Biomechanics Practical
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
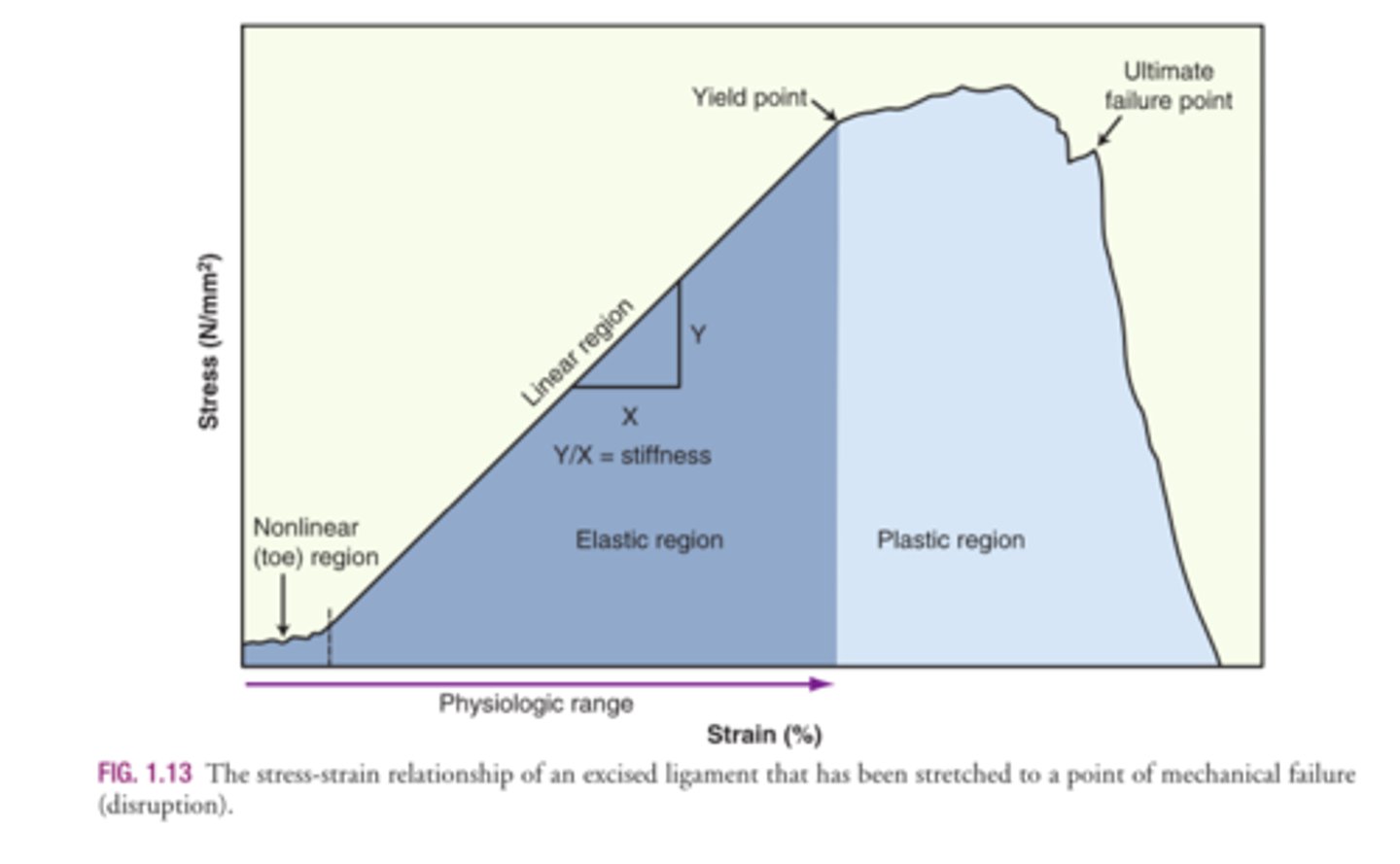
1. Yield Point
2. Plastic Region
1. At what point is a tissue elongated past its physiological range?
2. At which region is the tissue permanently deformed?
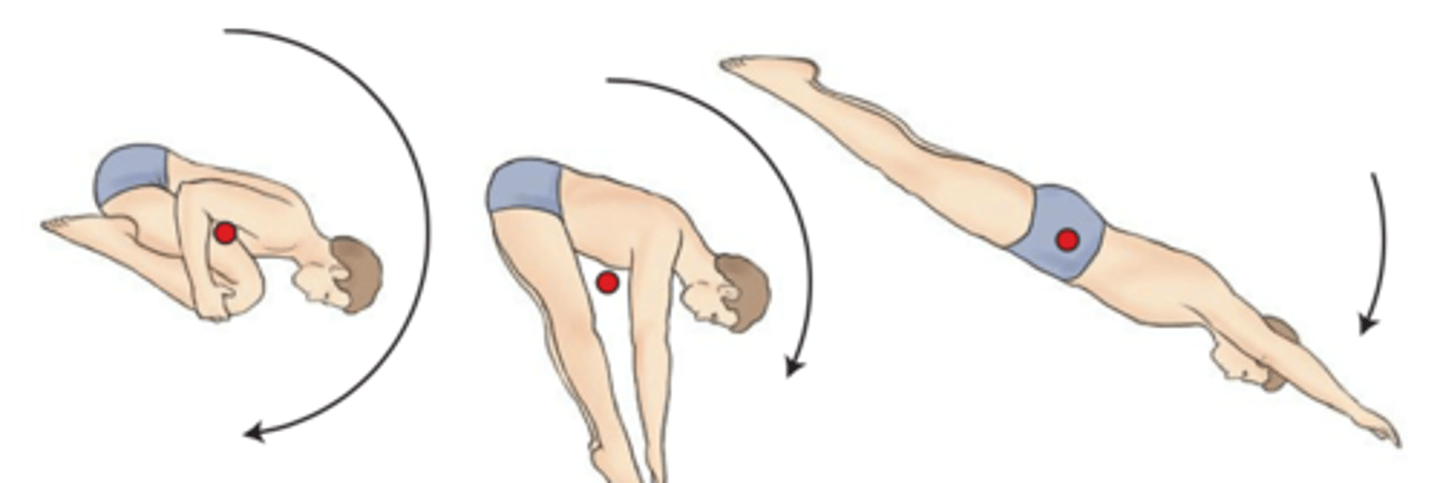
Diver C (far right)
Which diver has the slowest angular velocity?
