Strayer 12
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
European Economic Community (EEC)
Reduced tariffs and developed common trade policies.

Marshall Plan
A plan that the US came up with to revive war-torn economies of Europe. This plan offered $13 billion in aid to western and Southern Europe.

National Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
an association of European and North American countries, formed in 1949 for the defense of Europe and the North Atlantic against the perceived threat of Soviet aggression. By 2005, the alliance consisted of 26 countries, including several eastern European nations. NATO's purpose is to safeguard member countries by political and military means.

Soviet Union Recovery
Utilized convict laborers and looting from war to rebuild

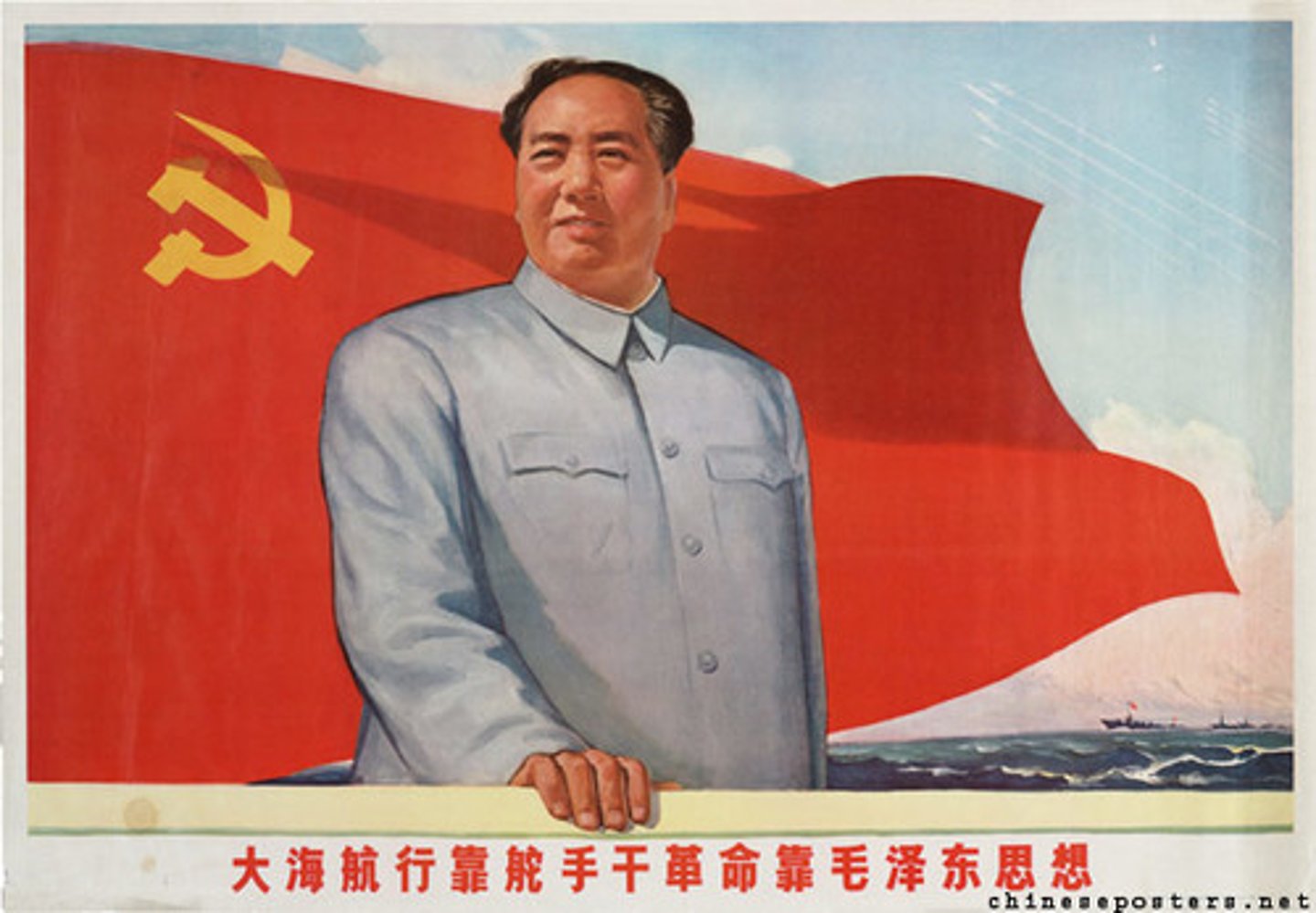
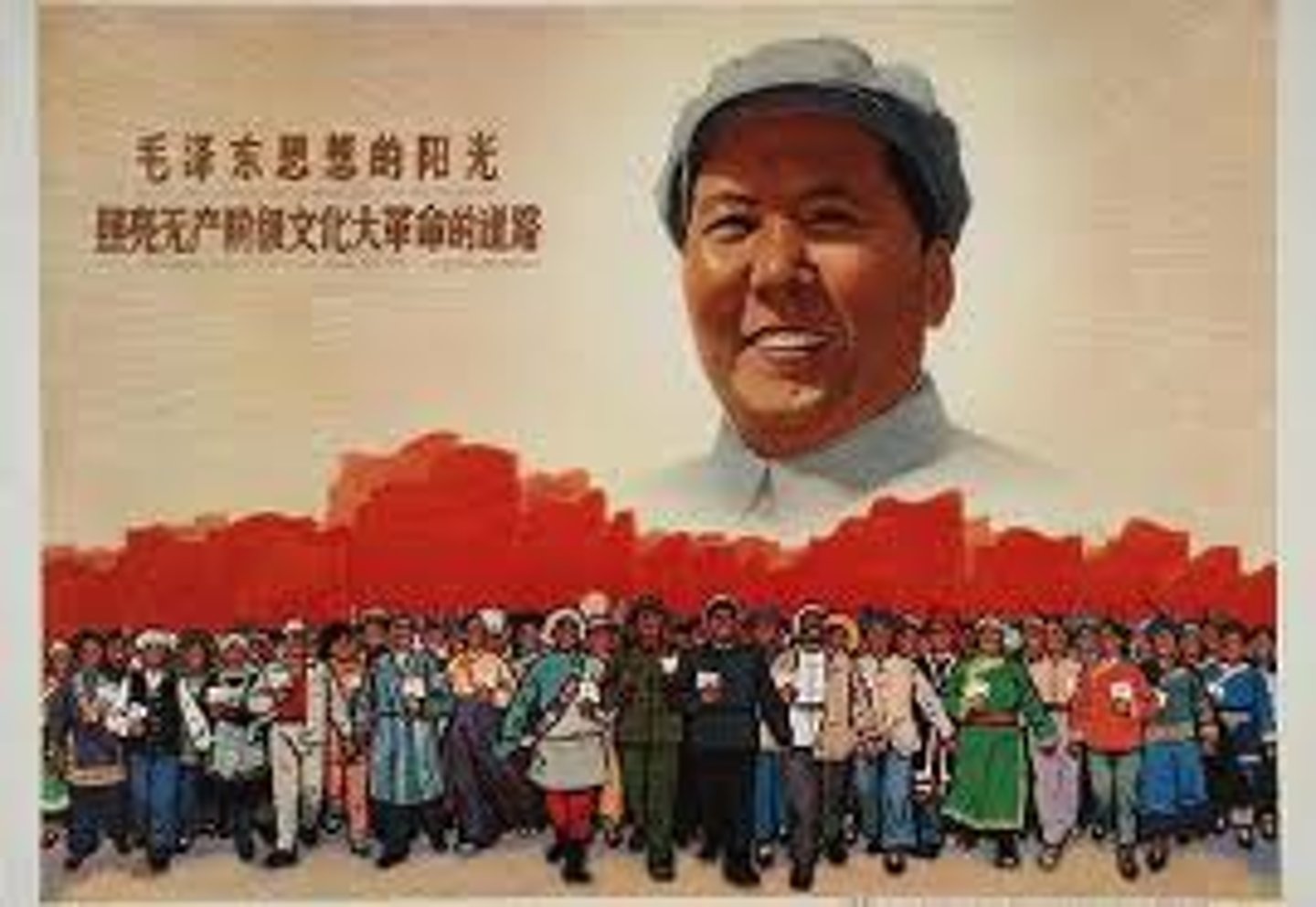
Mao Zedong
(1893-1976) Leader of the Communist Party in China that overthrew Jiang Jieshi and the Nationalists. Established China as the People's Republic of China and ruled from 1949 until 1976.

