Unit C: Ch 16: Cellular Reproduction
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Chromatin
An active string of uncoiled DNA
(Think the tin of messy sewing supplies)
Chromatid
A coiled string of DNA; 1 strand chromosome
Two identical halves of a chromosome
Sister chromatid
The identical twin of a chromatid; 2 strand chromosome
Centrome
The identifying centre bit of a chromosome
Homologous pair
Two chromatids that are not identical, but contain the same subset of genetic instructions (X).
Can also be in reference to 2 two chromatid chromosomes (like XX), but that is typically referred to as something else
Tetrad
A group of 2 chromosomes, which are both 2 chromatid pairs. Typically in reference to what is found in early meiosis.
Karyotype
A display of the chromosomes of a person in a certain numbered configuration
Autosome
Any Chromosome that is not a sex chromosome
Germ Cell/ Stem Cell/ Gamete
AKA a sex cell
contain half as many chromosomes as somatic cells do
Produced through meiosis
Haploid cells
Somatic Cell
body cells
Produced through mitosis
Diploid cells
Histones
The proteins chromatid is coiled around
“-ploid” suffix and ploidy
The number of chromosomes in a cell
Ha-
Di-
Tri-
Etc.
Mitosis
The asexual process of cell replication
What is the order of stages in mitosis?
Interphase
Propase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
Interphase (and the 3 steps)
Initiate; growth stage
Cells spend most their time here
Chromatin
G1
Replicate everything BUT the DNA
Requires lots of energy
Quick check everything was done right before proceeding
S
Each of the 46 chromosomes is replicated
G2
Double check everything was done right and there are no errors in the process
What happens if interphase is rushed or skipped?
Cells are uncontrollably replicating, and become useless bits of matter replicating and getting in the way, AKA cancer.
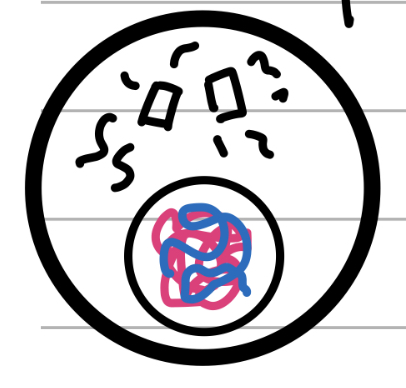
Prophase (mitosis)
Prepare
Centrioles move to the poles
Spindle fibres form
Centromeres form between sister chromatids
Nuclear membrane begins dissolving
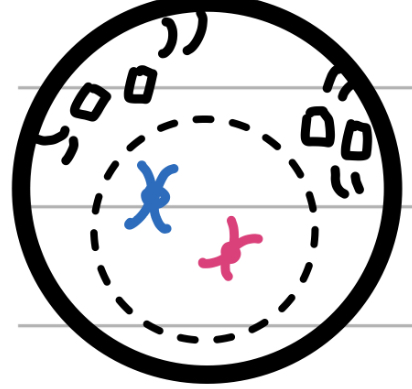
Metaphase (mitosis)
Middle
spindle fibres grab onto chromosomes
Chromosomes get lined up
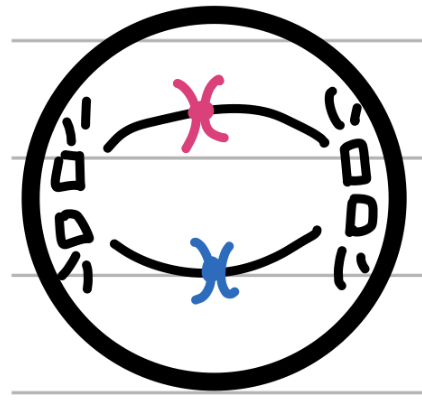
Anaphase (mitosis)
AHHHH!
