Unit 3: Early Europe and Colonial Americas, 200–1750 CE
3.3(3)Studied by 725 people
Card Sorting
1/278
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:19 AM on 4/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
279 Terms
1
New cards
Jesus Christ
He founded Christianity in the first century C.E.
2
New cards
Church Peace
began with Constantine's victory at the Milvian Bridge in 312 C.E.
3
New cards
Catacomb
an underground passageway used for burial
4
New cards
The Annunciation
The Angel Gabriel announces to Mary that she will be the virgin mother of Jesus.
5
New cards
The Visitation
Mary visits her cousin Elizabeth to tell her the news that she is pregnant with Jesus.
6
New cards
Christmas or the Nativity
The birth of Jesus in Bethlehem.
7
New cards
Adoration of the Magi
Traditionally, three kings, who are also astrologers, are attracted by a star that shines over Jesus’s manger.
8
New cards
Massacre of the Innocents
After Jesus is born, King Herod issues an order to execute all male infants in the hope of killing him.
9
New cards
Baptism of Jesus
John the Baptist, Jesus’s cousin, baptizes him in the Jordan River.
10
New cards
Calling of the Apostles
Jesus gathers his followers, including Saint Matthew and Saint Peter, as his ministry moves forward.
11
New cards
Miracles
To prove his divinity, Jesus performs a number of miracles, like multiplying loaves and fishes, resurrecting the deceased Lazarus, and changing water into wine at the Wedding at Cana.
12
New cards
Giving the Keys
Sensing his own death, Jesus gives Saint Peter the keys to the kingdom of heaven, in effect installing him as the leader when he is gone, and therefore the first pope.
13
New cards
Transfiguration
Jesus transfigures himself into God before the eyes of his apostles; this is the high point of his ministry.
14
New cards
Palm Sunday
Jesus enters Jerusalem in triumph, greeted by throngs with palm branches.
15
New cards
Last Supper
Before Jesus is arrested, he has a final meal with his disciples in which he institutes the Eucharist—that is, his body and blood in the form of bread and wine; at this meal he reveals that he knows that one of his apostles, Judas, has betrayed him for 30 pieces of silver.
16
New cards
Crucifixion
After a brief series of trials, Jesus is sentenced to death for sedition.
17
New cards
Deposition
The taking down of Jesus’s dead body from the cross
18
New cards
Lamentation
Jesus being mourned by his family and friends after his crucifixion and descent from the Cross.
19
New cards
Entombment
The burial of Jesus
20
New cards
Pieta
The lamentation of Jesus’s death
21
New cards
Resurrection
On Easter Sunday, three days later, Jesus rises from the dead.
22
New cards
New Testament
Also important are four author portraits of the Evangelists, who are the writers of the principal books, or gospels, of the \____.
23
New cards
Gospels
the first four books of the New Testament that chronicle the life of Jesus
24
New cards
Catacomb paintings
show a sensitivity toward artistic programs rather than random images.
25
New cards
Lunette
a crescent-shaped space, sometimes over a doorway, that contains sculpture or painting
26
New cards
Orant figure
a figure with its hands raised in prayer
27
New cards
Greek Chapel
Named for two Greek inscriptions painted on the right niche.Three niches for sarcophagi.
