geography exam 3
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
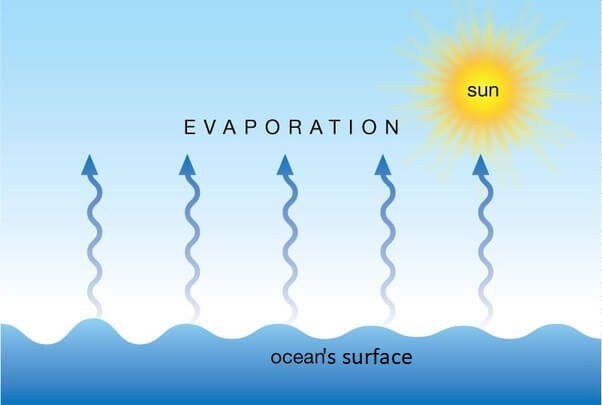
evaporation
process of liquid transforming into a gas. accounts for movement of water to the air
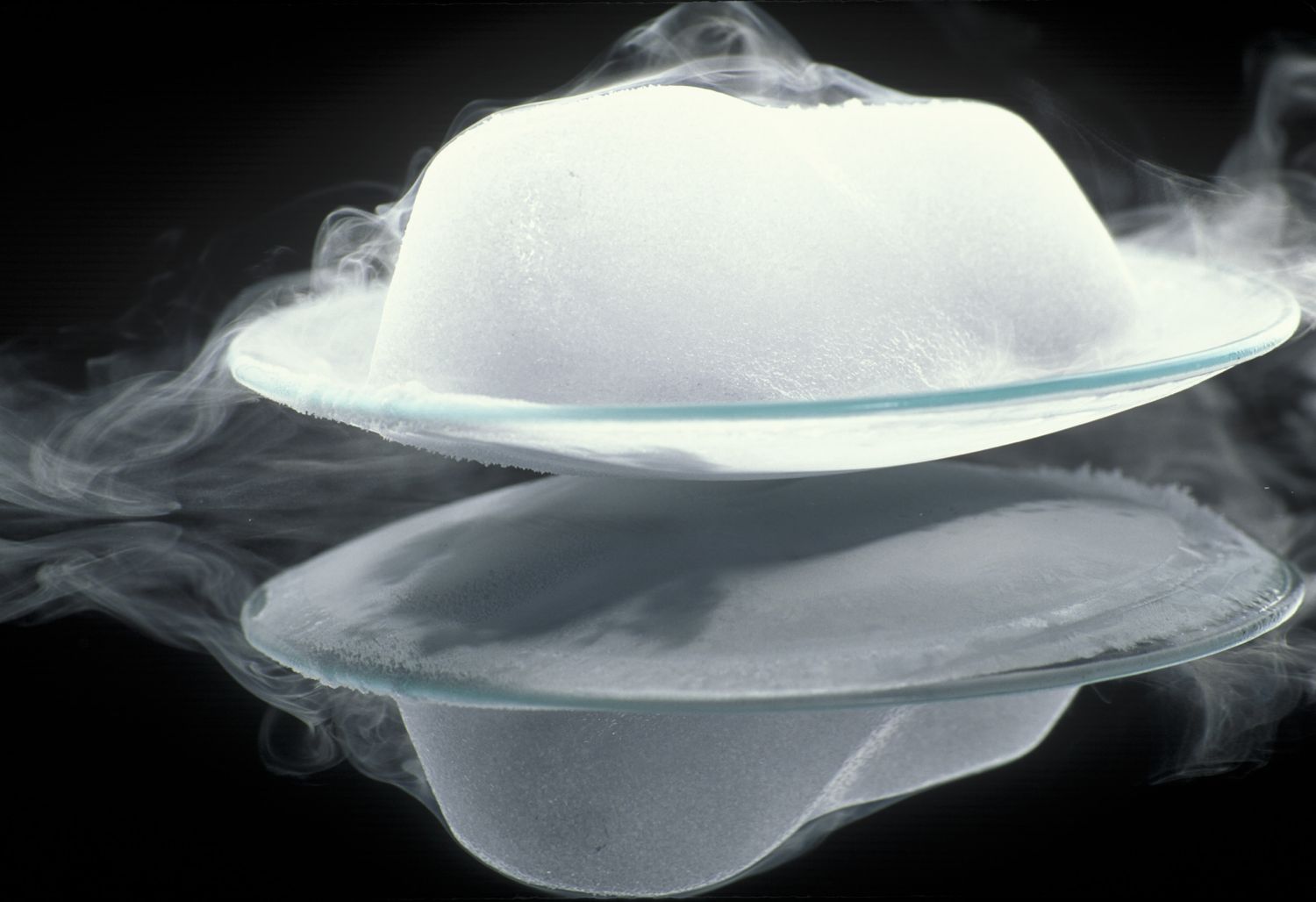
sublimation
process of a solid transforming into a gas
when a liquid is transformed into a solid…
energy is released from the liquid
average dry adiabatic lapse rate
10C/1000m
dry adiabatic lapse rate definition
the rate at which the temperature of a parcel of dry air decreases as the parcel is lifted into the atmosphere.
moist adiabatic lapse rate definition
the rate at which a saturated parcel of air warms or cools when it moves vertically
wet adiabatic lapse rate is ___ than dry adiabatic lapse rate, because ___
less, condensation heats the air
water penetrates soil by
infiltration
the amount of water that would evaporate and transpire under optimum moisture conditions
potential evapotranspiration
__ would decrease the rate at which evapotranspiration occurs
humidity
if precipitation and soil moisture are inadequate to meet potential evapotranspiration demands, the moisture condition is described as
deficit
an increase in temperature leads to decrease in
relative humidity
the hydrogen bonding in water creates ___, a cohesive force that enables one to slightly overfill a glass with water or allows denser objects, such as a needle, to float on water
