Muscular System lab Review pg 42
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Question-and-answer flashcards covering muscle names, origins, insertions, actions, regional anatomy, and comparisons among smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle fibers.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
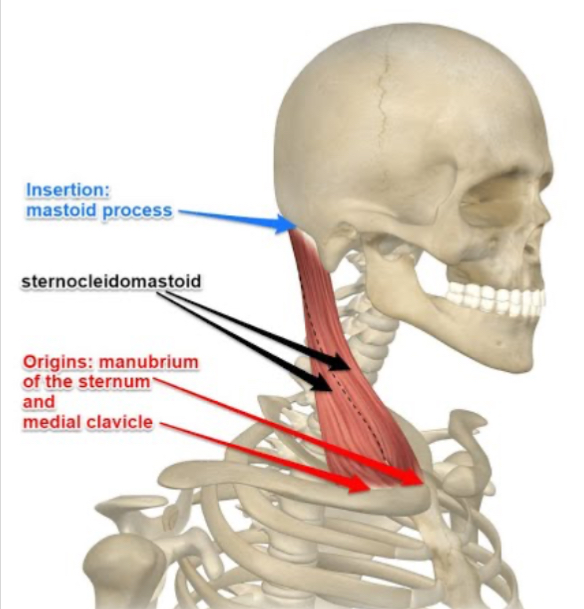
What action does the sternocleidomastoid perform?
Flexes the neck and rotates the head to the opposite side.
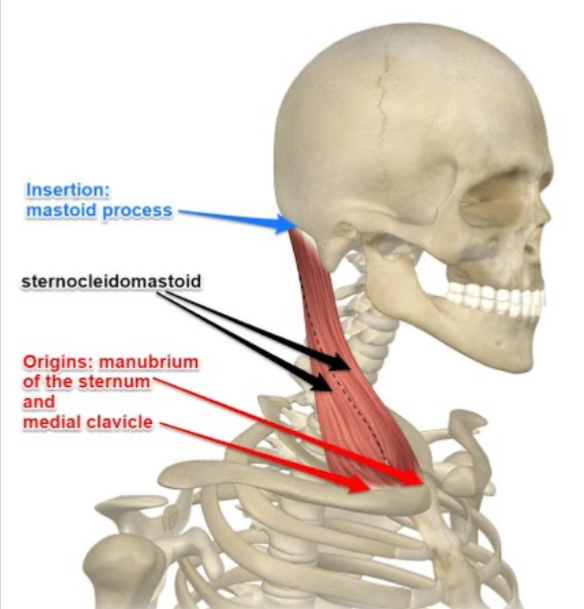
Where does the sternocleidomastoid insert?
Mastoid process of the temporal bone.
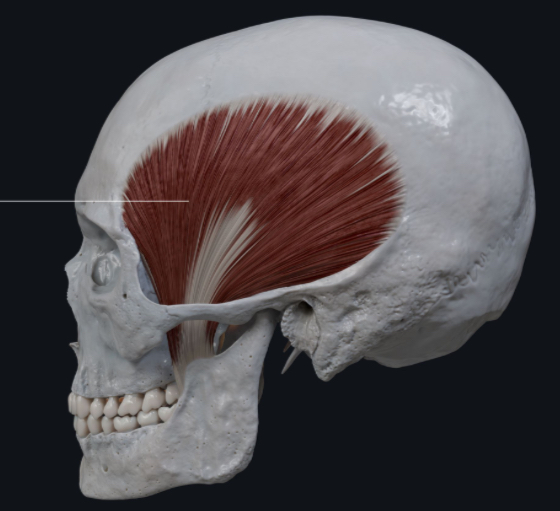
What is the primary action of the temporalis muscle?
Elevates and retracts the mandible.
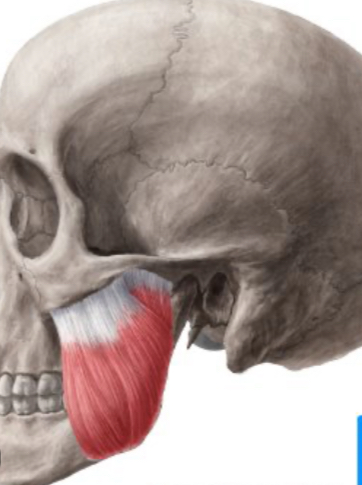
Which muscle elevates and protracts the mandible?
Masseter.
