Chapter 7: Thermochemistry (7%)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
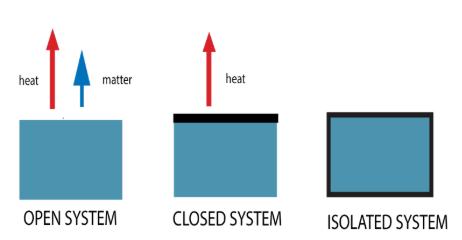
isolated systems
Isolated vs. Closed vs. Open Systems
Cannot exchange matter or energy (heat and work) with the environment
EX: an insulated bomb calorimeter
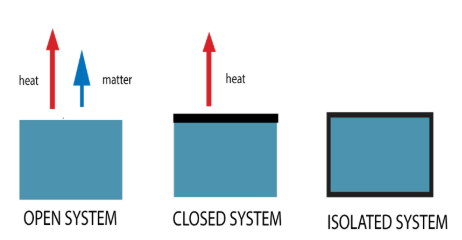
closed systems
Isolated vs. Closed vs. Open Systems
Can exchange energy (heat and work) but not matter with the environment
EX: a steam radiator
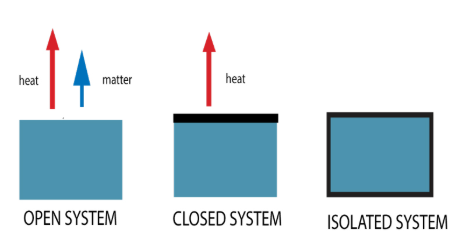
open systems
Isolated vs. Closed vs. Open Systems
Can exchange both energy (heat and work) and matter with the environment
EX: a pot of boiling water
change in system’s internal energy = heat added to system - work done by system (ΔU = Q - W)
Write out the formula for the 1st Law of Thermodynamics
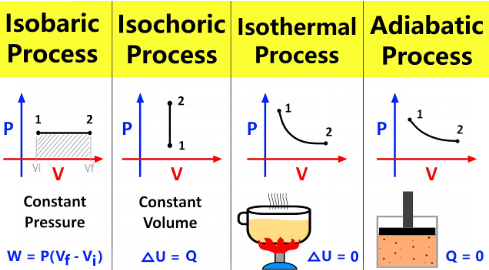
isothermal processes
Isothermal vs. Adiabatic vs. Isobaric vs. Isovolumetric (Isochoric) Processes
Occur at a constant temperature
1st Law of Thermodynamics ΔU = Q - W simplifies to Q = W
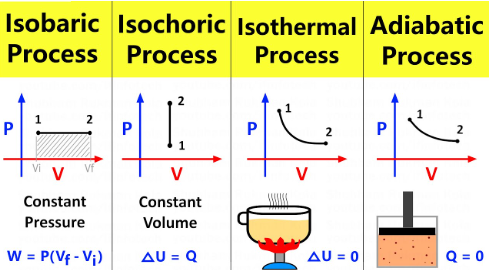
adiabatic processes
Isothermal vs. Adiabatic vs. Isobaric vs. Isovolumetric (Isochoric) Processes
Exchange no heat with the environment
1st Law of Thermodynamics ΔU = Q - W simplifies to ΔU = - W
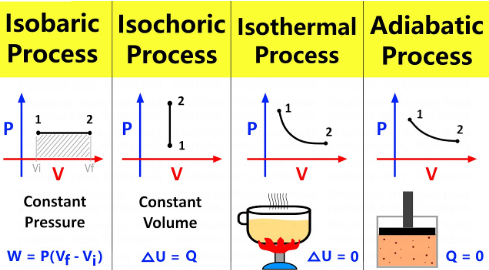
isobaric
Isothermal vs. Adiabatic vs. Isobaric vs. Isovolumetric (Isochoric) Processes
Occur at constant pressure
Do not alter the 1st Law of Thermodynamics (remains as ΔU = Q - W)
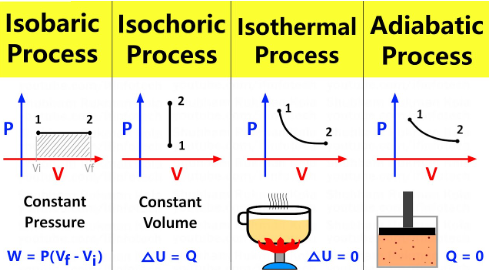
isovolumetric processes (isochoric)
Isothermal vs. Adiabatic vs. Isobaric vs. Isovolumetric (Isochoric) Processes