surface tension
nimbo- and -nimbus mean
that the clouds are producing precipitation
3 stages of thunderstorm development
mature, dissipating, cumulus
the amount of heat energy required of raise the temp of 1g of water by 1°C
calorie
true or false - during the adiabatic process, the warming and cooling of air parcels is caused by heat exchange between air parcels and the surrounding environment
false
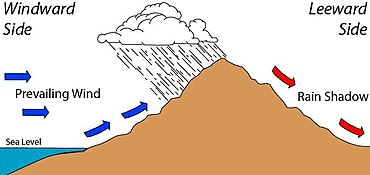
rain shadow
dry regions on the leeward side of mountain ranges
pressure systems that reside within the source region for mP air masses
Aleutian low and Icelandic low
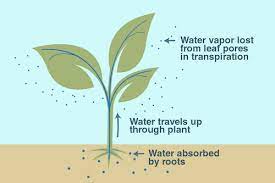
transpiration
the movement of water within a plant and into the atmosphere from plants
water covers ___ percent of earth
71
oceans are the largest reservoir, the majority of remaining water is tied up in ___
ice sheets
how much of all water consists of freshwater?
2.78%
surface water percentages
ice and glaciers: 99.3%
freshwater lakes: 0.33%
atmosphere: 0.03%
rivers and streams: 0.003%
cohesion
molecules attach to other molecules of the same kind, leads to surface tension
adhesion
molecules attracted to molecules of other substances - leads to capillary action
capillary action
upward movement against gravity (straws)

