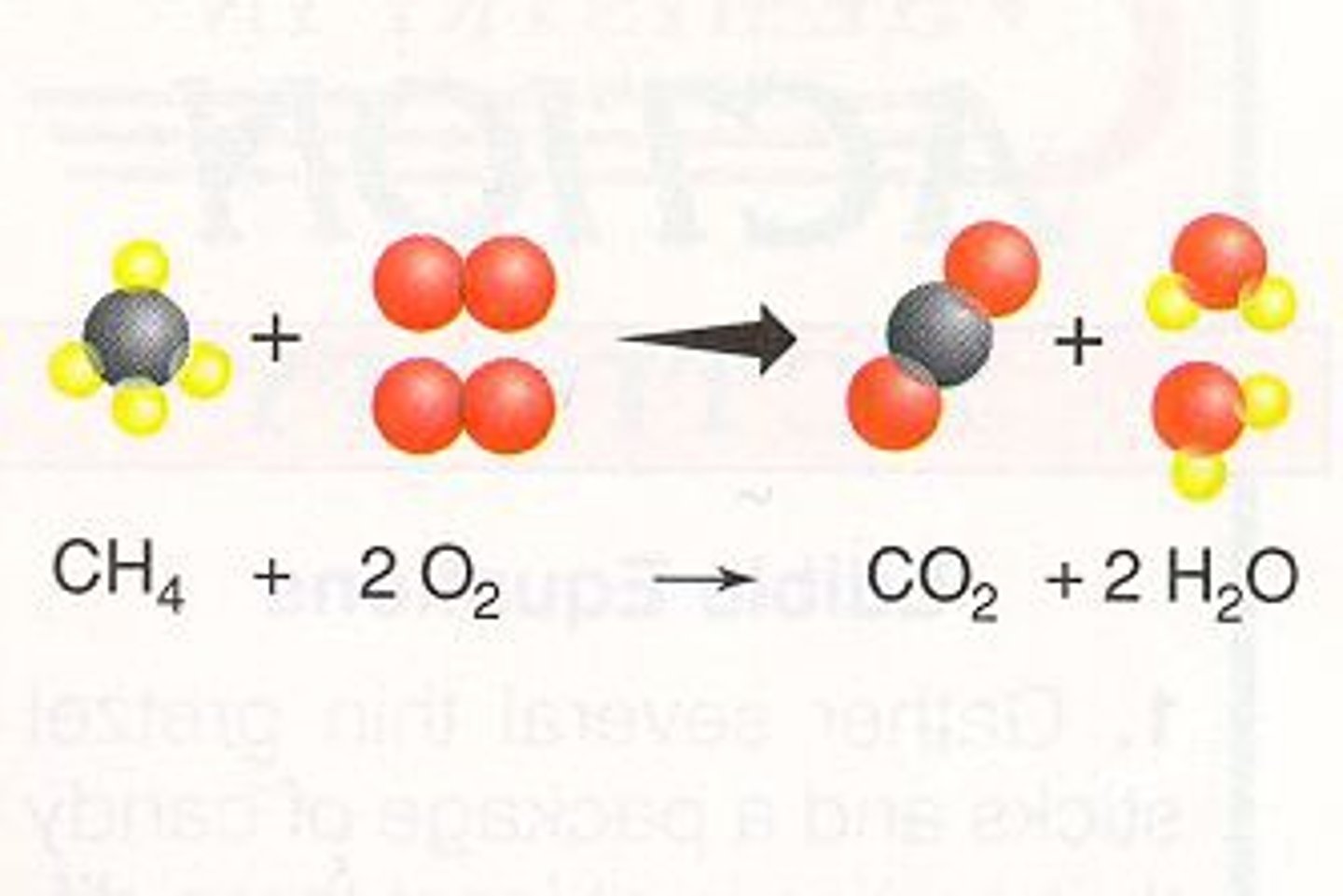
Ion
A particle with a positive or negative charge. It forms when an atom has an unequal number of protons and electrons. It may have a (cation) positive charge (loss of electrons to have more protons than electrons) or an (anion) negative charge (gain of electrons to have more electrons than protons).