The Great Leap Forward
Started by Mao Zedong, combined collective farms into People's Communes, failed because there was no incentive to work harder, ended after 2 years.

Cultural Revolution
(1966-1976) Political policy in started in China by Mao Zedong to eliminate his rivals and train a new generation in the revolutionary spirit that created communist China. The Cultural Revolution resulted in beatings, terror, mass jailings, and the deaths of thousands.

Cold War
Tension between US and Soviet Union post-WWII.
Red Guards
the Radical youth of the Cultural Revolution in China starting in 1966. Often wore red armbands and carried Mao's Little Red Book. Mobilized to purge capitalist elements.

Warsaw Pact
An alliance between the Soviet Union and other Eastern European nations. This was in response to the NATO
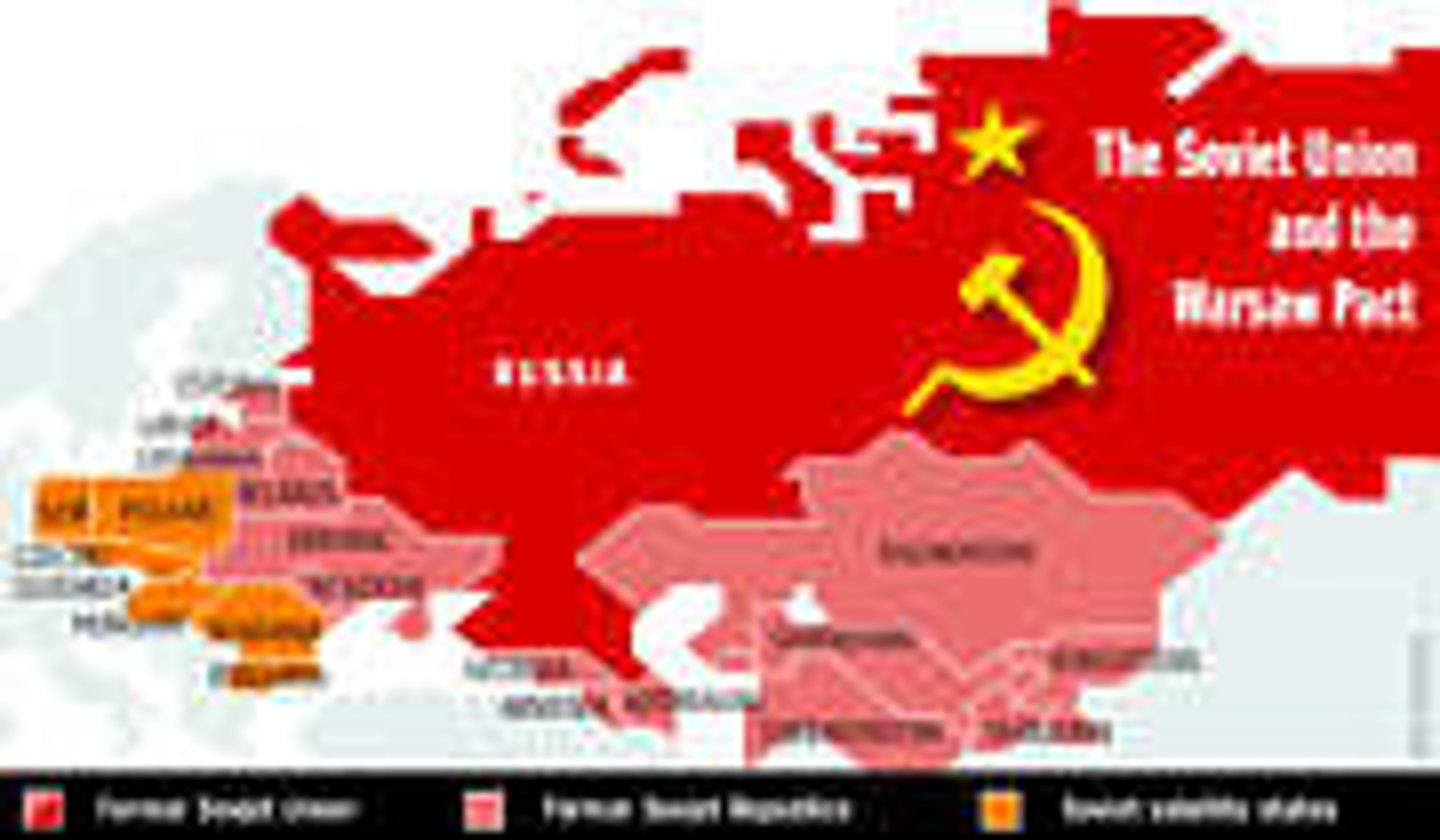
The Iron Curtain
A political barrier that isolated the peoples of Eastern Europe after WWII, restricting their ability to travel outside the region

Proxy Wars
During the Cold War, local or regional wars in which the superpowers armed, trained, and financed the combatants.

