BIO 300 Summer Class 3.4 Study Guide
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
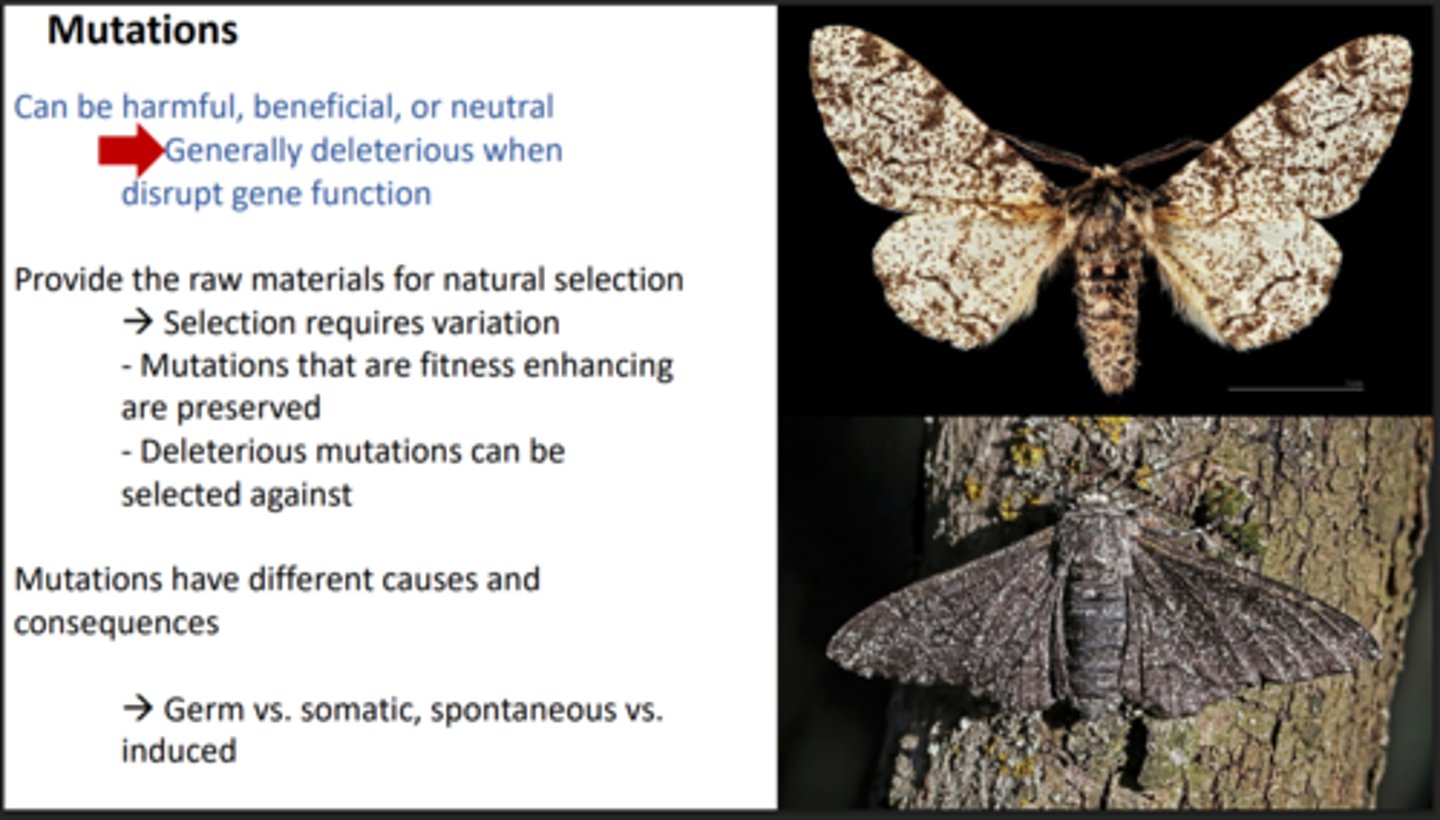
Consequences of Mutations
Harmful, Beneficial, or Neutral. Deleterious when it disrupts gene function.
What does it mean to say that Mutations provide the raw materials for natural selection?
Natural selection requires variation,
A mutation provides this variation.
Beneficial mutations are kept while deleterious mutations are selected against.
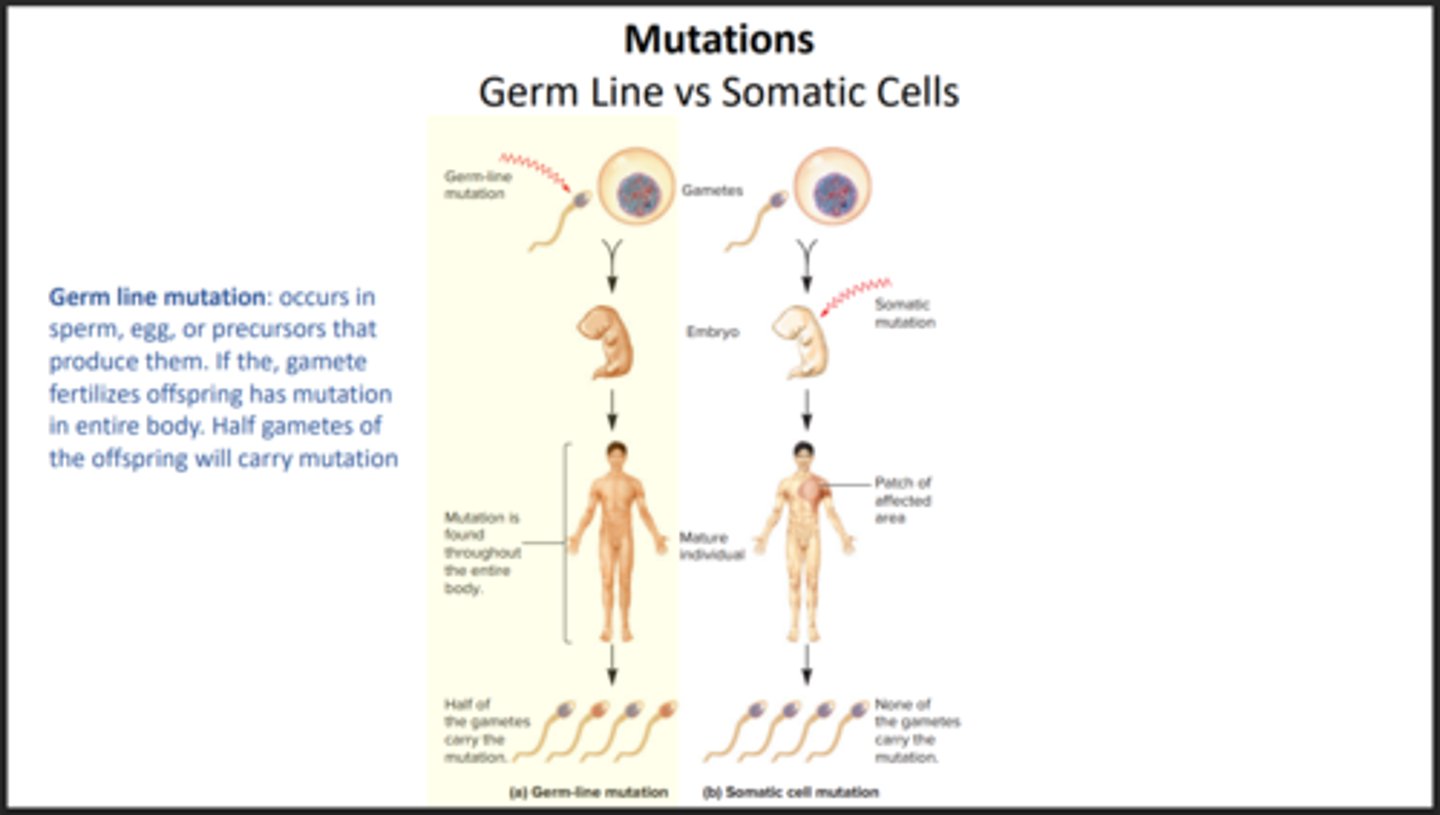
Germ-Line mutation
Mutation that occurs in Sperm/Egg and is able to be passed down onto offspring.