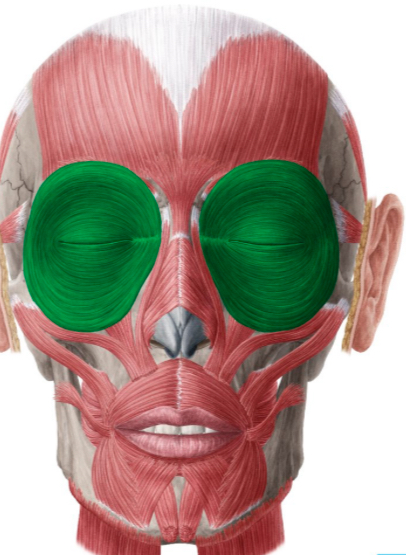
Which facial muscle closes the eyelids (squint/blink)?
Orbicularis oculi muscle
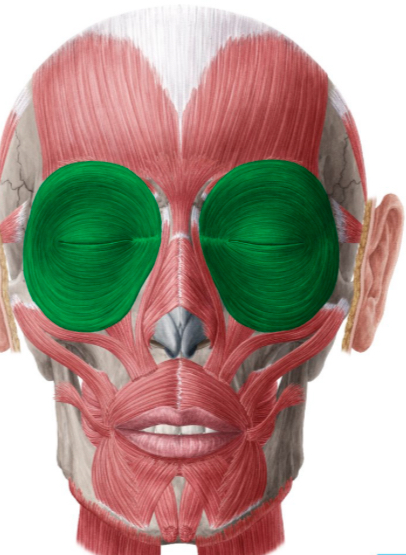
What action is produced by the orbicularis oris?
Closes and protrudes the lips.
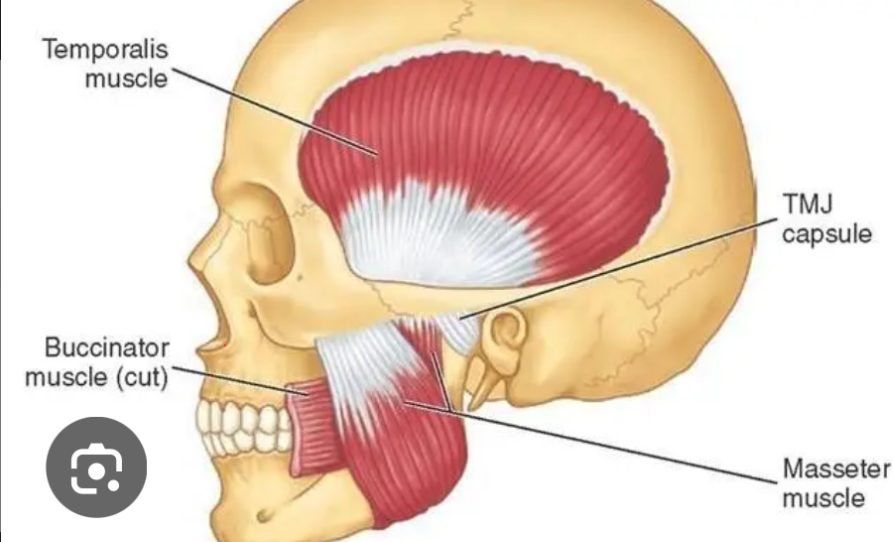
Name the muscle that compresses the cheeks to assist in mastication.
Buccinator.
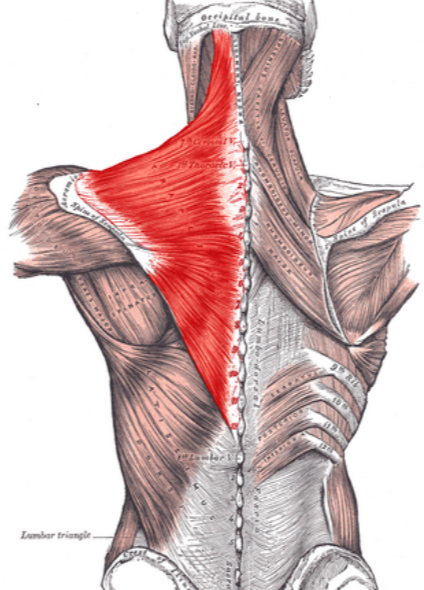
What action does the trapezius perform on the scapula?
Elevates, adducts (retracts), and stabilizes the scapula; also extends the neck.
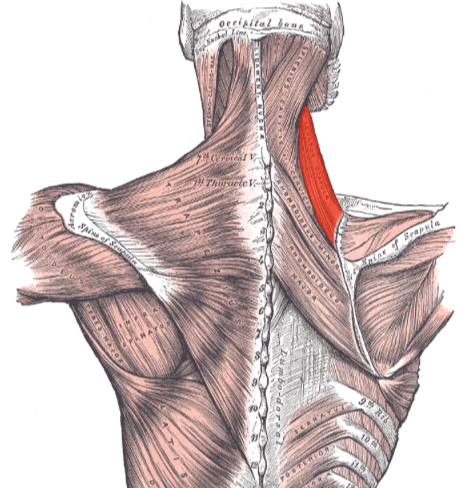
Which muscle elevates the scapula?
