Nuclear Processes
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/44
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
Chernobyl Power Plant
nuclear power plant in Russia that had an explosion in 1986 & released radioactive materials into the air
2
New cards
Isotope
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
3
New cards
proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
4
New cards
electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge
5
New cards
strong force
attractive force that acts between protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus
6
New cards
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
7
New cards
atomic mass
the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element
8
New cards
amu
atomic mass unit
9
New cards
Fission
The splitting of an atomic nucleus to release energy.
10
New cards
reactant
a substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction.
11
New cards
product
A substance produced in a chemical reaction
12
New cards
gamma radiation
High-energy radiation emitted by the nuclei of radioactive atoms. VERY Low ionization high penetration
13
New cards
alpha particle
A cluster of 2 protons and 2 neutrons emitted from a nucleus in one type of radioactivity
High ionization VERY low penetration
High ionization VERY low penetration
14
New cards
beta particle
a high-speed electron with a 1- charge that is emitted during radioactive decay
Medium ionization Medium penetration
Medium ionization Medium penetration
15
New cards
half-life
length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay
16
New cards
control rods
neutron-absorbing rods that help control the reaction by limiting the number of free neutrons
17
New cards
radioactive decay
A spontaneous process in which unstable nuclei lose energy by emitting radiation
18
New cards
Uranium-235
an unstable, fissionable isotope of uranium
19
New cards
uranium enrichment
A process that results in an increase in the amount of the fissionable isotope of uranium in a given mass of uranium. Used mostly for nuclear weapons, naval propulsion, and smaller quantities for research reactors.
20
New cards
uranium - 238
most stable form of uranium, used in control rods
21
New cards
Cation
A positively charged ion
22
New cards
Anion
A negatively charged ion
23
New cards
Ion
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge.
24
New cards
Ionization ability
ability of radioactive emissions to strip electrons from molecules, potentially causing damage
25
New cards
Penetration ability
Ability of radioactive emissions to pass through materials
26
New cards
Neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
27
New cards
Fukushima Daiichi
Japanese nuclear power plant severely damaged by the tsunami associated with the March 2011 Tohoku earthquake that rocked Japan. Most radiation drifted over the ocean away from population centers, but the event was history's second most serious nuclear accident.
28
New cards
AZX notation
Standard nuclear notation shows the chemical symbol, the mass number and the atomic number of the isotope.
29
New cards
percent abundance
the naturally occurring amount of a certain isotope of an element
30
New cards
abundance formula
(percent abundance in decimal * atomic mass) + (percent abundance in decimal * atomic mass)
31
New cards
Plum Pudding Model
soup of positive charge with electrons scattered within
Helped understand that an atom is stable and deflection of cathode rays in the presence of a negatively charged particle.
Helped understand that an atom is stable and deflection of cathode rays in the presence of a negatively charged particle.
32
New cards
Rutherford Gold Foil
Wanted to prove plum pudding model
Chamber of lead that hold radioactive material (U or Rd) with a little whole that emits neutrons when it goes through fission. Catches alpha rays that goes through gold foil on detectors.
Shows that atom is mostly empty space with a nucleus of protons.
Chamber of lead that hold radioactive material (U or Rd) with a little whole that emits neutrons when it goes through fission. Catches alpha rays that goes through gold foil on detectors.
Shows that atom is mostly empty space with a nucleus of protons.
33
New cards
Nuke bomb energy
Nuclear energy is compact and radioactive elements go through fission uncontrollably. (Nuclear chain reaction happens very quickly) so a lot of energy is emitted.
U235 is used more because is has less neutrons and more unstable so goes through fission with slow neutrons + more frequently.
U235 is used more because is has less neutrons and more unstable so goes through fission with slow neutrons + more frequently.
34
New cards
Power plant energy
Nuclear reaction is more controlled using U238 control rods because it has more neutrons and needs fast neutrons to go through fission (so less often than U235) and can absorb neutrons. (makes fission slower) less energy is emitted
35
New cards
Safety with Nuclear Energy
Confining radioactive in high density materials (lead, steel) because alpha decay has low penetration.