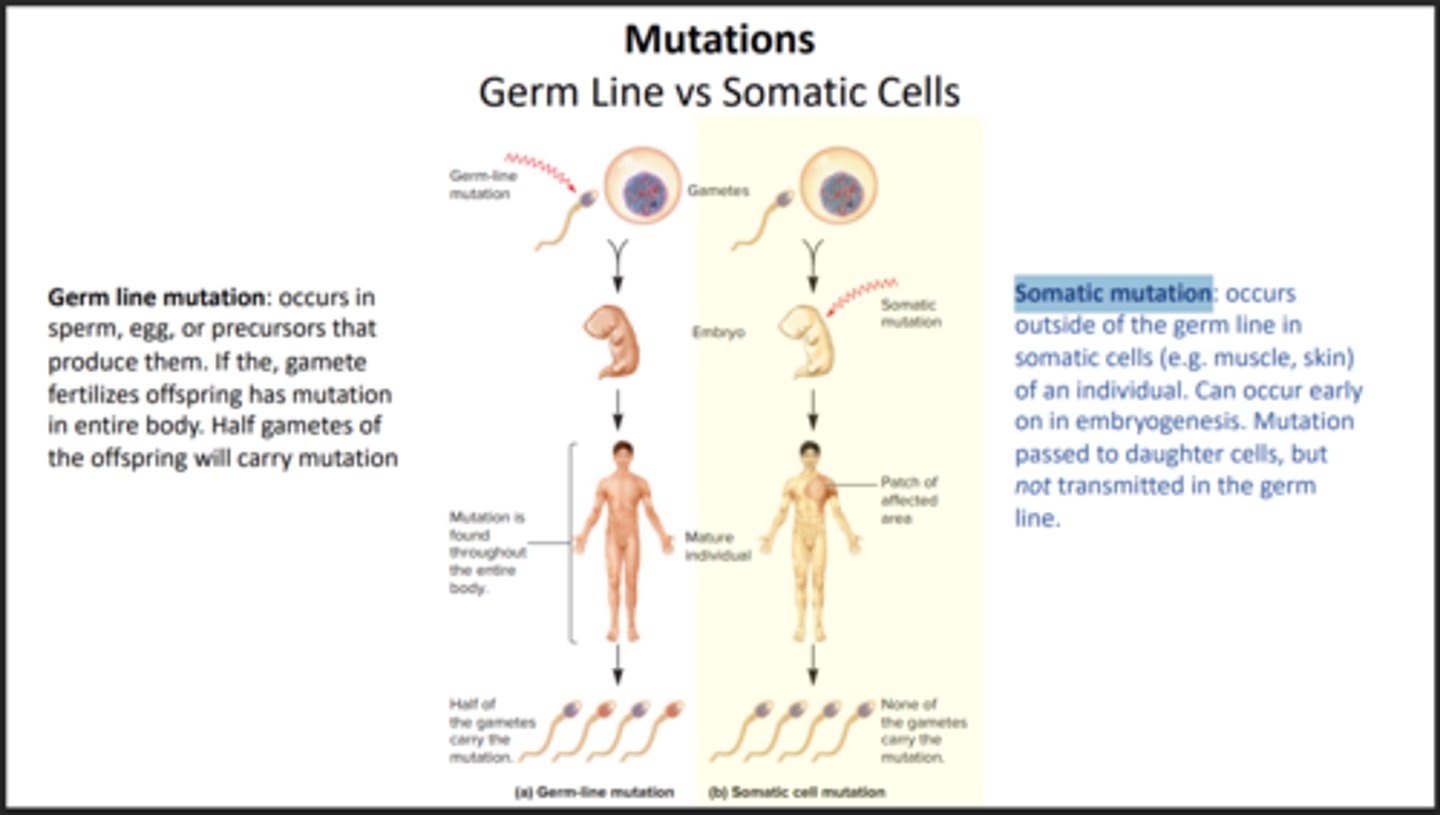
Somatic Mutation
Mutation that occurs in body cells and is not able to be passed down onto offspring
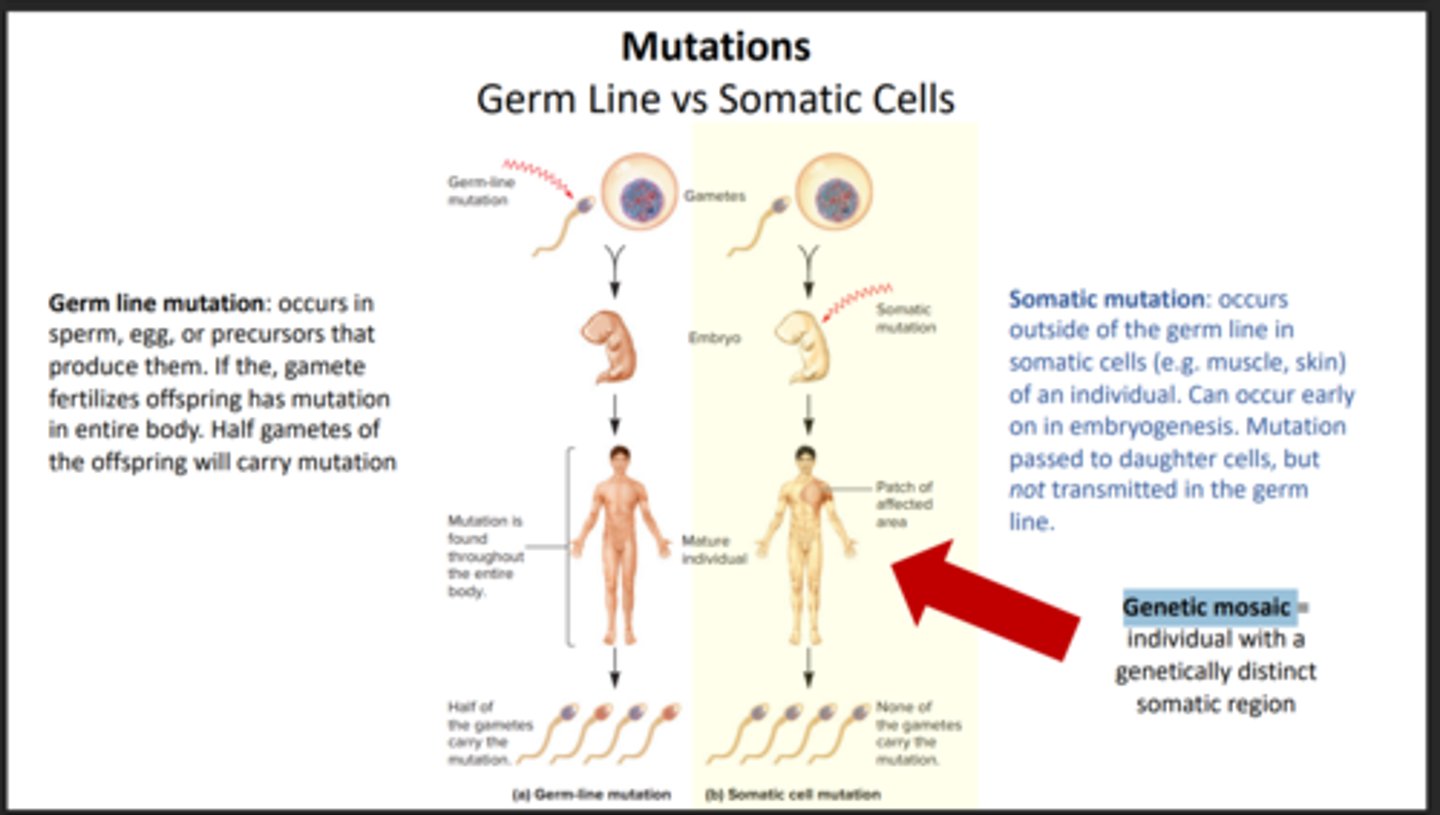
Genetic mosaic
An individual with a genetically distinct somatic region
Classes of mutations
Base pair substitution, removal of bases, addition of bases.

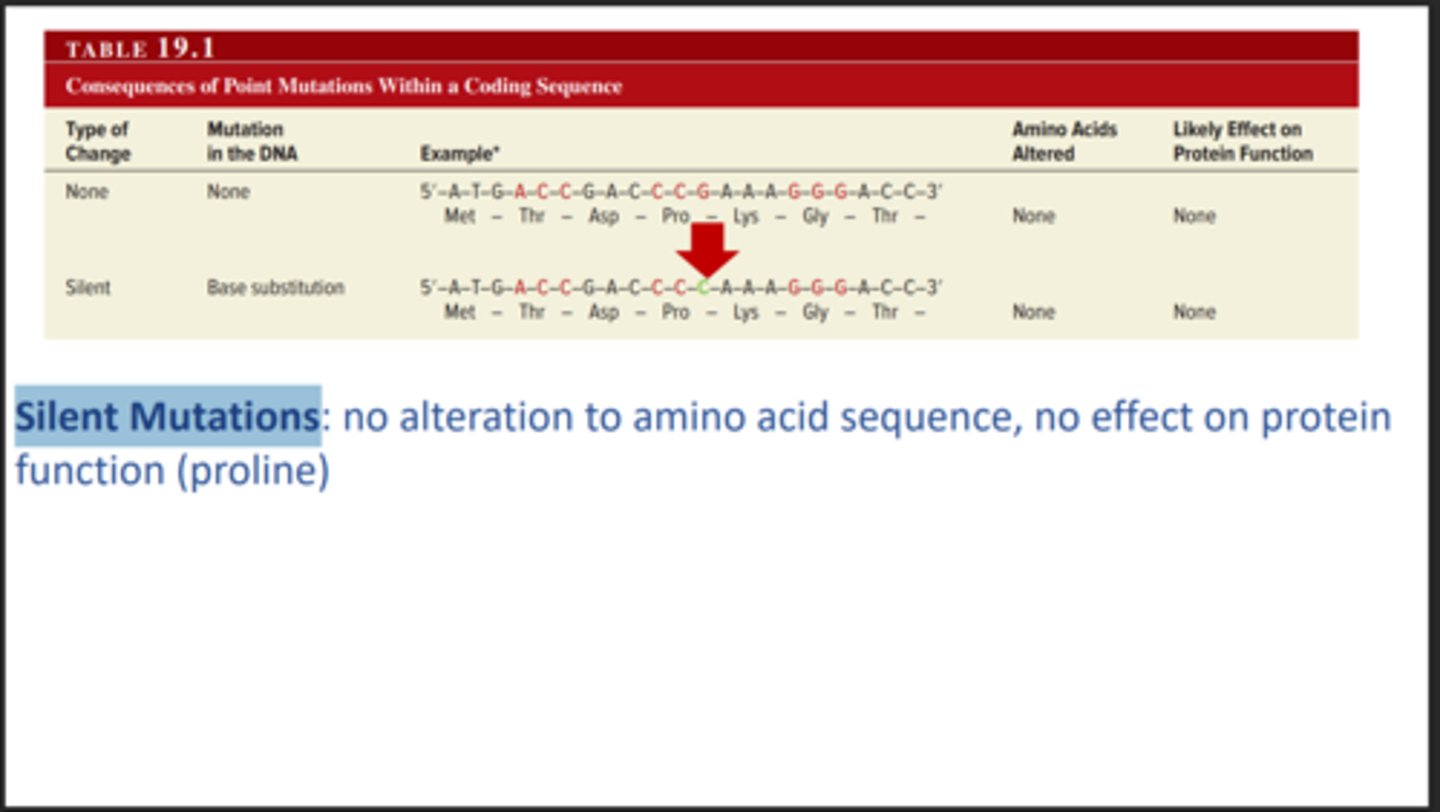
Silent mutation
Amino Acid Sequence doesn’t change. No Effect.