Levator scapulae.
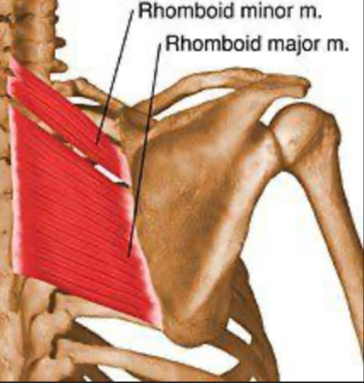
Which two back muscles retract (adduct) the scapula?
Rhomboid major and rhomboid minor.
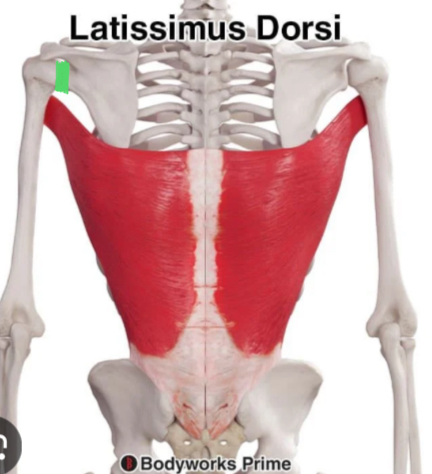
What are the three actions of latissimus dorsi at the glenohumeral joint?
Extends, adducts, and medially rotates the shoulder (glenohumeral joint).
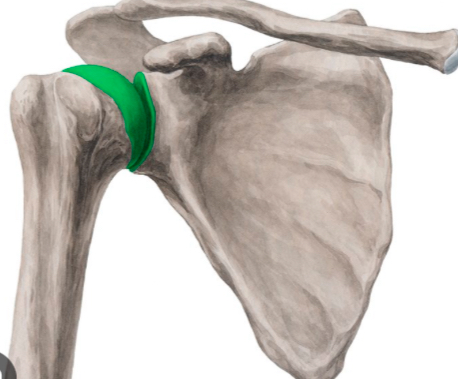
Which muscle abducts the glenohumeral joint and originates from the supraspinous fossa?
Supraspinatus.
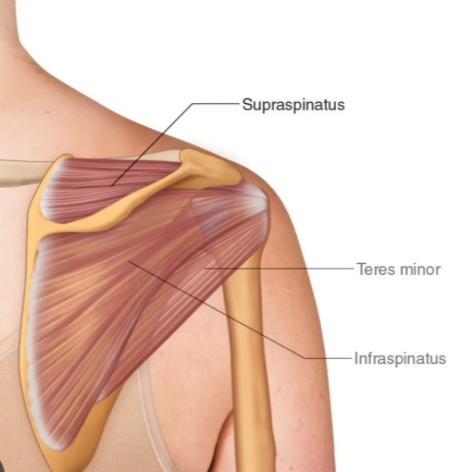
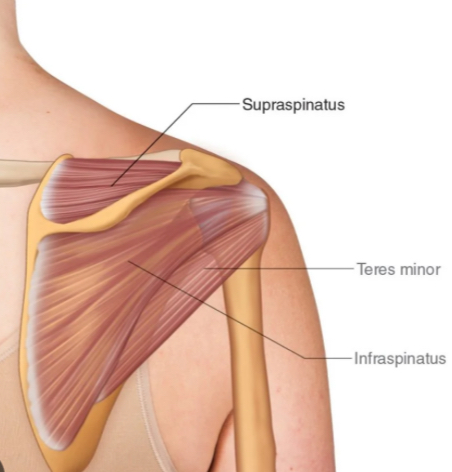
Name the rotator-cuff muscle that laterally rotates the humerus and inserts on the middle part of the greater tubercle.
Infraspinatus.
Which rotator cuff muscle medially rotates the humerus and inserts on the lesser tubercle?
Subscapularis.