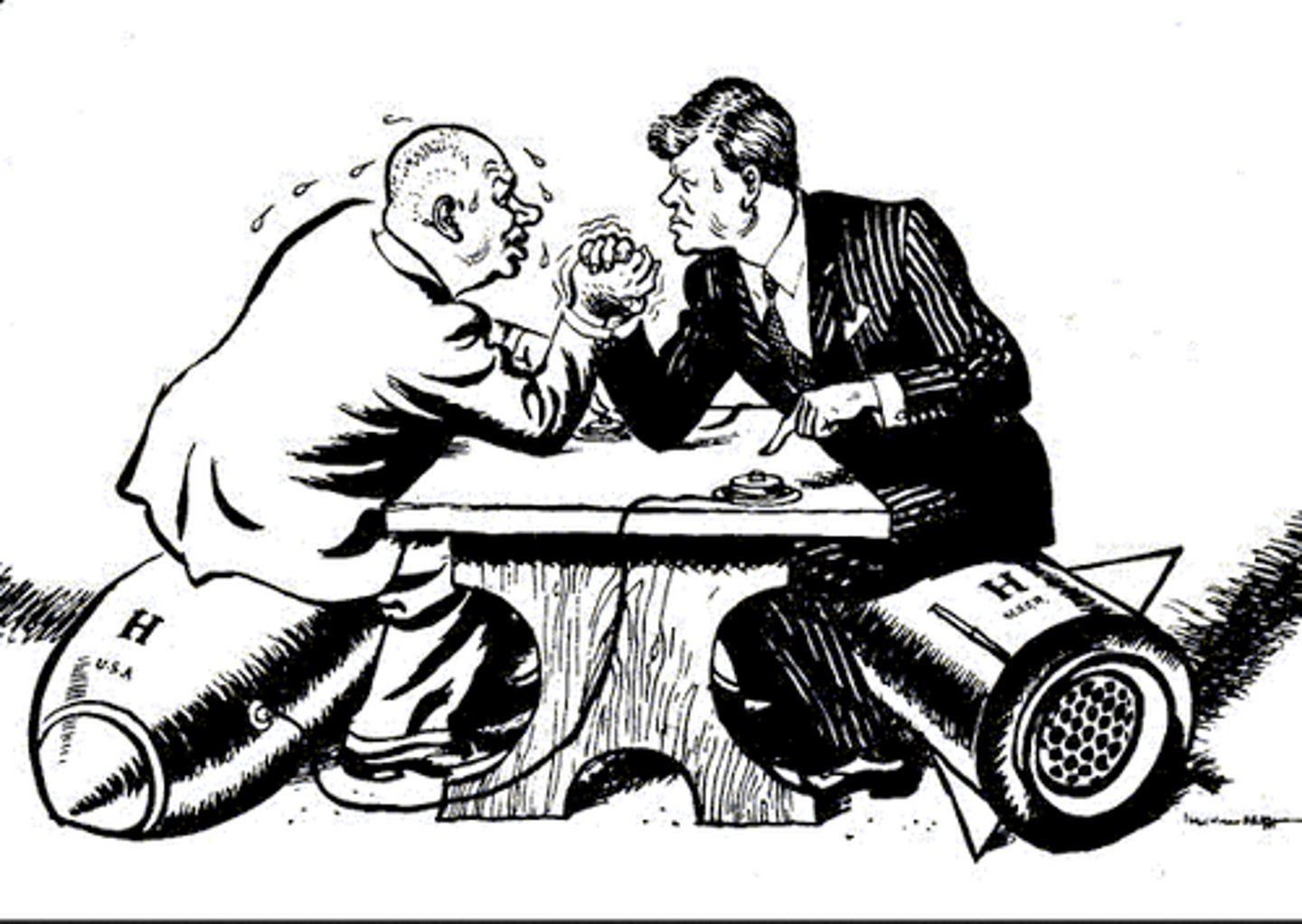
Cuban Missile Crisis
1962 crisis that arose between the United States and the Soviet Union over a Soviet attempt to deploy nuclear missiles in Cuba 13-day standoff

