AQA A level Chemistry 3.2.2 Group 2
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is the trend in atomic radius down Group 2, and why? (4)
- Atomic radius increases.
- The number of principal energy levels increases.
- There is more shielding.
- Weaker attraction between the nucleus and outer electrons.
What is the trend in first ionisation energy down Group 2, and why? (3)
- First ionisation energy decreases.
- The number of principal energy levels increases, causing more shielding.
- Weaker attraction between the nucleus and the outer electron.
What is the trend in melting point down Group 2, and why? (3)
- Melting point decreases.
- The size of the atom/ion increases.
- Weaker electrostatic attraction between positive ions and delocalised electrons.
What happens when Group 2 elements react with water? (2)
The metal atom loses electrons and becomes a metal 2+ ion
Why does reactivity increase down Group 2? (3)
- Atoms become larger.
- The distance between the nucleus and outer electron increases.
- There is more shielding
How does the reactivity of Group 2 elements with water change down the group? (2)
- Reactivity increases
- The reaction becomes more vigorous
What is the reaction of magnesium with liquid water? (2)
- Mg (s) + 2H₂O (l) → Mg(OH)₂ (s) + H₂ (g)
- Very slow reaction
What is the reaction of magnesium with steam? (2)
- Mg (s) + H₂O (g) → MgO (s) + H₂ (g)
- Very fast reaction
What is the reaction of calcium with water? (2)
Ca (s) + 2H₂O (l) → Ca(OH)₂ (s) + H₂ (g)
What is the reaction of strontium with water? (2)
Sr (s) + 2H₂O (l) → Sr(OH)₂ (aq) + H₂ (g)
What is the reaction of barium with water? (2)
Ba (s) + 2H₂O (l) → Ba(OH)₂ (aq) + H₂ (g)
Sketch and label a diagram of the apparatus that will be used for the reaction of magnesium with steam (5)
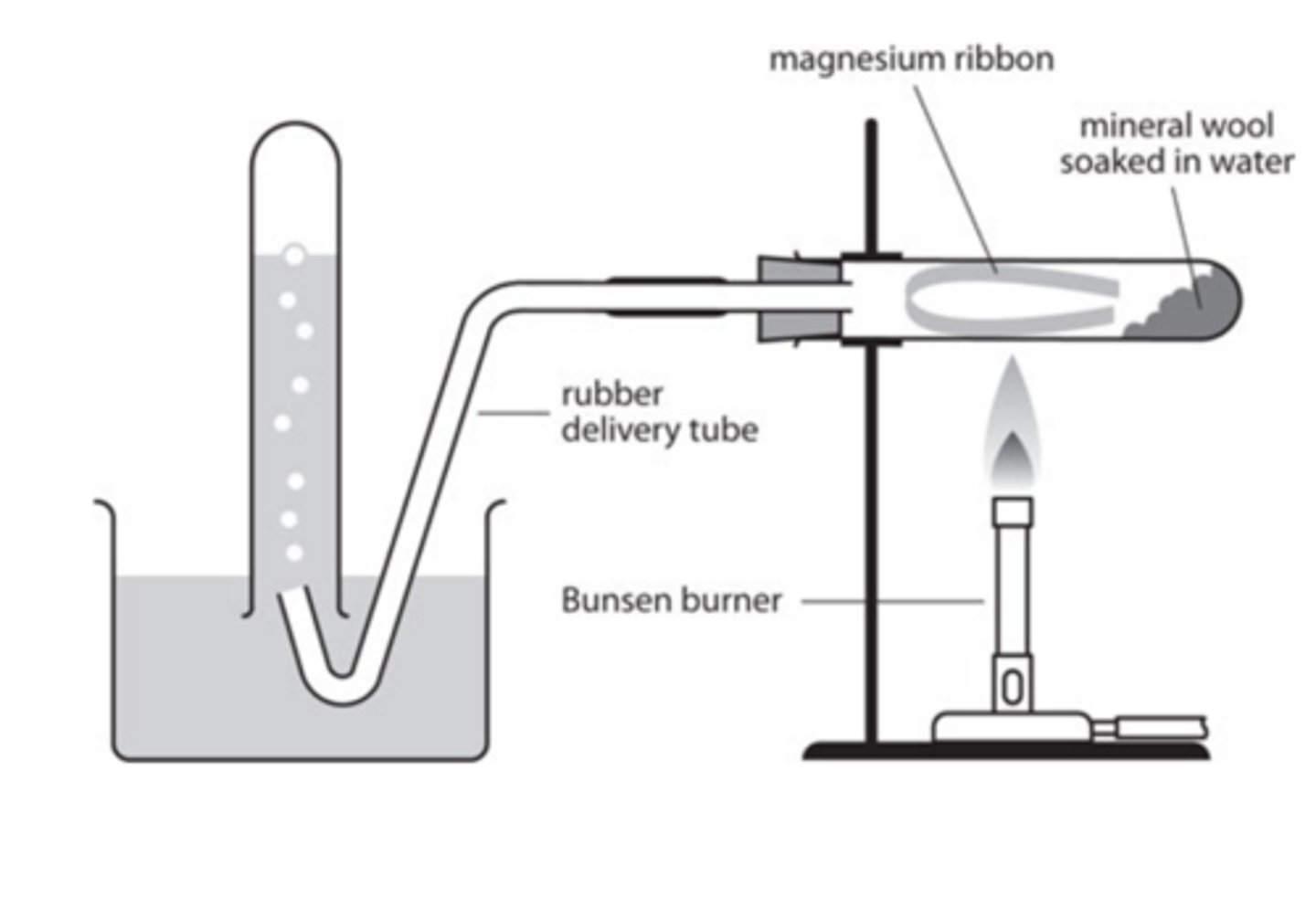
What is the least soluble group 2 hydroxide? (1)
Mg(OH)2 (basically insoluble)
What is the most soluble group 2 hydroxide? (1)
Ba(OH)2
What happens to the solubility of group II hydroxides in water down the group? (1)
Solubility in water increases down the group
What happens to the pH of group II hydroxides as a base down the group? (1)
The pH increases down the group because there are more hydroxide ions in the solution.
What is observed when sodium hydroxide is added to magnesium chloride? (2)
- White ppt
- Because magnesium hydroxide is insoluble in water
Write the ionic equation for the reaction between magnesium chloride and sodium hydroxide. (2)