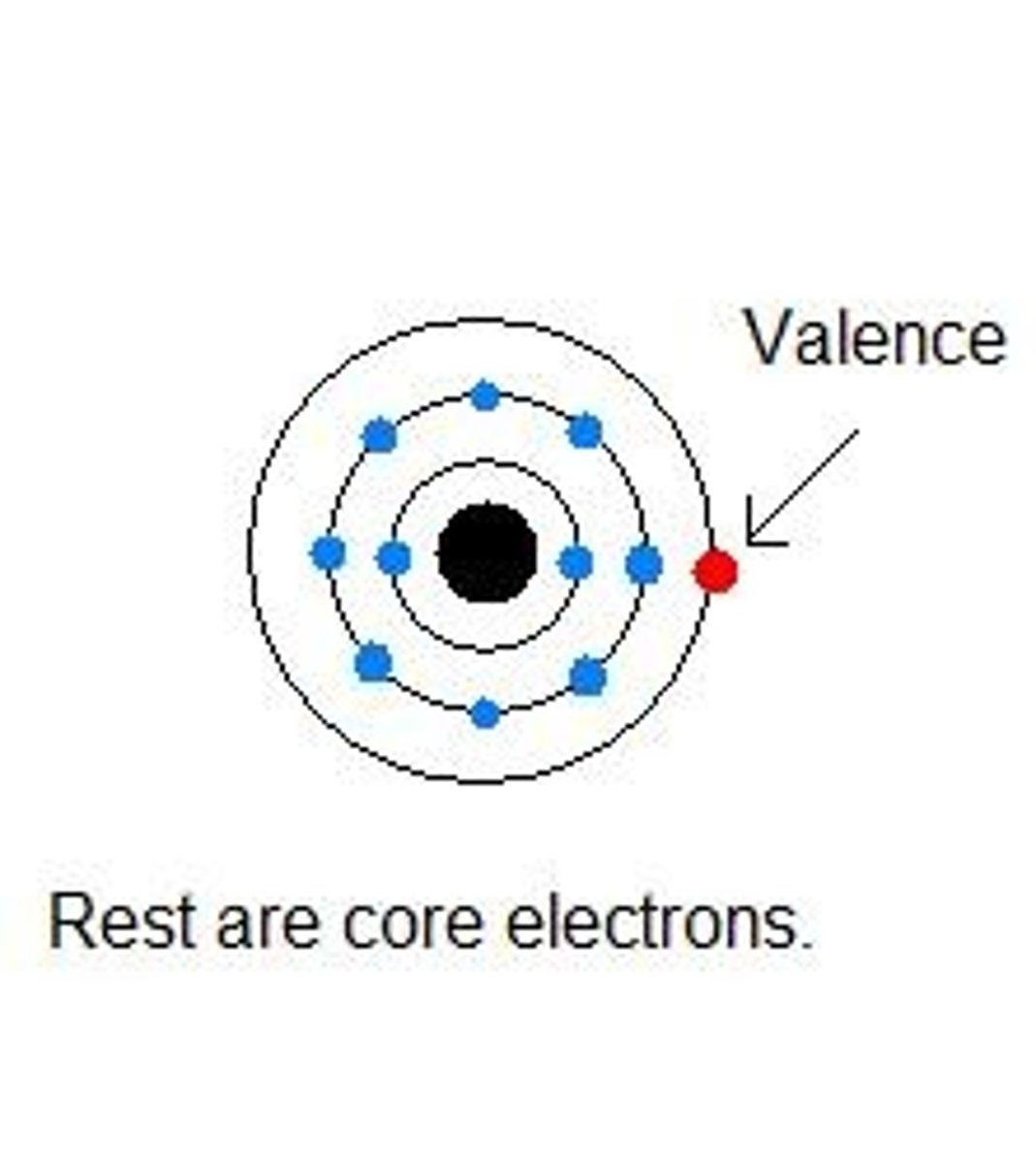
Valence Electrons
The electrons available to be lost, gained, or shared during bonding. Located in the outermost energy level of the atom.
Covalent bond
The bond between atoms that form when valence electrons are shared. A characteristic of nonmetals bonding with nonmetals (ex H₂O and O₂)
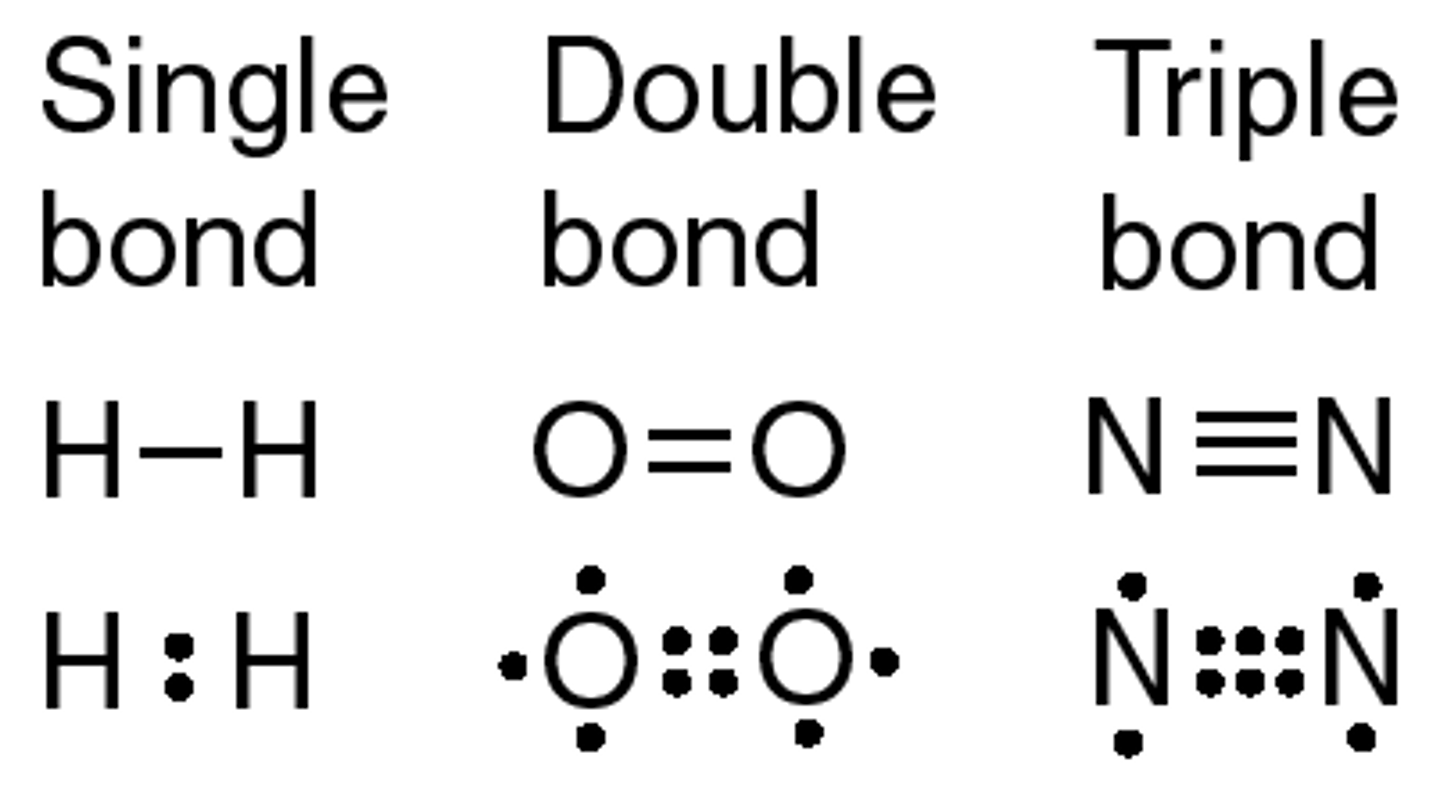
Ionic bond
Bond between atoms that forms from the transfer of electrons when valence electrons are lost from one atom and gained by another atom creating ions that are attracted to each other. A characteristic of metals bonding with nonmetals (ex NaCl).