Spindle fibres pull apart and pull away
Cell begins to stretch apart
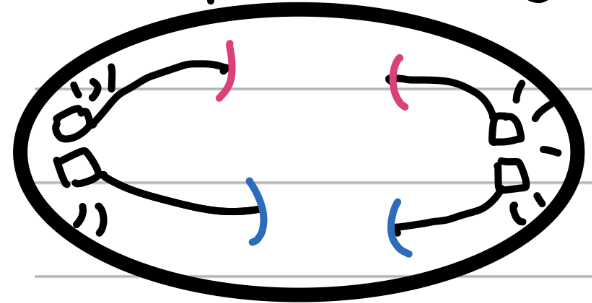
Telophase (mitosis)
The End
the cells begin splitting apart
In plants, the cell plate forms from the inside and becomes the cell wall (internal force)
In animals, a contractile ring in the membrane pinches inwards (external force)
Nuclear membrane begins forming
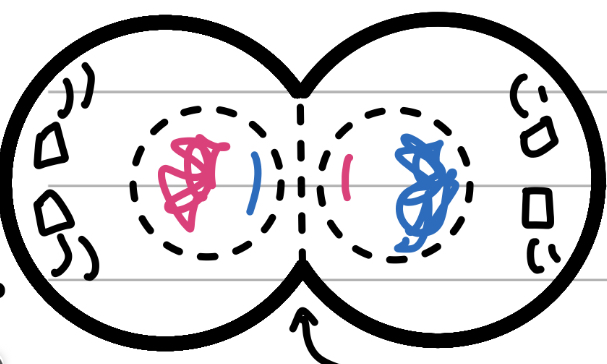
Cytokinesis (mitosis)
Cut
Not really a step, more the final split of the two cells that begins in anaphase
Chromatid becomes chromatin again
Nuclear membrane has reformed
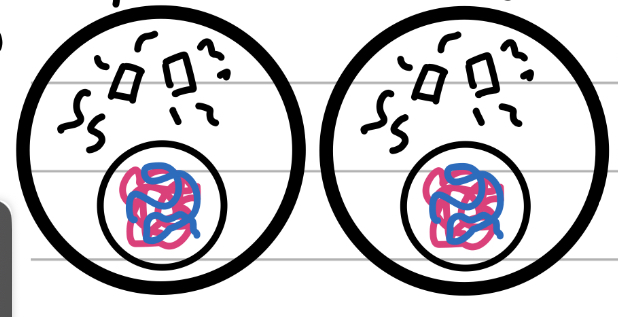
Chromosomes
Counted by centromeres, a tightly coiled movable DNA package only visible during cell division
Meiosis
The process in which gametes are produced
Consists of 1 DNA replication and 2 cell division processes reminiscent of mitosis
Allows for genetic variation
Diploid → Haploid
Prophase I
tetrads crossover at random to create slightly different chromatids (increases genetic variation)
Centrioles move to the poles
Spindle fibres form
Centromeres form between sister chromatids
Nuclear membrane begins dissolving
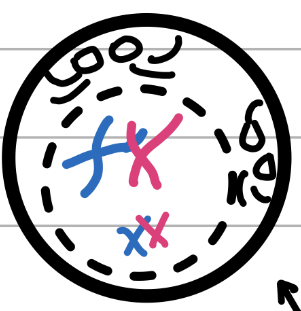
Metaphase I
Middle
spindle fibres grab onto chromosomes
Chromosomes get lined up
Nuclear membrane is gone
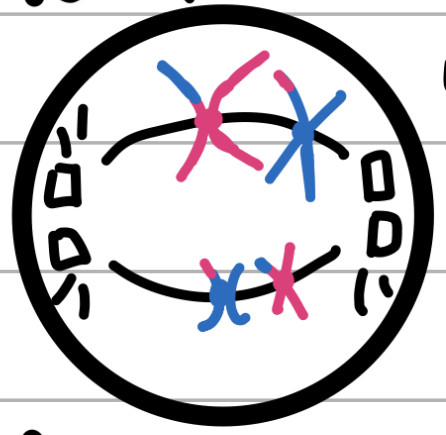
Anaphase I
AHHHH!
