Lecture 14/15 - Measurement and interpretation of the leukogram
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the white blood cell concentration?
Measurement of nucleated cells per volume of blood
How can WBC be calculated?
-Manual count (hemocytometer)
-Automated count
-Estimated from blood smear
What are the common sources of error with an automated WBC?
-Leukocyte clumping
-Leukocyte lysis (usually due to age)
-Large or clumped platelets
-Cellular debris
-nRBCs
Why would a blood smear be used to determine WBC?
-Verifies accuracy of automated count
-WBC = (average WBC)(objective power2)
How is the absolute cell count calculated?
Multiply differential count (in %) by WBC
Which is more important when looking at a manual WBC: absolute cell counts or relative percentages?
Absolute cell counts
What is a leukocytosis?
Increased WBC
What is a leukopenia?
Decreased WBC
What is a neutrophilia
Increased absolute neutrophil count
What is a neutropenia
Decreased absolute neutrophil count
What is a left shift
Presence of immature neutrophils (usually bands)
What is a lymphocytosis
Increased absolute lymphocyte count
What is a lymphopenia
Decreased absolute lymphocyte count
What is a monocytosis
Increase in absolute monocyte count
What is a monocytopenia
Decrease in absolute monocyte count
What is a eosinophilia/basophilia
Increase in absolute eosinophil/basophil count
What is a eosinopenia/basopenia
Decrease in absolute eosinophil/basophil count
What are 6 common leukogram patterns that may be observed?
Stress (glucocorticoid)
Adrenaline/excitement
Antigenic stimulation
Inflammation
Granulocytic hypoplasia
Neoplasia (leukemia)
Which leukogram pattern is commonly found in clinically ill animals?
Stress leukogram
What is the cause of a stress leukogram?
-Glucocorticoids (cortisol-mediated shifts)
-Chronic and sustained stress
When is something considered moderate vs mild?
Moderate if levels are 2x or higher/lower than upper reference level
What are the common changes in WBC types that you will see with a stress leukogram? Which one is the number one sign?
-Mild to moderate leukocytosis
-Neutrophilia (shift from marginating to circulating pool)
-Lymphopenia - #1 sign
-± monocytosis (mild)
-± eosinopenia
What is the cause of an adrenaline/excitement leukogram?
-Epinephrine mediated shifts
-Immediate
What are the common changes in WBC cells that you will see with an adrenaline/excitement leukogram?
-Leukocytosis (mild to moderate)
-Neutrophilia (rapid shift from marginating to circulating)
-Lymphocytosis (splenic contraction)
-± Monocytosis
What species are excitement leukograms most common in?
Cats and young horses
What is the cause of an antigenic stimulation in a leukogram?
Chronic immune stimulation or cytokine production
What are the general features of acute inflammation?
-Neutrophilia
-Left shift
-Toxic change to neutrophils
-± Monocytosis (same pregenitor cell as neutrophils/increased macrophage demand)
What occurs with overwhelming/uncompensated acute inflammation?
Neutropenia with a left shift
What are the key features of severe inflammation with WBCs?
-Neutrophilia (>50-100K/uL)
-Leukemoid response
What are the causes of severe inflammation causing a neutrophilia?
-Pancreatitis
-Peritonitis
-Pneumonia
-IMHA
-Other causes of severe localized/systemic inflammation
What is the leukemoid response? What do you need to check?
-Strong leukocytosis that needs to be differentiated from neoplasia
-Check blood smear for blast cells/other neoplastic chages
What is a regenerative left shift? What is the key sign?
-Bone marrow is responding appropriately
-Segmented neutrophils outnumbers bands
What is a degenerative left shift? What is the key sign?
-Bone marrow is overwhelmed by inflammatory response
-Band neutrophils outnumber segmented neutrophils OR left shift with a neutropenia
What is the species difference with acute inflammation?
Cattle have small neutrophil storage - usually manifests as neutropenia in early stages followed by rebound neutrophilia
What WBC changes are common with chronic inflammation?
-Rebound neutrophilia ± left shift
-± monocytosis (same progenitor cells)
How can you diagnose chronic inflammation?
Need serial data - may look similar to acute inflammation with no other information
How long does the rebound response generally take?
3-5 days
What is granulocytic hypoplasia?