condensation
gas to liquid

vaporization
liquid to gas

deposition
gas to solid
the H2O molecule is
polar
water molecules stick to each other due to their
polarity
capillary action is responsible for
pulling of water molecules on each other
solid phase (ice)
water is most dense at 4°C, below this temp hydrogen bonds form, creating a crystal structure that is less dense than liquid water, 9% increase in volume
liquid phase (water)
assumes the shape of its container, some hydrogen bonding between molecules
gas phase (water vapor)
invisible/compressible gas, each molecule is completely separate
latent heat
the energy associated with phase changes
energy is absorbed during
melting, evaporation, and sublimation
energy is released during
freezing, condensation, and deposition
facts about calories
+ means absorbed by the compound
- means released from the compound
latent heat of vaporization
+540 cal
latent heat of condensation
-540 cal
latent heat of melting
+80 cal
latent heat of freezing
-80 cal
latent heat of sublimation
+680 cal
latent heat of deposition
-680 cal
to raise the temp of 1g of water from 0 degrees to boiling at 100 degrees, we must add ____. no phase changes occur at this point
100 calories
going through all 3 states would take a total of ___ calories either absorbed or released
720
sublimation and deposition only require ___ calories to be absorbed or released
680
humidity
a measure of the water vapor content of air. main way to characterize atmospheric moisture. varies with season, time, and location.
humidity is determined by
the air temperature and water vapor content
warmer air can hold
more moisture
relative humidity formula
actual water vapor in air / max water vapor possible in air at that temp x 100
saturation
the maximum amount of water vapor a parcel of air can hold. when the air is saturated, RH is at 100%
more water vapor added or decrease in temp will cause
condensation
relative humidity - cooler air
lesser maximum water vapor possible
relative humidity - warmer air
greater maximum water vapor possible
dew point temperature
the temp at which the air mass reaches saturation, and condensation begins to form water droplets
dew
forms when water vapor condenses on a cold surface on calm, clear nights. not a form of precipitation
frost
occurs when cooling at constant pressure produces saturation at an air temp below freezing. water vapor deposits on cold surface
when you see clouds or fog, you see air that has reached the
dew point temperature
relative humidity daily patterns
at temp rises through the day, RH falls. RH is highest at dawn, lowest in late afternoon
relative humidity seasonal patterns
RH is lower in summer, higher in winter. more insolation in summer than winter.
vapor pressure
air pressure made by water vapor molecules at a given temp
saturation vapor pressure
when the air contains as much water vapor as possible
vapor pressure increases with
increased concentration of water vapor molecules
specific humidity
the mass of water vapor in grams per mass of air in kg at any specified temp. changes only in amounts of water vapor changes.
as temps increase, SVP
increases
sling psychrometer
TD = dry bulb temp
TW = wet bulb temp
relative humidity depends on TD and TW
atmospheric stability
the tendency of a parcel of air to stay in place, rise, or sink
stable conditions
air parcel does not want to move upwards. tends to return to its starting place.
conditionally unstable
if air parcel is less than saturated, it will resist movement unless forced. stable at lower elevations, but if it reaches saturation, it becomes unstable
unstable conditions
air parcel temp is higher than that of surrounding environment. parcel will rise until it reaches air with similar density
adiabatic
the warming and cooling rates for a parcel of expanding or compressing air. caused by changes in pressure, not energy
relative humidity
ratio of the amount of water vapor actually in the air compared to the max water vapor the air at the temp can hold
adiabatic processes - 2 major rules
rising air parcels expand and cool as they move up
sinking air parcels are compressed and warmed as they move lower
normal lapse rate
decrease in temp with increase in altitude at average of 64C/1000m
dry adiabatic rate
rate at which dry air cools by expansion (if ascending) or heats by compression (if descending). dry air = RH is less than 100% saturation. DAR = 10c/1000m
moist adiabatic rate
the rate at which an air parcel at saturation changes in temp as it moves up or down in atmosphere. MAR = 6c/1000m
lifting condensation level (LCL)
air moving up in atmosphere will cool at the DAR until it reaches saturation. at dew point temp, it reaches saturation. leading to condensation and clouds. this altitude is called the LCL
___ and ___ are key to cloud classification
altitude, shape
3 basic forms of clouds
flat - stratiform
puffy - cumuliform
wispy - cirroform
4 altitude classes of clouds
low (0-2000m)
middle (2000-6000m)
high (6000-13000m)
vertically developed (13000m and above)
cloud prefix meanings
stratus - layered
cumulus - heaps
nimbo - storm or rain
alto - high
cirrus - curl of hair, feathery