Spindle fibres pull apart and pull away
Cell begins to stretch apart
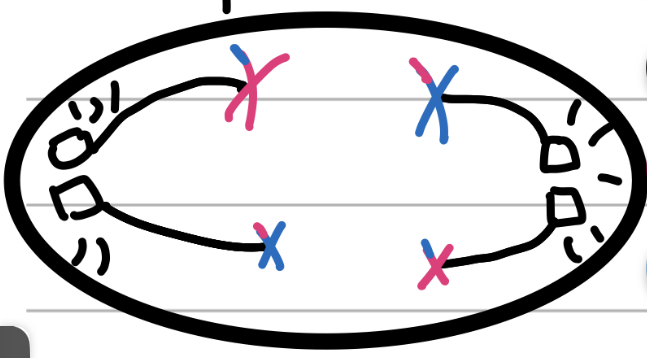
Telophase I
The End
the cells begin splitting apart
In plants, the cell plate forms from the inside and becomes the cell wall (internal force)
In animals, a contractile ring in the membrane pinches inwards (external force)
Nuclear membrane begins forming
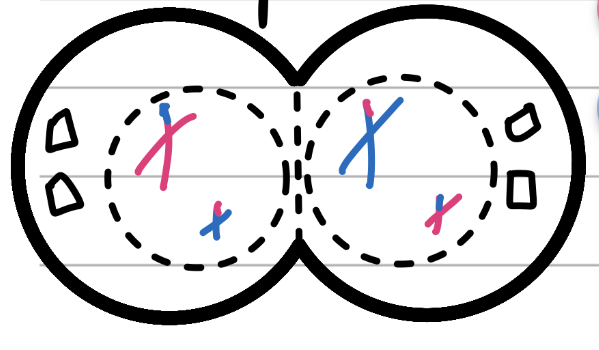
Cytokinesis I
Cut
Not really a step, more the final split of the two cells that begins in anaphase
Chromatid becomes chromatin again
Nuclear membrane has partially reformed, fully reformed or not reformed at all
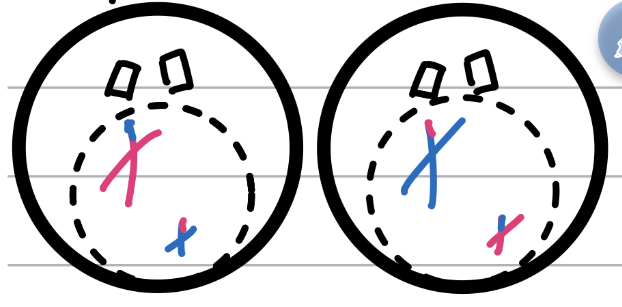
Prophase II
Prepare
Centrioles move to the poles
Spindle fibres form
Centromeres form between sister chromatids
Nuclear membrane begins dissolving
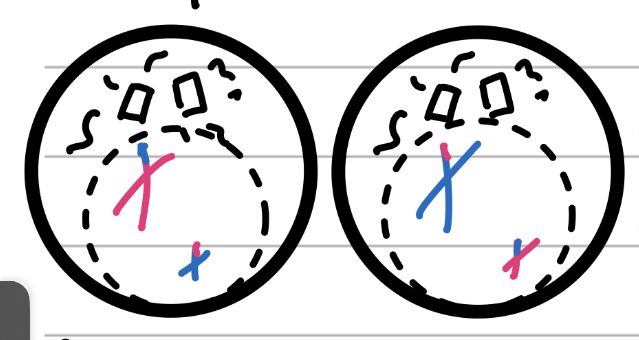
Metaphase II
Middle
spindle fibres grab onto chromosomes
Chromosomes get lined up
Nuclear membrane is gone
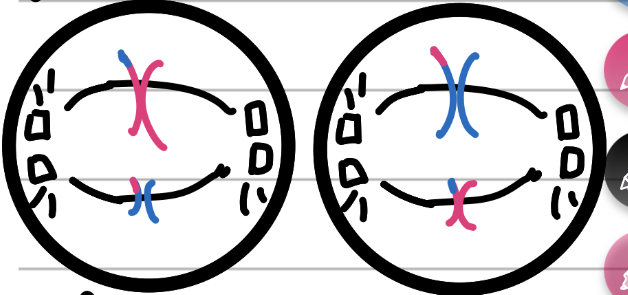
Anaphase II
AHHHH!