Geological confinement: nukes are far underground and put in casks so radiation emitted to the surface is less.
Casks are made of high density materials and very tight (airtight sealed)
Geological confinement: nukes are far underground and put in casks so radiation emitted to the surface is less.
Casks are made of high density materials and very tight (airtight sealed)
36
New cards
Enriched Uranium
U238 that is used to have a higher oncentration of U235.
Put in centrifuges that spin super fast and U235 sits in middle U238 sits in outer and then is removed.
Put in centrifuges that spin super fast and U235 sits in middle U238 sits in outer and then is removed.
37
New cards
Alpha decay formula
releases Helium and subtract that from original element

38
New cards
Beta decay formula
neutron turn into a proton and electron is released
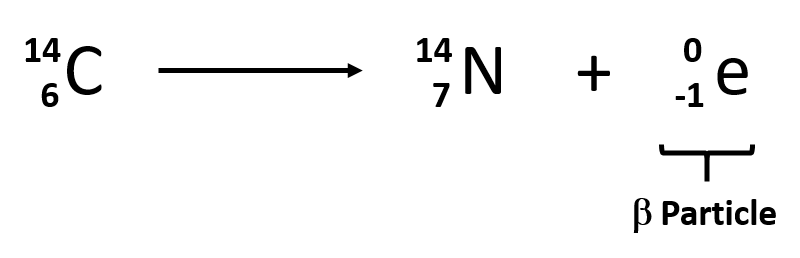
39
New cards
Gamma Decay formula
nothing is released except gamma radiation
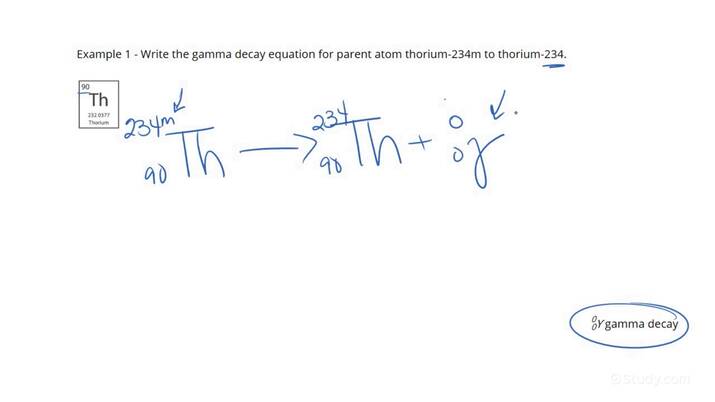
40
New cards
Fission Formula
needs to be balanced on both sides a neutron is released and neutrons are added in the product.
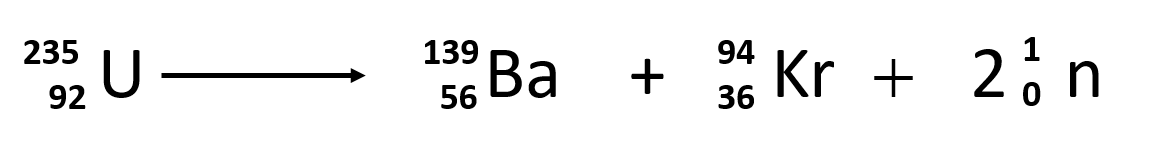
41
New cards
Half life question that decays to a certain amt?
Divide sample by 2 then divide until you reach the amt and count the days (time in general)
42
New cards
Half life question that asks for a fraction?
Write out a table of hrs to fraction and keep going until that fraction then count the time it takes.
43
New cards
Half life in regard to nuclear waste
Half life is the amt of time it takes for half of a radioactive element to become stable. Radioactive material can never fully decay so this is why nuclear waste needs to be stored properly or a way that radioactive energy will not be emitted too much.
Half life can takes minutes to years which also requires proper storage so half life decaying radioactivity emits less.
Half life can takes minutes to years which also requires proper storage so half life decaying radioactivity emits less.
44
New cards
effects of high ionization
Alpha and beta have high ionization so it can break molecules and cause DNA mutations by breaking nucleotides and cause diseases such as cancer.
45
New cards
Radioactive
when nucleus is split it releases radioactive energy