BOTANY- LAB -NOTES
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1
New cards
Cell wall
The outermost layer of the cell that distinguishes plant cells from animal cells. It limits the size of the protoplast and prevents rupture of the plasma membrane.
2
New cards
Protoplast
The nucleus and cytoplasm of the cell where organelles are suspended.
3
New cards
Nucleus
The most prominent structure within the protoplast of eukaryotic cells. It is usually spherical in shape.
4
New cards
Cytoplasm
The jelly-like material inside the cell.
5
New cards
Vacuole
The clear area filled with fluid (cell sap) inside the cell.
6
New cards
Chloroplastids
The oval green bodies inside the cells responsible for photosynthesis.
7
New cards
Guard cells
Bean-shaped cells scattered all over the area of the leaf blade.
8
New cards
Primary wall
The single wall that bounds the cell.
9
New cards
Middle lamella
The intercellular layer between the primary walls of adjacent cells.
10
New cards
Ergastic substances
Passive products of the protoplast, including storage products and waste products.
11
New cards
Crystals
Usually composed of calcium compounds, such as calcium carbonate, found in different shapes and sizes.
12
New cards
Calcium oxalate crystals
Crystals shaped like raphides, druses, prisms, or sand crystals.
13
New cards
Calcium carbonate crystals (cystoliths)
Outgrowths of the cell wall encrusted with calcium carbonate, resembling a bunch of grapes.
14
New cards
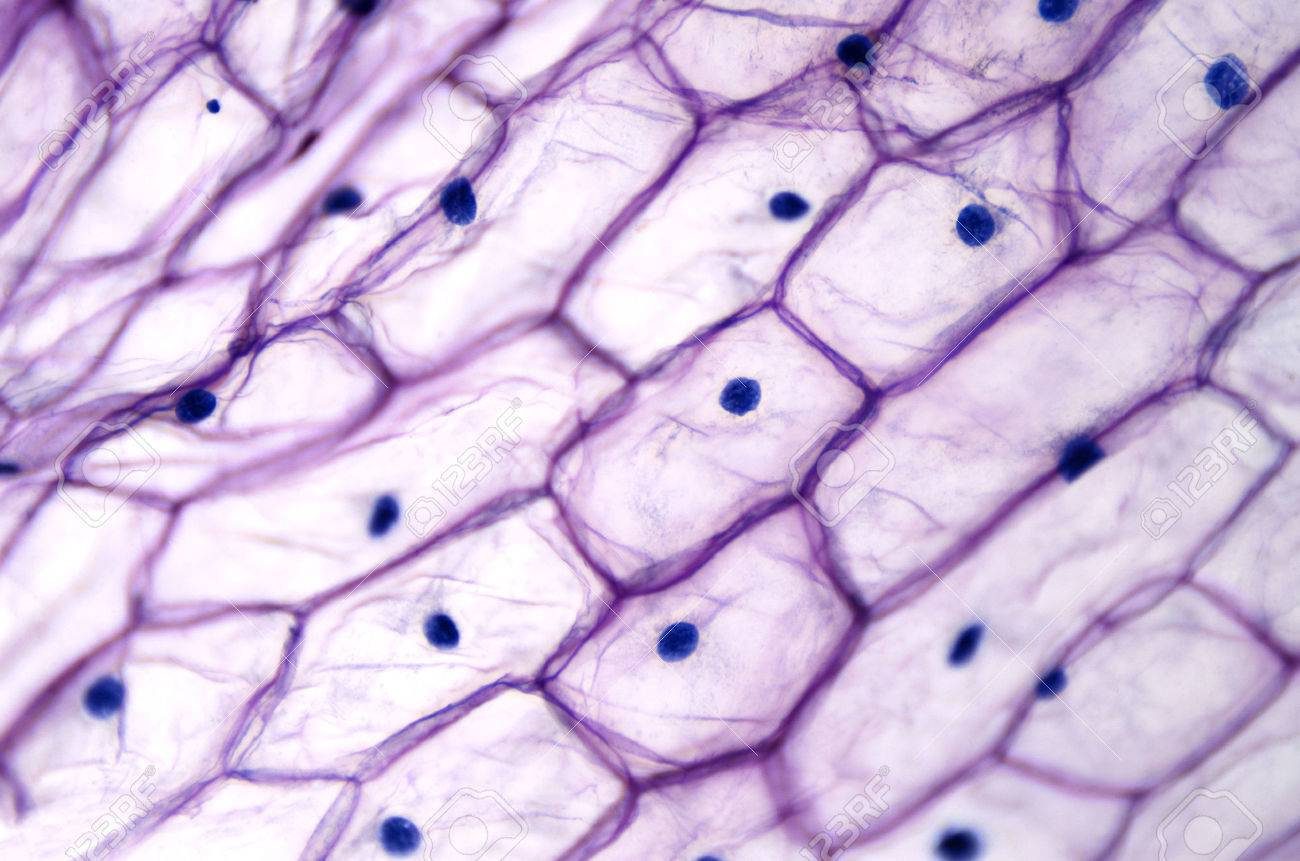
Onion epidermal cell
Cells from the epidermis of an onion bulb (Allium cepa L.).