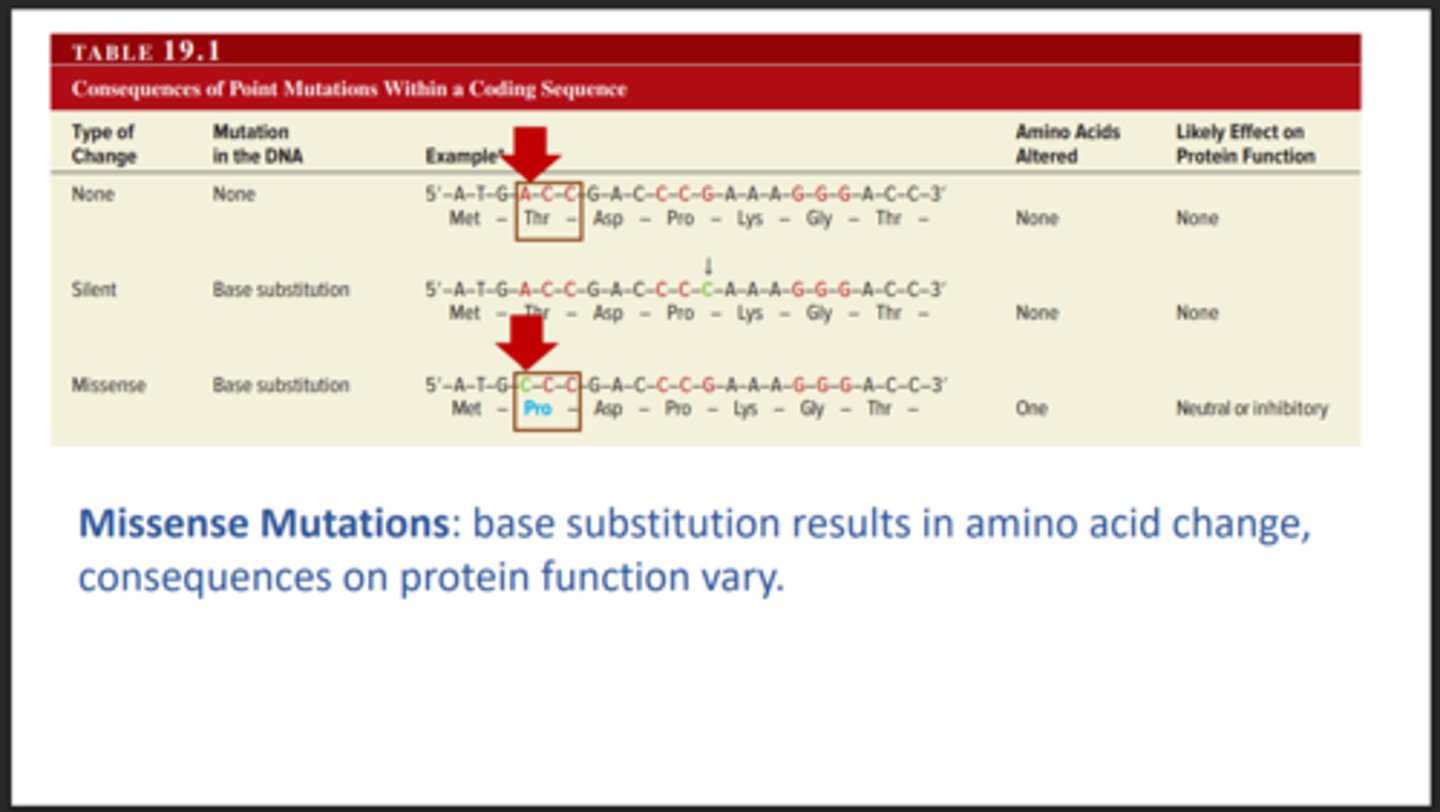
Missense mutation
Changes a single amino acid. This type of mutation can be mild or serious.
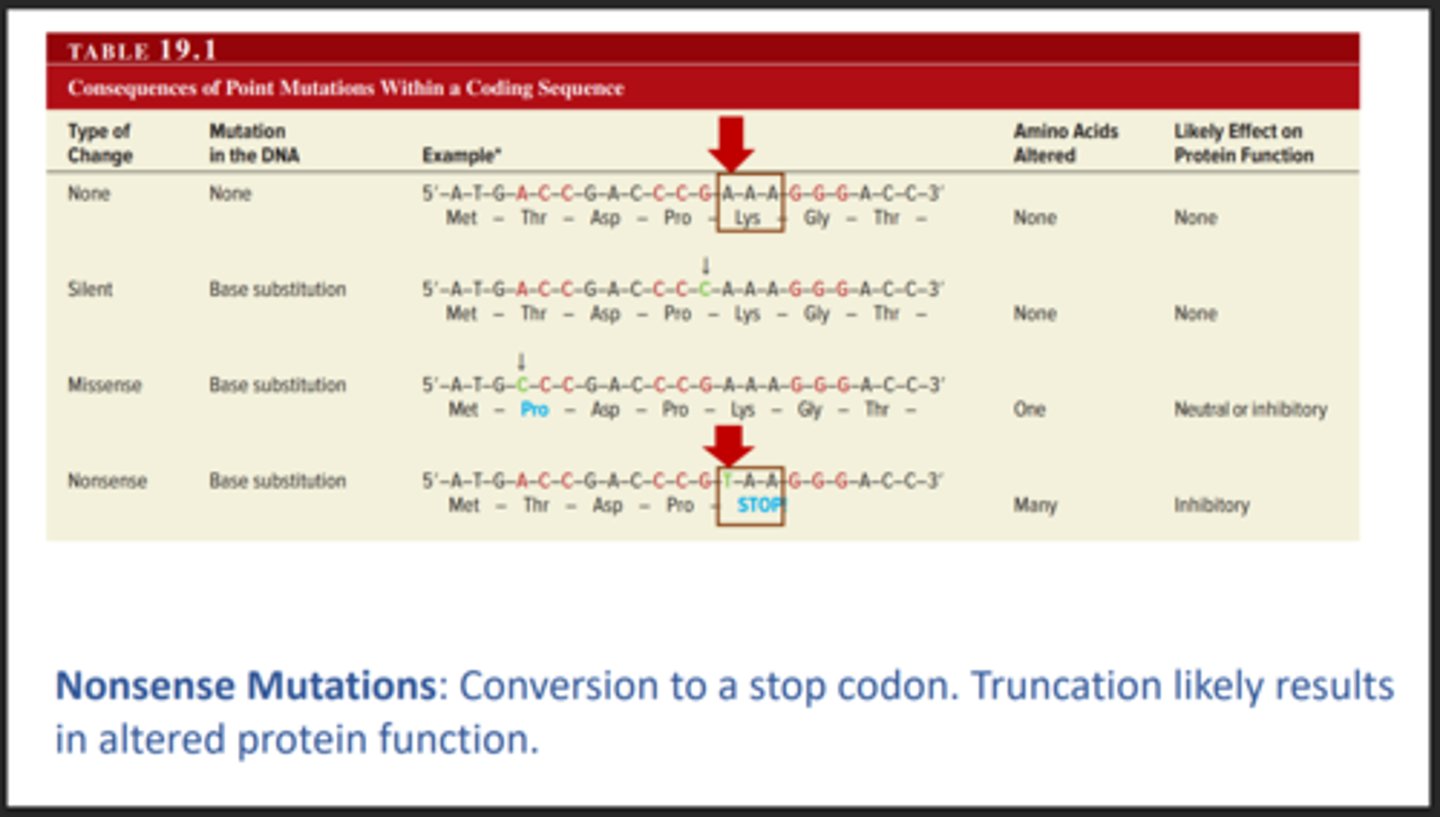
Nonsense mutation
A type of mutation that creates and early stop, this results in the protein being cut off short
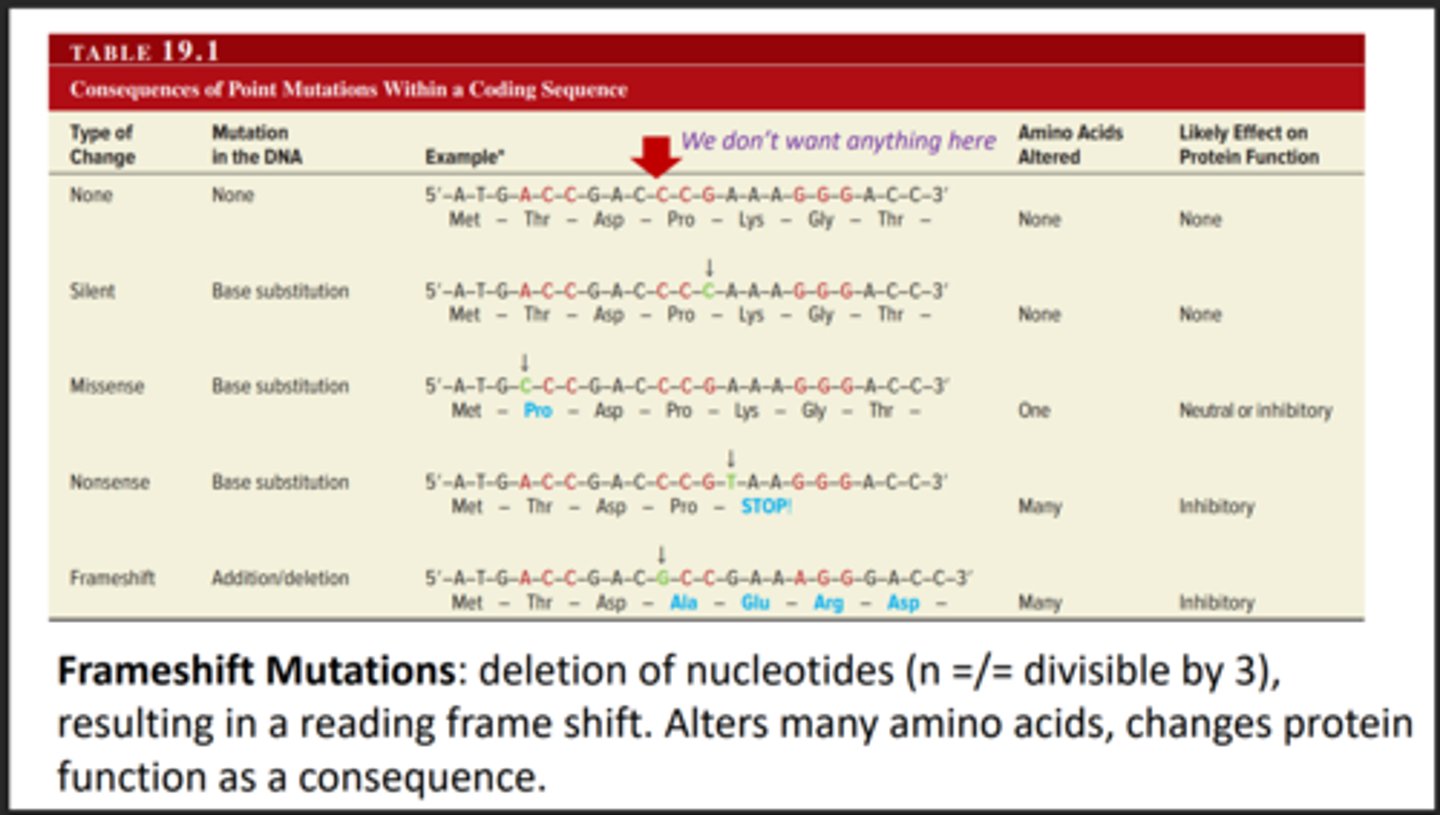
Frameshift mutation
Addition or removal of bases results in the shifting of the reading frame. Changes many AA
Wild type vs mutant allele
Wild type is the most prevalent genotype while a mutation can change a wild type into a mutant allele
Reversion Mutation
Mutant changes back to the normal gene (WT).