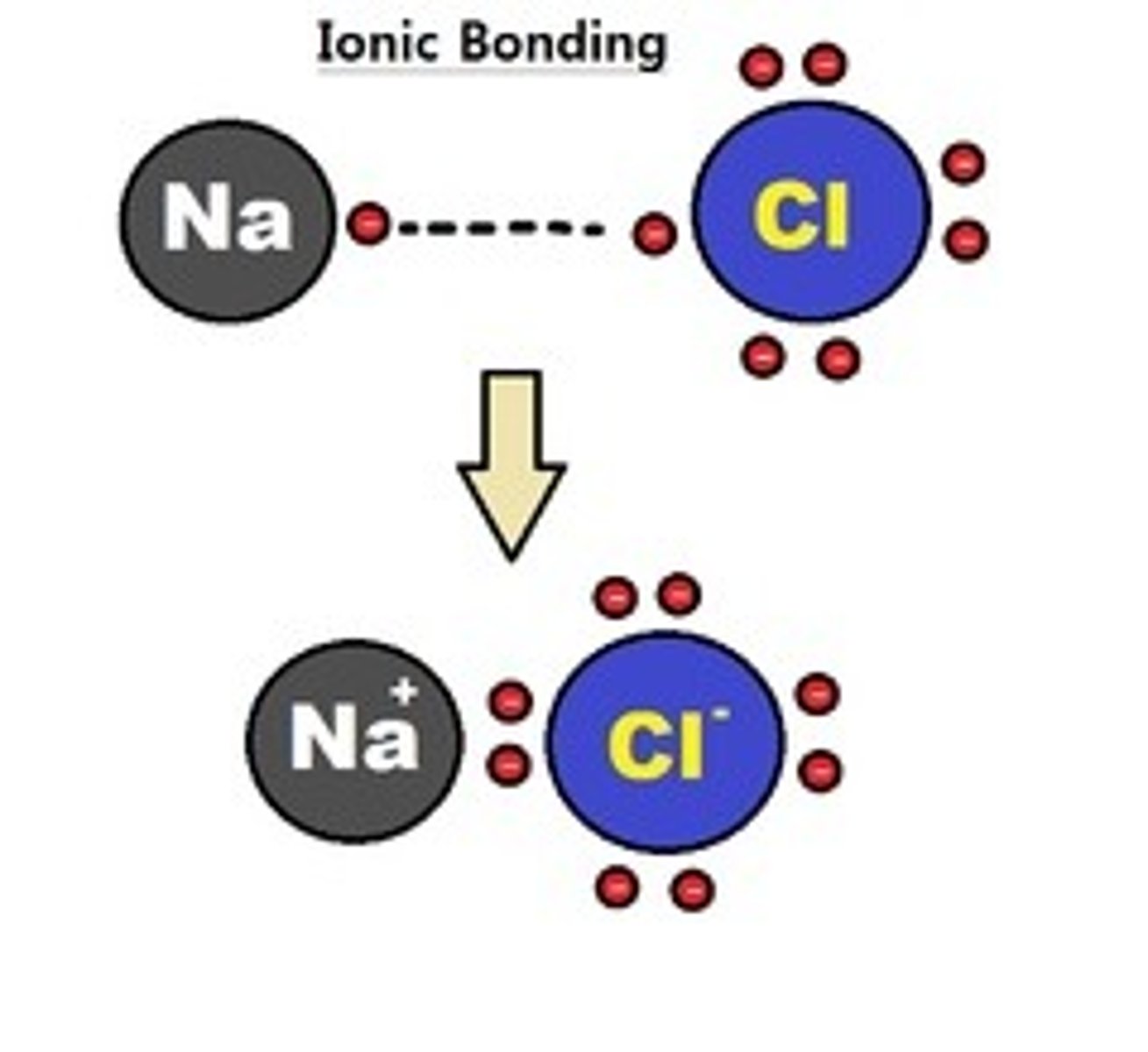
Diatomic
Means being made from two atoms that are the same type bonded together by covalent bonds: H₂, O₂, N₂, Cl₂, F₂, Br₂ ,I₂.
