Chemistry unit 3 - Physical Chemistry
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 19 - Energetics, Ch 20 - Rates of reactions Ch 30 - reversible reactions and equilibria pg 207 - 253
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is an exothermic reaction?
A reaction that gives out heat to the surroundings so their temperature increases
Give examples of exothermic reactions
Reacting metals with acids to form salts (salt preparations)
Neutralisation reactions
Displacement reactions
Combustion reactions
Write the chemical equation of the reaction of a metal with an acid of Zinc and Hydrochloric acid
Zinc + Hydrochloric acid → Zinc chloride + Hydrogen gas
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Write the chemical equation of the neutralisation reaction
NaOH(s) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(s) + H2O(l)
Sodium Hydroxide + Dilute Hydrochloric acid → Sodium Chloride + Water
Give an example of a displacement reaction
2Al(s) + Fe2O3 (s) → Al2O3(s) + 2Fe(l)
Aluminium + Iron oxide → aluminium oxide + iron
What is Enthalapy change?
The amount of heat taken in or released to make or break bonds, it is measured in kJ/mol
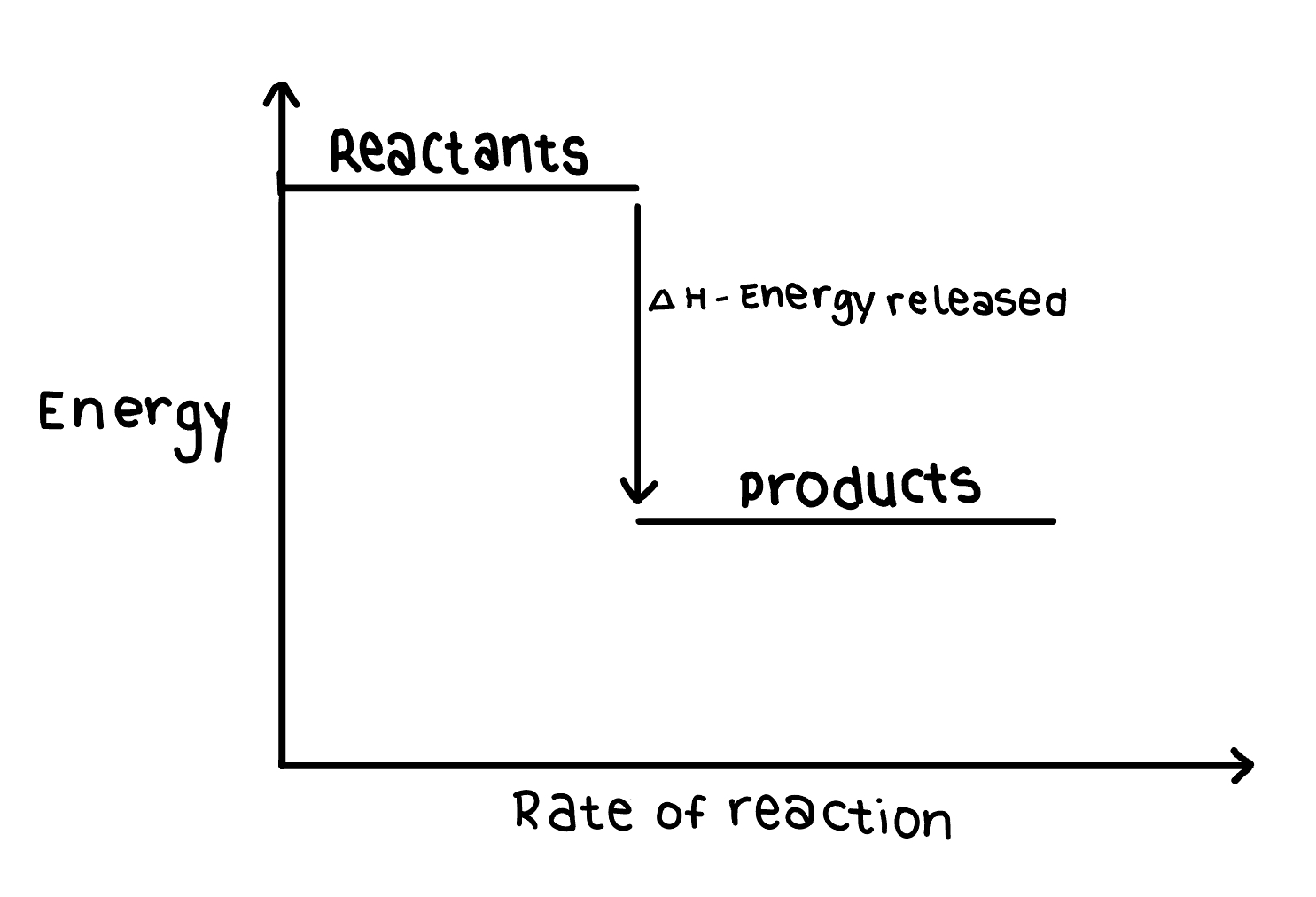
What does the Enthalapy change of an exothermic reaction look like?