Occur at a constant volume
1st Law of Thermodynamics ΔU = Q - W simplifies to ΔU = Q
state functions
State Functions vs. Process Functions
Properties of a system that depend only on the system's current condition (initial and final states) and not on the specific path or process taken to get there
Describe the physical properties of a system in an equilibrium state
Pathway independent
EX: temperature, pressure, volume, internal energy, enthalpy, entropy, density, Gibbs free energy
process functions
State Functions vs. Process Functions
Quantities that describe the transition between equilibrium states of a system
Describe the pathway taken from one equilibrium to another
Pathway dependent
EX: work (W), heat (Q)
298K, 1atm, 1M
state the temperature, pressure, and concentration defined as Standard Conditions
standard state
The _________ _____ of an element is its most prevalent form under standard conditions
gas (g)
Gas (g) vs. Liquid (l) vs. Solid (s)
the standard state of H2
liquid (l)
Gas (g) vs. Liquid (l) vs. Solid (s)
the standard state of H2O
solid (s)
Gas (g) vs. Liquid (l) vs. Solid (s)
the standard state of NaCl
gas (g)
Gas (g) vs. Liquid (l) vs. Solid (s)
the standard state of O2
solid (s) (graphite)
Gas (g) vs. Liquid (l) vs. Solid (s)
the standard state of C
melting (fusion), freezing (crystallization or solidification)
Phase Changes
WORD BANK: Sublimation, Condensation, Deposition, Freezing (Crystallization or Solidification), Vaporization (Evaporation or Boiling), Melting (Fusion)
——
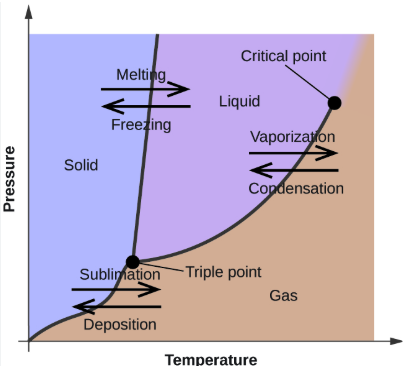
the phase changes that occur at the boundary between the SOLID and the LIQUID phases (2)