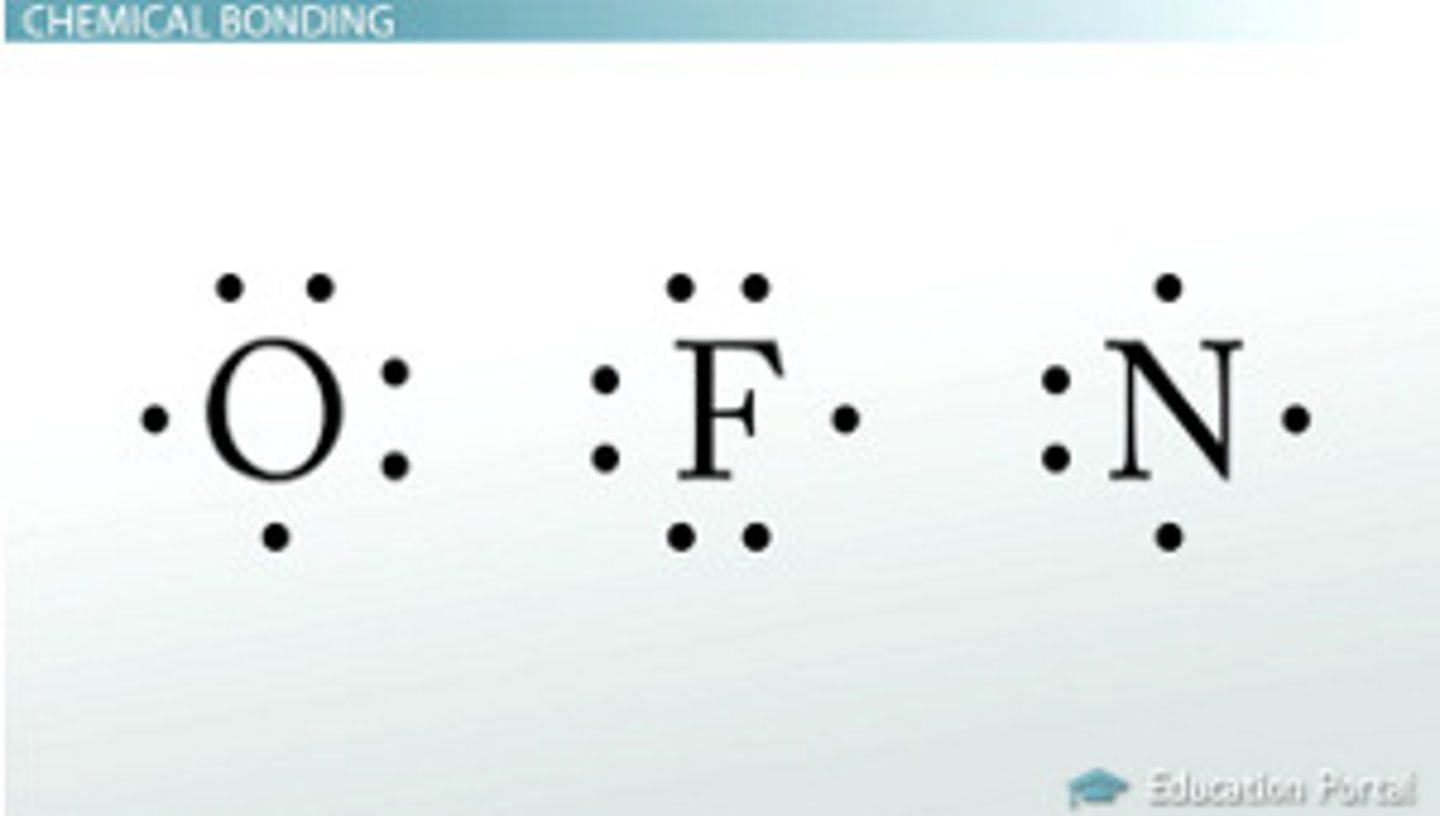
Lewis Dot Structure
diagram of a molecule using dots to represent valence electrons an atom has
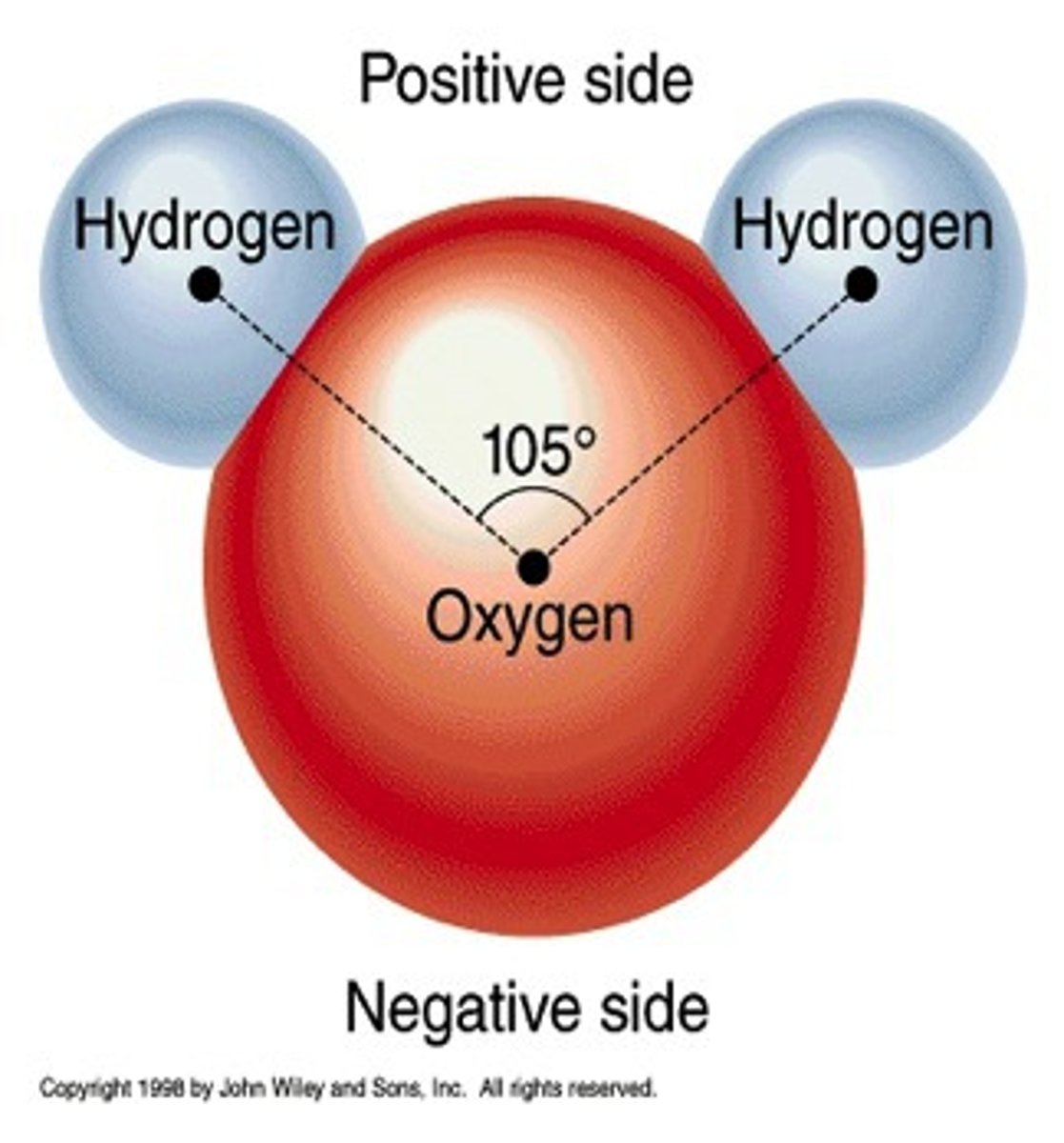
polar molecule
A molecule in which one side of the molecule is slightly negative and the opposite side is slightly positive, water is an example of a polar molecule