The Enthalapy change itself is negative because the reactants are losing energy (you always look at it from the perspective of the reactants)
The energy of the reactants is higher than that of the products
What is an endothermic reaction?
A reaction that absorbs heat from the surroundings so the temperature of the surroundings decreases
What are some examples of endothermic reactions?
Thermal decomposition
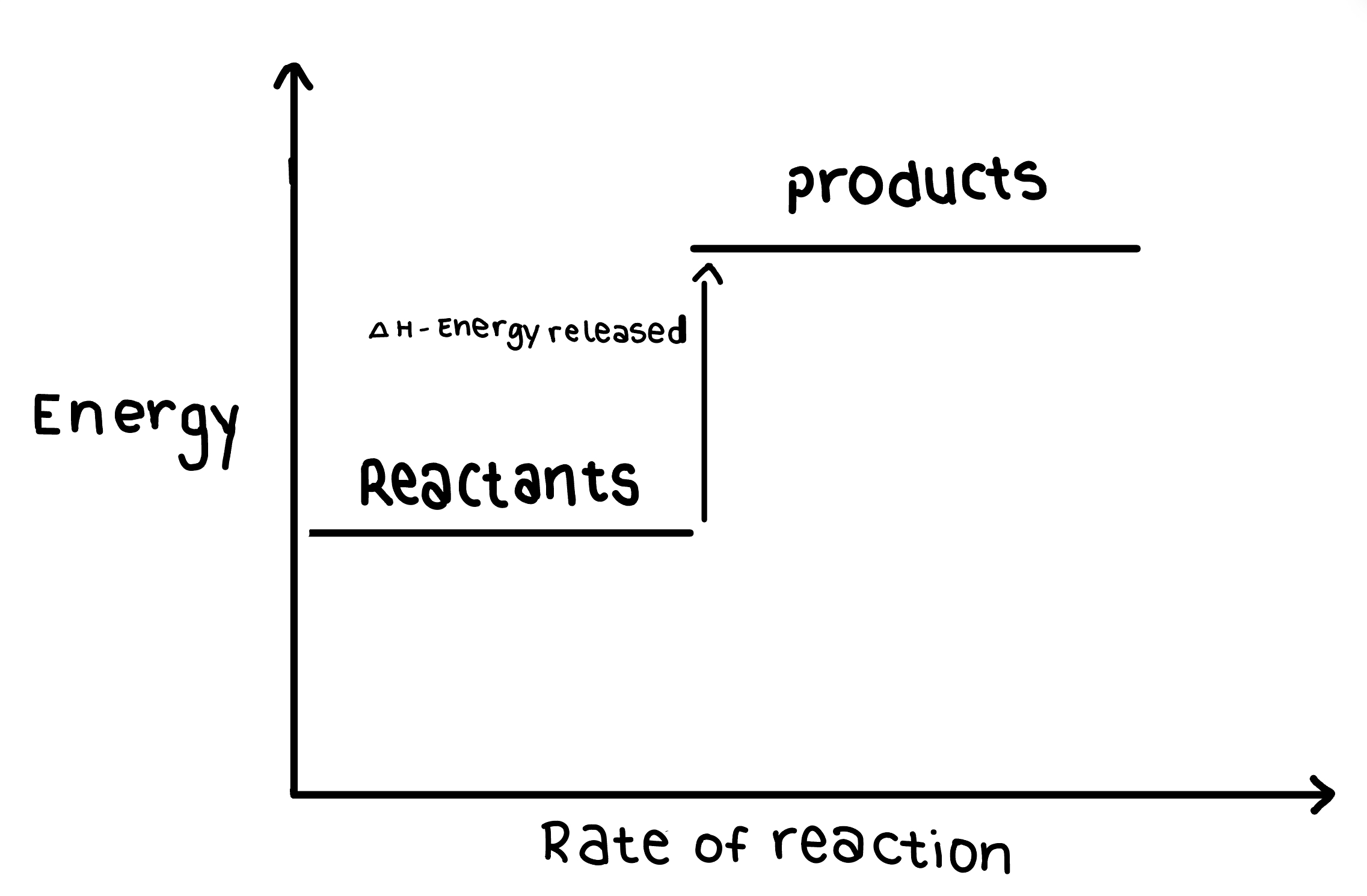
Describe the Enthalapy change in an endothermic reaction
The energy of the reactants is lower than that of the products
The Enthalapy change is positive
What is the specific heat capacity?