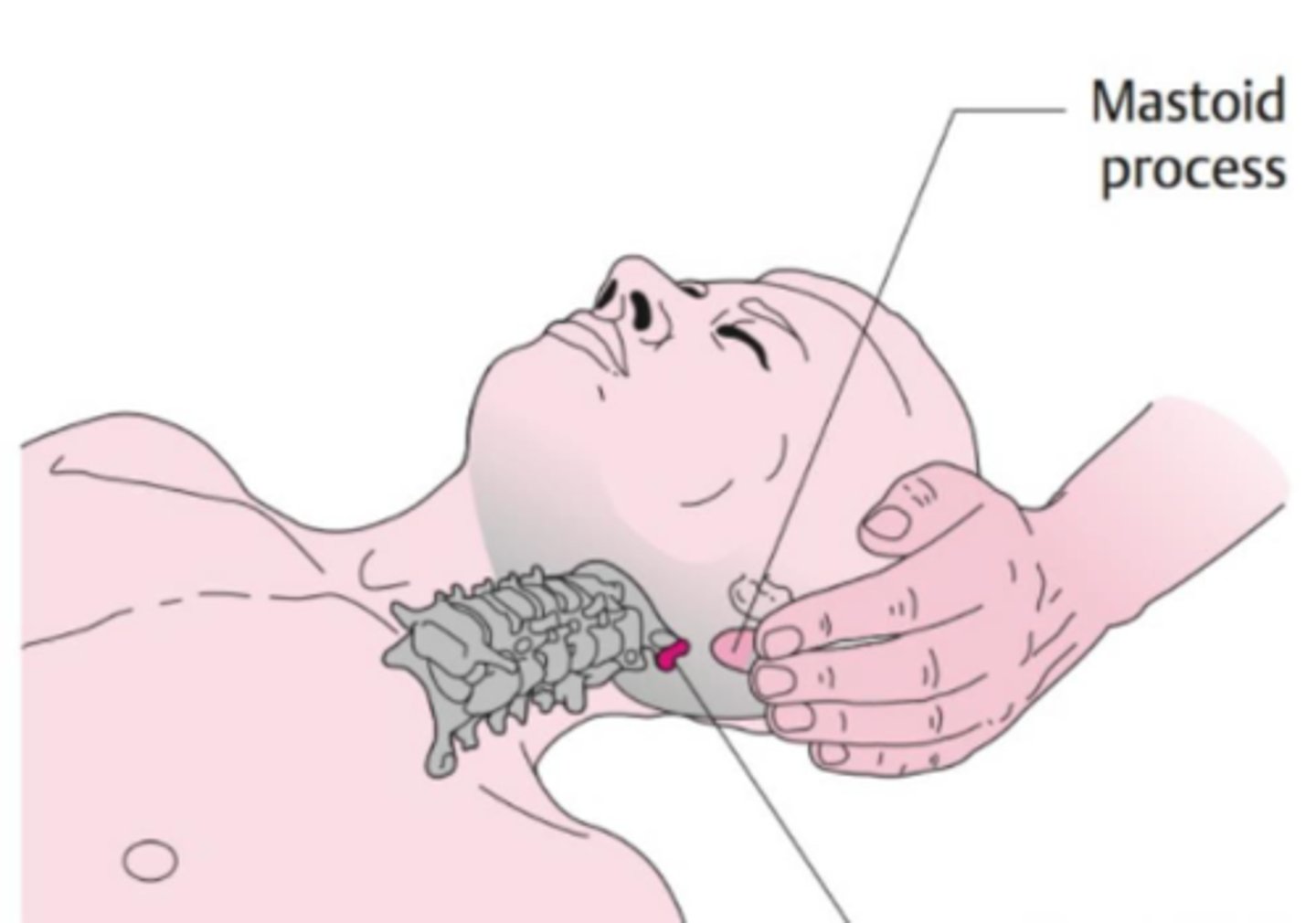
Transverse Process of C1
What is this person palpating in dark red?
Spinous Process of L4/L5
What structure is this person palpating?
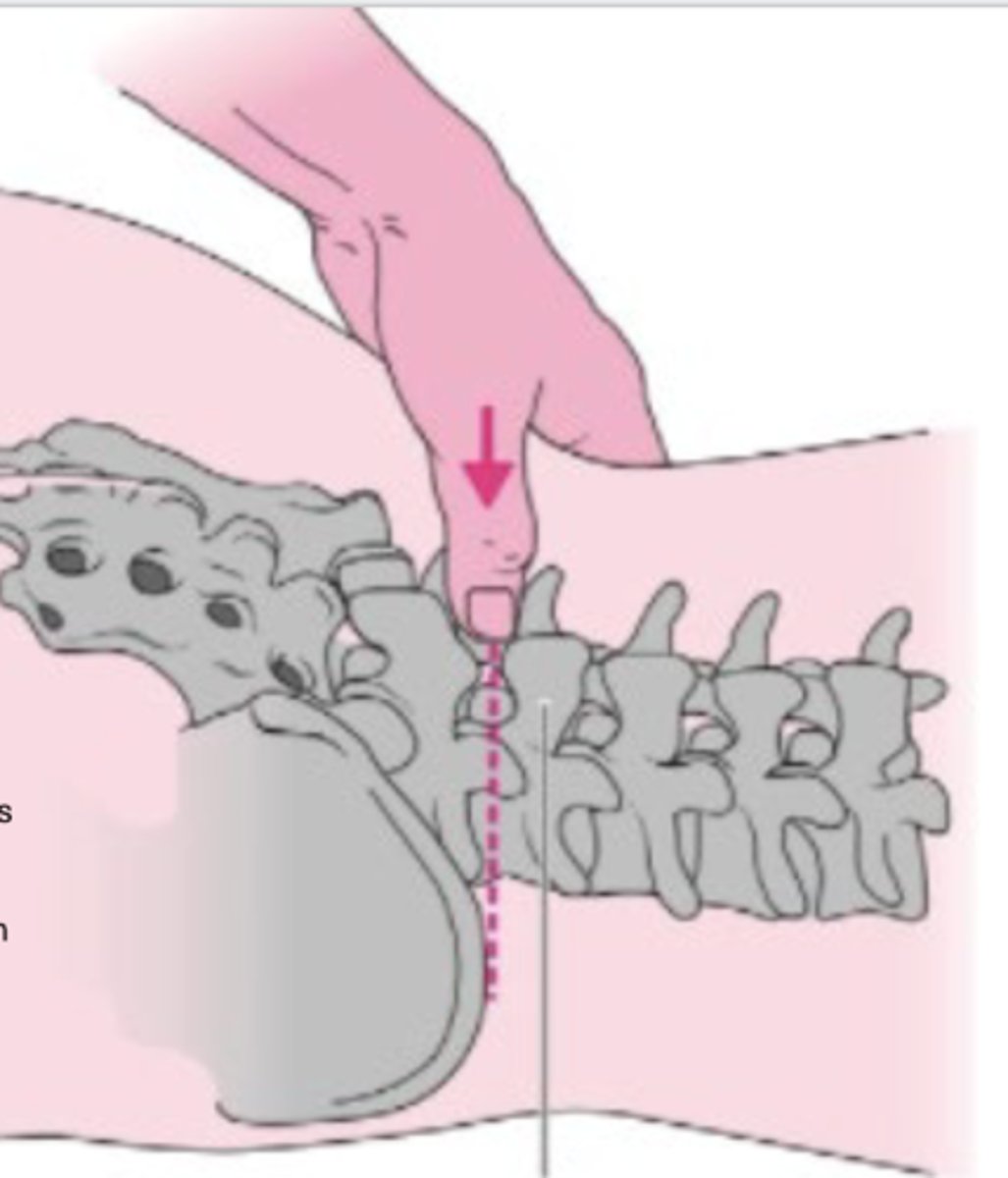
Spinous Process of S2
What structure is this person palpating?