nonpolar molecule
A molecule that shares electrons equally and does not have oppositely charged ends

Compound
A substance comprises atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds.
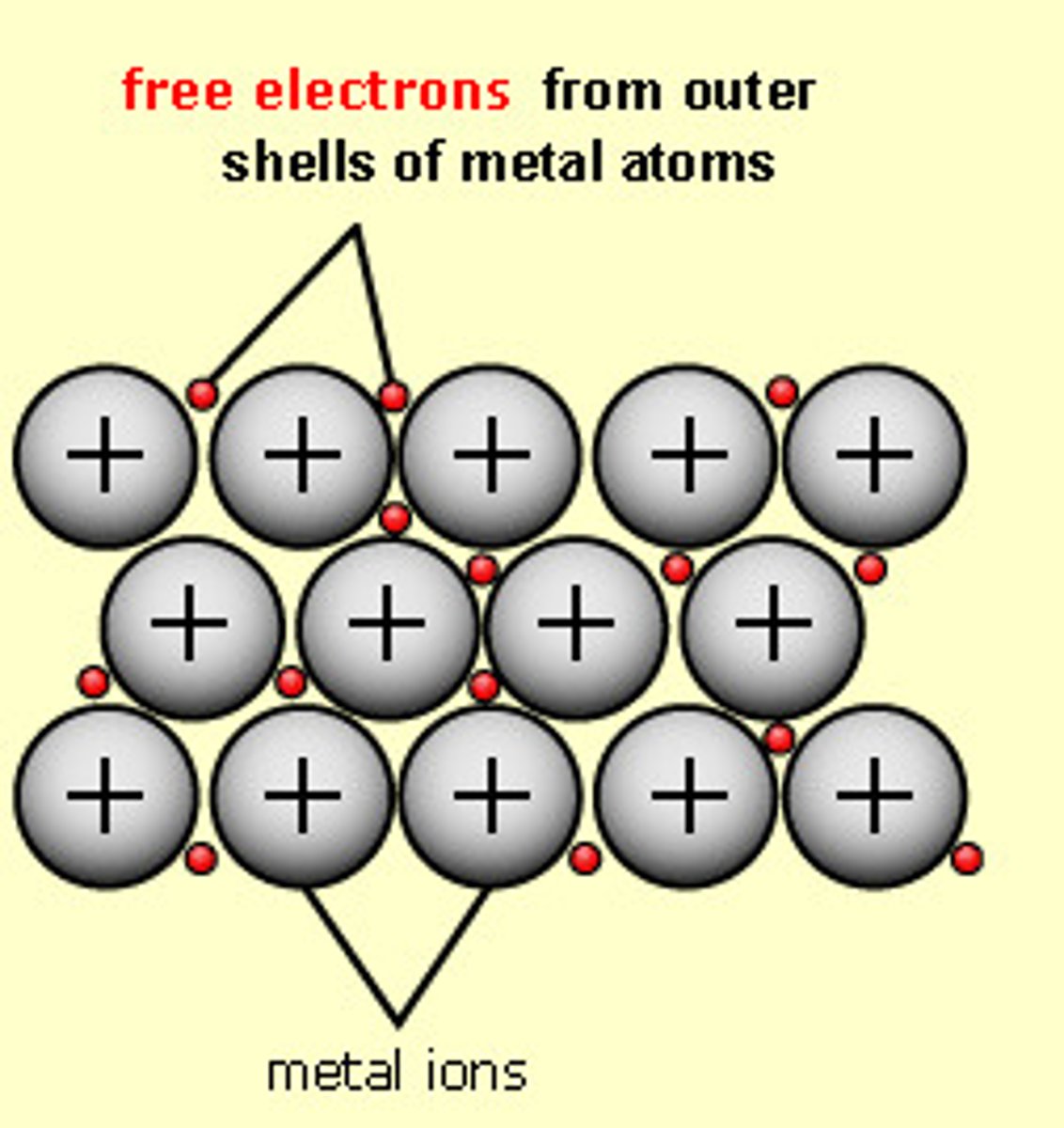
metallic bond
an attraction between a positive metal ion and the electrons surrounding