Biology Paper 1 (separate higher)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Eukaryote
Cell with a true nucleus, e.g. an animal cell or plant cell
Prokaryote
Contains no true nucleus, typically uni-cellular, e.g. bacteria
Animal cells
Eukaryotic, contains a cell membrane, cytoplasm, & membrane bound organelles - mitochondria, ribosomes, and a nucleus
Plant cells
Eukaryotic, contains a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vacuole, & membrane bound organelles - mitochondria, ribosomes, chloroplasts, and a nucleus
Bacteria cells
Prokaryotic, uni-cellular, contains a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, & often contains a slime capsule, flagella, and pili, as well as ribosomes. Instead of a nucleus contains circular strands of dna, plasmids
Light microscope
Small microscope, made up of an eye piece lens, objective lens, coarse focus, fine focus, stage, arm, & light source
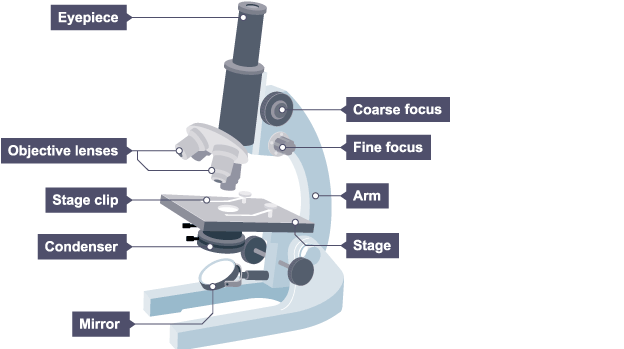
Advantages
Cheap
Portable
Can view live subjects
Disadvantages
Low resolution & magnification
Electron microscope
Two types TEM and SEM, offers high resolution and magnification, allowing for the detailed observation of cellular structures. Works in a vacuum so no live subjects. Can view in 3D.
Very expensive and large & requires training to use (specialist)
Image size =
Actual size × magnification