28
New cards
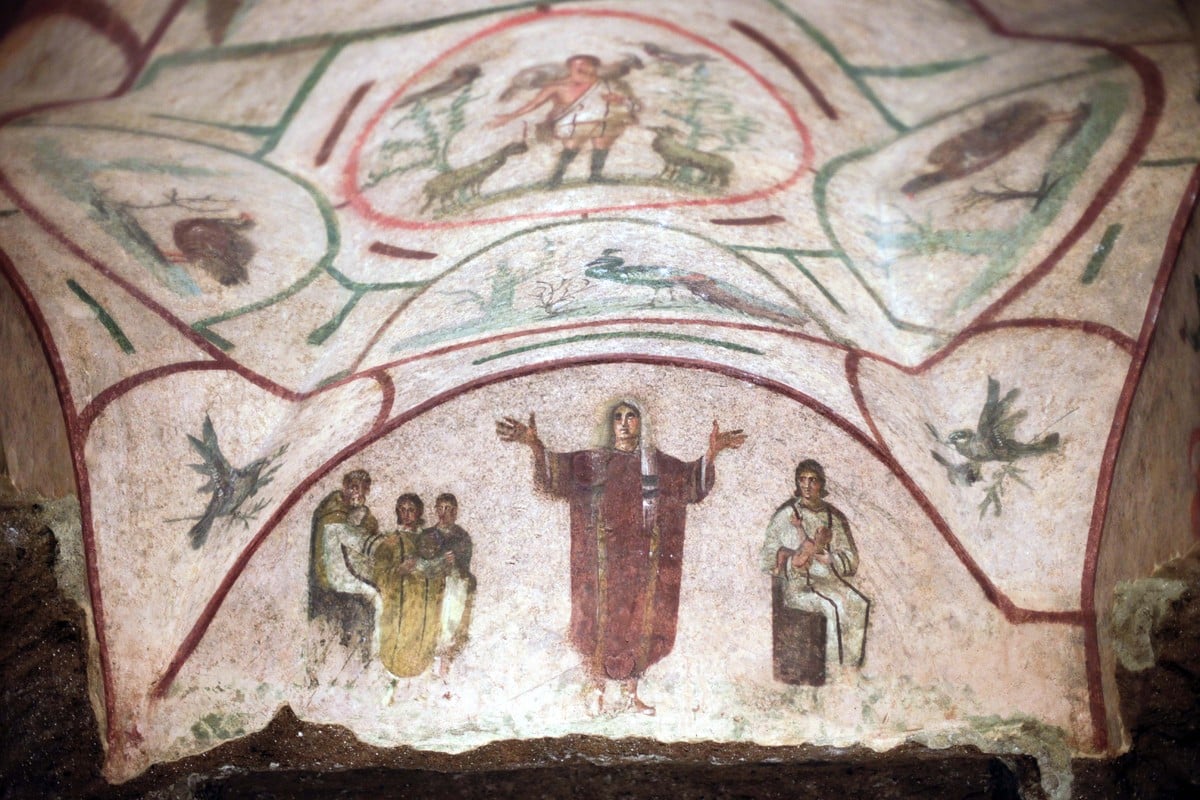

Orant fresco
Fresco over a tomb niche set over an arched wall; cemetery of a family vault.
29
New cards

Good Shepherd fresco
Restrained portrait of Christ a pastoral motif in ancient art going back to the Greeks.
30
New cards
Loculi
openings in the walls of catacombs to receive the dead
31
New cards
Cubicula
small underground rooms in catacombs serving as mortuary chapels
32
New cards
Transept
an aisle in a church perpendicular to the nave, where the clergy originally stood
33
New cards
Basilicas
with their large, groin-vaulted interiors and impressive naves, were meeting places for the influential under the watchful gaze of the emperor’s statue.
34
New cards
Transept
an aisle in a church perpendicular to the nave, where the clergy originally stood
35
New cards
Nave
the main aisle of a church
36
New cards
Narthex/vestibule
was positioned as a transitional zone in the front of the church.
37
New cards
Atrium
was constructed in front of the building, framing the façade.
38
New cards
catechumens
Atria also housed the \____, those who expressed a desire to convert to Christianity but had not yet gone through the initiation rites.
39
New cards
Spolia
in art history, the reuse of architectural or sculptural pieces in buildings generally different from their original contexts
40
New cards
Apse
the endpoint of a church where the altar is located
41
New cards
Clerestory
the third, or window, story of a church
42
New cards
Coffer
in architecture, a sunken panel in a ceiling
43
New cards
Ambulatory
a passageway around the apse or altar of a church
44
New cards
Central plan
a church having a circular plan with the altar in the middle
45
New cards
Axial Plan
a church with a long nave whose focus is the apse; so-called because it is designed along an axis
46
New cards
Spolia
tall slender columns taken from the Temple of Juno in Rome, erected on this site; a statement about the triumph of Christianity over paganism.
