Funds Exam 2
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Florence Nightingale EF: Temp
Infants and elderly need warmer rooms to maintain their body temperature and health.
Florence Nightingale EF: Ventilation
Supplying continuous fresh air
Florence Nightingale EF: Lighting
Should be bright enough to see and perform tasks but soft enough to not cause strain
Florence Nightingale EF: Humidity
Maintaining moisture to maintain respiratory passages
Florence Nightingale EF: Noise and odor
Noise should be minimized and odors eliminated for better comfort
Florence Nightingale EF: Interior design and Neatness
Keeping a clean softer room allows patients to feel more “at home”
What are Florence Nightingale’s Environmental factors
Temp, ventilation and humidity, lighting, odor control, noise control, interior design, and privacy
What populations are more sensitive to temperature changes and why
Infants, thermoregulation has not ben developed. The elderly loose subcutaneous fat and skin becomes thin making thermoregulation difficult.
What is the safest stance for lifting and transferring patient?
Wide base of legs, shoulder width apart
You should move patients in the direction away from your body
False, keeping patient closer to the body is safest and allows more control
When lifting, how should you bend down/up?
Bend at the knees, not at the hips
It is important to have the bed at what setting before beginning movement with a patient?
Bed and/or chair must be in locked position
How should you move patients with weakness on one side?
Always move them towards their stronger side for better support.
What is hemoglobin?
Oxygen carrying blood cells
Hematocrit
Non oxygen carrying blood cells measured as a percentage of total blood volume.
Suction settings range
80-120
6 Rights of medication administration
Right patient, route, medication, dose, time, documentation
6 PATIENT Rights of medication administration
Right education, to refuse, assessment, response, and evaluation