it, electrons are a "sea" around the positive metal ions
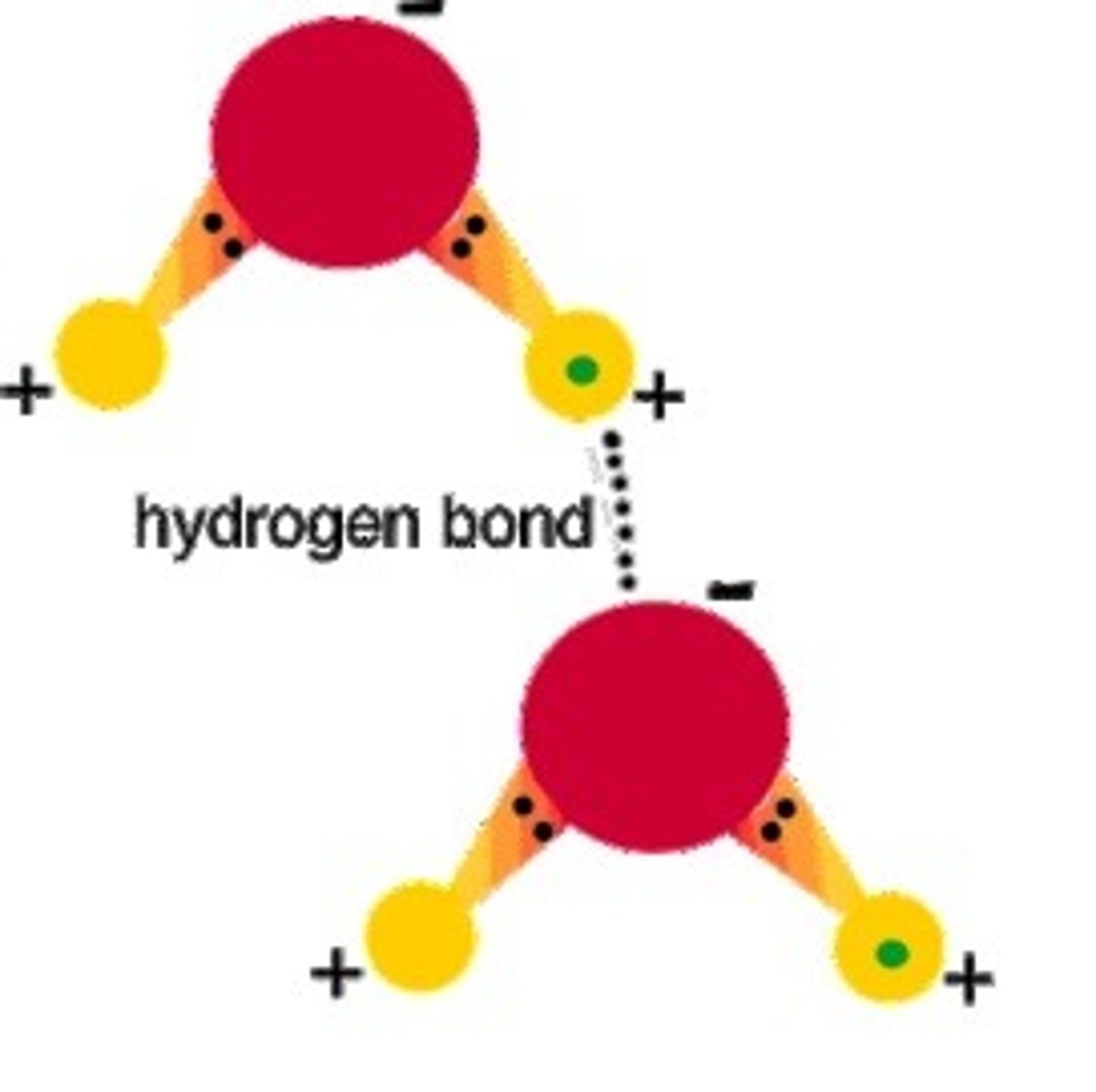
Hydrogen bond
A type of weak molecular chemical bond is formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of one polar covalent molecule is attracted to the slightly negative atom of a polar covalent bond in another molecule.