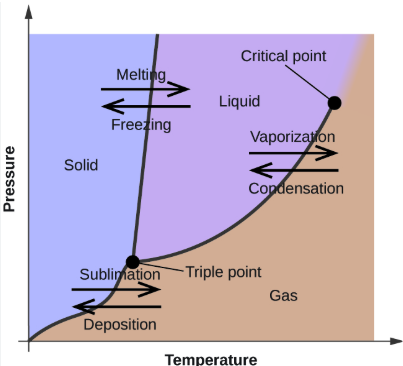
vaporization (evaporation or boiling), condensation
Phase Changes
WORD BANK: Sublimation, Condensation, Deposition, Freezing (Crystallization or Solidification), Vaporization (Evaporation or Boiling), Melting (Fusion)
——
the phase changes that occur at the boundary between the LIQUID and the GAS phases (2)
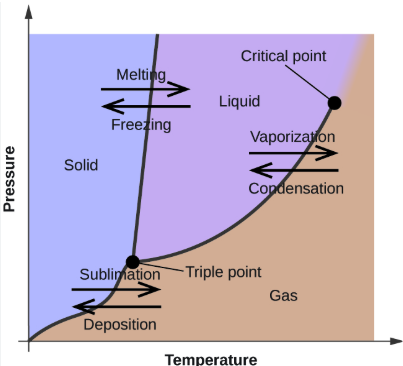
sublimation, deposition
Phase Changes
WORD BANK: Sublimation, Condensation, Deposition, Freezing (Crystallization or Solidification), Vaporization (Evaporation or Boiling), Melting (Fusion)
——
the phase changes that occur at the boundary between the SOLID and GAS phases (2)
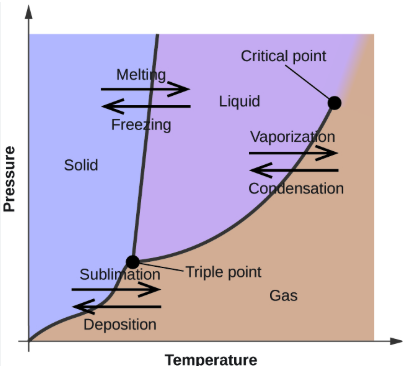
critical point
Phase Changes
The temperature above which the liquid and gas phases are indistinguishable
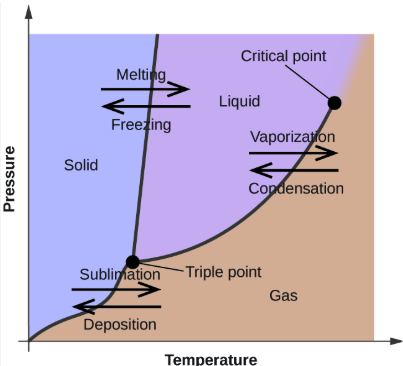
triple point
Phase Changes
The temperature at which all 3 phases of matter exist in equilibrium
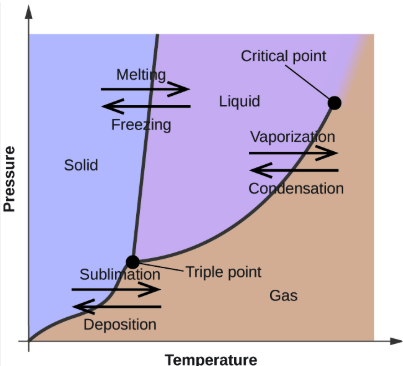
temperature, pressure
Phase Changes
The phase diagram for a system graphs the phases and phase equilibria as a function of ________________ and ___________
temperature
A scaled measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance
increases
When a substance’s thermal energy INCREASES, its temperature ___________
heat
The transfer of energy from one substance to another as a result of their differences in temperature
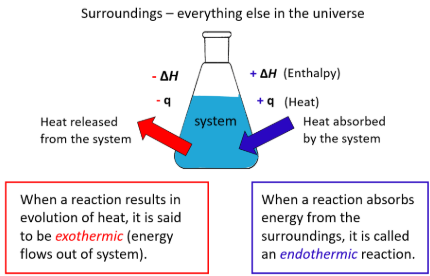
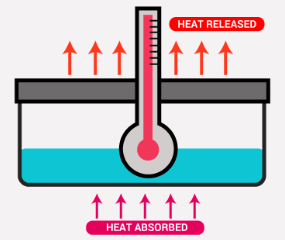
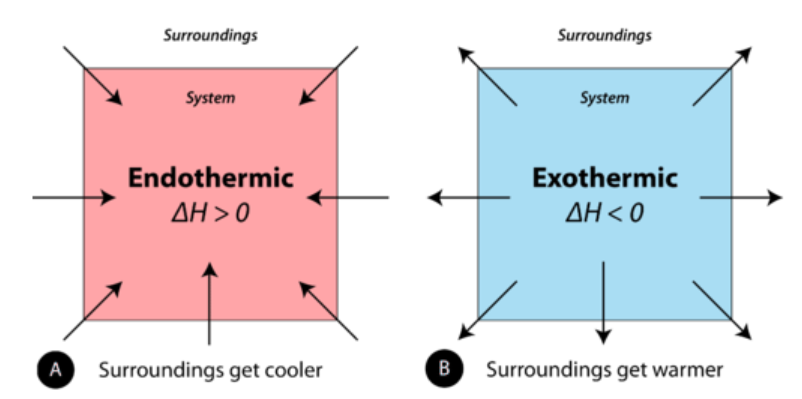
endothermic (ΔQ > 0)
Endothermic vs. Exothermic
Processes in which the system ABSORBS heat