Spindle fibres pull apart and pull away
Cell begins to stretch apart
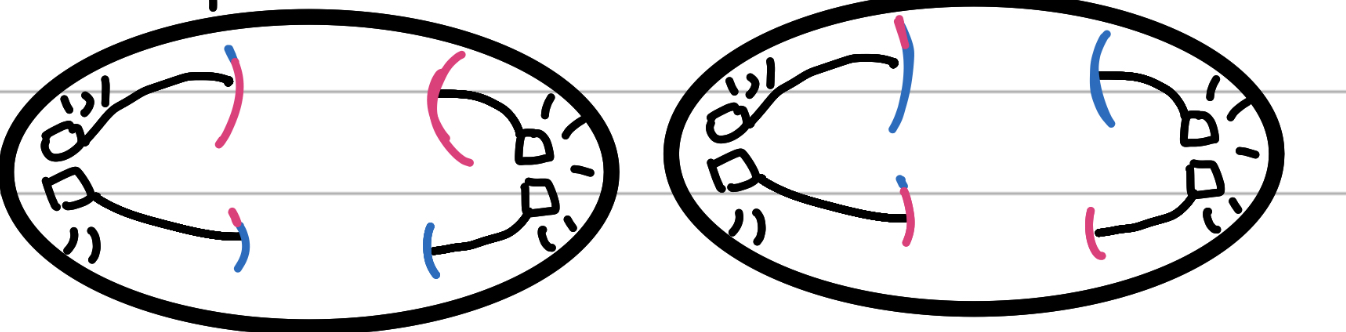
Telophase II
The End
the cells begin splitting apart
In plants, the cell plate forms from the inside and becomes the cell wall (internal force)
In animals, a contractile ring in the membrane pinches inwards (external force)
Nuclear membrane begins forming
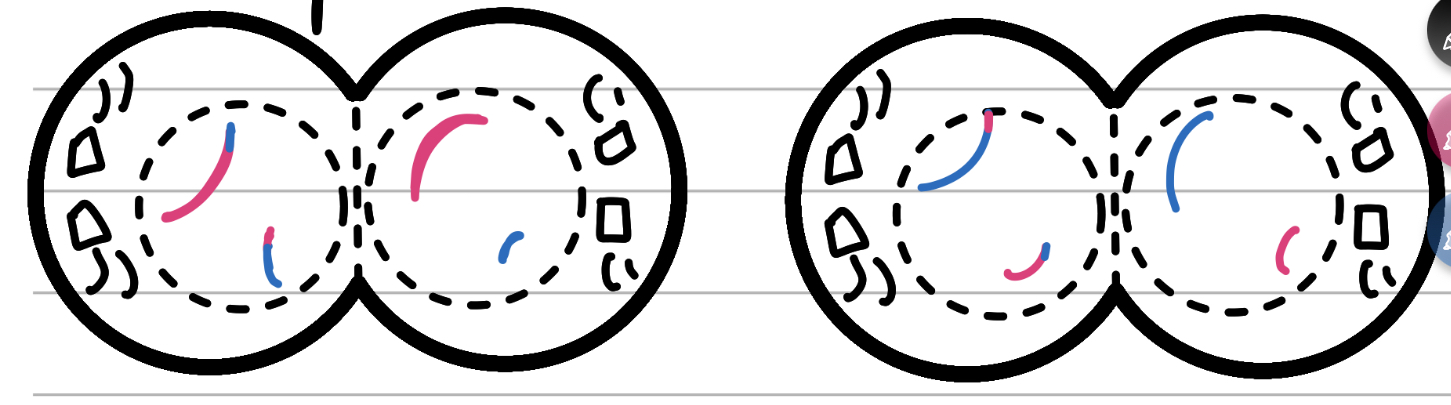
Cytokinesis II
Cut
Not really a step, more the final split of the two cells that begins in anaphase
Chromatid becomes chromatin again
Nuclear membrane has fully reformed
Non-disjunction, trisomy and monosomy
When the original chromosome pair does not split properly in meiosis I and causes an imbalance.
Trisomy: three chromosomes where there should be two
Monosomy: one chromosome where there should be two
Why are pregnancies in older women more likely to produce babies with genetic disorders?
The spindle fibre proteins aren’t as readily available and chromosomes aren’t pulled apart properly.
What is the technical term for down syndrome?
