Alkanes and Alkenes
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Alkane
A group of saturated hydrocarbons
the term saturated means that they only have single carbon-carbon bonds, there are no double bonds (remember carbon can only have a maximum of 4 bonds)
Structure of an alkane example (propane model)
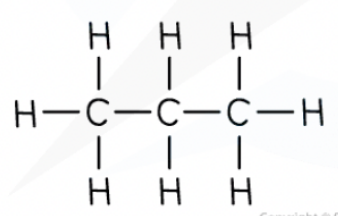
general formula for alkanes
CnH2n+2
How do alkanes react
Alkanes are generally unreactive compounds but they do undergo combustion reactions, can be cracked into smaller molecules and can react with halogens in the presence of light
List the alkanes (starting from the one with only one carbon to 5 carbons)
Methane
Ethane
Propane
Butane
Pentane
Using the formula, what is propane molecular formula (Propane has 3 carbons)
CnH2n+2 (n = number of carbons)
C3H(2×3)+2 = C3H8
What happens when Alkanes and halogens are in the presence of ultraviolet light
A substitution reaction, one atom is swapped with another atom. Alkanes undergo a substitution reaction with halogens in the presence of ultraviolet radiation
Alkene
Alkenes are a homologous series of hydrocarbon compounds with at least one double bond between two of the carbon atoms on the chain
The double bond can be written as carbon to carbon double bond or as C=C
Structure of an alkene model (Propene model used)
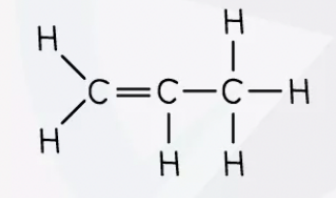
General formula for alkenes
CnH2n
Using the formula, what is propene molecular formula (Propene has 3 carbons)
CnH2n = C3H2×3
C3H6
Which is more reactive, alkanes or alkenes and why
The double bond alkenes have means they can make more bonds with other atoms by opening up the C=C bond and allowing incoming atoms to form another single bond with each carbon atom of the functional group
Each of these carbon atoms now forms 4 single bonds instead of 1 double and 2 single bonds
This makes them much more reactive than alkanes
How to work out if a substance is an alkane or an alkene
bromine water test
Bromine water is an orange-coloured solution
When bromine water is added to an alkane, it will remain as an orange solution as alkanes do not have double carbon bonds (C=C) so the bromine remains in the solution
But when bromine water is added to an alkene, the bromine atoms add across the C=C bond, hence the solution no longer contains free bromine so it loses its colour