stratus cloud
low blanket, large-scale lifting

nimbostratus
nimbus = rain, continuous cloud cover and rain, usually a passing warm front
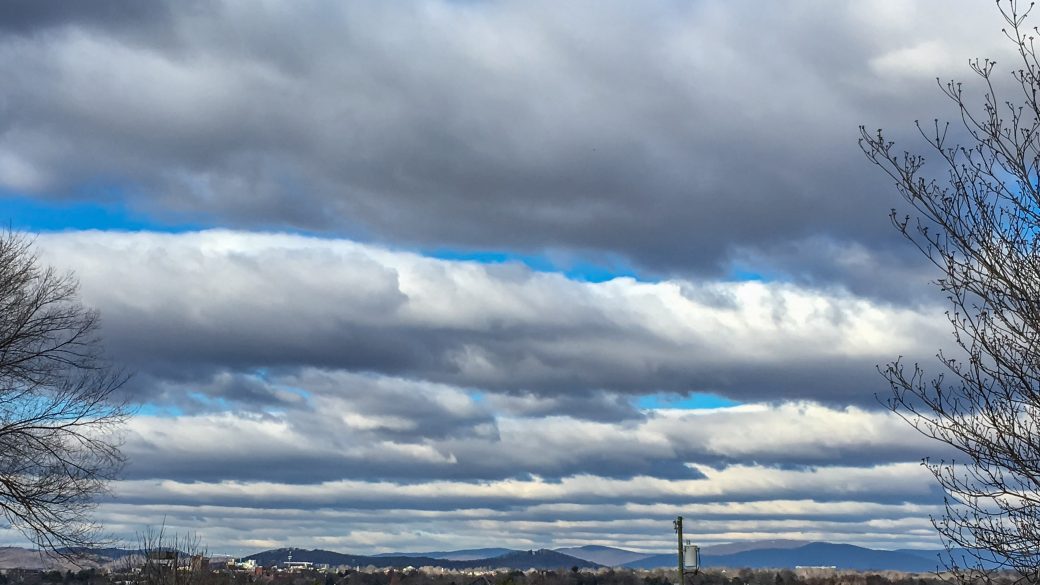

stratocumulus
blanket of cumulus cover

altocumulus
sheet of small cotton balls, some instability and convection

altostratus
mid-level blanket, smooth texture, large scale lifting
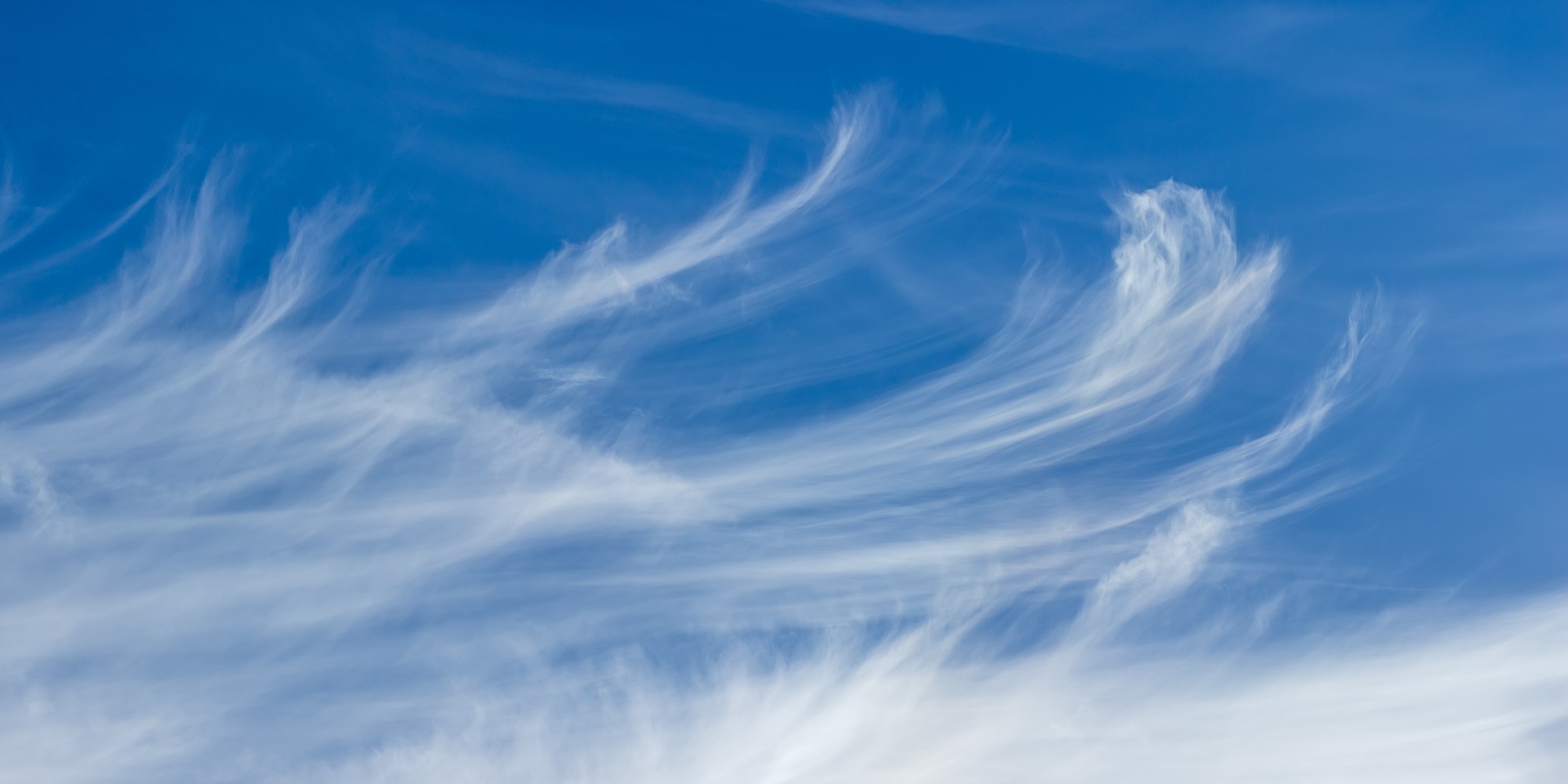