Embryonic lethal mutation
Mutations that are deadly for embryos
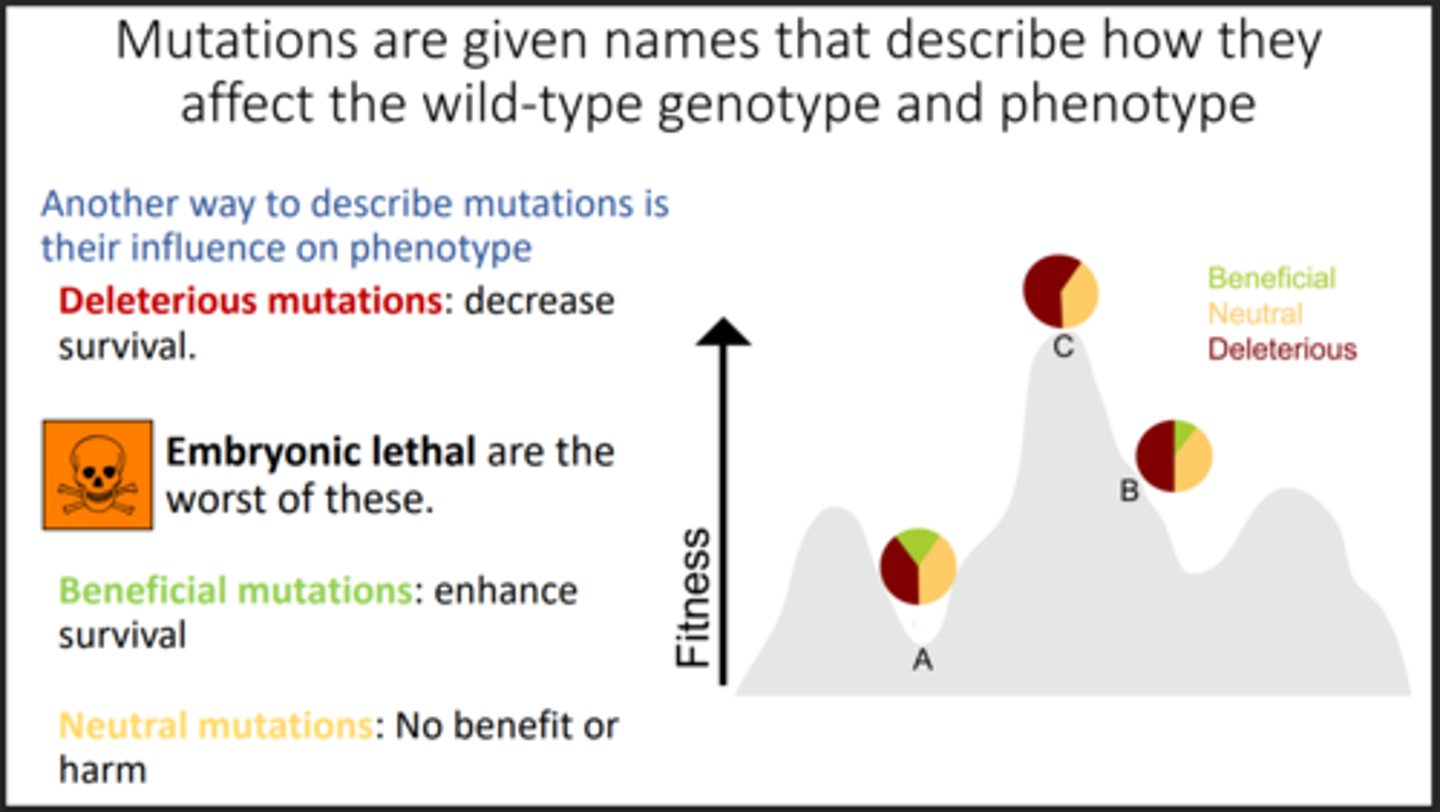
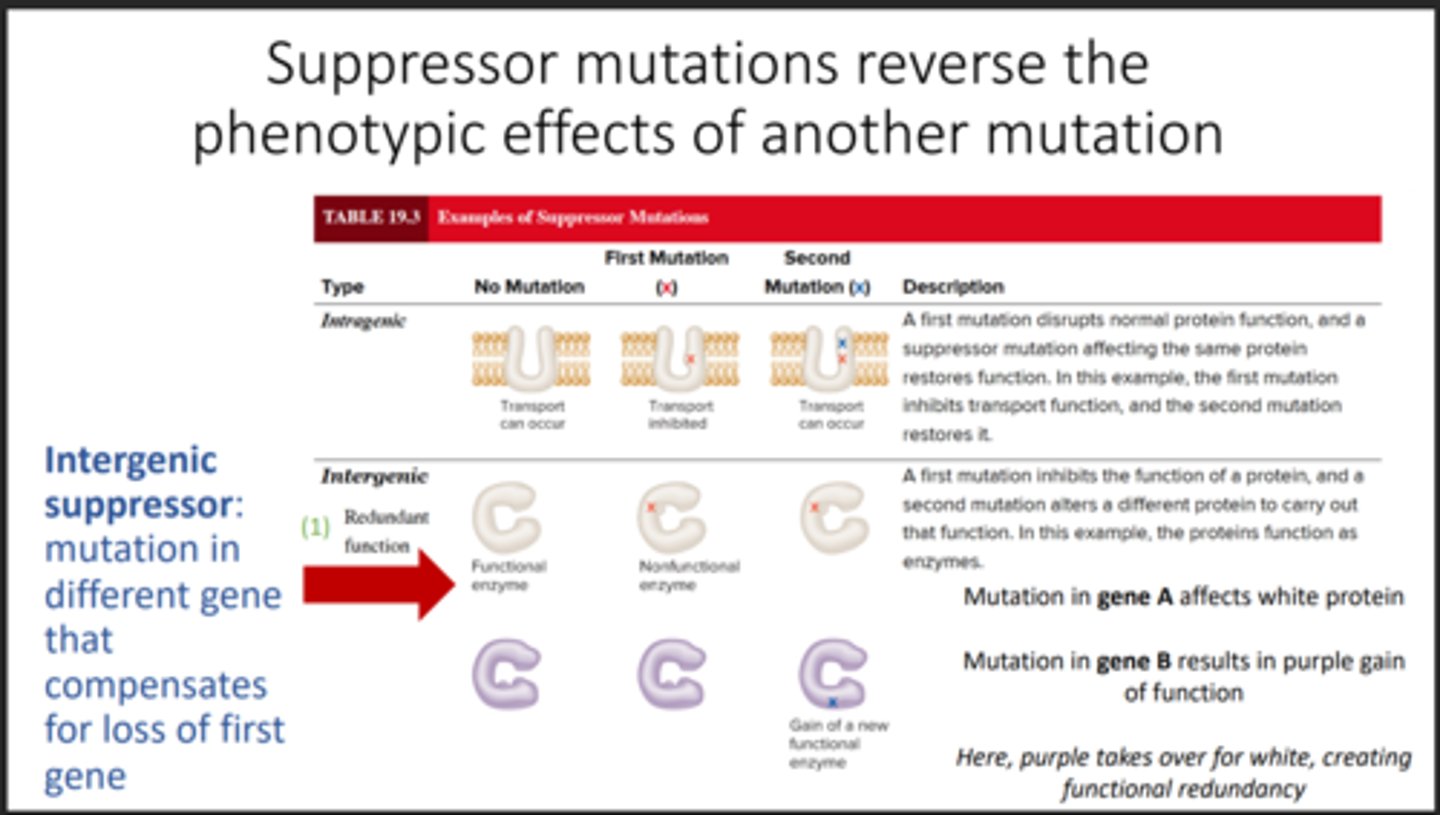
Suppressor mutation
A second mutation that hides the first mutation
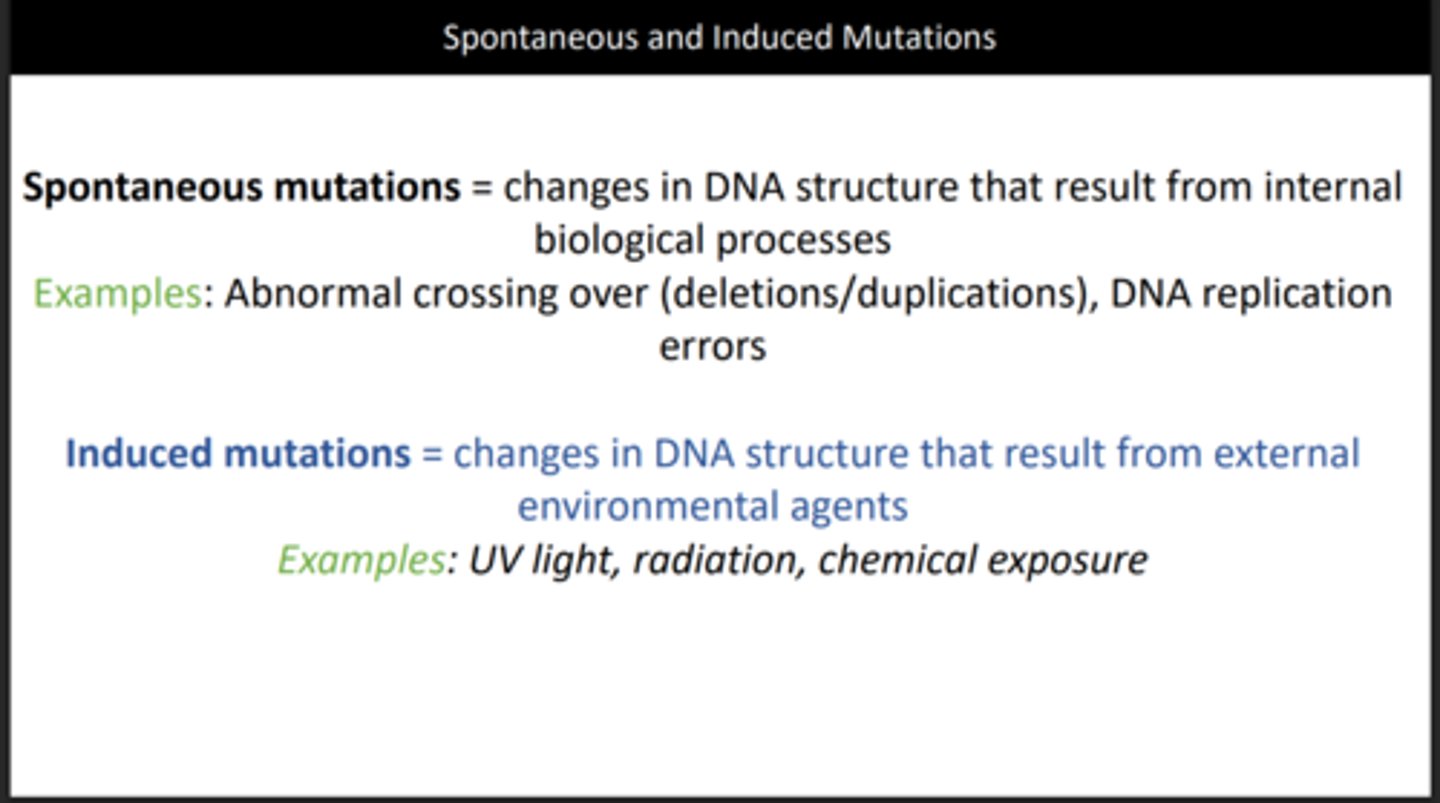