47
New cards
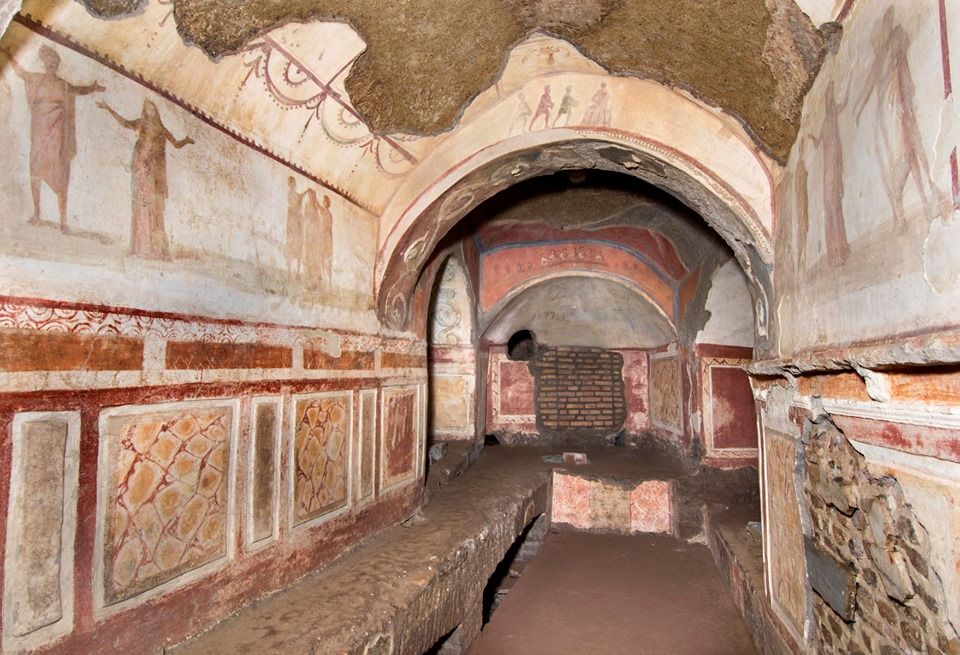

Catacomb of Priscilla
passageways beneath Rome that extend for about 100 miles and contain the tombs of 4 million dead. Has some 40,000 burials. Called in that name because she was the donor of the land for her family’s burial.
48
New cards
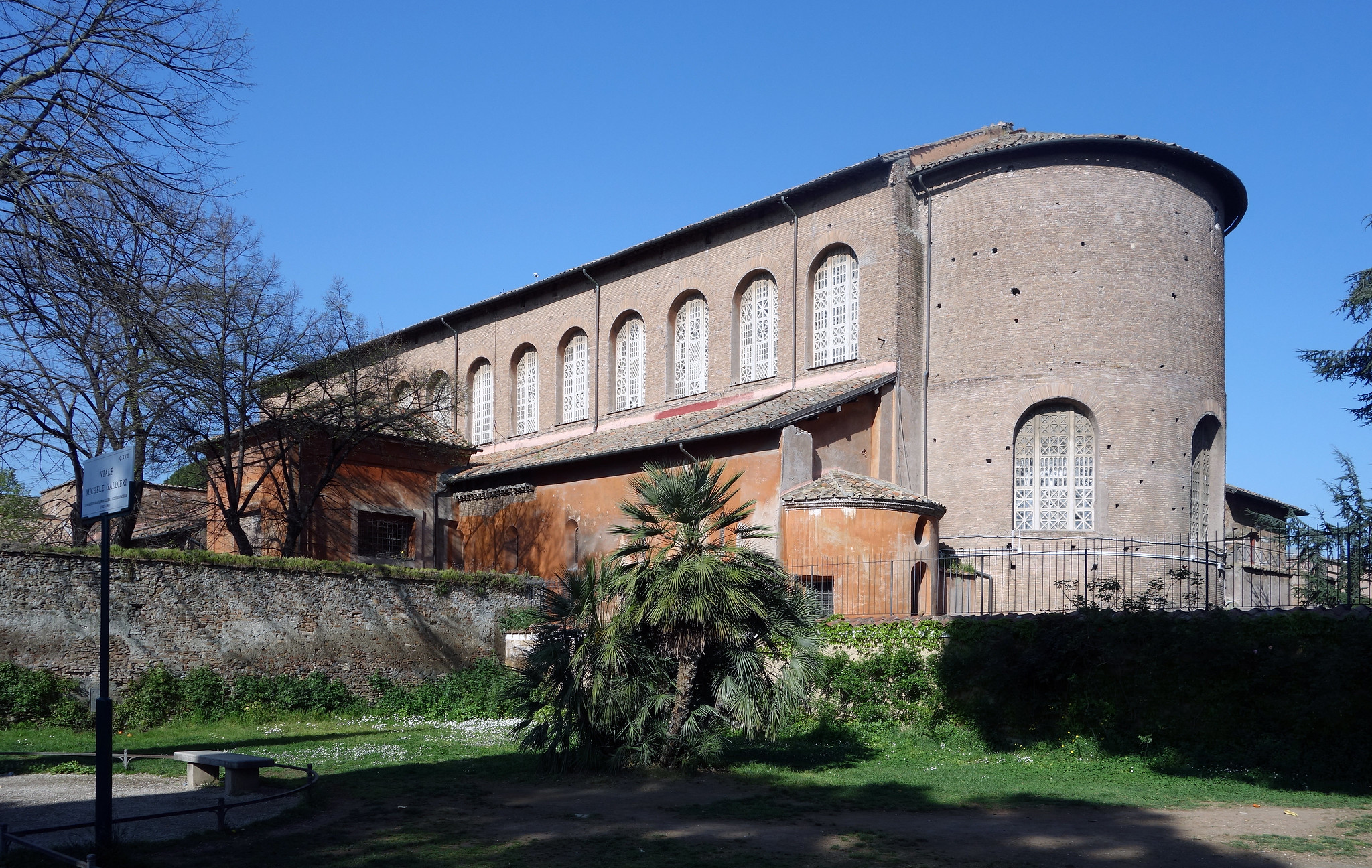

Santa Sabina
Early Christian parish church. As in the Jewish tradition, men and women stood separately; the men stood in the main aisle, the women in the side aisles with a partial view. Founded by Pope Celestine I (422–432).