Anion
A negatively charged particle, where there are more electrons than protons present in the particle
Cation
A particle with a positive charge, where there are more protons than electrons present in the particle
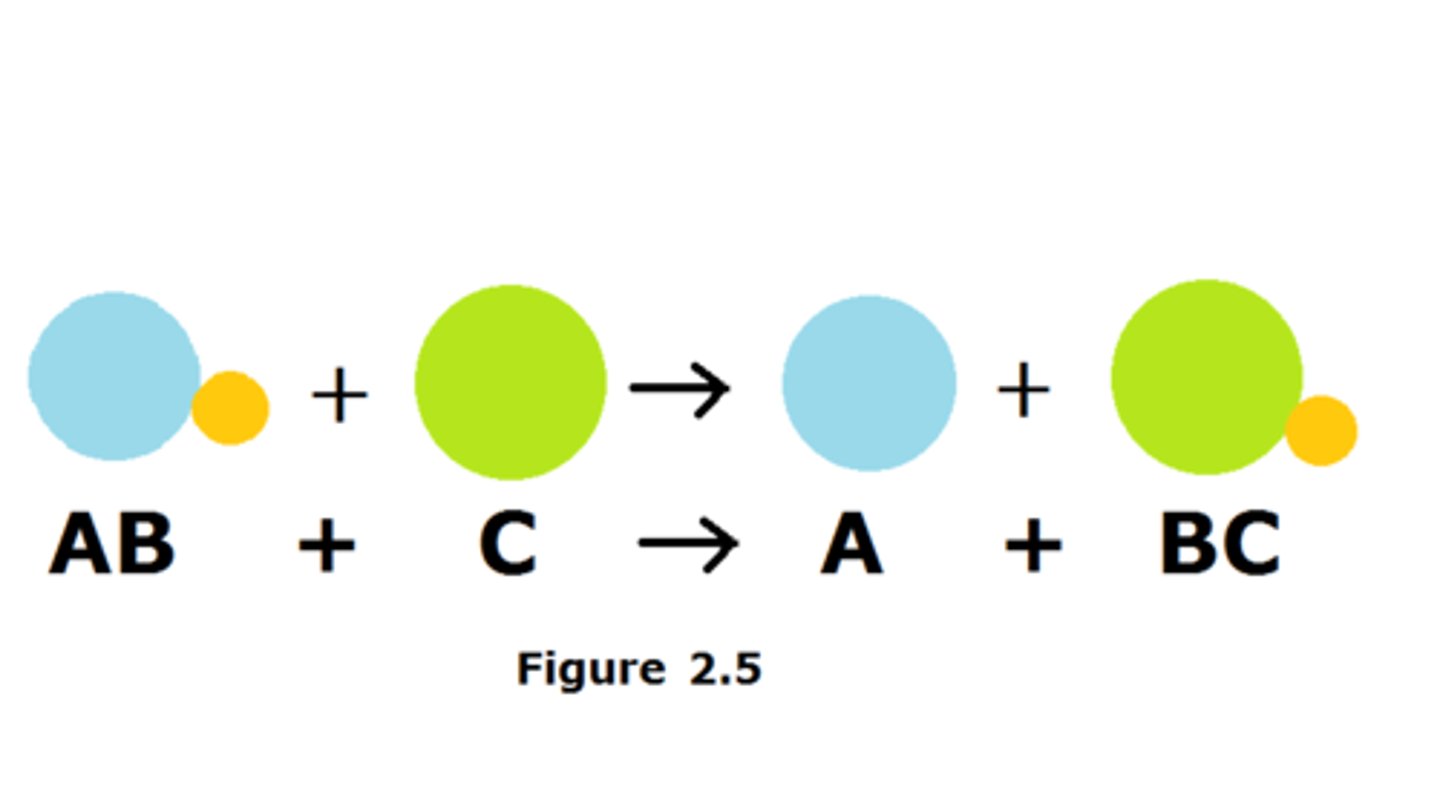
Single replacement reaction
A chemical reaction where one compound reactant breaks apart to recombine chemically and form one new product.