Both up glide
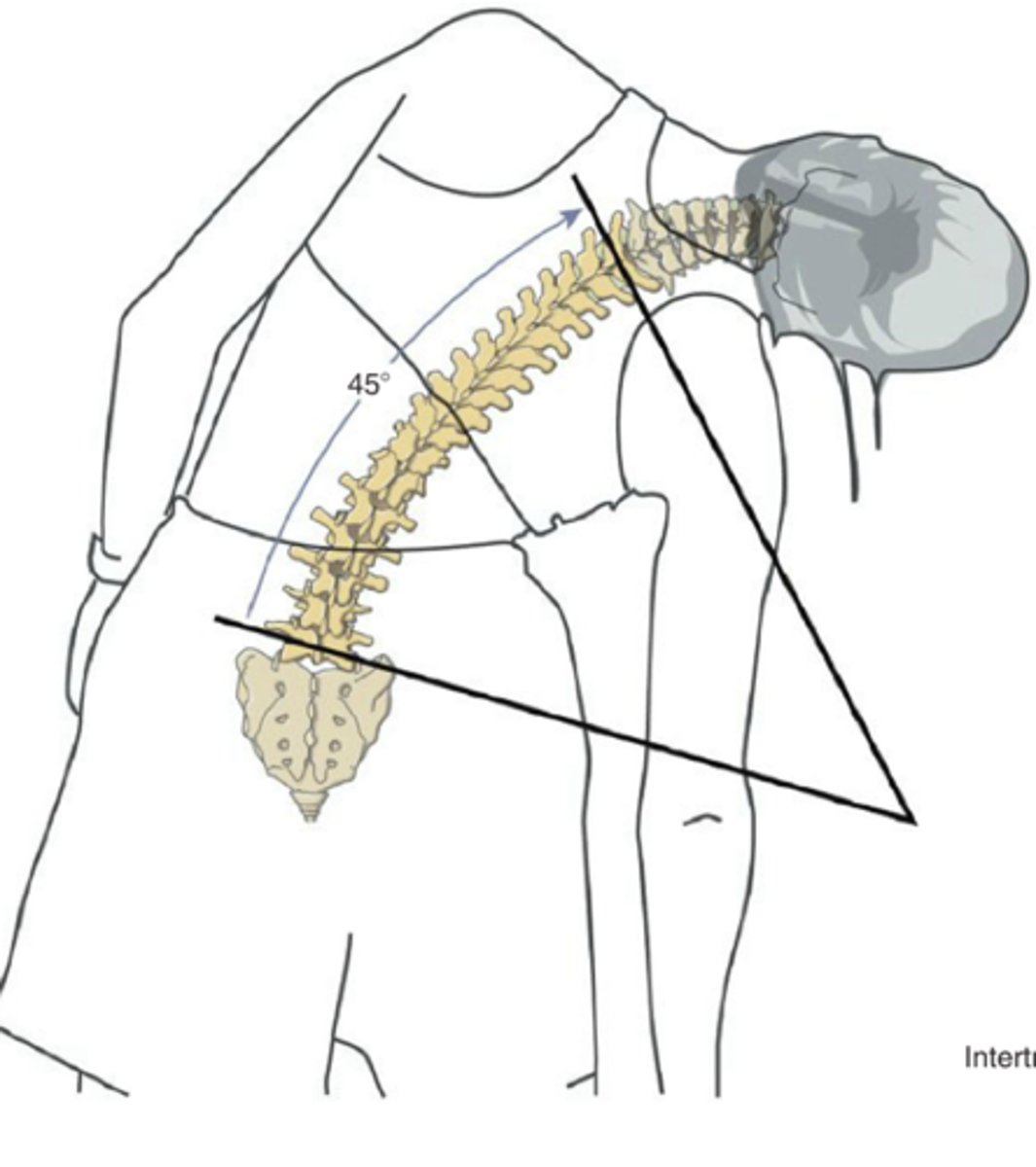
Thoracic Region:
In thoracolumbar flexion, the facets are doing what?
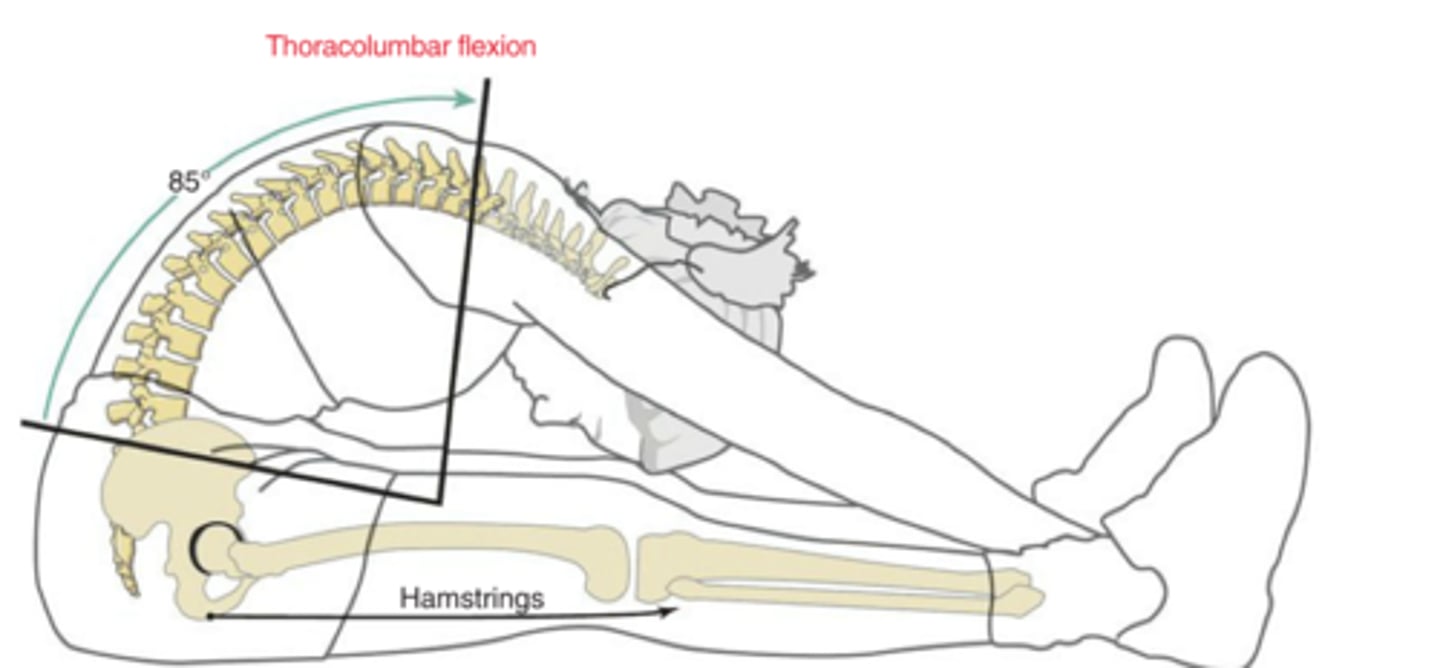
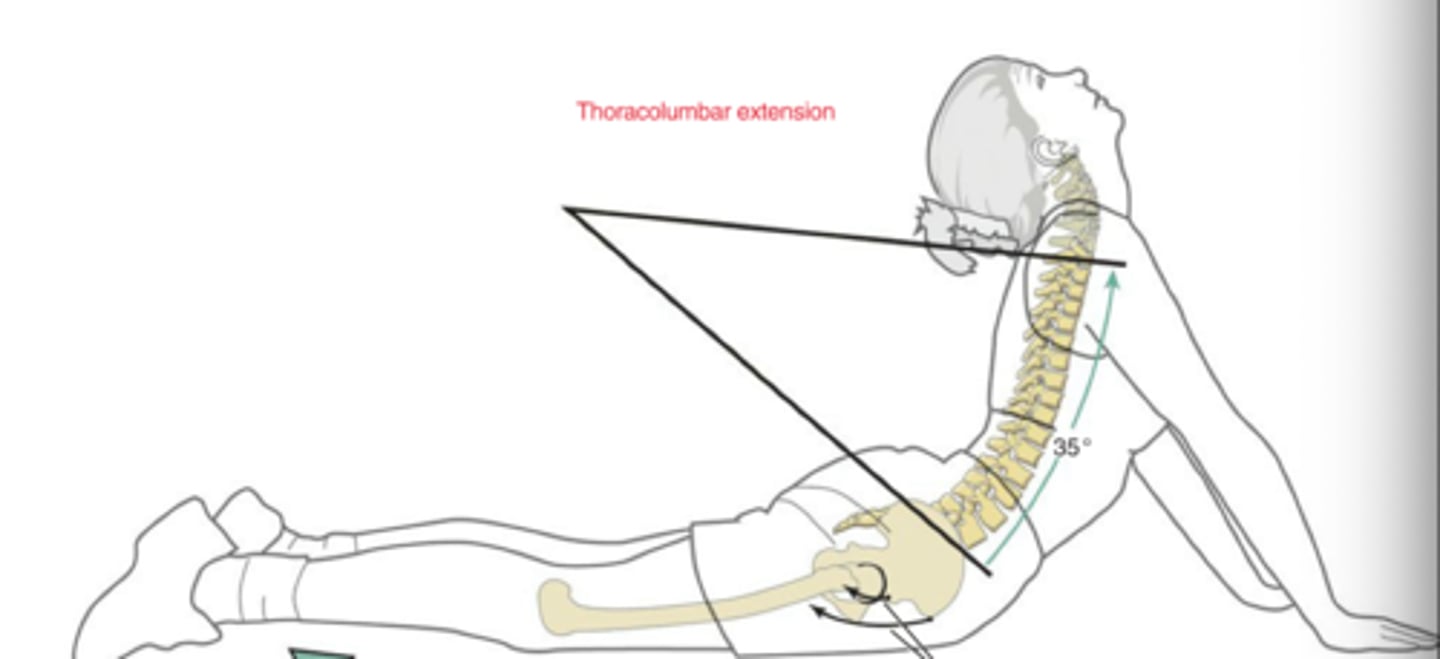
Both down glide
Thoracic Region:
In thoracolumbar extension, the facets are doing what?