49
New cards
Iconoclastic controversy
the destruction of religious images in the Byzantine Empire during the eighth and ninth centuries
50
New cards
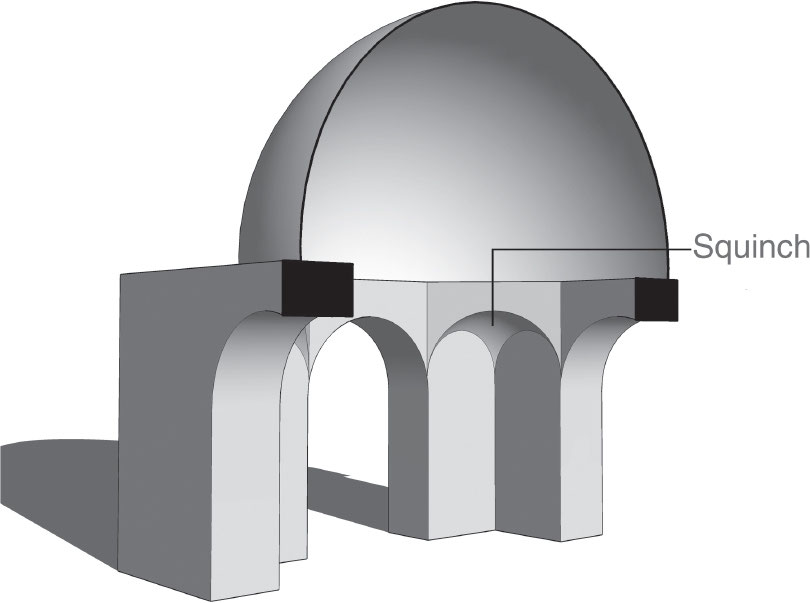
Squinch
the polygonal base of a dome that makes a transition from the round dome to a flat wall
51
New cards
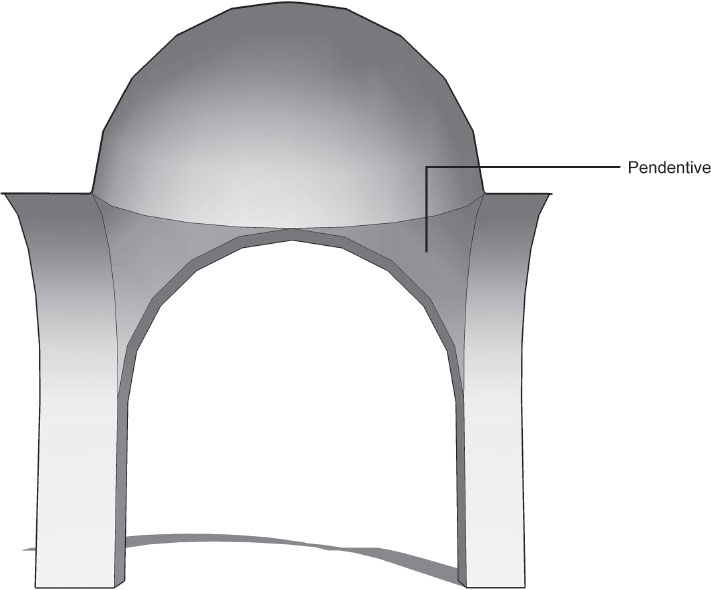
pendentive
supports the dome on four corner piers.