Spontaneous vs induced mutation
Spontaneous mutations - Naturally occurring mutations
Induced mutation - Mutations caused by chemicals or radiation
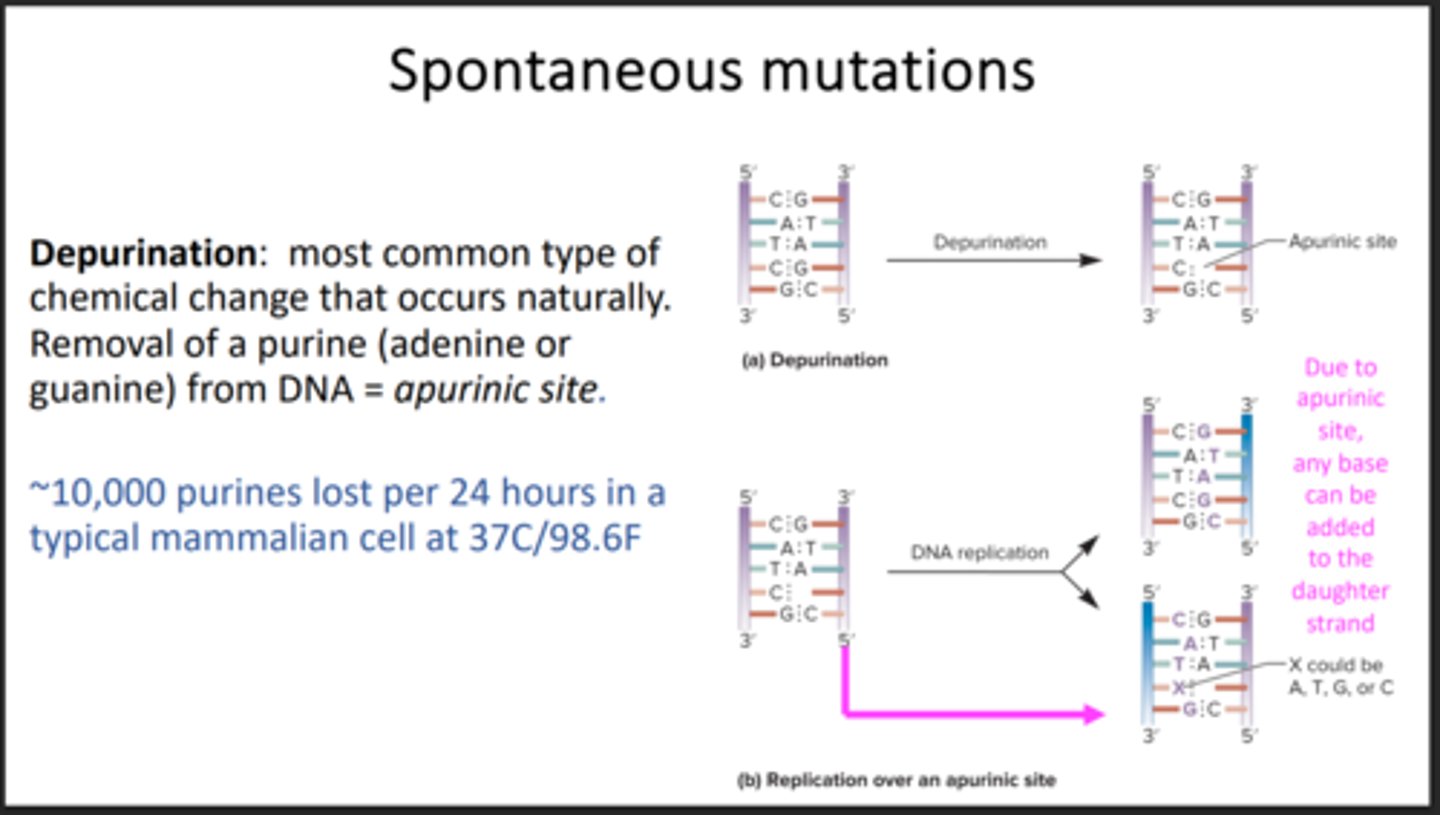
Depurination
Losing an Adenine or Guanine
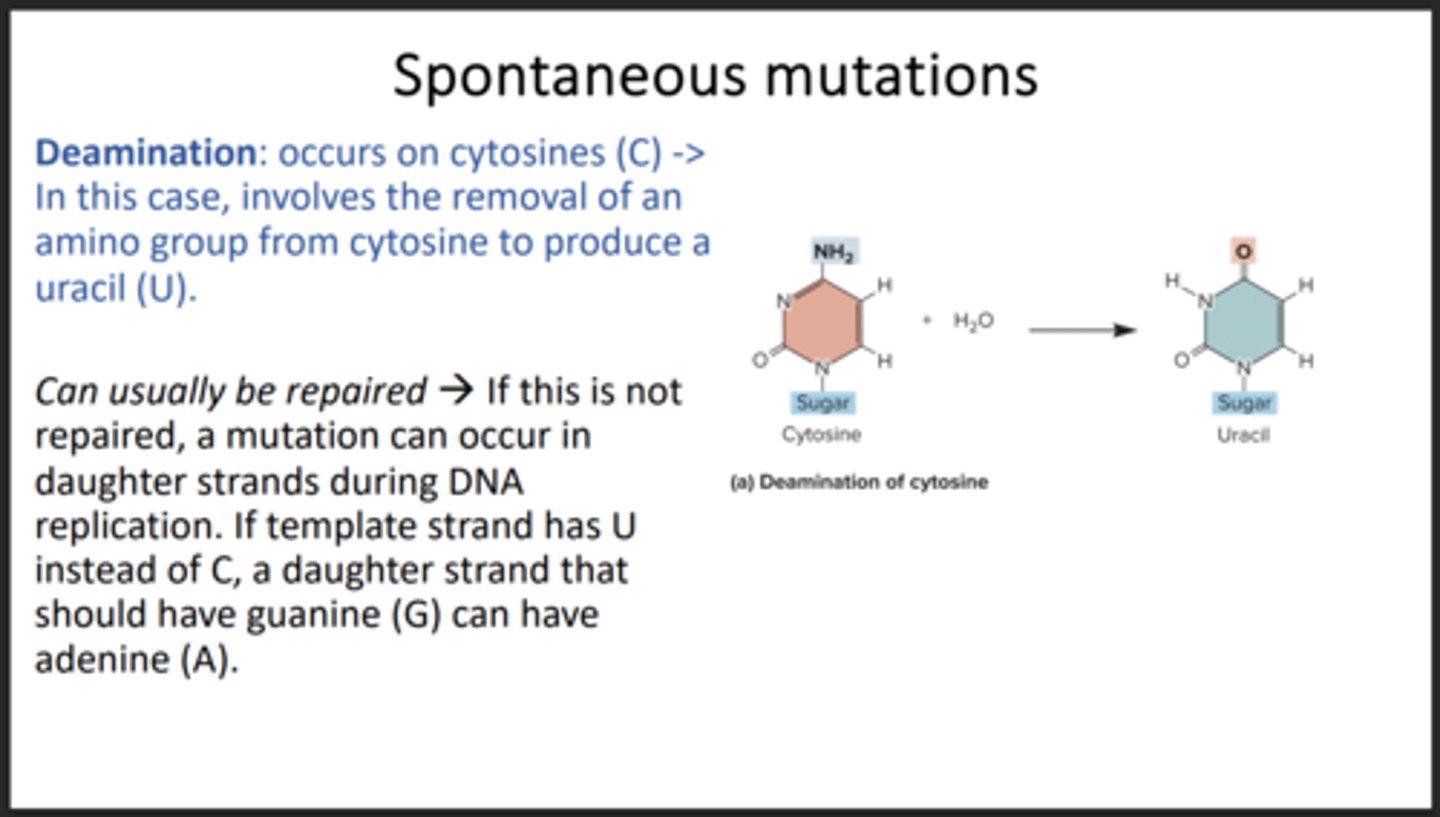
Deamination