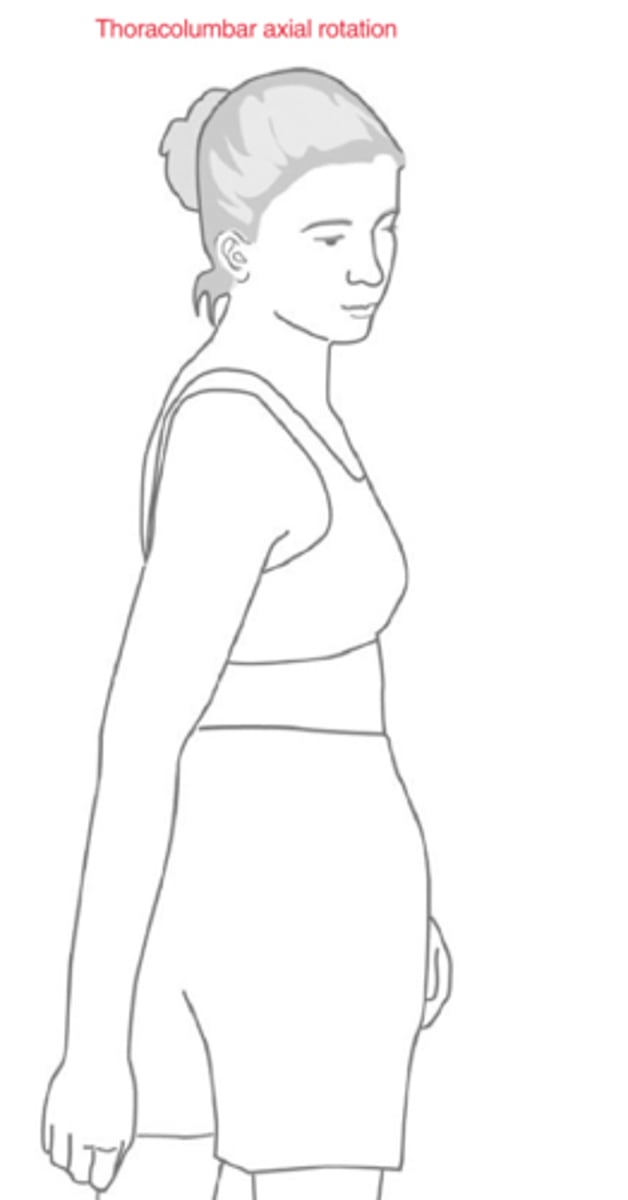
1. Right open, left compression
2. Left open, right compression
Thoracic Region:
1. In thoracolumbar right axial rotation, the facets are doing what?
2. In thoracolumbar left axial rotation, the facets are doing what?
1. Right down glide, Left up glide
2. Left down glide, Right up glide
Thoracic Region:
1. In thoracolumbar right lateral flexion, the facets are doing what?
2. In thoracolumbar left lateral flexion, the facets are doing what?
Force Couple
(according to Reese: Same direction = force couple)
Is this force couple or synergy?
Synergy
(According to Reese: Opposite direction = synergy)
Is this force couple or synergy?
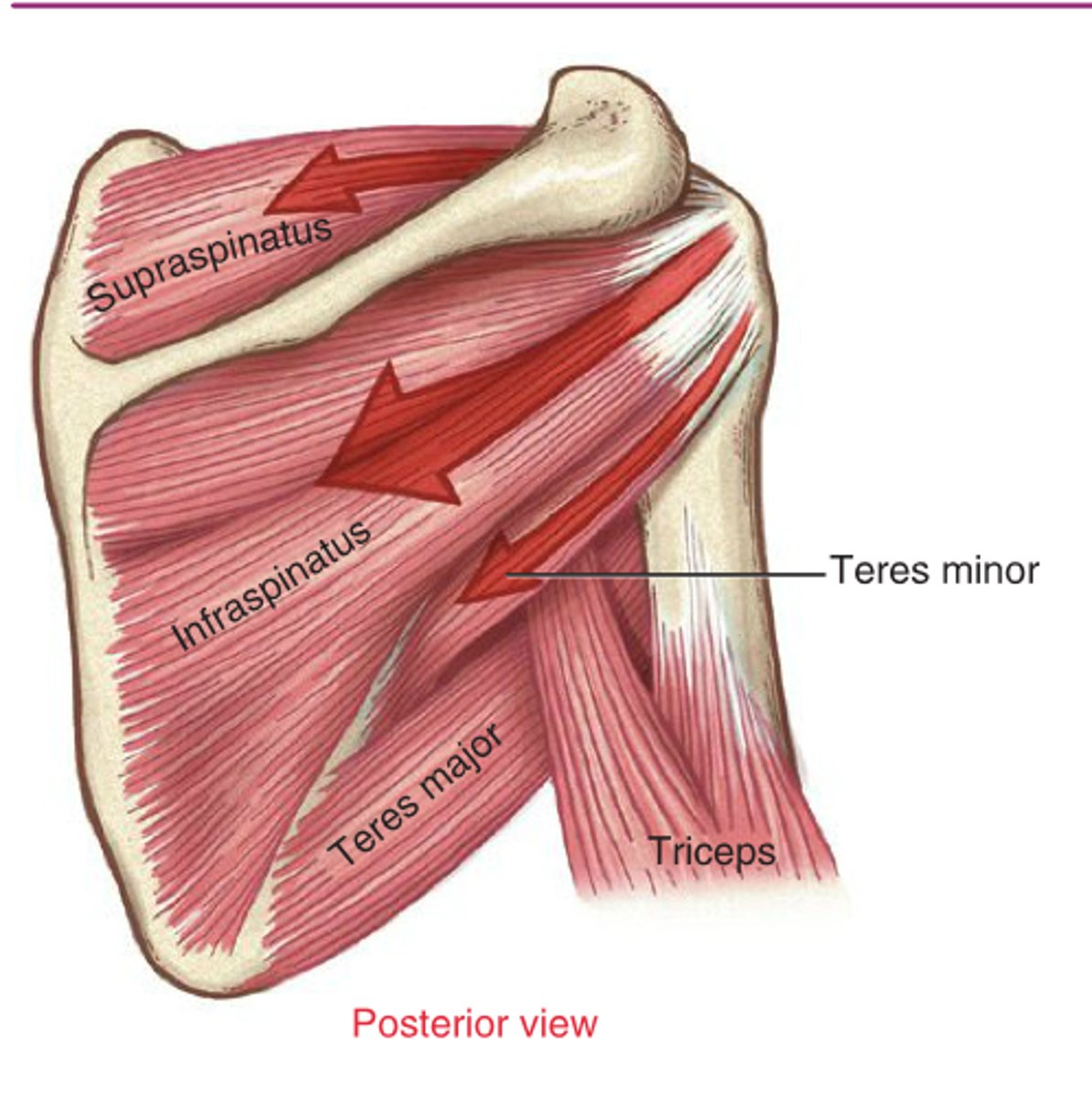
Synergy
Are the muscles here acting in synergy or forced couple?