52
New cards
Iconostasis
a screen decorated with icons, which separates the apse from the transept of a church
53
New cards
Cathedral
the principal church of a diocese, where a bishop sits
54
New cards
Icon
a devotional panel depicting a sacred image
55
New cards
Arcade decoration
walls and capitals are flat and thin and richly ornamented
56
New cards
Cornice
a projecting ledge over a wall
57
New cards
Dome
the first building to have a dome supported by pendentives
58
New cards
Spolia
bricks taken from ruined Roman buildings reused here
59
New cards
Martyrium design
circular plan in an octagonal format
60
New cards
Martyrium
a shrine built over a place of martyrdom or a grave of a martyred Christian saint
61
New cards
Theotokos
the Virgin Mary in her role as the Mother of God
62
New cards
Paten
a plate, dish, or bowl used to hold the Eucharist at a Christian ceremony
63
New cards
Eucharist
the bread sanctified by the priest at the Christian ceremony commemorating the Last Supper
64
New cards
XP or Chi Rho
the Christian monogram made up of the Greek letters khi and rho, the first two letters of Khristos, the Greek form of Christs name
65
New cards
Chalice
a cup containing wine, used during a Christian service
66
New cards
Genesis
first book of the Bible that details Creation, the Flood, Rebecca at the Well, and Jacob Wrestling the Angel, among other episodes
67
New cards
Illuminated manuscript
a manuscript that is hand decorated with painted initials, marginal illustrations, and larger images that add a pictorial element to the written text
68
New cards
Encaustic
a type of painting in which colors are added to hot wax to affix to a surface
69
New cards
Roman Emperor Constantine the Great
The eastern half, founded by \______ at Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul), flourished for one-thousand years beyond the collapse of its western counterparts.
70
New cards
trading center
Constantinople was the \_____ of early medieval Europe, directing traffic in the Mediterranean and controlling the shipment of goods nearly everywhere.
71
New cards
iconoclasm
This meant that every church and monastery had to be redecorated, causing a burst of creative energy throughout Byzantium.
72
New cards
Medieval Crusaders
some more interested in the spoils of war than the restoration of the Holy Land, conquered Constantinople in 1204, setting up a Latin kingdom in the east.
73
New cards
figures
Perspective is unimportant because \_____ occupy a timeless space, marked by golden backgrounds and heavily highlighted halos.
74
New cards
pagan association
Nudity also had a \____, connected with the mythological religions of ancient Greece and Rome.
75
New cards
great precision
The manuscript painter had to possess a fine eye for detail, and so was trained to work with \____, rendering minute details carefully.
76
New cards
Purple
the color usually reserved for Byzantine royalty, can be seen in the mosaics of Emperor Justinian and Empress Theodora.
77
New cards
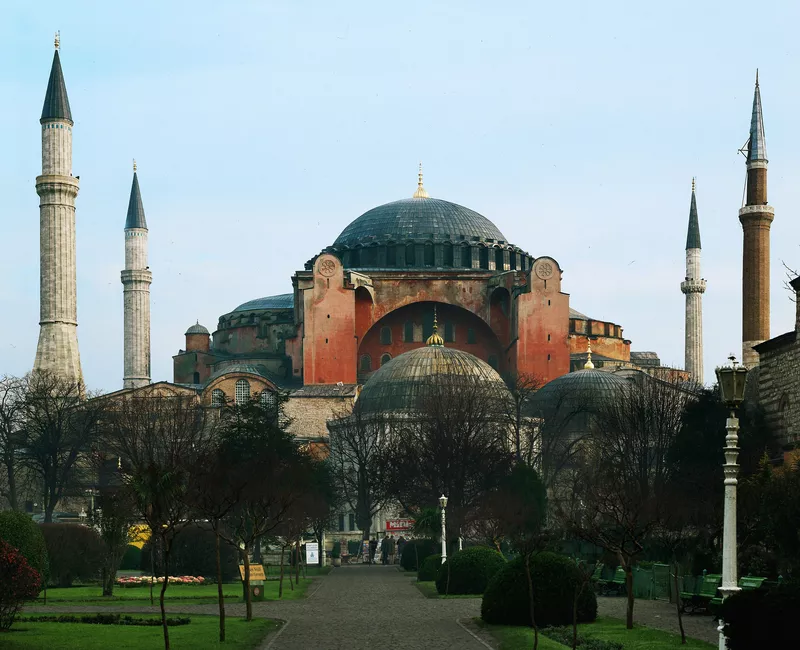

Hagia Sophia
Originally a Christian church. Built on the site of another church that was destroyed during the Nike Revolt in 532.Patrons were Emperor Justinian and Empress Theodora. Converted into a museum in 1935; reconverted into a mosque in 2020.