Decreased bone marrow production of neutrophils
What are some causes of granulocytic hypoplasia?
-Immune-mediated destruction
-Chemotherapy/drugs/toxins
-Bone marrow diseases
-Cyclic neutropenia (grey collies)
What WBC findings will you see with granulocytic hypoplasia?
Persistent and progressive neutropenia with NO left shift
What is acute leukemia? What is the outcome?
-Neoplastic transformation of hematopoietic precursors
-Rapid clinical course with poor prognosis
What are the key signs of acute leukemia?
-Immature/blast cells with prominent nucleoli
-Mitotic capability
-Marked leukocytosis (>50-100k)
What is chronic leukemia? What are the common signs? Which cell type is most commonly involved?
-Disease of accumulation - mutations over time allow for prolonged survival and avoidance of apoptosis
-Usually will see no overt clinical signs
-Usually lymphoid but can be any leukocyte
What is the difference between acute and chronic leukemia?
Acute involves immature cell types while chronic involves mature cell types
What are the common causes of an eosinophilia?
-Parasitic (usually GI parasites)
-Hypersensitivity responses
-Paraneoplastic diseases (IL-5 producing tumors)
What is the clinical significance of an eosinopenia?
-Not clinically significant
-May be a component of stress leukogram
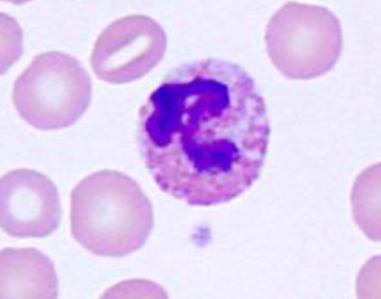
What cell type is this? What species is it commonly found in?
-Heterophils
-Found in rabbits, guinea pigs, gerbils, elephants, etc
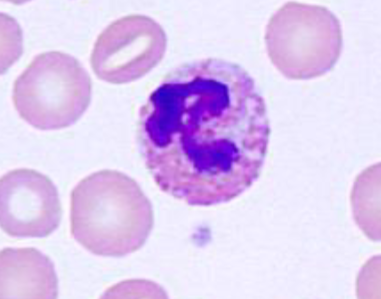
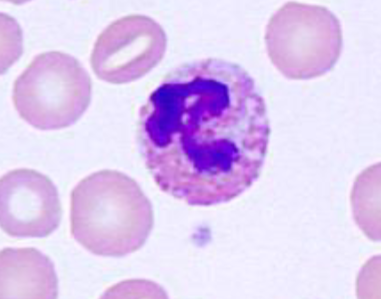
What are heterophils?
-Functionally equivalent to neutrophils
-Contain rod-shaped pink cytoplasmic granules (do not confuse with eosinophils)
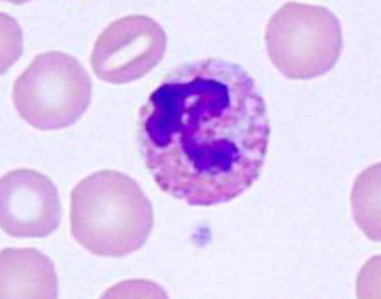
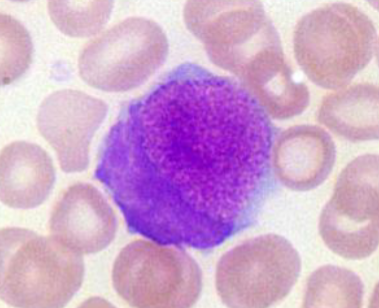
What cell type is this? What species is it found in?
-Foa-Kurloff cells
-Found in guinea pigs and capybaras
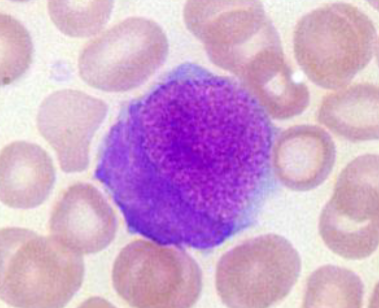
What are species differences with WBC in birds and reptiles?
-Heterophils
-Azurophils (reptiles)
-Nucleated RBCs
-Nucleated thrombocytes
-Leukocyte morphology is highly variable between species