Mg2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) → Mg(OH)2(s)
What is observed when sodium hydroxide is added to barium chloride? (1)
No precipitate is seen because barium hydroxide is soluble in water
What is the test for hydroxide ions? (2)
- Magnesium chloride solution is added to a solution containing hydroxide ions
- A white precipitate of Mg(OH)₂ is formed
What is the test for magnesium ions? (2)
- Sodium hydroxide solution is added to a solution containing magnesium ions
- A white precipitate of Mg(OH)₂ is formed
What is the most soluble group 2 sulfate? (1)
MgSO4
What is the least soluble group 2 sulfate? (1)
BaSO4 (insoluble)
What happens to the solubility of group II sulfates in water down the group? (1)
Decreases down the group
How do you test for sulfate ions? (2)
- Add acidified barium chloride solution to a solution containing sulfate ions
- A white precipitate of BaSO₄ is formed
How do you test for barium ions? (2)
- Add sulfuric acid to a solution containing barium ions.
- A white precipitate of BaSO₄ is formed
Why must an unknown solution be acidified with HCl or HNO₃ before testing for barium ions? (2)
Acidification removes carbonate ions that could interfere with the test
Why is H₂SO₄ not used to acidify the solution before testing for barium ions? (2)
- H₂SO₄ contains sulfate ions
- Which would form a white precipitate and interfere with the test
What are the two reactions for the extraction of titanium by magnesium? (2)
- TiO₂(s) + 2Cl₂(g) + 2C(s) → TiCl₄(g) + 2CO(g)
- TiCl₄(g) + 2Mg(l) → Ti(s) + 2MgCl₂(l)
What is the condition needed for the extraction of titanium by magnesium? (1)
Very high temperatures (600-900°C)
What is the use of Ca(OH)₂ in agriculture? (1)
Ca(OH)₂ is used to neutralise acidic soils
What is the ionic equation for Ca(OH)₂ neutralising acids? (2)
H⁺ + OH⁻ → H₂O
What is Mg(OH)₂ used for in medicine? (2)
- Known as 'milk of magnesia'
- Used to neutralise stomach acid (HCl) and treat indigestion.
What are the uses of CaO and CaCO₃ in flue gas desulfurisation? (3)
- CaO and CaCO₃ are used to neutralise SO2
- Which can cause acid rain
- Thus preventing its emission
Why can CaCO₃ not be used to treat indigestion? (1)
It produces CO₂ gas
What is the equation for CaO neutralising SO₂? (1)
CaO + SO₂ → CaSO₃
What is BaSO₄ used for in diagnostic medicine? (2)
- Used as a barium meal before x-rays or CT scans
- To identify damaged or diseased areas of the digestive tract
Why is BaSO₄ safe to use despite barium being toxic? (2)
BaSO₄ is safe because it is insoluble