Afghan Mujahideen
Islamic "holy warriors". Soviets fought against them in Soviet-Afghanistan war. Mujahideen gained control, aided by US, Saudi Arabia, Pakistan, Iran and China. US gave them Stinger missiles when it supported them against USSR...
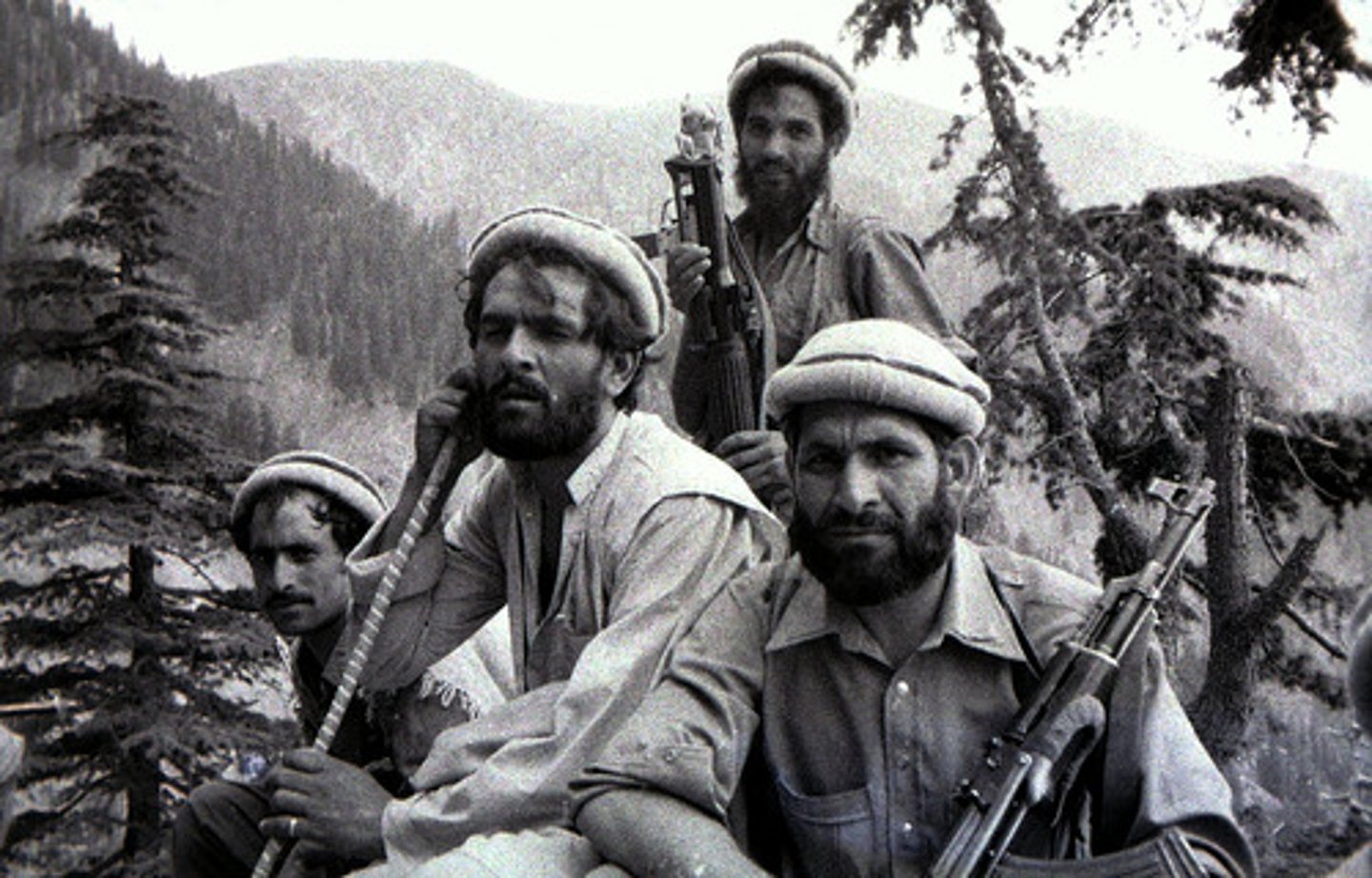

Decolonization
The collapse of colonial empires. Between 1947 and 1962, practically all former colonies in Asia and Africa gained independence.
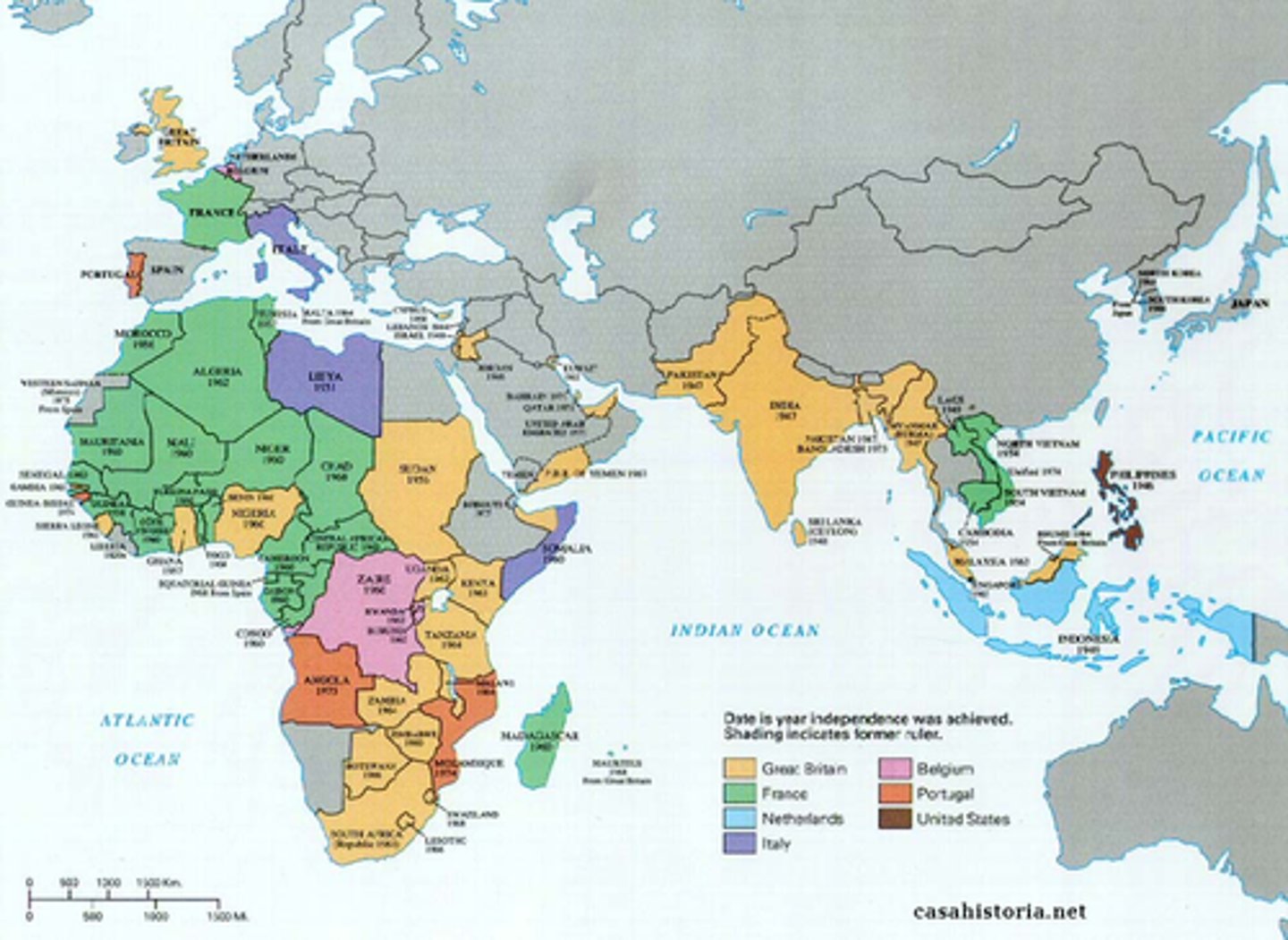
Nationalism
Ideology promoting independence and self-determination.
Indian National Congress
A movement and political party founded in 1885 to demand greater Indian participation in government. Its membership was middle class, and its demands were modest until World War I. Led after 1920 by Mohandas K. Gandhi, appealing to the poor. Lead India's independence movement.