78
New cards
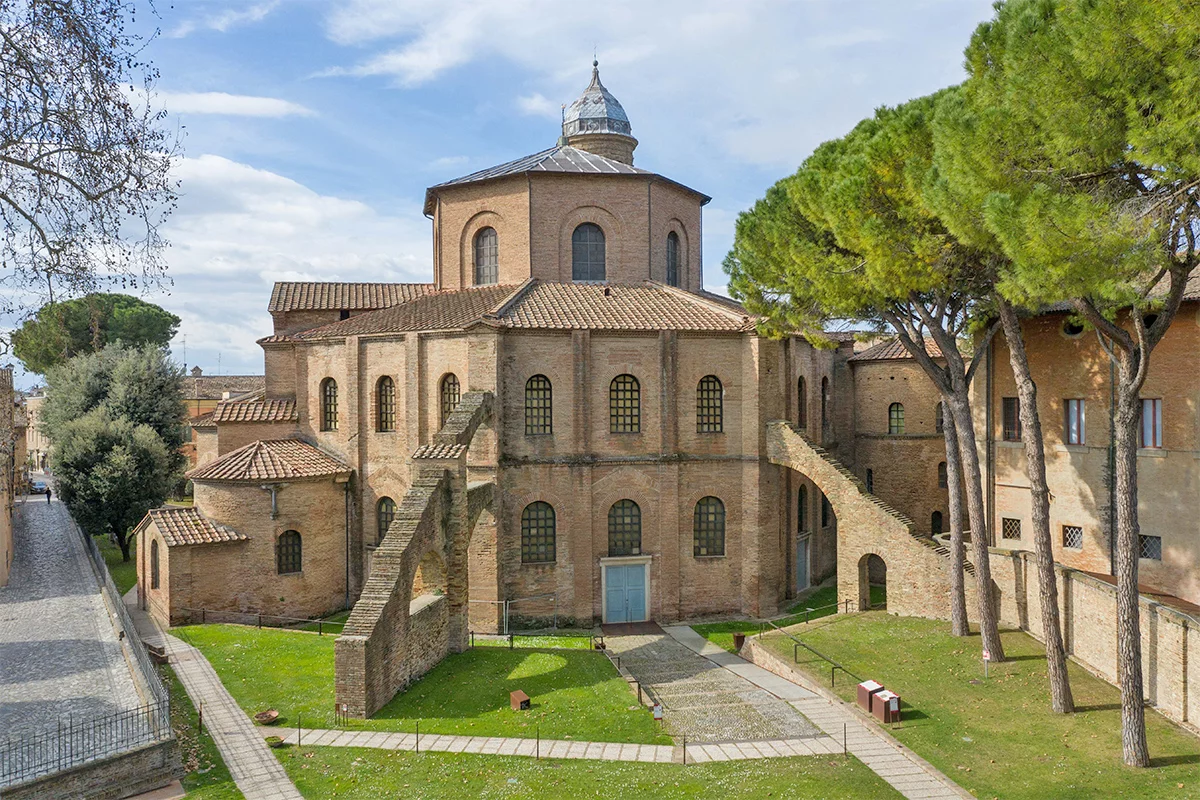

San Vitale
A Christian Church. Mysterious space symbolically connects with the mystic elements of religion. Banker Julianus Argentarius financed the building.