Trisomy 21
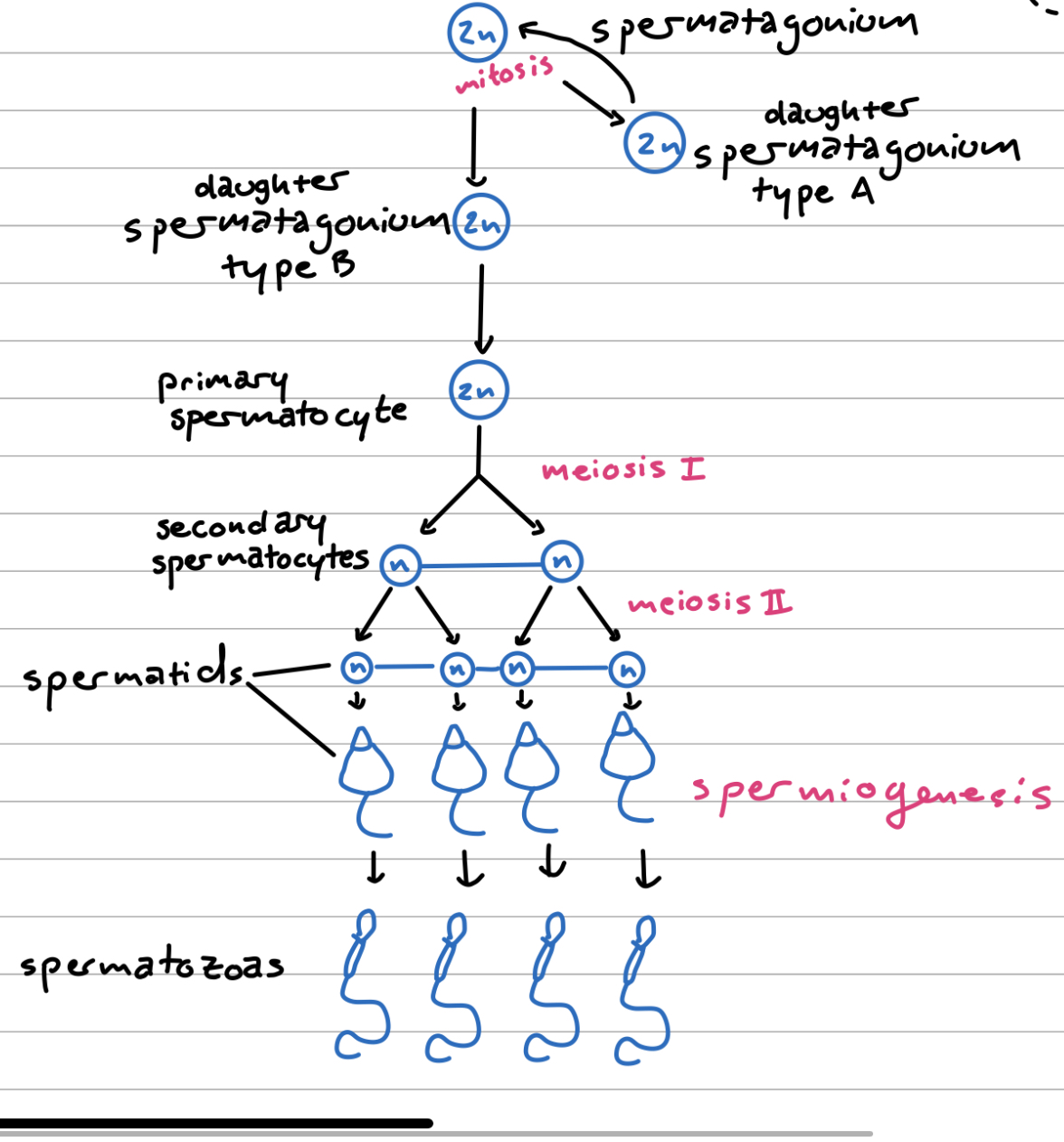
Spermatogenesis
The process of four haploid spermatozoa forming from one diploid spermatogonium
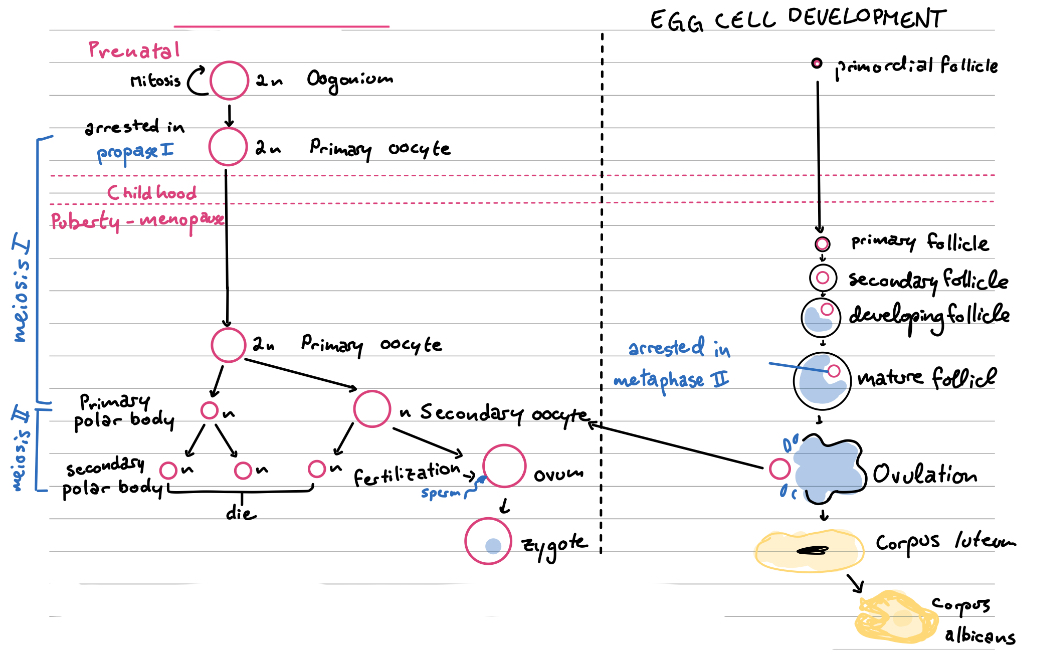
Oogenesis
The process by which a diploid oogonium cell becomes a single secondary oocyte by dividing and absorbing the cytoplasm of 3 discarded polar cells
Synapsis
The crossover fusion of chromosome pairs at the start of meiosis
Fraternal vs. Identical twins
Two eggs and two sperm to form two babies in utero at the same time
Vs.