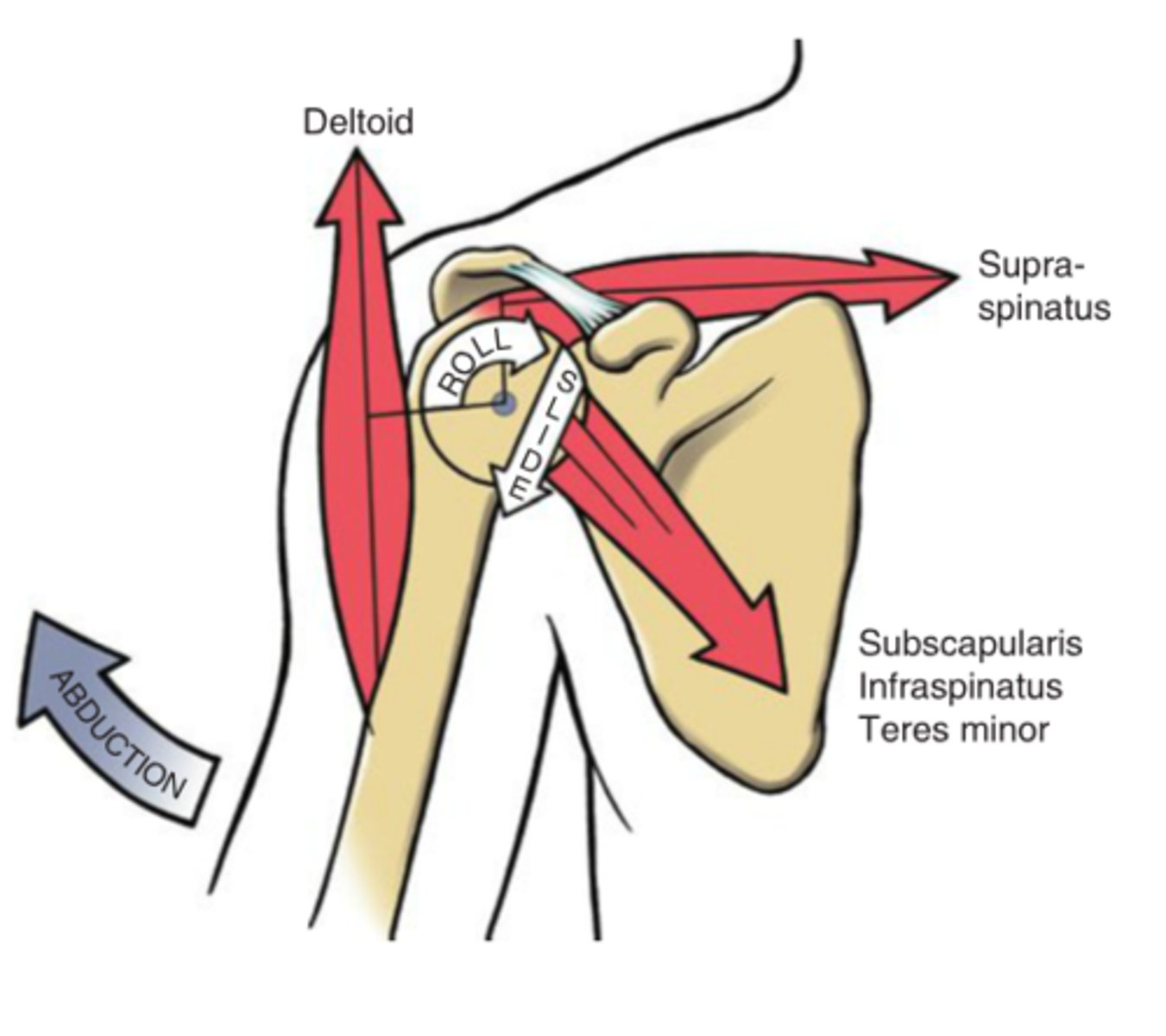
Force Couple
Are the muscles here acting in synergy or forced couple?