79
New cards
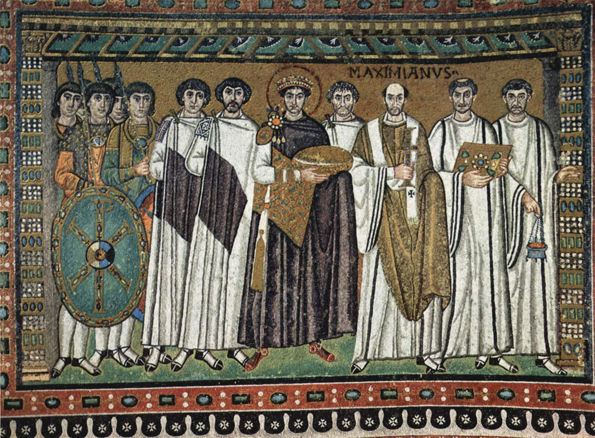

Justinian Panel
The Emperor, as the central image, dominates all; emperor’s rank indicated by his centrality, halo, fibula, and crown. Dressed in royal purple and gold. Divine authority symbolized by the halo
80
New cards
Archbishop Maximianus
patron of San Vitale
81
New cards
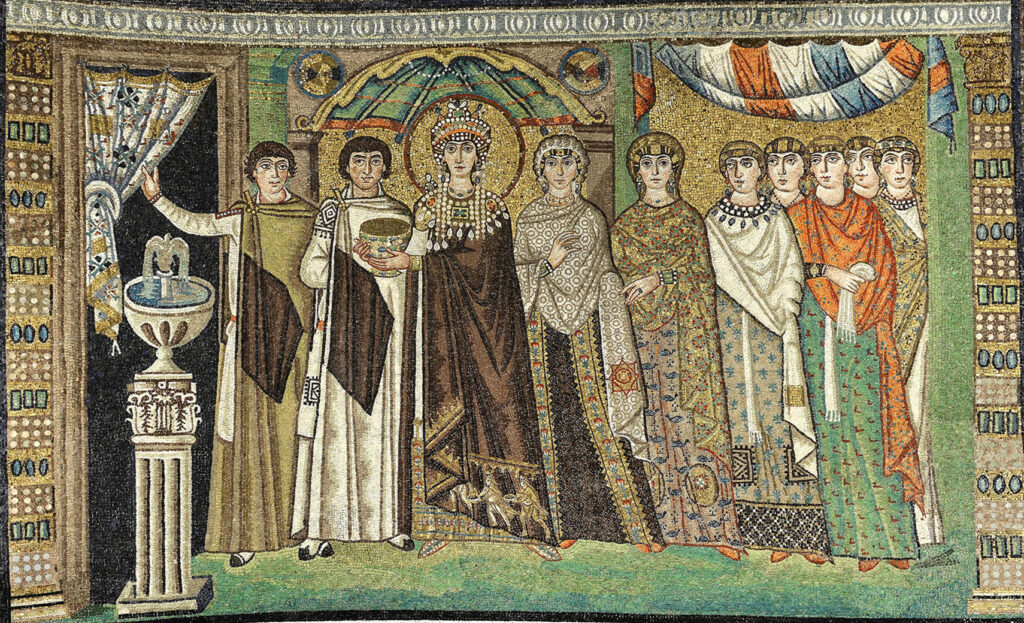

Theodora Panel
The Empress stands in an architectural framework holding a chalice for the Mass and is about to go behind the curtain. Slight displacement of absolute symmetry with the Empress. She is simultaneously frontal and moving to our left. Figures are flattened and weightless
82
New cards

Vienna Genesis
First surviving illustrations of the stories from Genesis. Genesis stories are done in continuous narrative with genre details. Written in Greek. Perhaps done in a royal workshop
83
New cards

Rebecca and Eliezer at the Well
Genesis 24: 15–61.She was shown twice, emerges from the city of Nahor with a jar on her shoulder to go down to the spring. She quenches the thirst of a camel driver, Eliezer, and his camels. Colonnaded road leads to the spring. Roman water goddess personifies the spring.
84
New cards

Jacob Wrestling the Angel
Genesis 32: 22–31.Jacob takes his two wives, two maids, and eleven children and crosses a river; the number of children is abbreviated. At night Jacob wrestles an angel. The angel strikes Jacob on the hip socket.