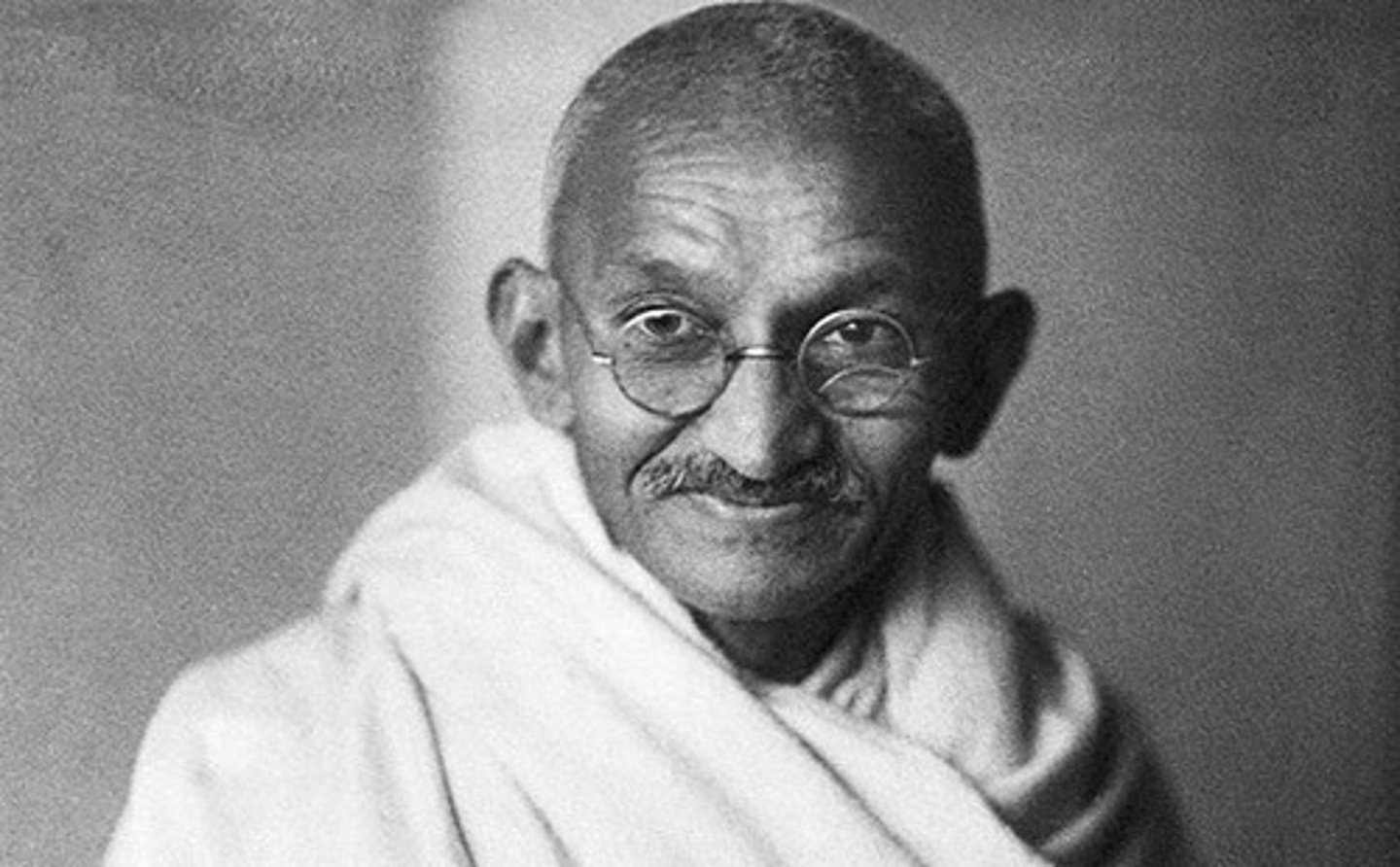
Mohandas Gandhi
Leader of the Indian independence movement and advocate of nonviolent resistance. After being educated as a lawyer in England, he returned to India and became leader of the Indian National Congress in 1920.