cirrus
feathery, ice crystals, first sign of weather change
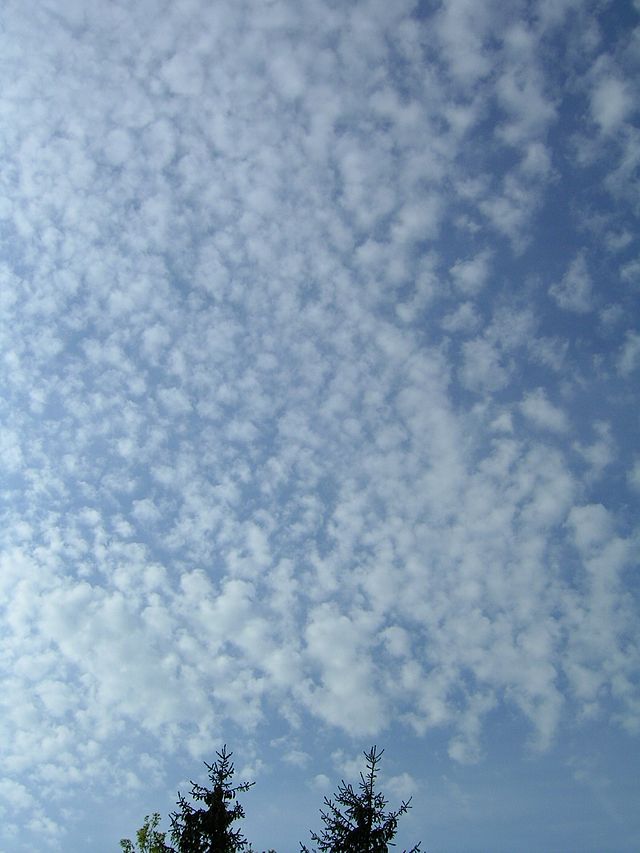

cirrocumulus
cotton balls, ice and cold water, some convection
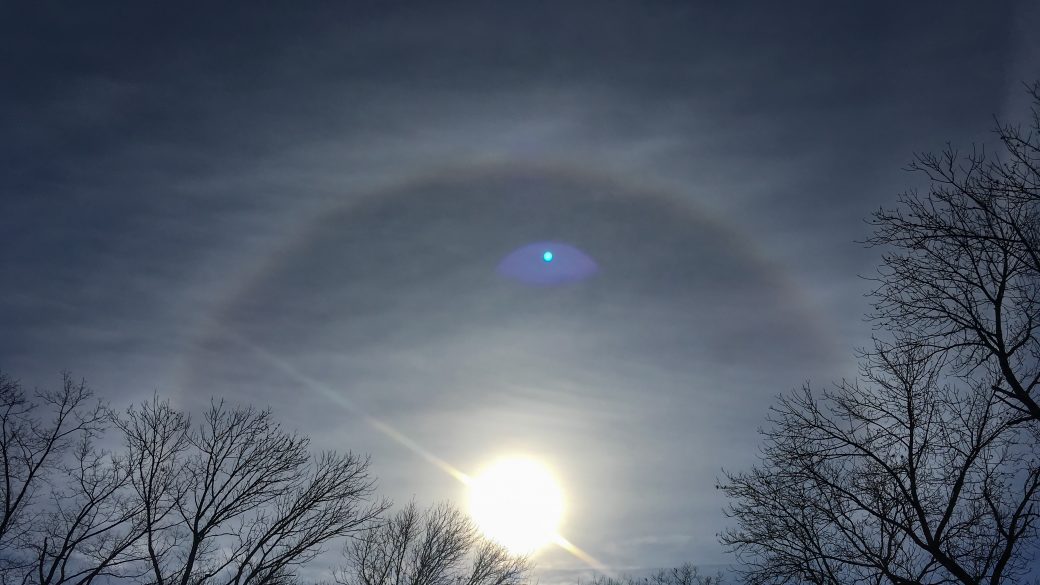