85
New cards
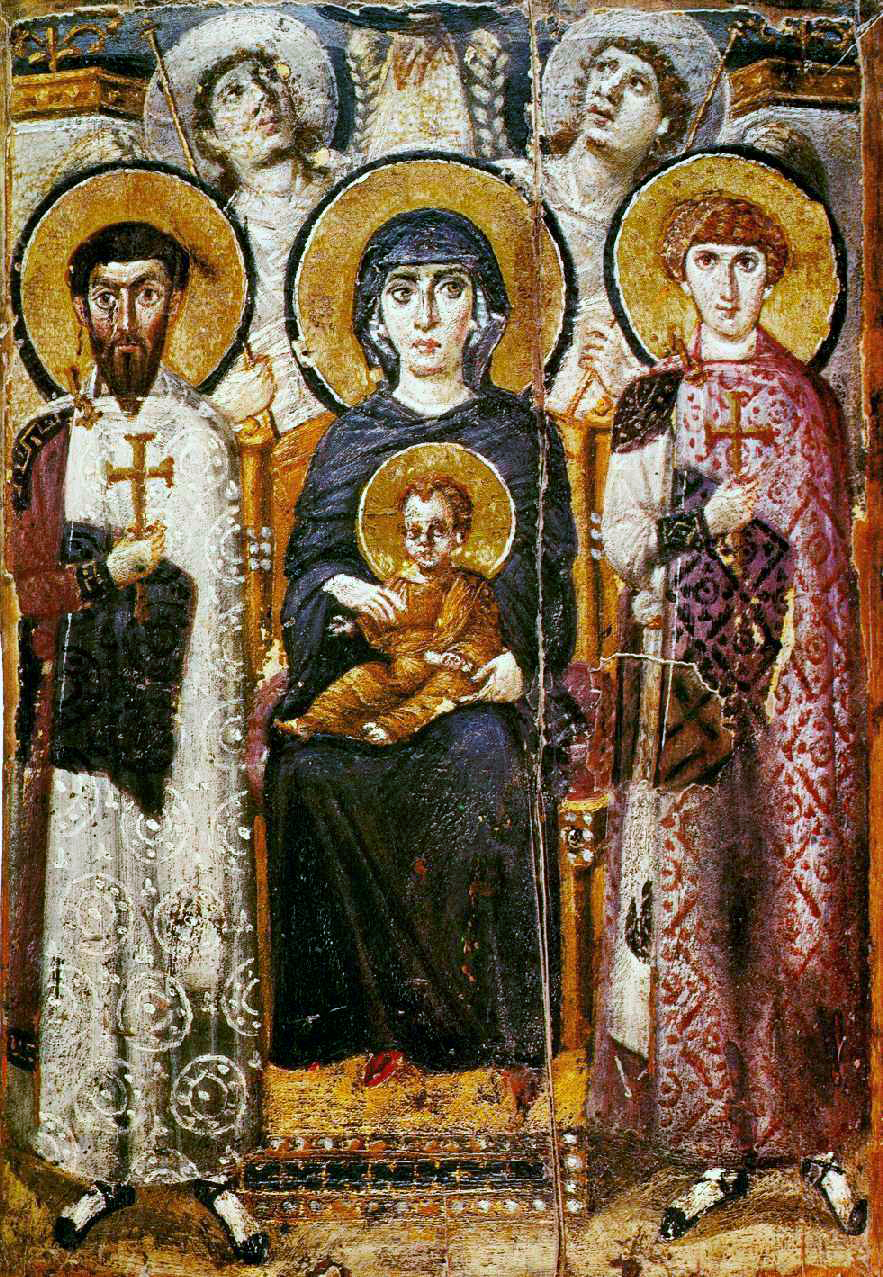

Virgin (Theotokos) and Child between Saints Theodore and George
Pre–Iconoclastic Controversy icon. Virgin and Child centrally placed; firmly modeled..Saints Theodore and George flank Virgin and Child. Angels in background look toward heaven.
86
New cards
Vikings from Scandinavia
The \_____, in their speedy boats, flew across the North Sea and invaded the British Isles and colonized parts of France.
87
New cards
Attila the Hun
This was the age of mass migrations sweeping across Europe, an age epitomized by the fifth-century king, \____, whose hordes were famous for despoiling all before them.
88
New cards
Dark Ages
So desperate was this era that historians named it the “\_____,” a term that more reflects our knowledge of the times than the times themselves.
89
New cards
Charlemagne
However, stability in Europe was reached at the end of the eighth century when a group of Frankish kings, most notably \______, built an impressive empire whose capital was centered in Aachen, Germany.
90
New cards
Scribes
These copied the Bible and medical treatises, not modern literature or folk stories.
91
New cards
Scriptorium
a place in a monastery where monks wrote manuscripts
92
New cards
vellum
A codex was made of resilient antelope or calf hide
93
New cards
parchment
sheep or goat hide
94
New cards
Merovingians
A dynasty of Frankish kings who, according to tradition, descended from Merovech, chief of the Salian Franks.
95
New cards
Chasing
to ornament metal by indenting into a surface with a hammer
96
New cards
Cloissonné
enamelwork in which colored areas are separated by thin bands of metal, usually gold or bronze
97
New cards
Zoomorphic
having elements of animal shapes
98
New cards
Fibula
a pin or brooch used to fasten garments; showed the prestige of the wearer.
99
New cards
Hiberno Saxon art
The art of the British Isles in the Early Medieval period.
100
New cards
Hibernia
the ancient name for Ireland.