Br₂ + 2KF --> 2KBr + F₂
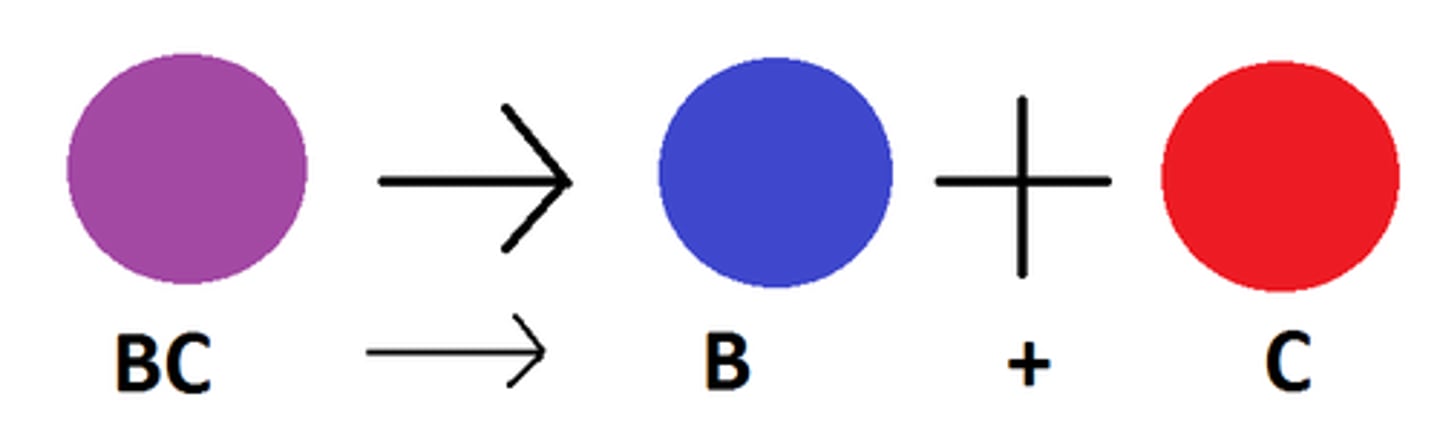
Decomposition Reaction
a reaction in which a single compound breaks down to form two or more simpler substances
2H₂O --> H₂ + O₂
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom, for example Carbon, there are unique 118 elements on the Periodic Table
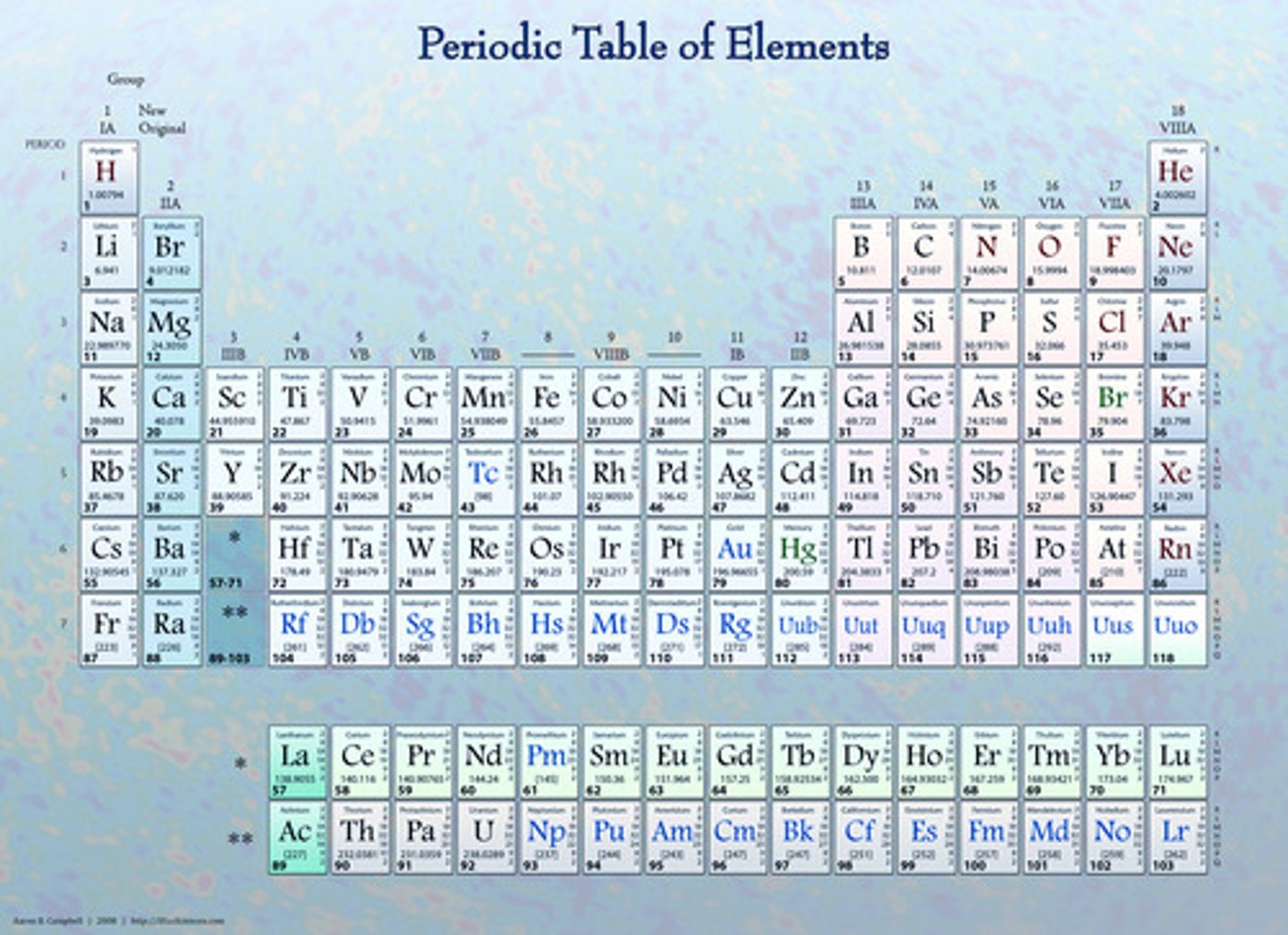
Periodic Table
A table that shows the elements, their atomic number, symbol, and average atomic mass; elements with similar chemical properties are grouped together.