cirrostratus
blanket of ice, halo, one day pre-front, lots of moisture aloft
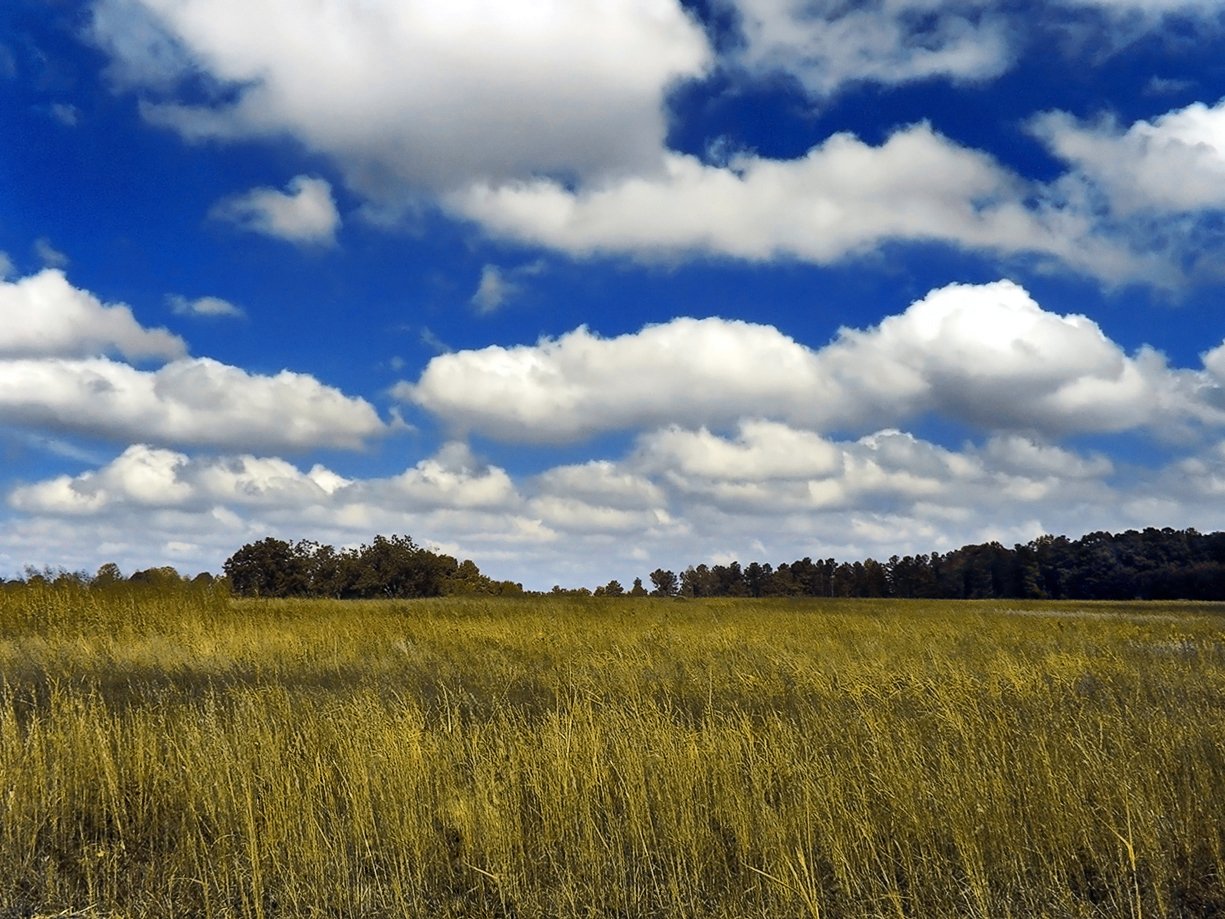

