Macromolecules - Biological Systems Lecture 1.3
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary terms and concepts related to biological macromolecules as discussed in the lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Polymer
A substance that has a molecular structure built up from a large number of similar units bonded together.
Carbohydrates
Large biological molecules that are a source of energy and provide structural support.
Nucleic Acids
Molecules that store genetic information and function in gene expression.
Proteins
Polymers made of amino acids that have a wide range of functions including catalyzing reactions and transporting substances.
Lipids
A diverse group of molecules that are not true polymers and are hydrophobic; include fats, phospholipids, and steroids.
Dehydration reaction
A process that synthesizes a polymer by removing a water molecule while forming a new bond.
Hydrolysis
A process that breaks down a polymer by adding a water molecule to break a bond.
Monosaccharides
The simplest form of carbohydrates, typically with the molecular formula that is a multiple of CH2O.
Nucleotide
The building block of nucleic acids, composed of a phosphate group, sugar, and nitrogenous base.
Fats
A glycerol molecule joined to three fatty acids
Phospholipids
A glycerol molecule joined to two fatty acids, third hydroxyl is joined to a phosphate group
Steroids
Carbon skeleton consists of four fused rings
_________________ usually have molecular formulas that are some multiple of the unit CH2O
Monosaccharides
Types of polysaccharides
Storage polysaccharides, Structural polysaccharides
Is lipid a true polymer
No
Lipids consists mostly of….
Hydrocarbon regions with relatively non-polar C-H bonds
Lipids like water
False
Type of lipids
Fats, phospholipids, and steroids
What is the difference between phospholipids and fats?
Fats store energy, phospholipids form membranes
DNA full name
Deoxyribonucleic acid
DNA
Encodes all information needed to create life’s diversity
RNA full name
Ribonucleic acid
RNA
Has several roles, but most basic is to deliver information from DNA to sites of protein synthesis
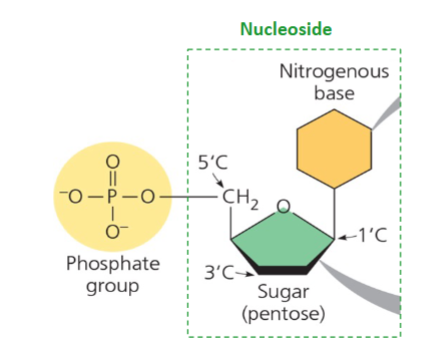
Name the structure
Nucleotide structure
Bases for DNA
Cytosine, Adenine, Thymine, Guanine
Bases for RNA
Cytosine, Adenine, Uracil, Guanine
Parts of the nucleotide structure (middle to outside)
Phosphate group, sugar (pentose), nitrogenous base
Base pairs (DNA)
Adenine paired with Thymine
Cytosine paired with Guanine.
Outside of DNA
Phosphate-sugar backbone
Inside of DNA
Nitrogenous bases
Base pairs (RNA)
Uracil paired with Adenine
Cytosine paired with Guanine.
If we have 30% adenine in a strand of DNA, what is the % of guanine?
30%
DNA strand direction
5’ to 3’
If the DNA strand is 5’ to 3’, what is the complementary stand
3’ to 5’
Antiparallel
Two complementary strands run in opposite directions
What is the matching strand
3’ A A T G 5’
The genetic code
DNA carries hereditary information
Linear order of bases in a gene
Amino acid sequence of a protein, protein structure, protein function
Sequence of bases along DNA (and RNA) are the same for each gene
False
Sequence of bases along DNA (and RNA) is unique for each gene
Steps of DNA replication
Double helix unravels
Free bases bond complementary bases on original template strands
Polymerisation connects the bases together forming two new daughter strands
RNA exists as a ___________
single strand
RNA occurs
Between two RNA molecules or between two stretches of same RNA molecule
Role of DNA
Serves as a template for RNA synthesis
Role of RNA
Copies the message of DNA and transports it to site of protein production: mRNA
mRNA
Linear, and carries message from DNA to protein assembly site
Protein assembly site
Ribosome, a complex protein made up of r(RNA) and proteins, accepts and the mRNA and produces the protein, with the help of tRNA
tRNA
Translate gene language into amino acid sequence
Ribozymes
RNA capable of performing biological function
Peptide bond
A bond between two amino acids
Polypeptide
A chain of amino acids
Protein
Made up one or more polypeptides
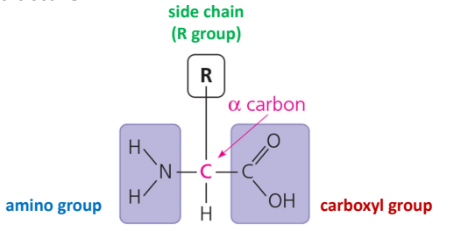
Name the structure
Typical AA structure
The AA alphabet
Specific properties of AA affect protein tertiary structure
Four levels of protein structure
Primary structure
Secondary structure
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
Primary structure
Linear polypeptide chain
Secondary structure
Alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheets (due to hydrogen bonds)
Tertiary structure
Main 3D shape, formed by interactions between side chains
Quaternary structure
Interaction between protein sub units
Examples of the linear sequence of AA
Transthyretin, a transport protein
Segments of the polypeptide chain form coiled or folded patterns due to _________ within the peptide backbone
Hydrogen bonding
Hydrophobic interactions
Away from water and towards each other
Protein denaturation
Structure depends on environmental conditions (pH, salt concentration, temperature)
Protein denaturation (extreme conditions)
Weak chemical bonds can break leading to unravelling of protein
Loss of structure (Protein denaturation)
Loss of function