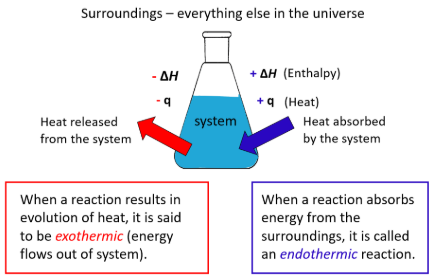
exothermic (ΔQ < 0)
Endothermic vs. Exothermic
Processes in which the system RELEASES heat
pressure
Enthalpy (ΔH) of a system is = to heat flow (Q) under constant __________
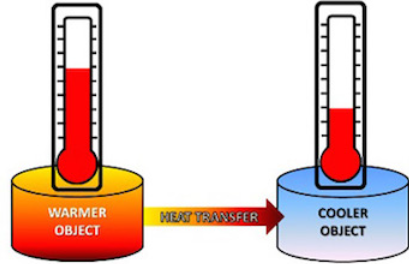
warmer, cooler

When substances of different temperatures are brought into thermal contact with each other, energy will move from the _________ substance to the _________ substance
q = mcΔT (mass x specific heat x change in temperature)
Write out the formula for calculating the amount of heat transfer/energy (q) (aka heat absorbed/released) NOT during a phase change
specific heat (c)
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1°C (or Kelvin)
temperature
Phase change reactions do NOT undergo changes in _____________
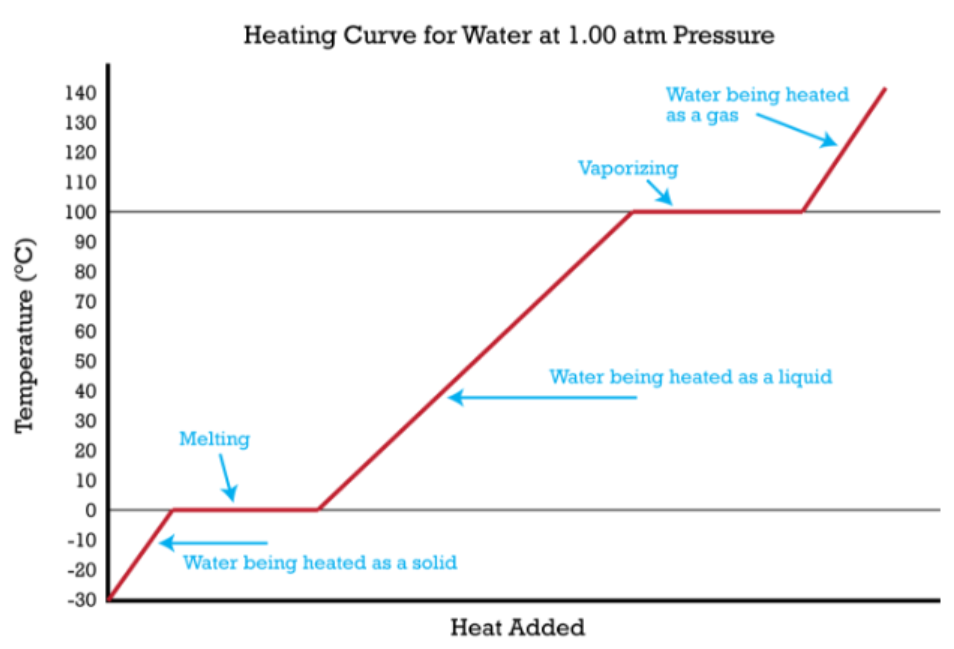
q = mL (mass x latent heat of formation)
Write out the formula for calculating the amount of heat transfer/energy (q) (aka heat absorbed/released) DURING a phase change
enthalpy
A measure of the potential energy of a system found in intermolecular attractions and chemical bonds
Equivalent to the total heat content of a system
It is equal to the internal energy of the system plus the product of pressure and volume
Can also be calculated using heats of formation, heats of combustion, or bond dissociation energies
positive, negative
Positive vs. Negative
Endothermic reactions have a ___________ ΔHrxn while exothermic reactions have a ___________ ΔHrxn
enthalpy of products - enthalpy of reactants
Write out the formula for calculating the generalized enthalpy of a reaction (ΔHrxn = ?)