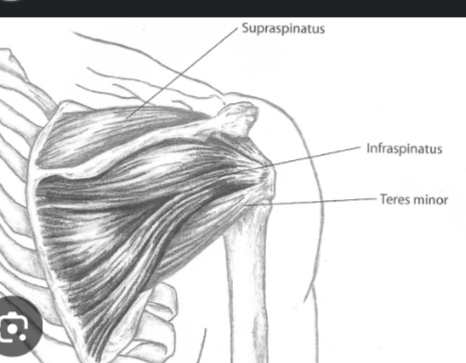
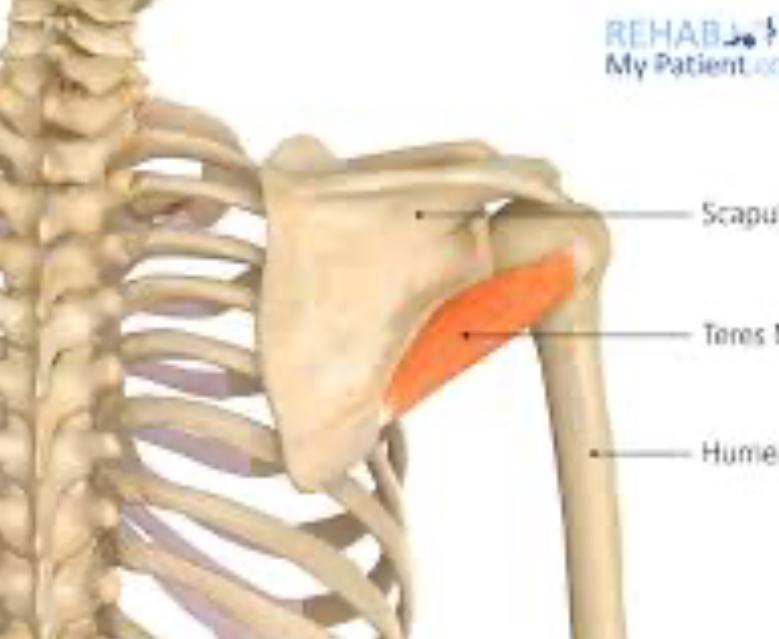
What is the action of teres minor?
Laterally rotates the glenohumeral joint.
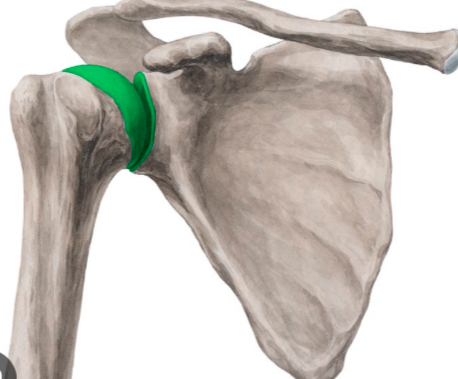
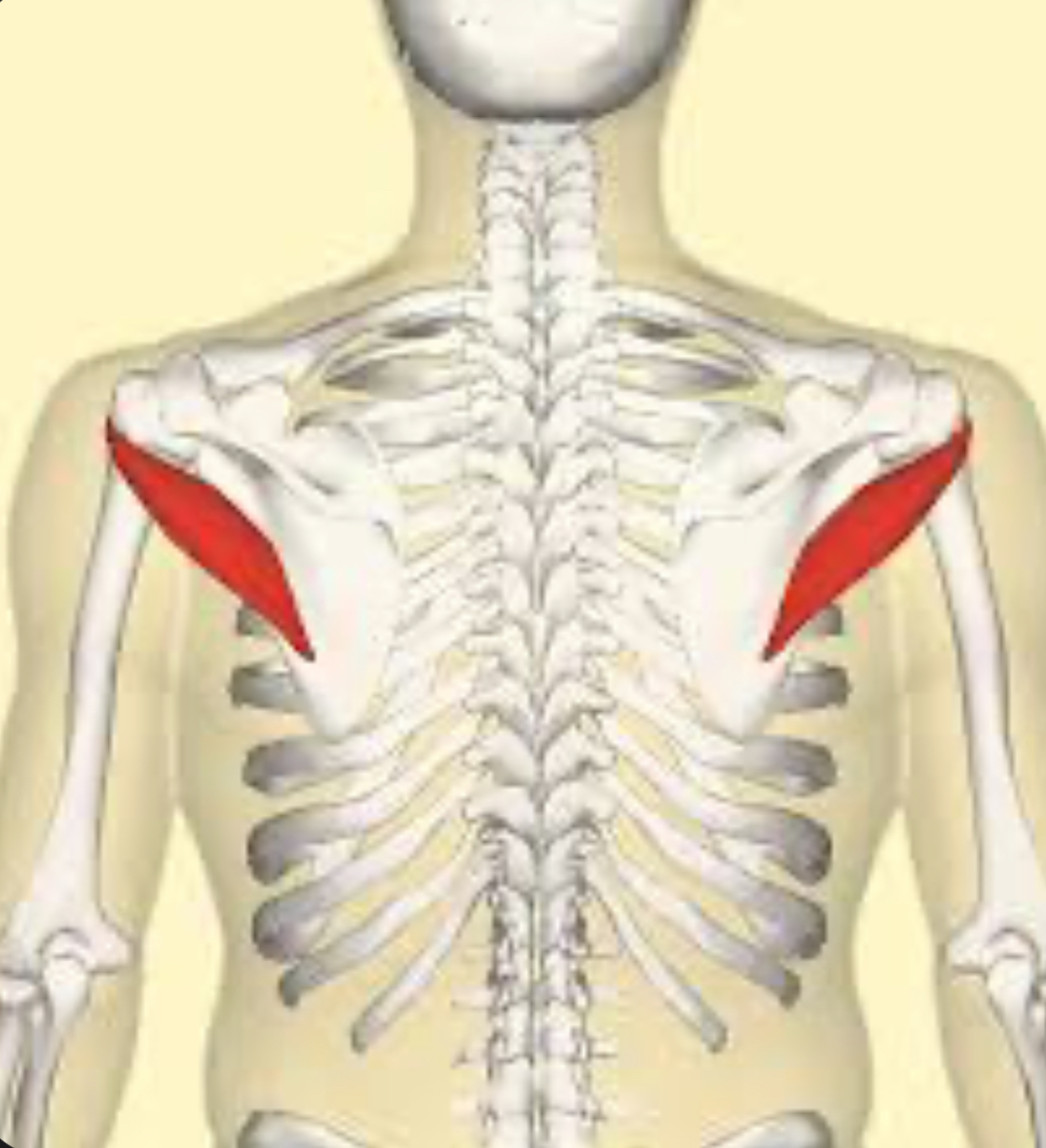
List the three actions of teres major.