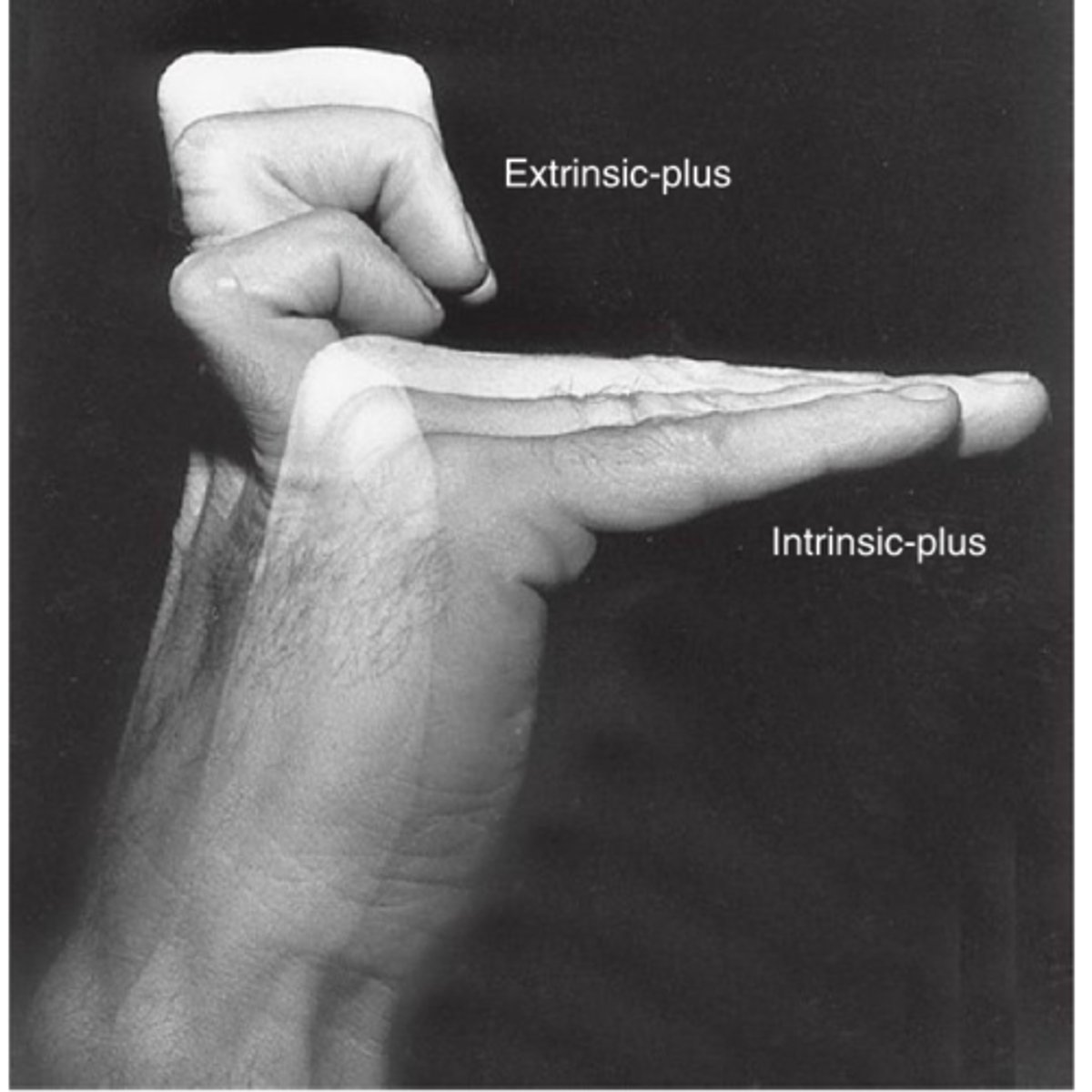
1. Intrinsic Plus (Extrinsic Minus also correct)
2. Lumbricals and Interossei (more spasticity than FDS and FDP)
1. What position is this hand in?
2. Which muscles are have more spasticity?
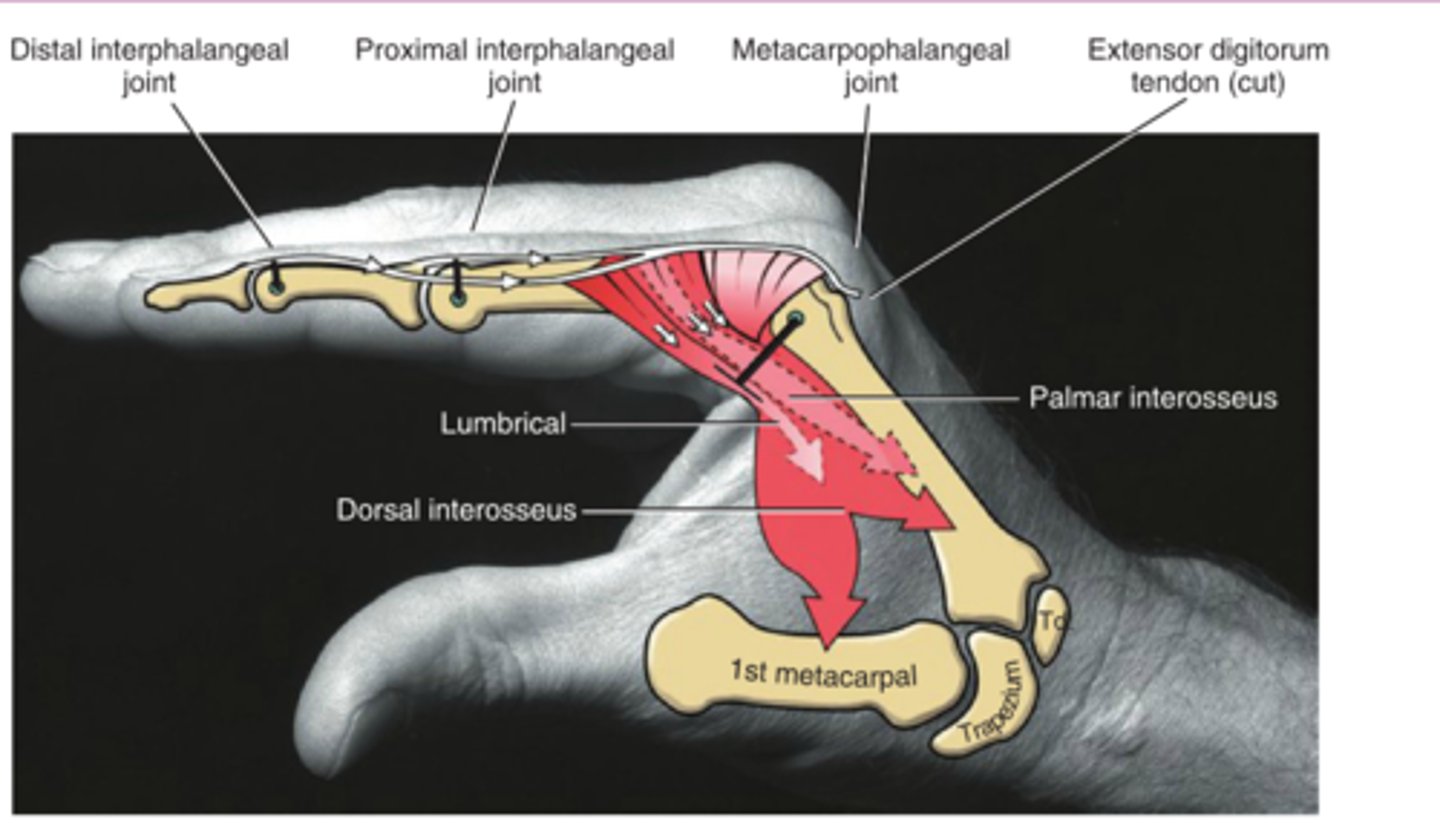
Longitudinal Arch
Distal Transverse Arch
Proximal Transverse Arch
What arches in the hand are needed to pick up an object? (Hint: There are 3.)
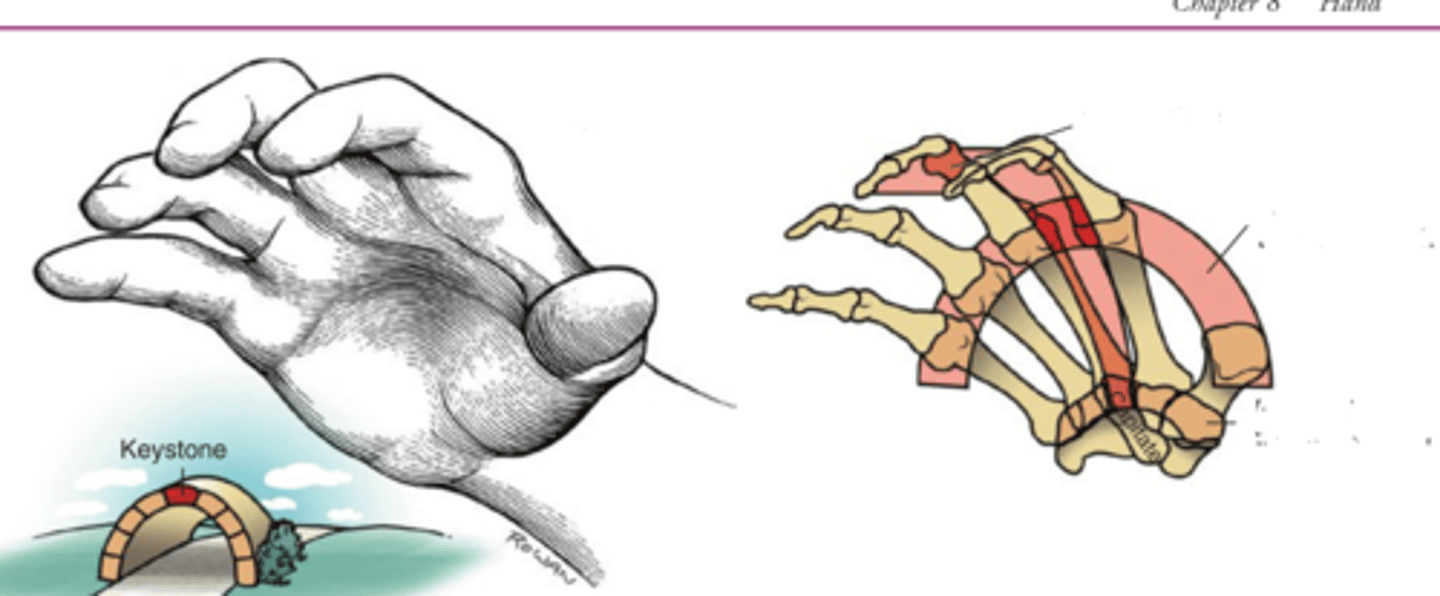
1. FDP and FDS(extrinsics) are overpowering the lumbricals and interossei muscles(intrinsics).
2. Ulnar
1. What puts the hand in an extrinsic plus (Intrinsic Minus) position?
2. If only the pinky and ring finger were in the claw position, what nerve is affected?
1. Tenodesis
2. During wrist extension, the extrinsic flexors are put in a stretched position, resulting in passive flexion of the fingers and thumb.