cumulus
larger cotton balls
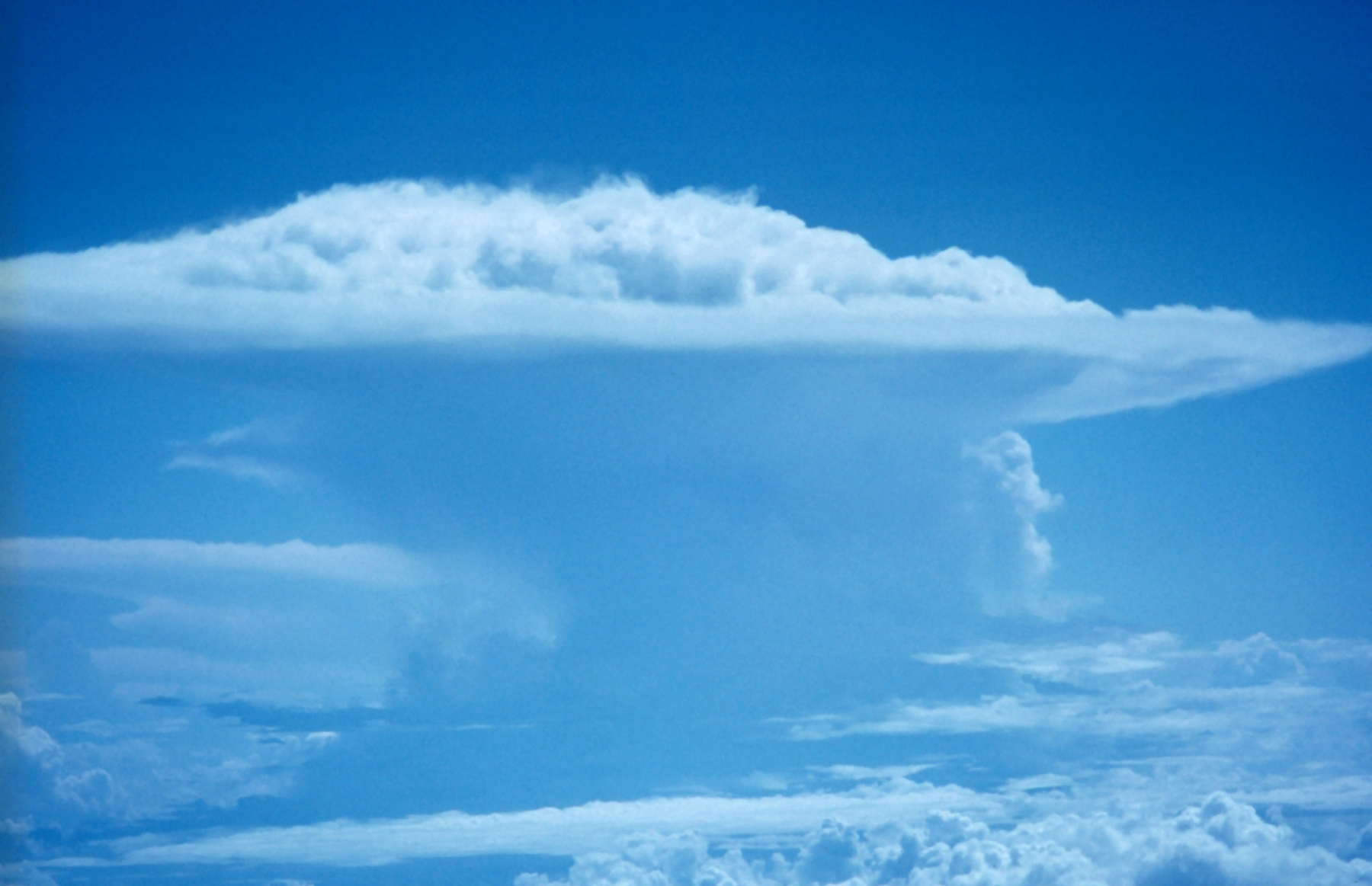

cumulonimbus
thunder, intense vertical development, signify instability, classic anvil shape

fog
ground level cloud that cuts visibility to <1km. forms above freezing temps.

advection fog
unsaturated air migrates to new places and reaches saturation. when warm moist air moves over cooler body of water.

evaporation fog
cold air lies over warmer body water, evaporation from water easily saturates the air
upslope fog
air cools as it moves upslope, common in winter and spring
valley fog
cold air drainage leads to chilled saturated air in valley
earth’s water distribution
ocean 97.22%
fresh 2.78%
surface 77.78%