The amount of heat needed to realise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1oC
What’s the formula for specific heat capacity
Q = mcΔT
What is a calorimetry experiment
An experiment used to determine the amount of energy released by a fuel
How can you measure the amount of heat given off when alcohols are burnt
Measure 100cm3 of cold water in a measuring cylinder
Add the water to a copper can
Measure the initial temperature of the water using a thermometer
Weigh the spirit burner with a lid on to prevent the alcohol from evaporating use a balance to measure the weight
Light the wick and place it under the copper can
Add an insulating card to prevent heat loss
Use shielding to prevent draught
Ensure a constant supply of oxygen is provided to prevent incomplete combustion
Leave the water until the temperature rises a reasonable amount, stir and then measure the maximum temperature reached
Weigh the spirit burner again with the lid on
Substitute into Q = mcΔT
Repeat experiment for accurate results
Safety precaution:
Wear eye protection
Do not carry a lit spirit burner again
Do not fill a spirit burner when there is a naked flame nearby
Sources of error:
Incomplete combustion
Heat loss
What is the formula for Enthalapy change
ΔH = q/n
Enthalpy change = Heat energy released/ number of moles
Describe how to conduct the Enthalpy change of a displacement reaction
Place a polystyrene cup in a glass beaker
Measure 50 cm3 of 0.200 mol/dm3 of copper (II) sulfate solution in a measuring cylinder and add it to the calorimeter
Measure the initial temperature of the solution
Add an excess of zinc
Stir the solution
Record the maximum temperature reached
Sub into the equation Q = mcΔT
Sources of error:
We assume the solution has the same density and specific heat capacity of pure water


Describe the practical for measuring enthalpy changes when salts dissolve in water
Place a polyesterne cup in a glass beaker
Add 100cm3 of water in the measuring cylinder and then pour the water into the calorimeter
Record the initial temperature of the water using a thermometer
Measure the mass of the reagent using a balance and add it to the water
Stir the solution vigorously until all the reagent has dissolved
Record the minimum temperature of the reaction
How can we determine if a reagent is in excess or is a limiting factor?
If there are 2 reagents:
The one with more moles reacting is the substance that is in excess
The reagent with less mole reacting is the substance that is the limiting factor
How does the temperature change of water indicate weather a reaction is endothermic or exothermic
In an endothermic reaction, the initial temperature of the water is higher than the final temperature (the temp of the water drops)
In an exothermic reaction, the initial temperature of the water is lower than the final temperature of the water (the temp of the water rises)
Describe the bond energetics in endothermic reactions
Bonds are broken, which is why energy is taken in and the temperature of the surroundings decreases. The internal temperature of the reaction itself increases (energy is taken in)
Describe the bond energetics in an exothermic reaction
Bonds are broken, so energy is given out and the temperature of the surroundings decreases. The internal temperature of the reaction itself decreases (because it gives out some of its energy)
Write the chemical equation of the combustion of methane
Methane + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2+ 2H2O
How can you identify a combustion reaction?
Reactants include oxygen
Carbondioxide and Water is produced
How can you identify a Neutralisation reaction?
Reactants include an alkali (an alkali can be spotted when it has OH that’s Hydroxide, all bases contain Hydroxide ions)
Reactants also include an acid ( an acid can be spotted when it has H in its formula, that’s Hydrogen, all acids contain Hydrogen ions)
The products are a salt and a anion of the alkaline
How can you identify a displacement reaction?
A more reactive element takes the place of the less reactive element