1. What is happening in this picture?
2. What causes it?
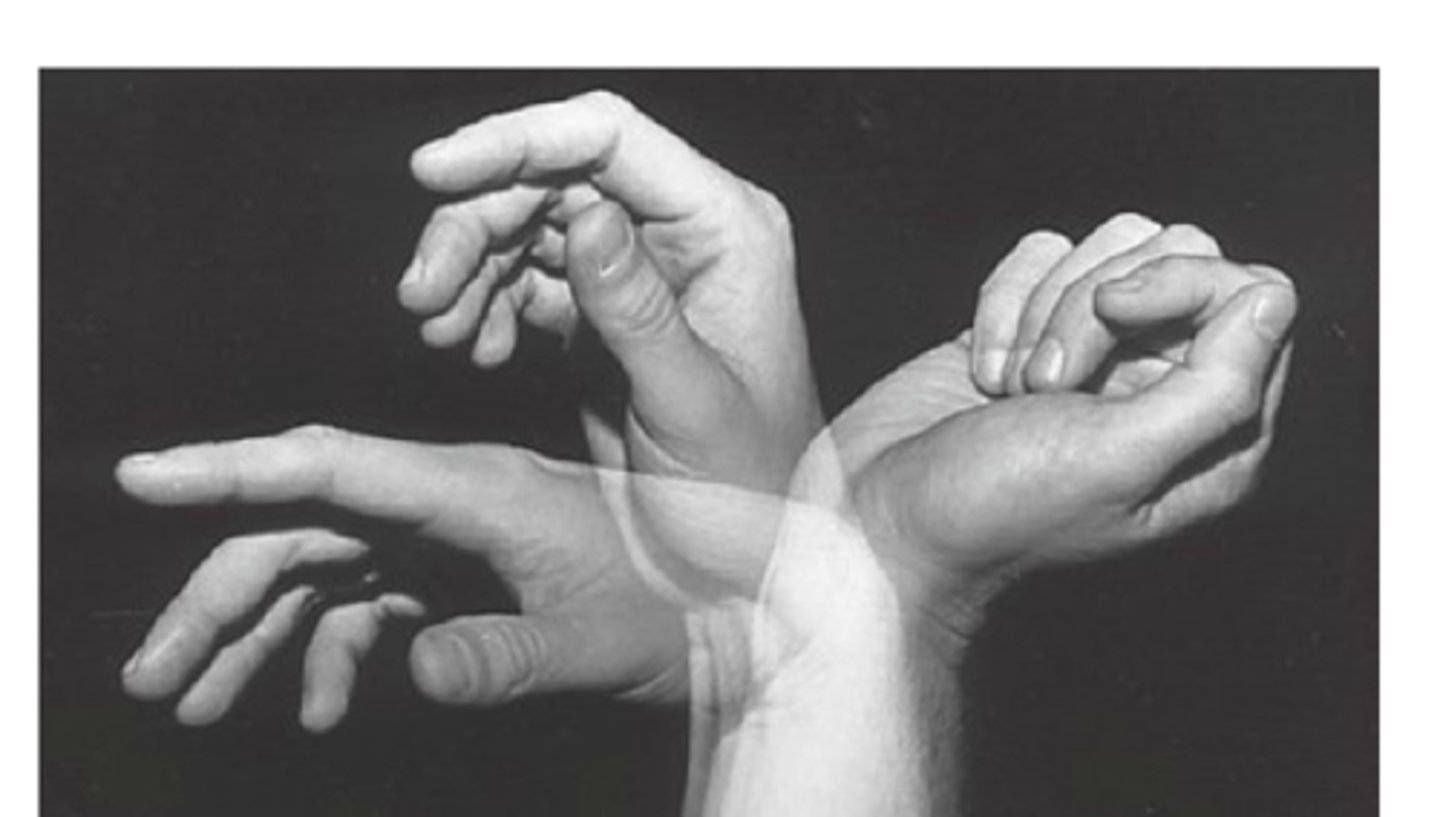
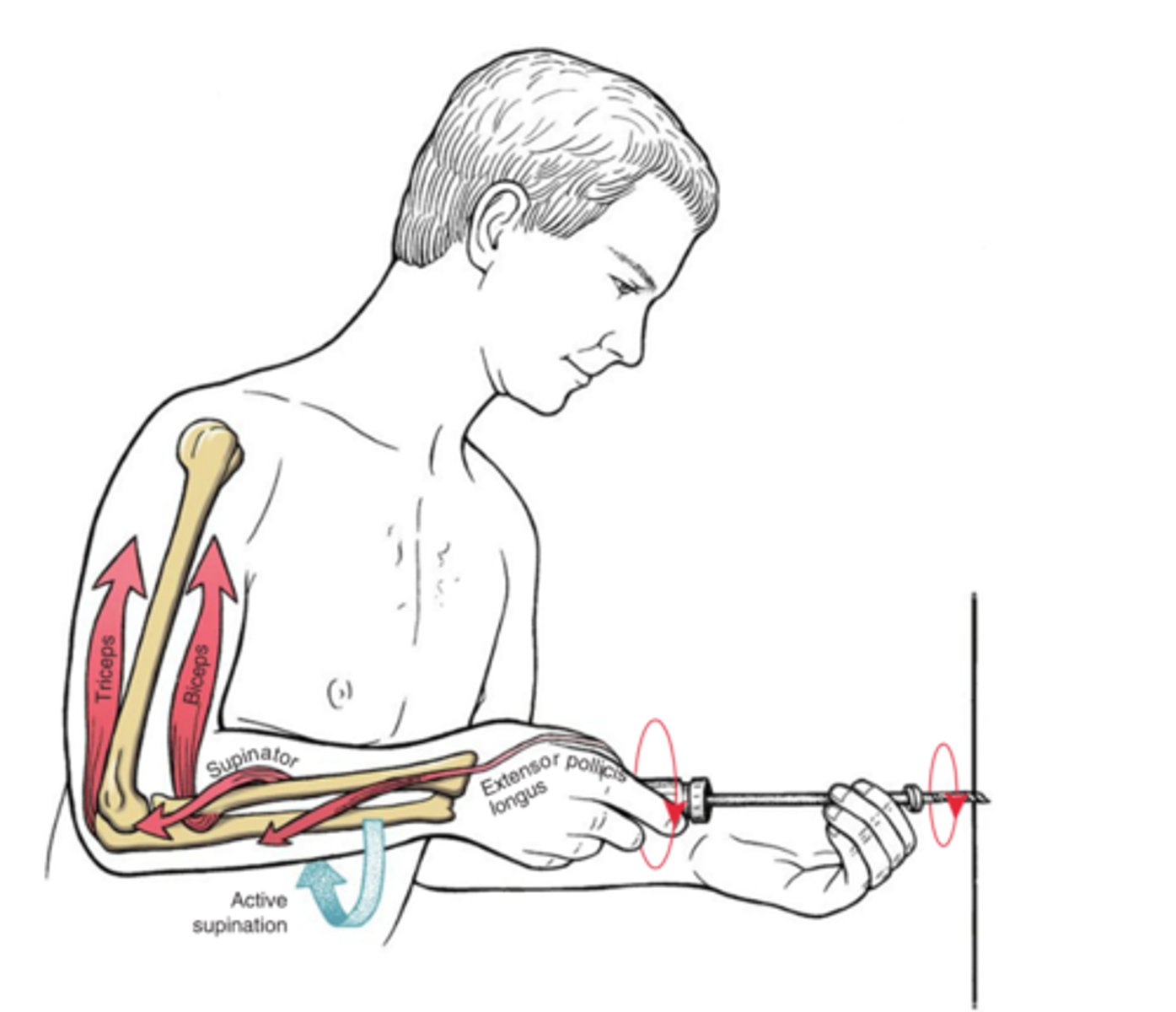
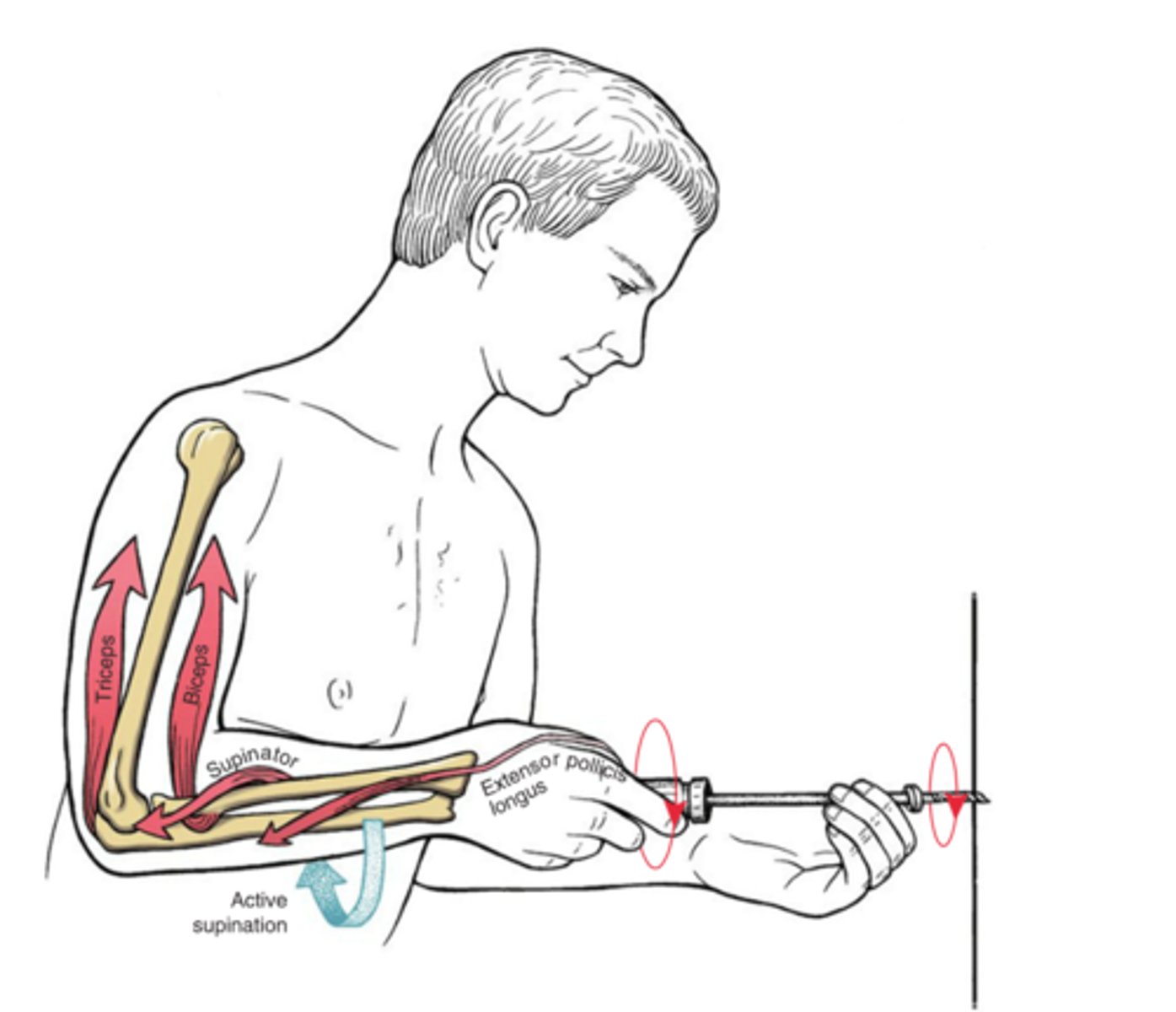
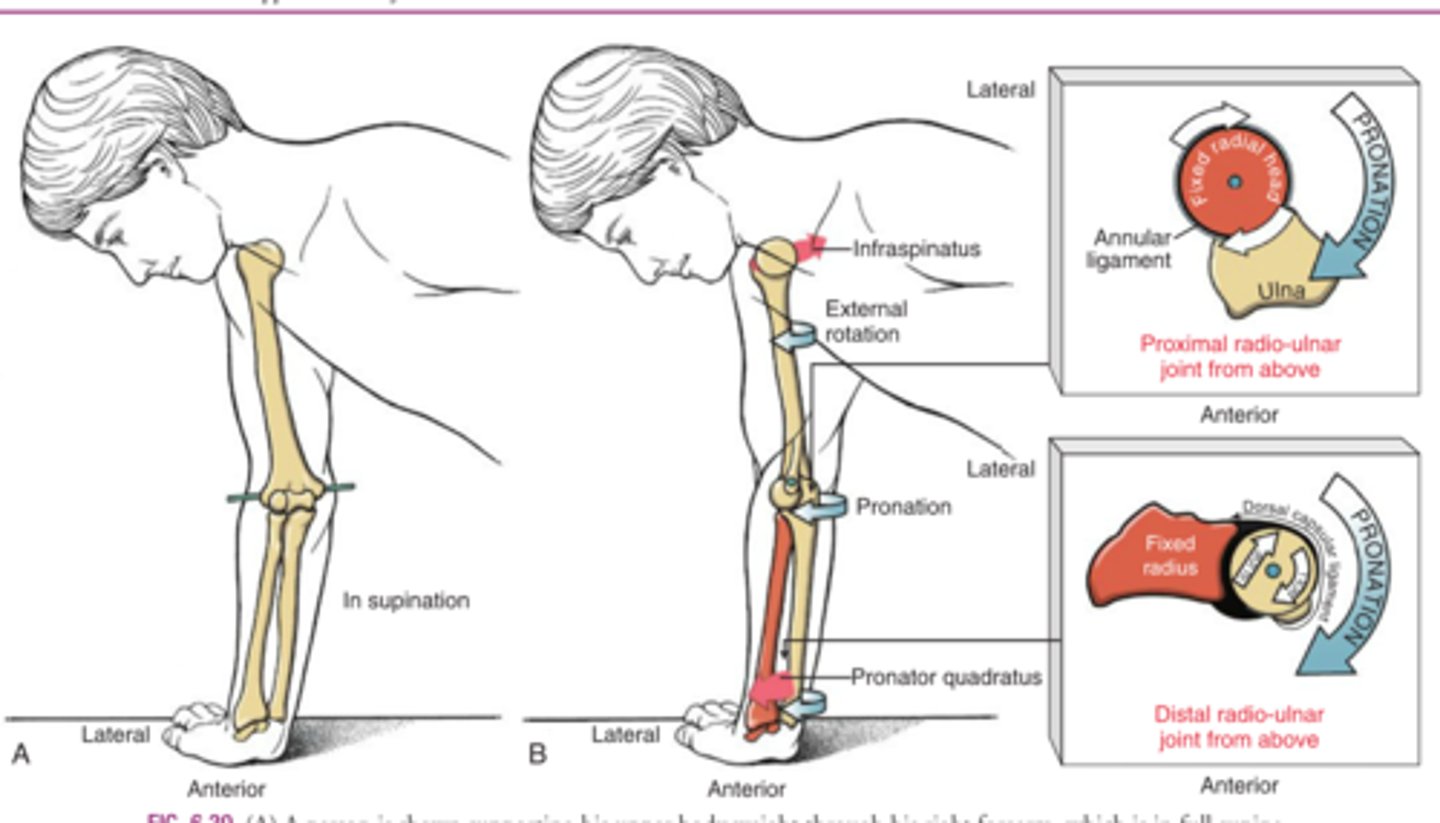
Supinator
(Law of Parsimony: the nervous system tends to activate the fewest muscles or muscle fibers possible for the control of a given joint action)
*Biceps are a powerful supinator and have ~3x the cross section than supinator. According to the law of parsimony, the biceps will not be recruited until more force is required to assist the supinator and EPL.
According to the law of parsimony, which muscle is recruited first during this action?