One egg and one sperm that then split to create to biologically identical babies (completely random)
Asexual reproduction pros and cons
Pros
fast
Good if the organism is thriving in it’s surroundings
Cons
Lack of variation
Sexual reproduction pros vs. cons
Pros
Genetic variation = adaptability
Diverse species
Cons
slower
Takes longer + more organisms
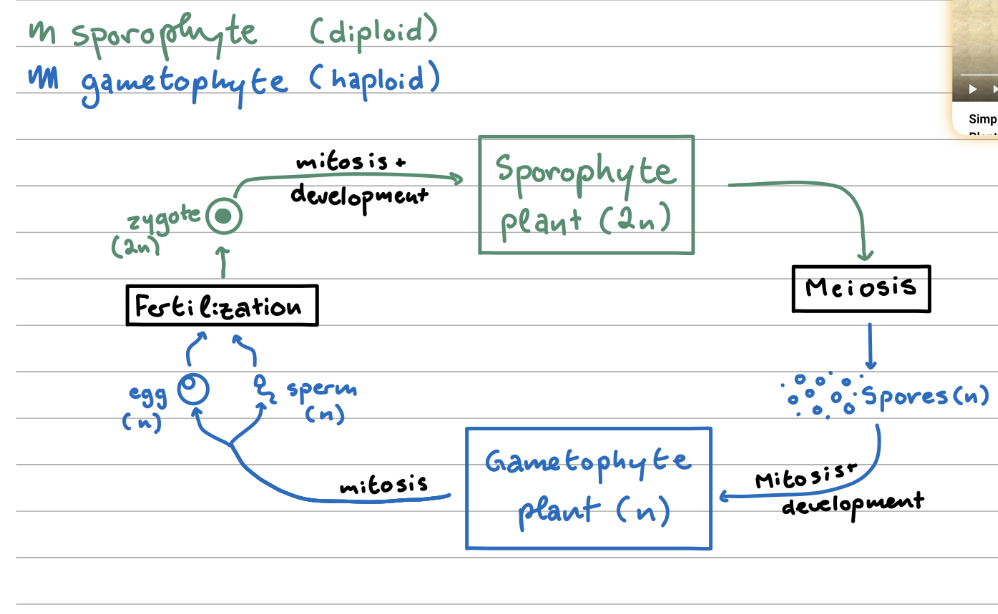
Sporophyte
Diploid generation of plants, produces haploid spores
Gametophyte
Haploid generation of plants, produces gametes that fertilize together to become diploids
Alternation of generations (describe the cycle)