Changing a C to a U
Trinucleotide repeat expansion (TNRE)
The expansion of repeating sequences, worsens in subsequent generations due to repeat of expansions
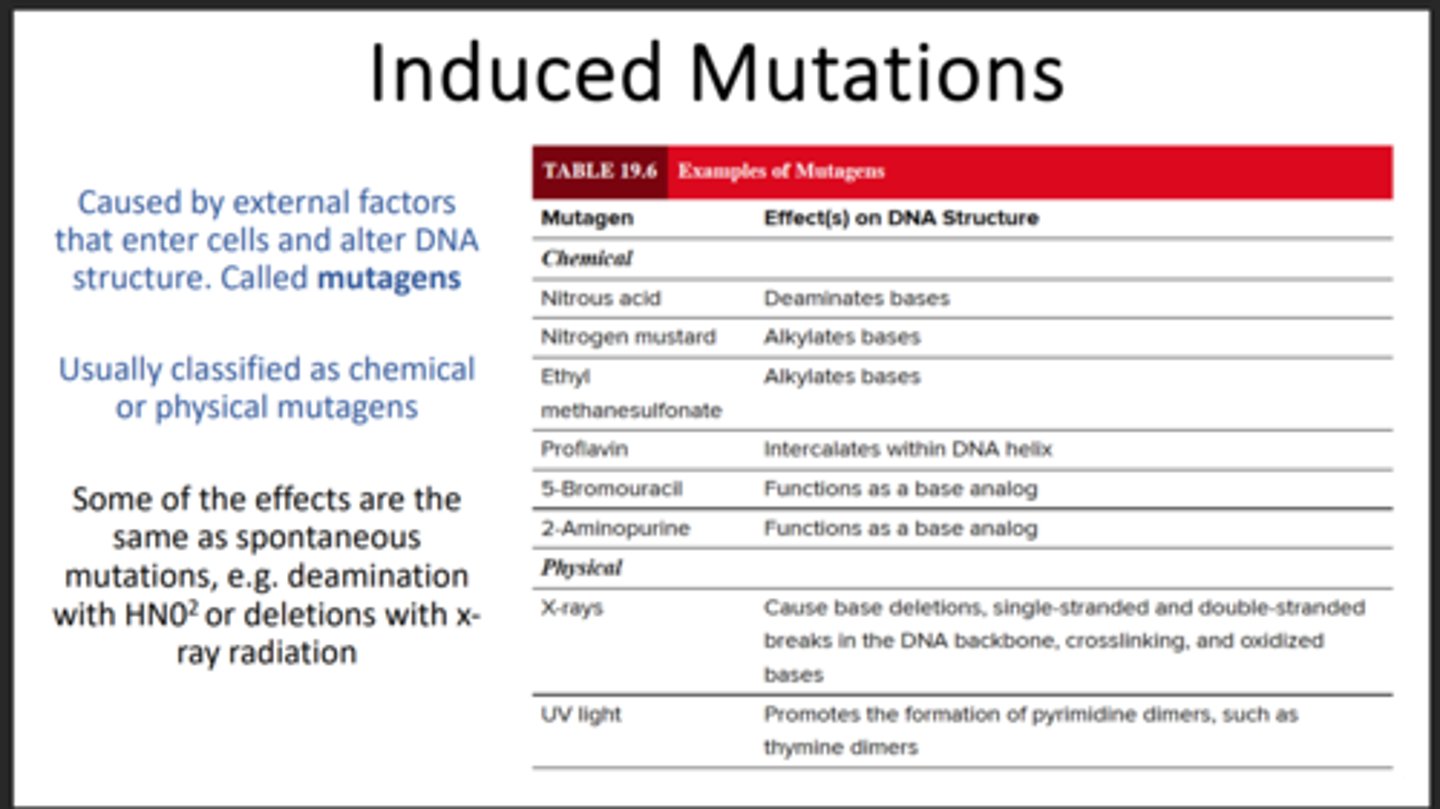
Mutagens
External agents causing induced mutations
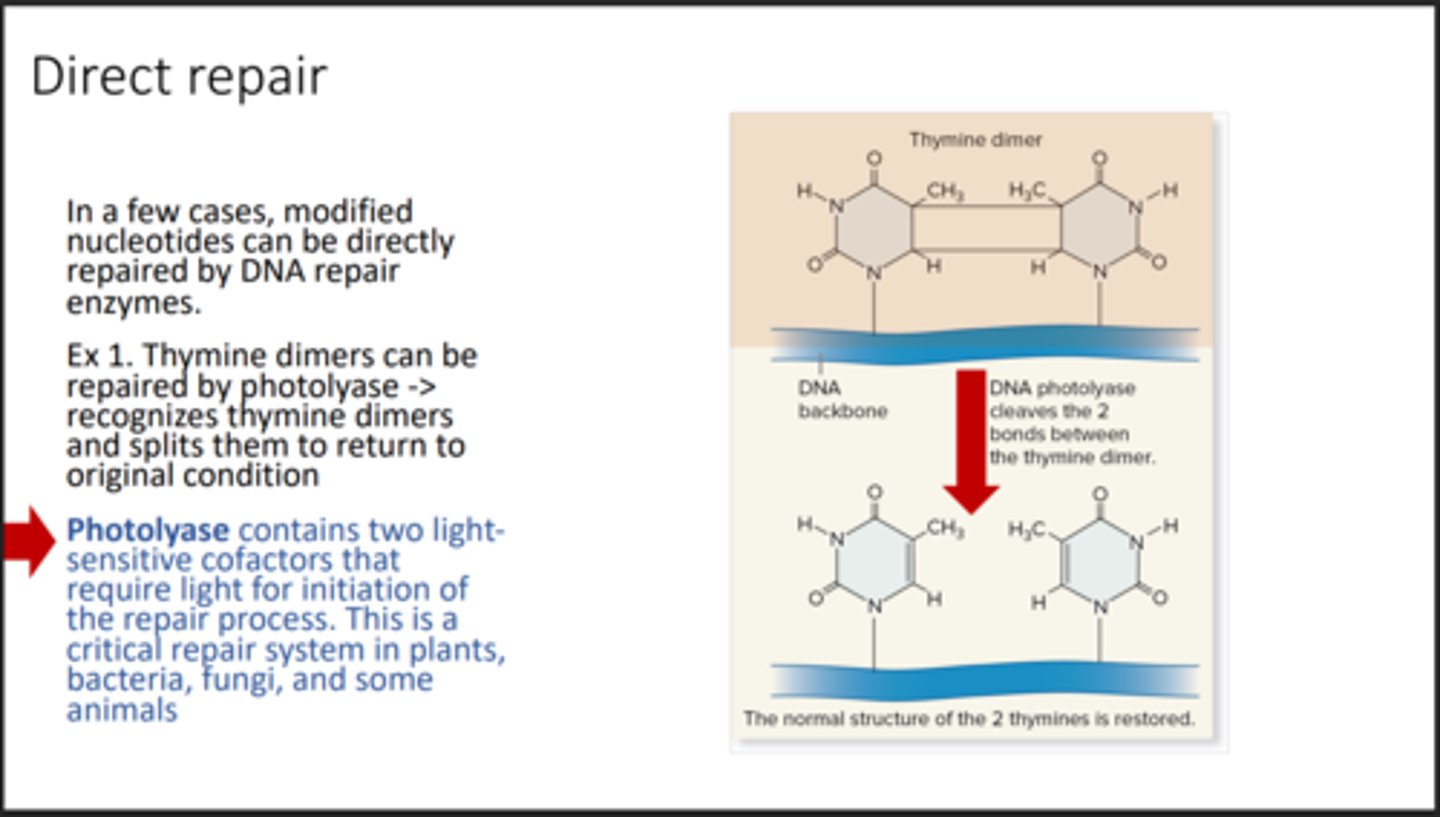