Extends, adducts, and medially rotates the glenohumeral joint.
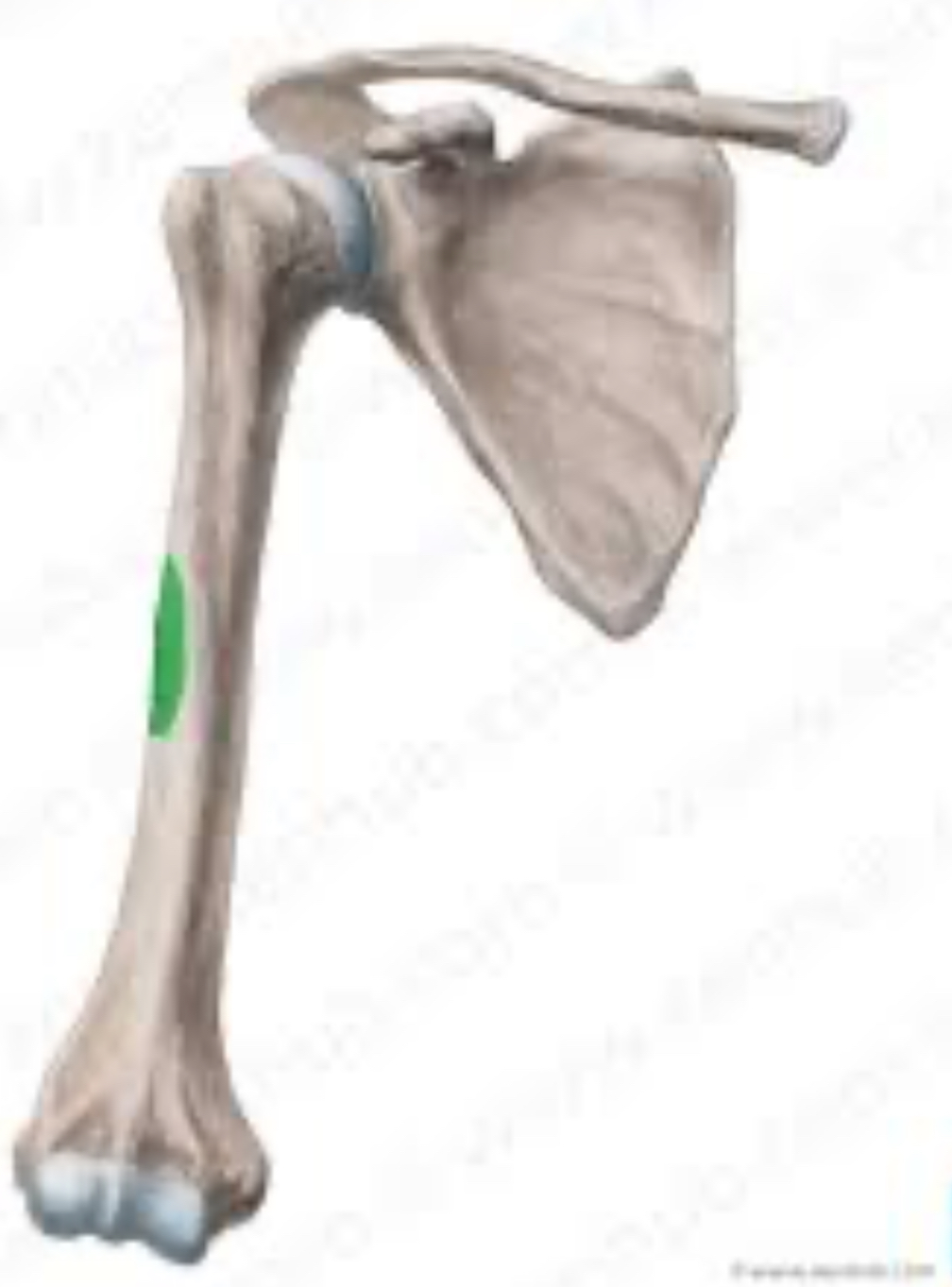
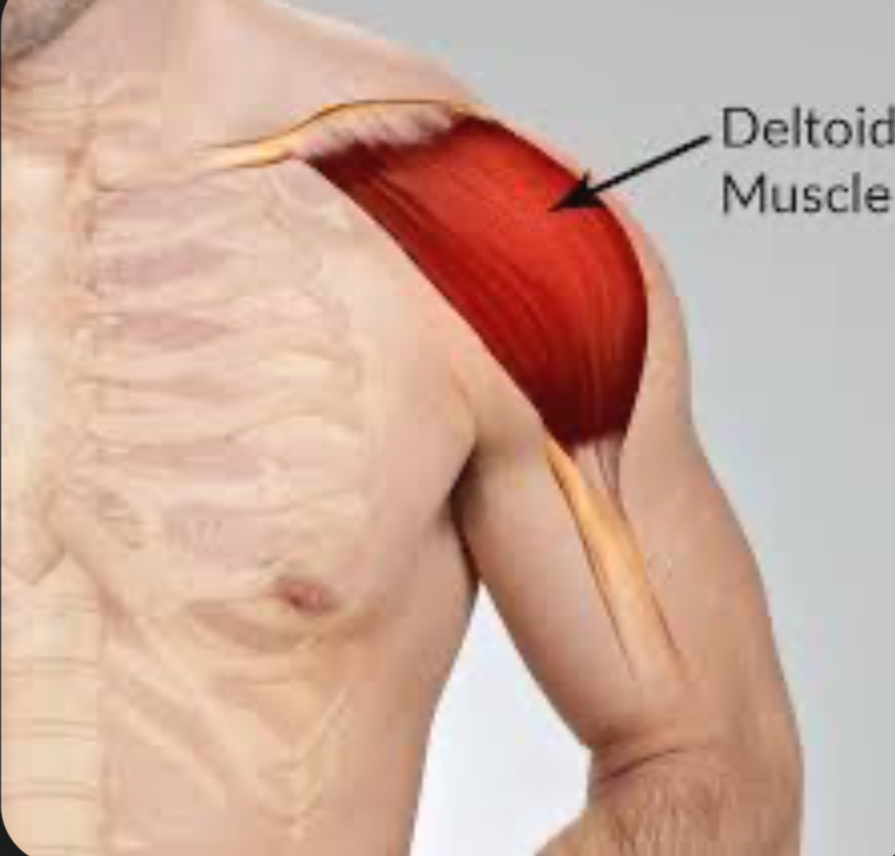
Which muscle abducts the shoulder and inserts on the deltoid tuberosity?
Deltoid.
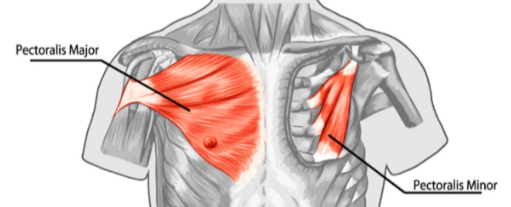
What is the main action of pectoralis major at the shoulder?
Flexes, adducts, and medially rotates the glenohumeral joint.
Which muscle depresses the scapula and lies deep to pectoralis major?
Pectoralis minor.
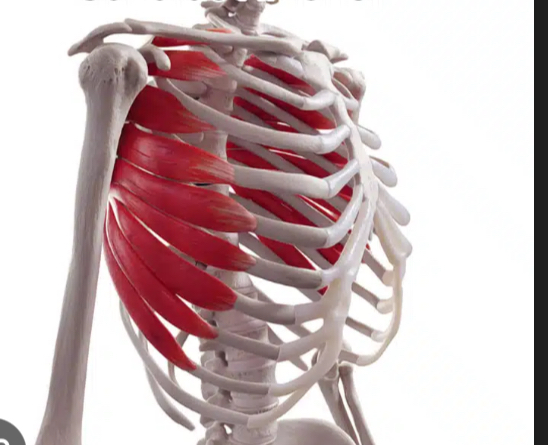
What action is produced by serratus anterior?