potential energy, potential energies
Hess’s Law states that the total change in __________ _________ of a system is = to the changes in __________ _________ of all the individual steps of the process (aka the enthalpy changes are additive)
The total enthalpy change of a chemical reaction is the same, regardless of whether the reaction occurs in one step or several
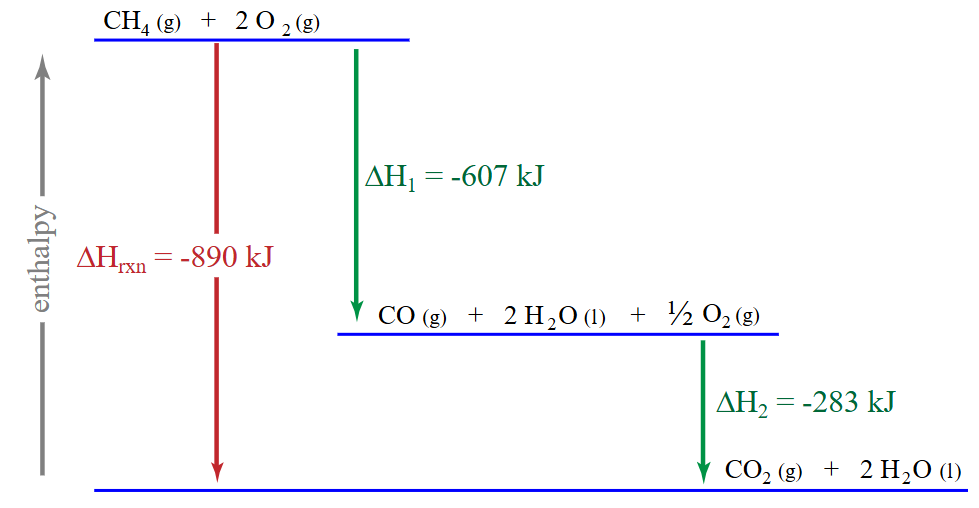
magnitude, sign
The enthalpy change for the reverse of any reaction has the same _____________ but the opposite _____ as the enthalpy change for the forward reaction
endothermic, exothermic
Exothermic vs. Endothermic
Bond breakage is generally _____________ while bond formation is generally _____________
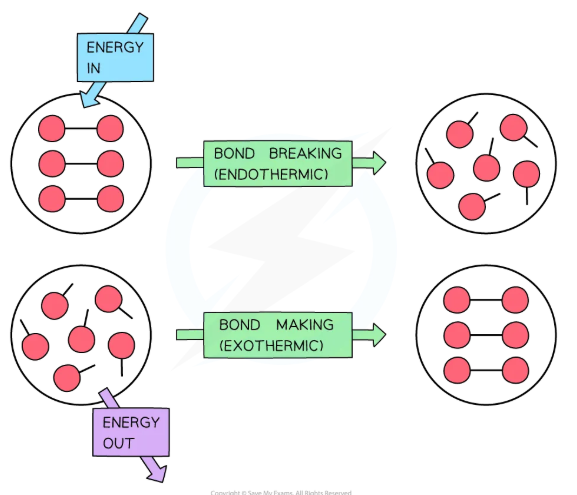
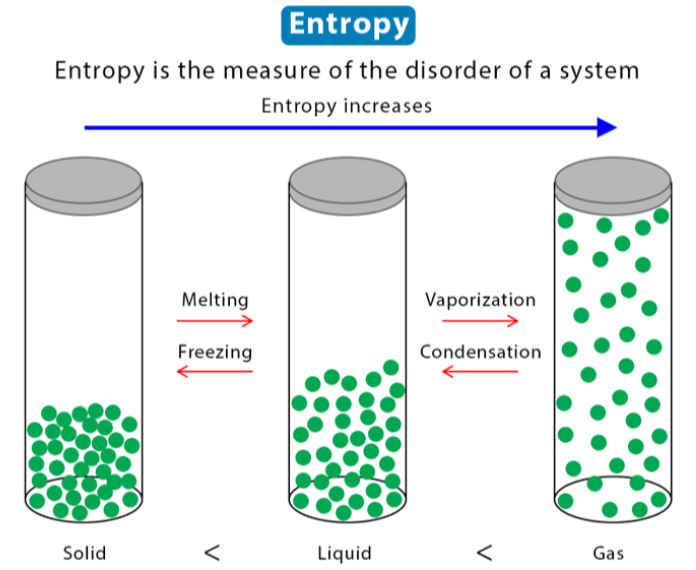
entropy

A measure of the degree to which energy has been spontaneously spread throughout a system or between a system and its surroundings
A ratio of heat transferred per mole per unit Kelvin
heat gained or lost in a reversible process / temperature in Kelvin
(Qrev / T)
Write out the formula for calculating entropy (ΔS)
increases
Increases vs. Decreases
When energy is distributed INTO a system at a given temperature, the entropy of the system ____________
decreases
Increases vs. Decreases
When energy is distributed OUT OF a system at a given temperature, the entropy of the system ____________
maximized
Minimized vs. Maximized
Entropy is ____________ at equilibrium
entropy of the universe = entropy of the system + entropy of the surroundings > 0 (aka the entropy of the universe is increasing)
Write out the formula for the 2nd Law of Thermodynamics
ΔH - TΔS
Write out the formula for Gibbs free energy (ΔG = ?)