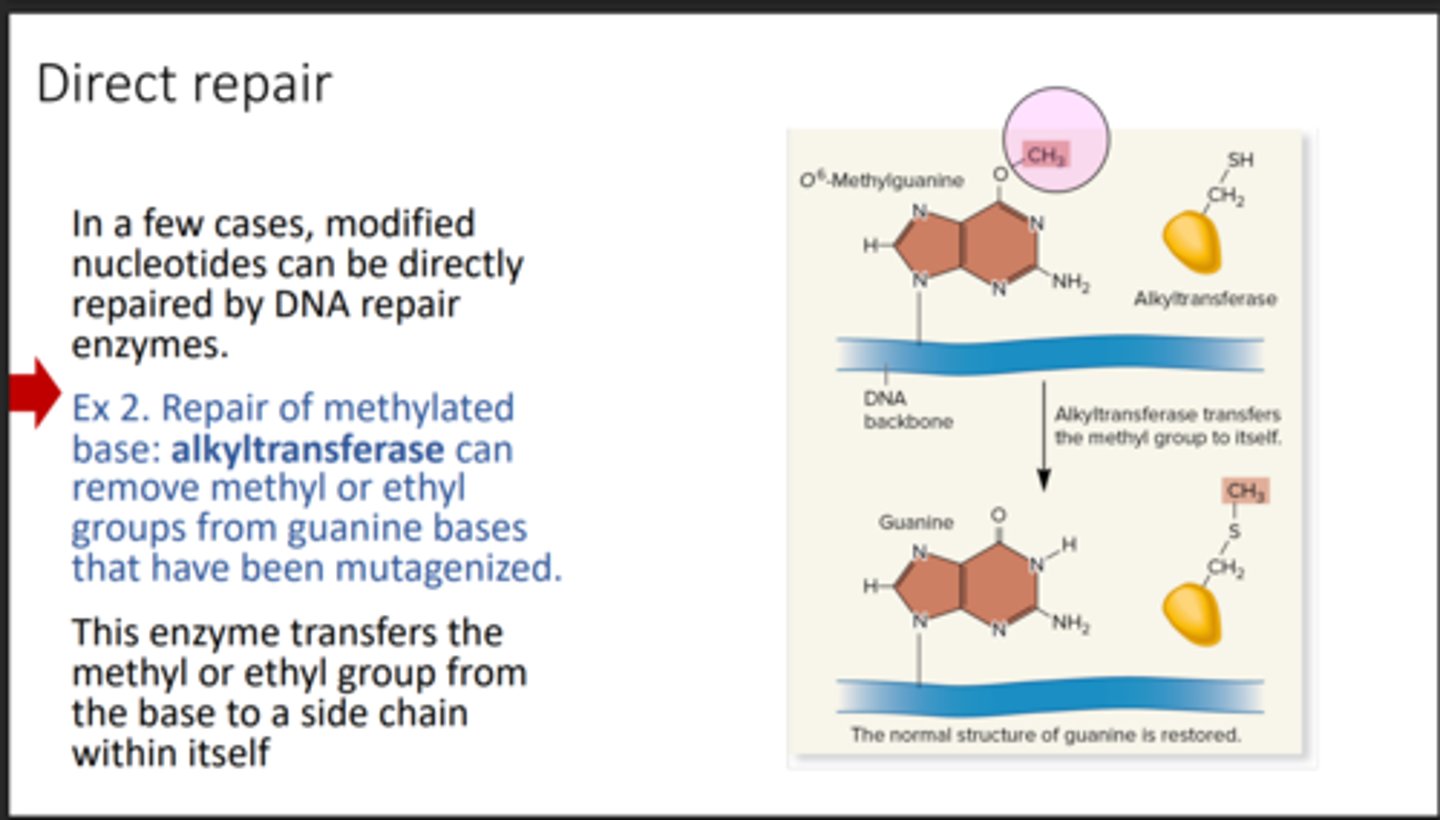
Direct repair
Fixes damaged DNA directly
Alkyltransferase
Removes methyl or ethyl groups from DNA
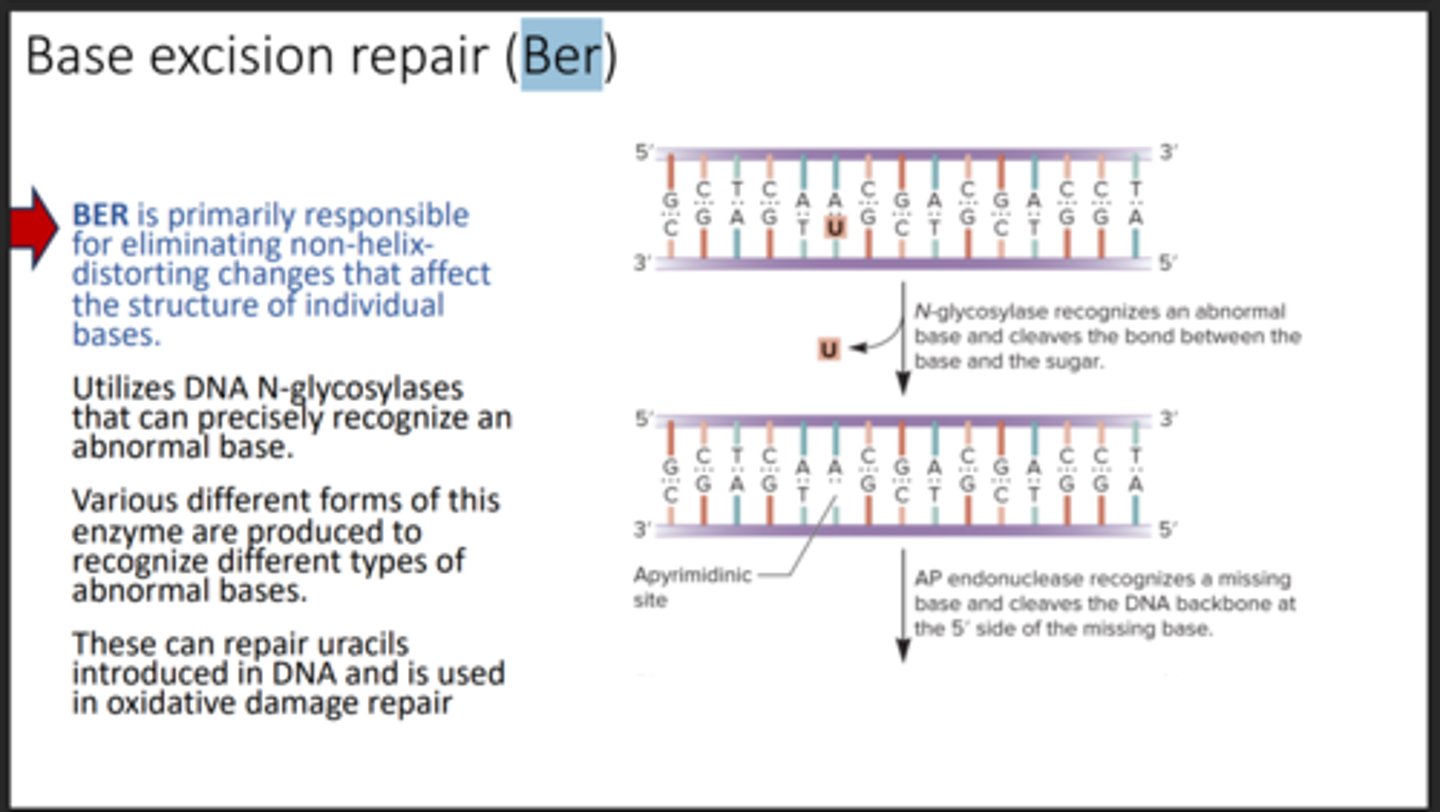
Base excision repair (BER)
Removes altered bases and repairs the site.