Abducts (protracts) the scapula.
Which elbow flexor also supinates the radius?
Biceps brachii.
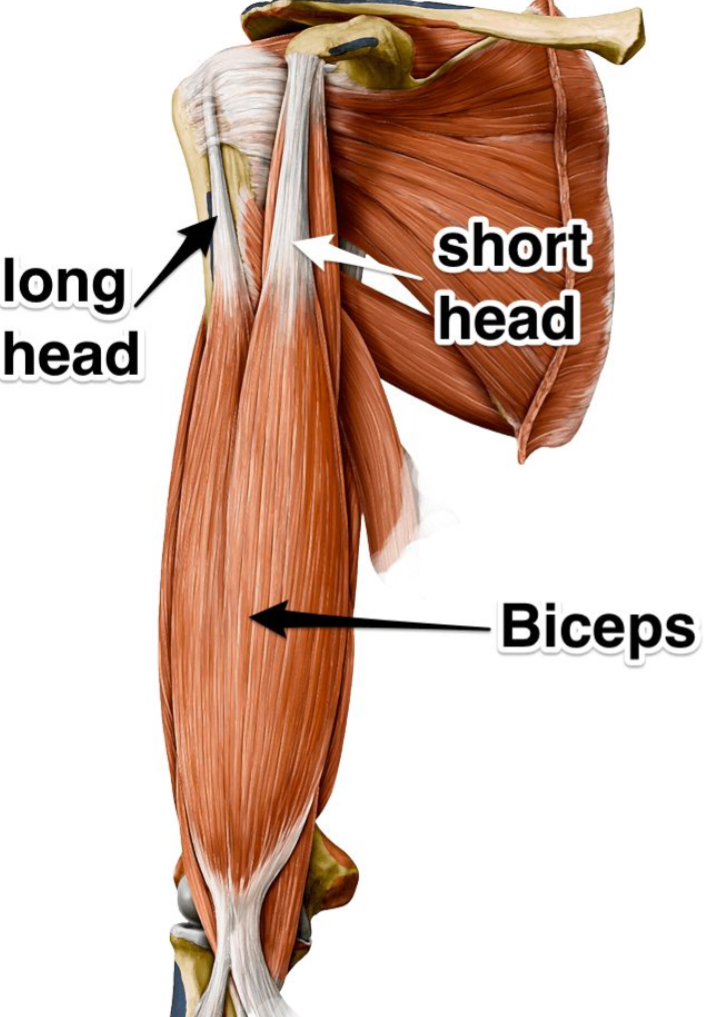
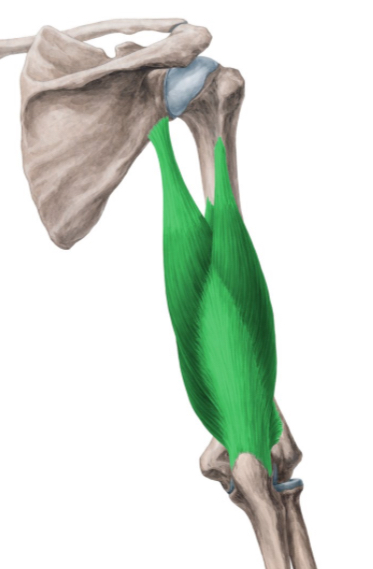
Where does the triceps brachii insert and what is its primary action?
Inserts on the olecranon process; extends the elbow.
Name the pure elbow flexor that inserts on the ulnar tuberosity and coronoid process.
Brachialis.
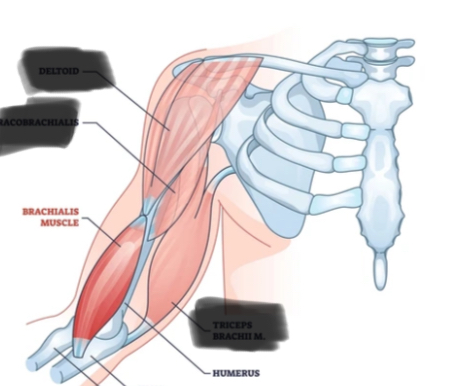
Which muscle flexes and adducts the wrist on the ulnar side?
Flexor carpi ulnaris.
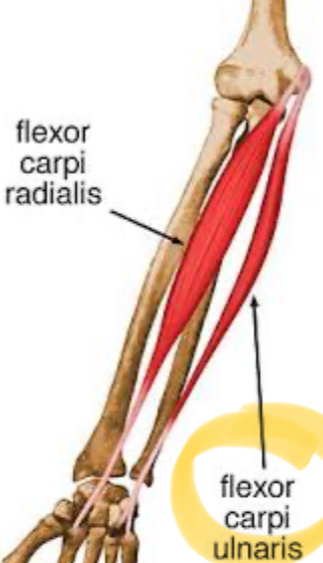
Which two muscles act to extend and abduct the wrist?