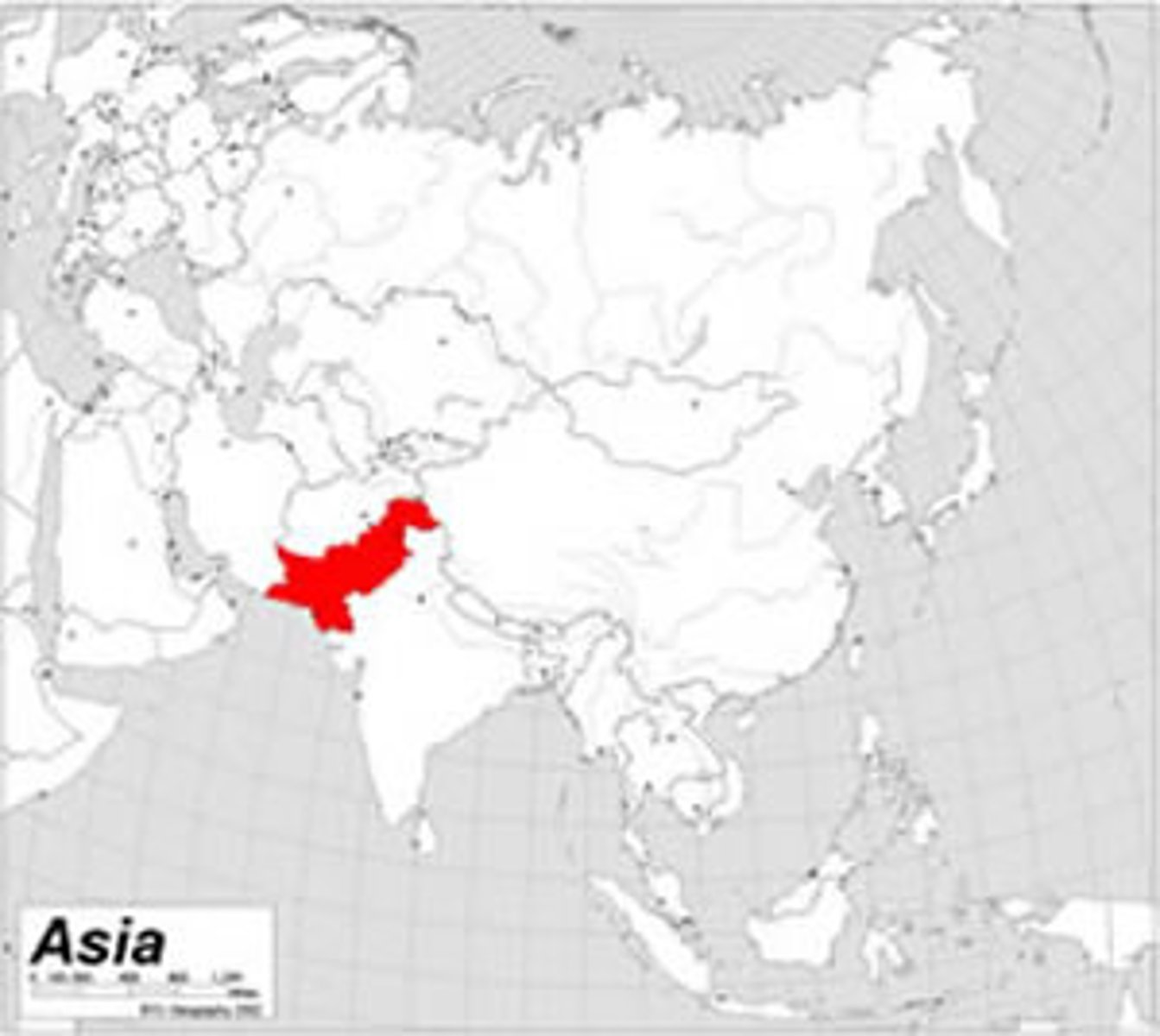
Muslim League
an organization formed in 1906 to protect the interests of India's Muslims, which later proposed that India be divided into separate Muslim and Hindu nations (Pakistan and India)

Pakistan
Created as a separate state for Muslims in 1947. Means pure state
Apartheid
System of institutionalized racial segregation in South Africa.