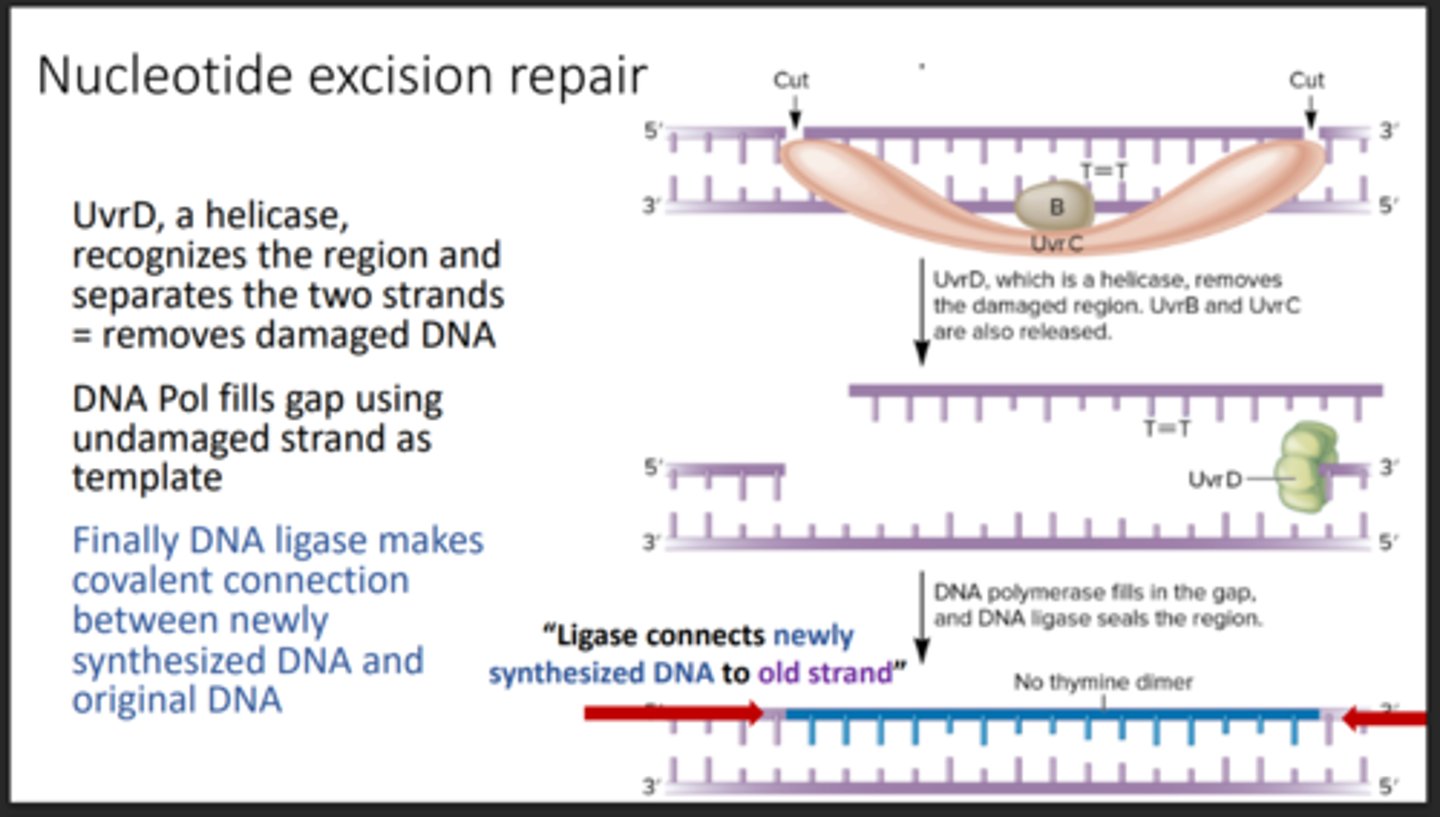
Nucleotide excision repair (NER)
Removes and replaces damaged DNA segments
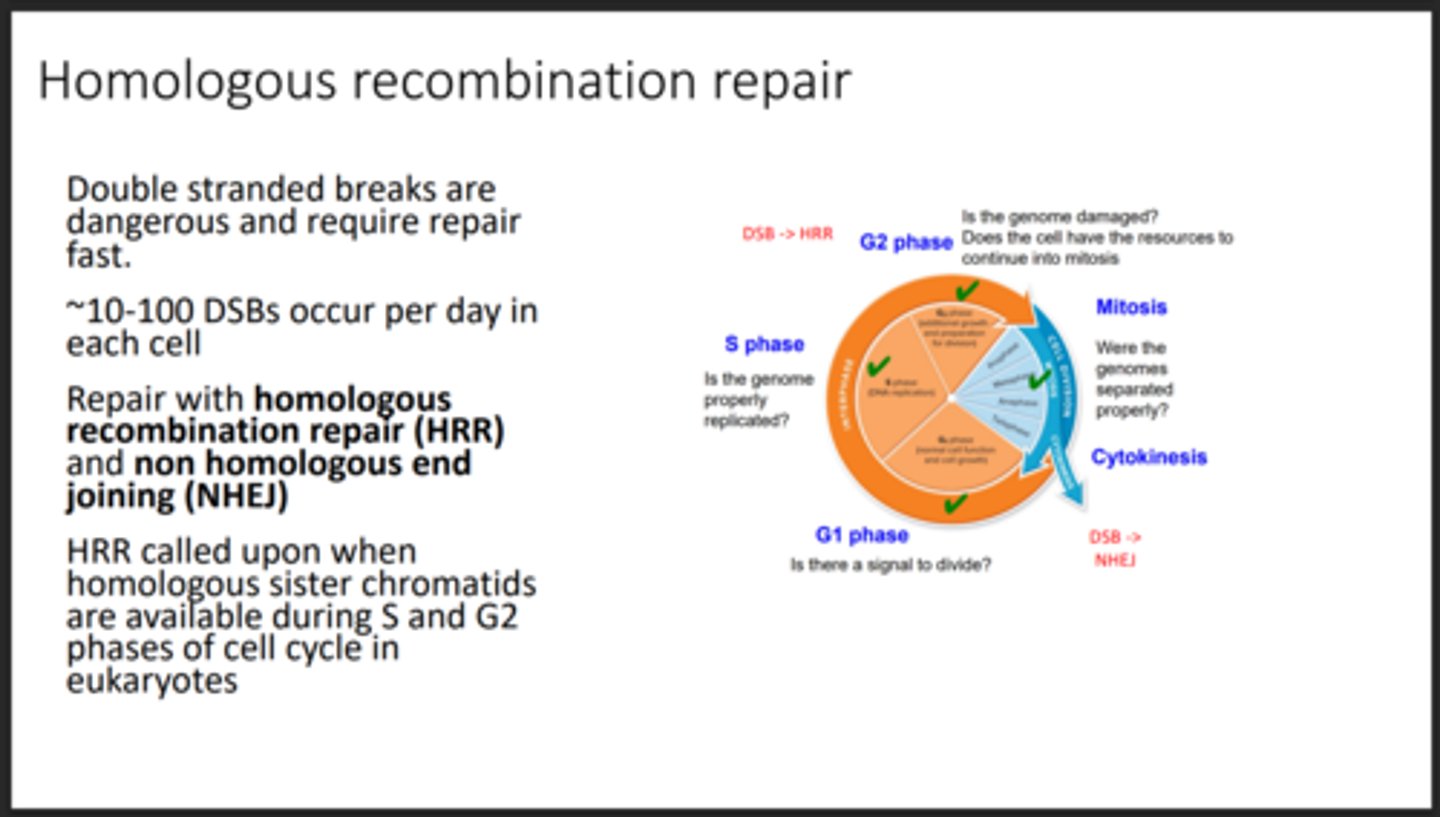
Homologous recombination repair
Repairs double-strand breaks accurately using homologous chromosomes
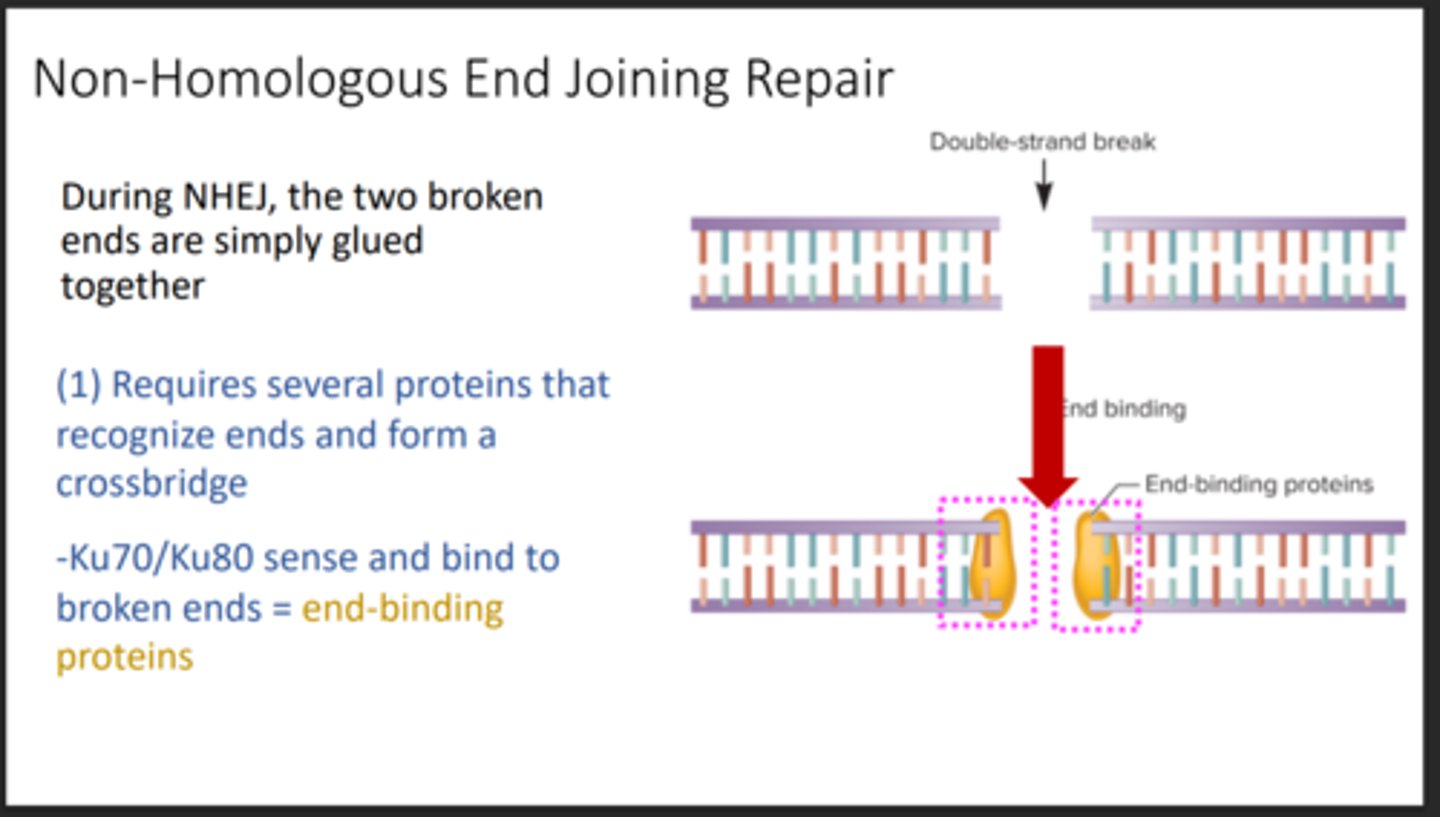
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)
Repairs double-strand breaks by directly joining broken ends
How often do Double Strand Breaks occur
Very common, occurs multiple times per day (10-100)