15
New cards

Digman leaf cells
Cells from the leaves of the aquatic plant Hydrilla verticillata.
16
New cards
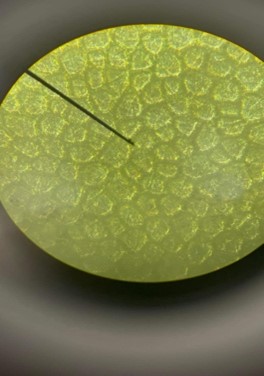
Cells of tomato fruit
Cells from the skin and pulp of a tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum L.).
17
New cards
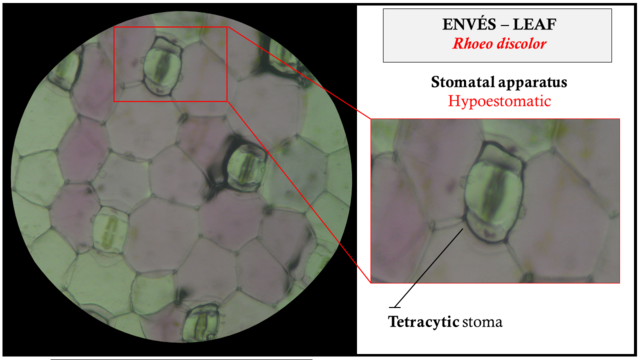
Bangka-bangkaan leaf cells
Cells from the leaves of the plant Rhoeo spathacea.
18
New cards
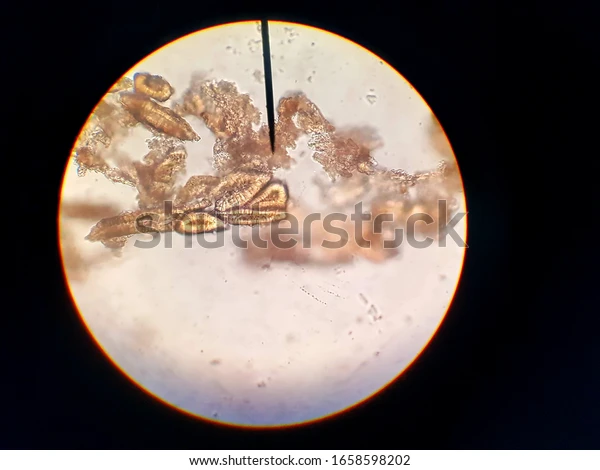
Cells of coconut shells
Cells from the shells of a coconut.
19
New cards
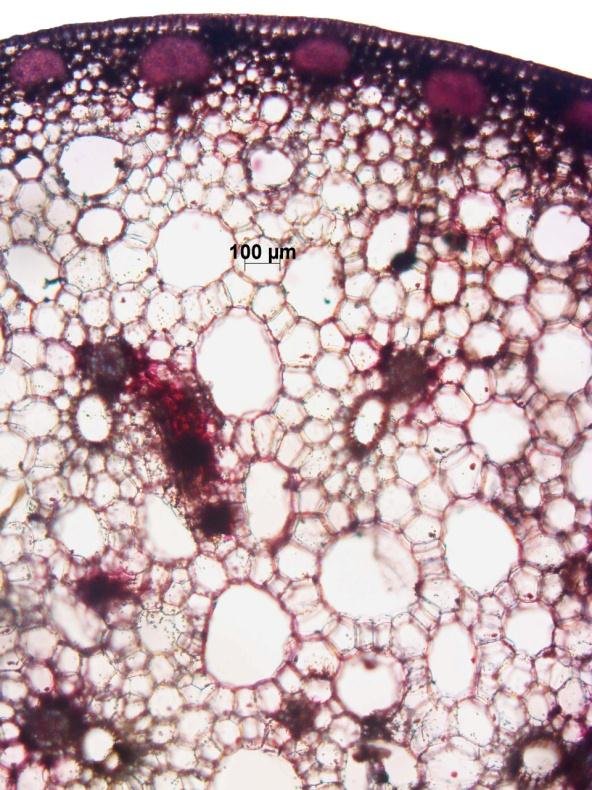
Petiole of gabi-gabi
Cells from the petiole of the plant Calocasia esculenta.