Nation Building
Efforts to establish a new political order post-independence.

Multiparty Democracy
Political system with multiple political parties competing.

Vampire States
Critique of corrupt African governments by critics.
Hugo Chavez
Venezuelan leader known for socialist policies. An example of authoritarian government in modern day

Vladimir Putin
Current Russian leader with authoritarian governance.

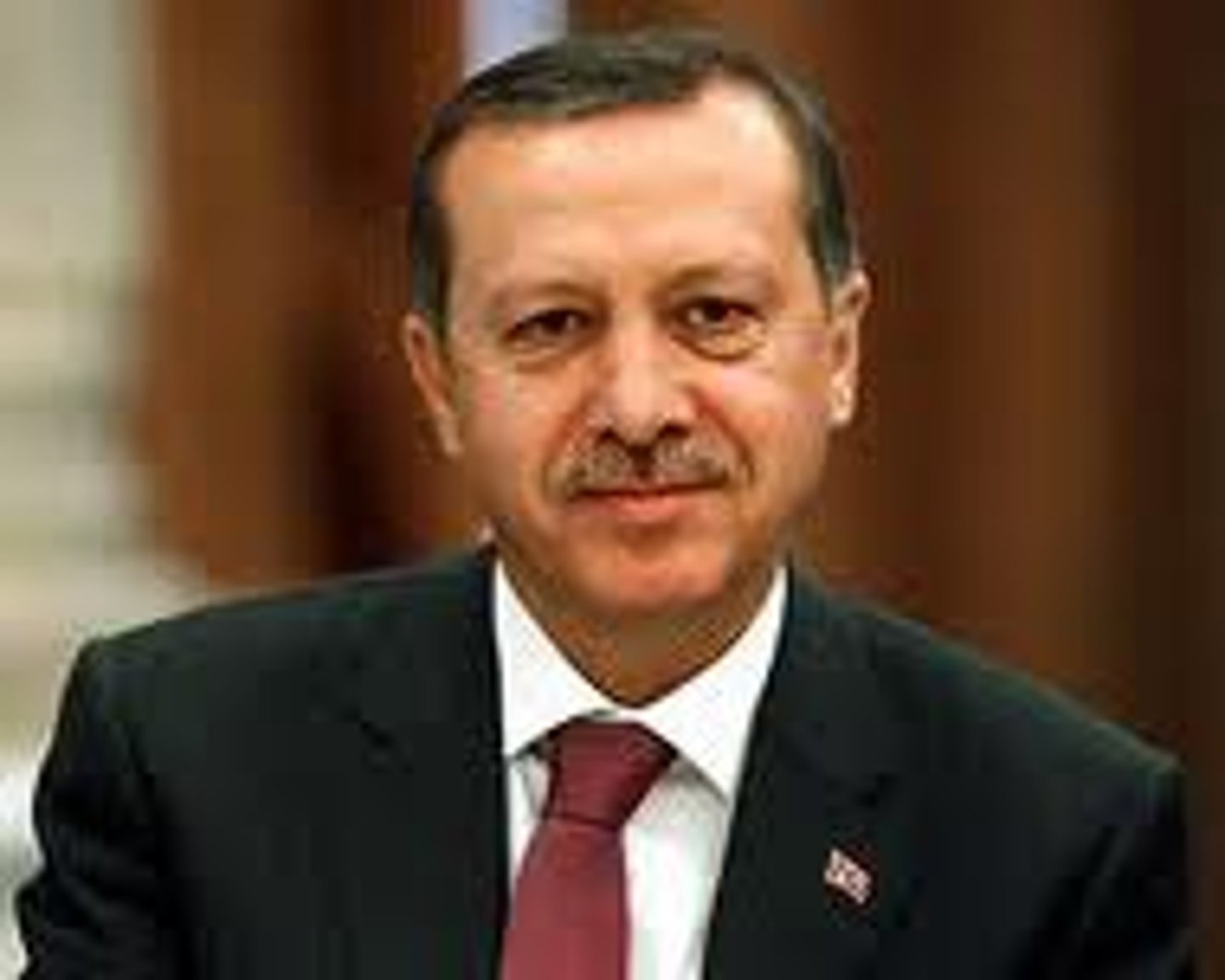
Recep Erdogan
Turkish president with increasing authoritarian control.