<0 (negative)
<0 vs. =0 vs. >0
ΔG for when a reaction proceeds in the forward direction TOWARDS equilibrium (spontaneous & exergonic)
=0
<0 vs. =0 vs. >0
ΔG for when a reaction is in dynamic equilibrium
>0 (positive)
<0 vs. =0 vs. >0
ΔG for when a reaction proceeds in the reverse direction AWAY FROM equilibrium (nonspontaneous & endergonic)
temperature
Gibbs free energy depends on _____________
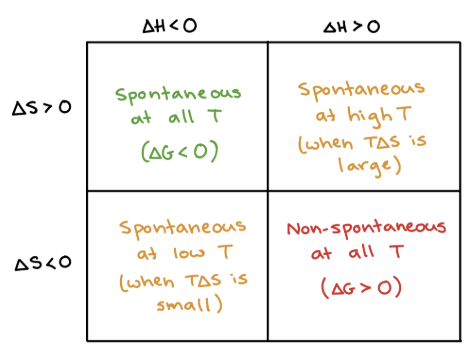
+, +
What are the signs of ΔH and ΔS when a process is SPONTANEOUS at HIGH T (temps in Kelvin)?
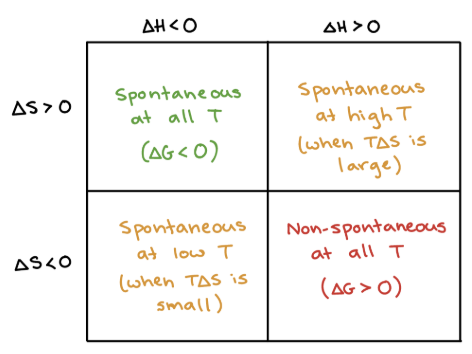
+, -
What are the signs of ΔH and ΔS when a process is NONSPONTANEOUS at ALL T (temps in Kelvin)?
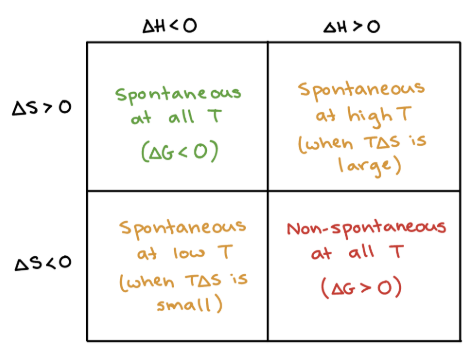
-, +
What are the signs of ΔH and ΔS when a process is SPONTANEOUS at ALL T (temps in Kelvin)?
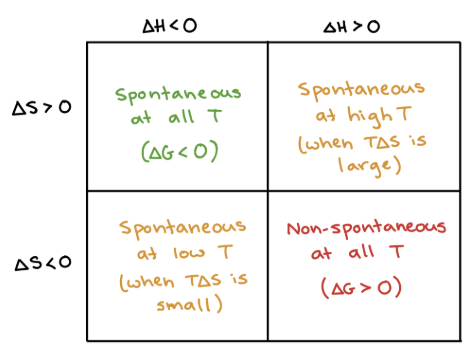
-, -
What are the signs of ΔH and ΔS when a process is SPONTANEOUS at LOW T (temps in Kelvin)?
-RT x ln(Keq)
Write out the formula for calculating the standard Gibbs free energy from the equilibrium constant Keq (ΔG°rxn = ?)
RT x ln(Q/Keq)
Write out the formula for calculating the Gibbs free energy from the reaction quotient Q (ΔGrxn = ?)
<0 (negative)
<0 vs. =0 vs. >0
ΔG for when Keq > 1
=0
<0 vs. =0 vs. >0
ΔG for when Keq = 1
>0 (positive)
<0 vs. =0 vs. >0
ΔG for when Keq < 1