20
New cards
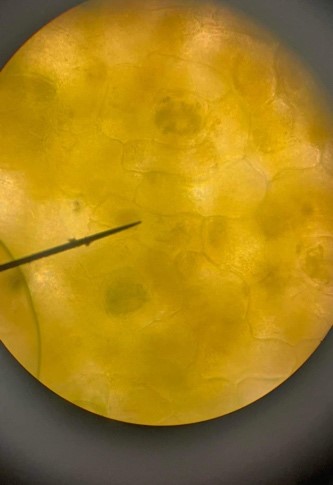
Midrib of dumb cane
Cells from the midrib of the plant Diffenbachia sp.
21
New cards
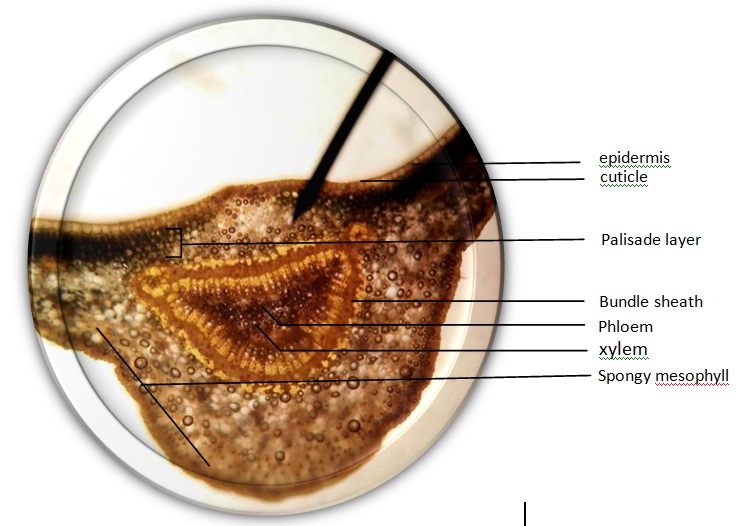
Santan leaf
Ixora sp.
22
New cards
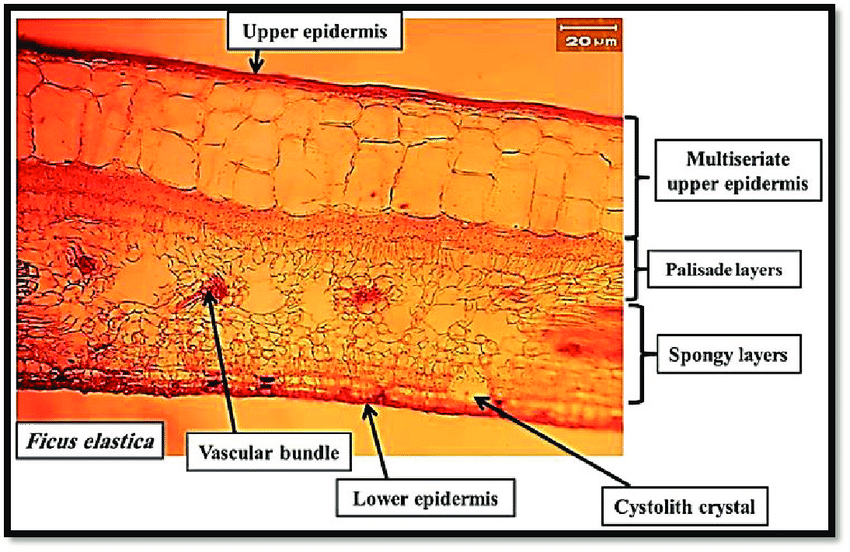
Indian rubber tree
Ficus Elastica