lecture 10 - principles of speed accuracy and coordination part 1
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what are seed accuracy trade offs
If you perform the same action more quickly it
will be done with less accuracy - when youre rushing to do smth you make more mistakes
what is fitts law with speed accuracy trade offs
Accuracy held constant (all dots in yellow lines) - had participants perform over and over again until they had 100% accuracy
Independent variables (changes): Amplitude (A) and
Width (W)
Dependent variable (what they measured): Movement time (MT) - how long it took you to move between targets
MT ~ A/W - Large amplitude movements to wide targets take the same time as small amplitude movements to narrow targets
to get a linear relationship - MT = a + b [Log2 (2A/W)]
[Log2 (2A/W)] = Index of difficulty (ID) *note this is the equation of a line = linear
...so MT is linearly related to ID
![<ul><li><p>Accuracy held constant (all dots in yellow lines) - had participants perform over and over again until they had 100% accuracy</p></li><li><p>Independent variables (changes): Amplitude (A) and</p></li><li><p>Width (W)</p></li><li><p>Dependent variable (what they measured): Movement time (MT) - how long it took you to move between targets</p></li><li><p>MT ~ A/W - Large amplitude movements to wide targets take the same time as small amplitude movements to narrow targets</p></li><li><p>to get a linear relationship - MT = a + b [Log2 (2A/W)] </p></li><li><p>[Log2 (2A/W)] = Index of difficulty (ID) *note this is the equation of a line = linear</p></li></ul><p>...so MT is linearly related to ID</p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/93f512f0-0040-42b5-a116-09bd0b716a8a.png)
what are independent and dependent variables
Independent variables: The variables an
experimenter changes (manipulates, controls)
Dependent variable: The variables an
experimenter measurers
what happens to MT if you increase target width
it decreases bc velocity increases
what happens to mt if amplitude decreases
it will also decrease
when is MT the lowest
when width of target increases and when amplitude decreases
what does fitts law look like in everyday
space button being so big
x’s on ads being so small or hard to see
what general law does fitts law represent
• General law of motor behaviour e.g. underwater, in space, in the lab, children, adults, fingers, hands, arms
• Extended to discrete movements (not just tapping task)
what are the two main effects for the linear speed-accuracy trade off
Two main effects:
1) For a given rapid MT, as A increases, We increases
2) As MT decreases, We (effective target width) increases
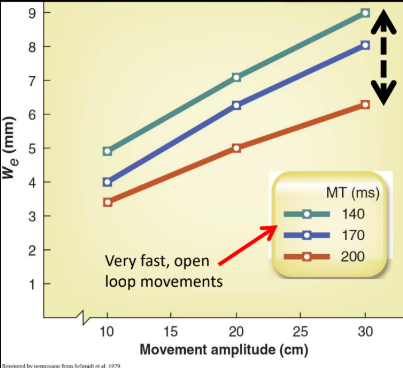
compare the linear speed accuracy trade off and fitts law
Variability ~ Velocity = We ~ A/MT
Not identical to Fitt’s Law (logarithmic vs. linear) but both open (very rapid) and closed (slower) control show speed accuracy tradeoff
what are the sources of error in very rapid movements
Every connection (synapse) is an analog process, susceptible to transient factors (e.g. amount of receptors / transmitter) Therefore, each connection can introduce error (noise)
...and, in general, when we produce more force (up to about 70% of max), we introduce more noise (variability)
what are some exceptions to the speed-accuracy trade off
max force - movements at around 70% of max force become less variable, slide 34
Movement timing :
Spatial accuracy: Accuracy of rapid movements for which the spatial position of the movement’s endpoint is important to task performance.
Timing accuracy: Accuracy of rapid movements for which the accuracy of the movement time is important to task performance.

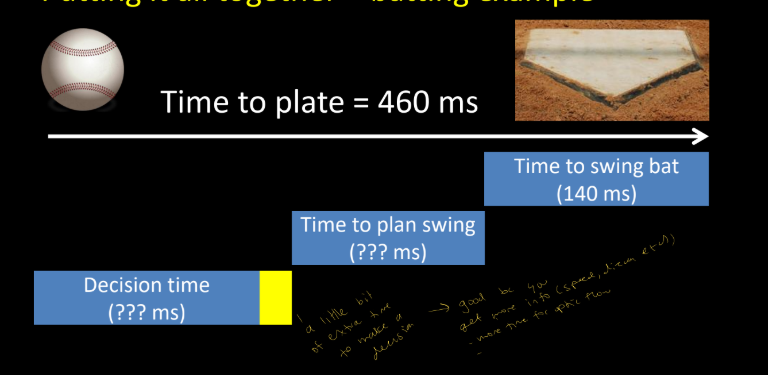
use the batting example to put it all together
Assumptions: - slide 40 - 51
- Average pitch takes ~460 ms to get to home plate
- Average swing takes ~160 ms to contact ball
1) Extra 20 ms of visual information = 3ft of extra ball flight = better prediction
2) A shorter swing means better timing accuracy for initiation and production
3) Assuming that the fast swing is close to the fastest (i.e. max force) it would be more spatially accurate
4) More force = harder hit