Extensor carpi radialis longus and extensor carpi radialis brevis.
What is the primary action of extensor digitorum?
Extends the fingers (digits).
Which muscle flexes the wrist and is often absent in some individuals?
Palmaris longus.
What action does brachioradialis perform at the forearm?
Flexes the forearm and assists in returning the radioulnar joints to neutral (supination/pronation).
Name the muscle group that extends the knee and includes rectus femoris.
Quadriceps femoris (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius).
Which quadriceps muscle also flexes the hip?
Rectus femoris.
What is the common insertion for the quadriceps femoris muscles?
Tibial tuberosity via the patellar ligament.
Which three muscles make up the hamstrings?
Biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus.
What actions are shared by semitendinosus and semimembranosus?
Extend the hip and flex the knee.
Which gluteal muscle is the primary hip extensor and lateral rotator?
Gluteus maximus.
Which gluteal muscle abducts the hip?
Gluteus medius.
Name the muscle that flexes and laterally rotates the hip while flexing the knee, often called the "tailor’s muscle."
Sartorius.
Which three muscles make up the adductor group learned (longus, brevis, magnus) and what is their primary action?
Adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus; all adduct the hip.
Which calf muscle crosses both the knee and ankle joints to flex the knee and plantar-flex the ankle?
Gastrocnemius.
What is the insertion of soleus and its action?
Inserts on the calcaneus via the Achilles tendon; plantar-flexes the ankle.
Which anterior leg muscle dorsiflexes and inverts the ankle?
Tibialis anterior.
Which muscle plantar-flexes and everts the ankle on the lateral compartment of the leg?
Peroneus (fibularis) longus.
What is the role of the diaphragm in respiration?
Primary muscle of inhalation; contracts to increase thoracic volume.
Which intercostal muscles elevate the ribs during inhalation?
External intercostals.
What action is performed by internal intercostals during forced exhalation?
Depress the ribs.
Which abdominal muscle runs vertically and flexes the vertebral column while compressing the abdomen?
Rectus abdominis.
Name two actions common to external and internal obliques.
Flex, laterally flex, and rotate the vertebral column; compress the abdomen.
Which deepest abdominal muscle compresses the abdomen without moving the spine?
Transverse abdominis.
Compare the control of contraction between smooth and skeletal muscle.
Smooth muscle is involuntary (myogenic/autorhythmic), whereas skeletal muscle is voluntary and contracts only in response to motor impulses from the CNS.
Where is cardiac muscle found and what structural feature is unique to it?
Found only in the heart; contains intercalated discs.
Which muscle fiber type (smooth, skeletal, or cardiac) has the slowest, most sustained contractions?
Smooth muscle.
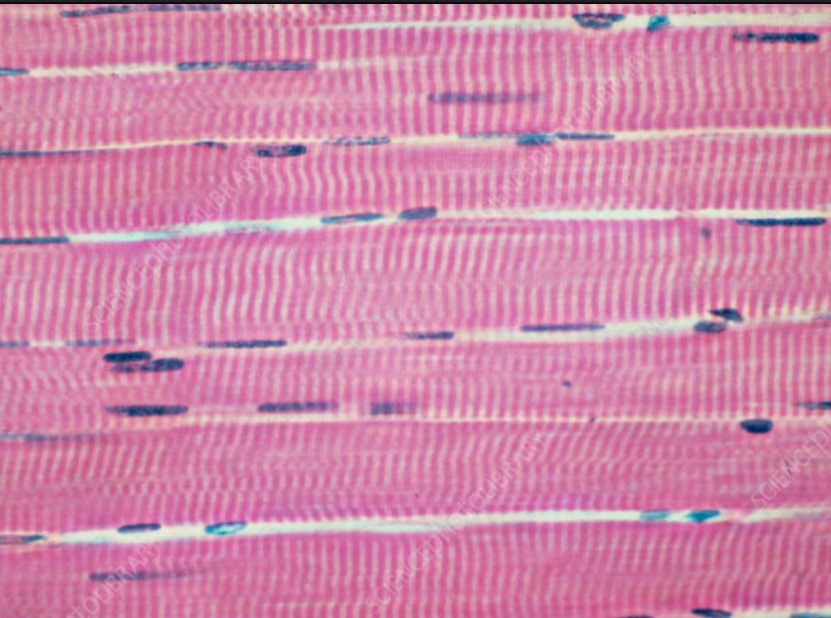
Which muscle fiber type has multinucleate cells located at the periphery?
Skeletal muscle.