Patient identifiers
DOB, wristband, name, and medical record number
Scheduled and routine medication orders
Medications with frequency and timing
Stat or one time medication orders
Medications given immediately as prescribed or a single dose administered at a specific time for a particular condition
What oral medications can never be crushed?
Sublingual, coated, extended release and sustained release
Oral medication routes
Sublingual, feeding tubes, buccal, and oral administration.
Topical forms of medications
Patch, cream, suppository, ear/eye drops, and inhalant
Trophic level of medication
Lowest concentration in the body
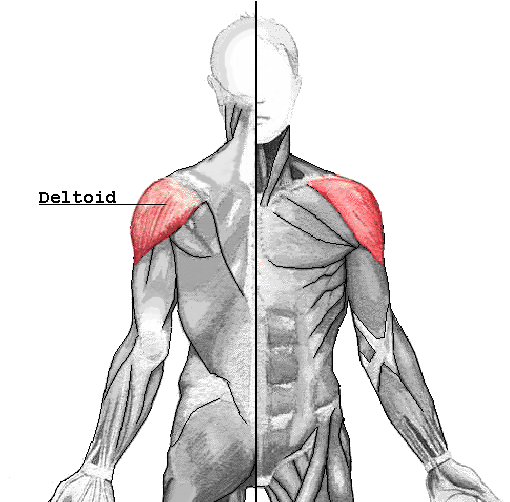
IM Sites: Deltod
Upper arm, shoulder
IM Sites: Dorsolateral
Upper thigh, lateral gluteal area
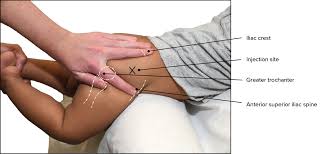
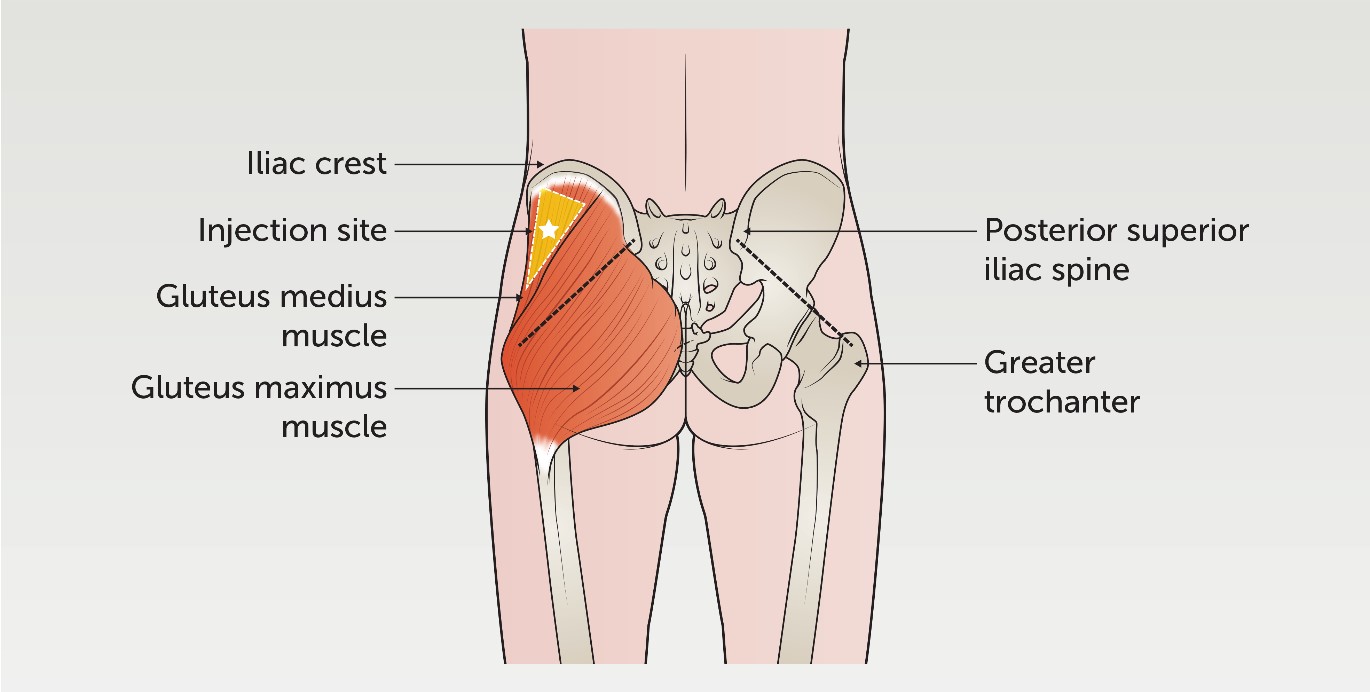
IM Sites: Ventrogluteal
On the hip
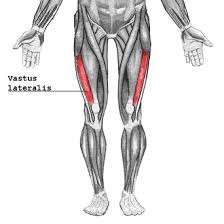
IM Sites: Vastus Lateralis
Outer thigh
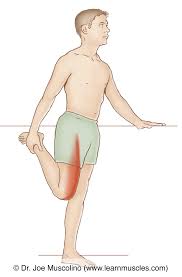
IM Sites: Rectus Femorus
Front of the thigh
Schedule I Drugs
Illegal drugs not intended for medical use with high probability of abuse
Schedule II Drugs
Drugs that have some medical use but also have a high potential for abuse
Schedule III Drugs
Drugs with accepted medical use and lower potential for abuse
Schedule IV Drugs
Drugs with accepted medical use and a lower potential for abuse compared to Schedule III.
Schedule V Drugs
Accepted medical uses with minimal abuse potential.
What kind of needle do you use when drawing form a ampule?
A filter needle, prevents microscopic fragments of glass from being administered
What is a concern regarding infiltration when a catheter is shifted out of place
Medication or fluid could leak into the surrounding tissues, causing swelling, pain, or tissue damage.
Water soluble vitamins
Vitamin B complex and Vitamin C
Fat soluble vitamins
Vitamins A , D, E, and K
Function of fiber in diet
Increases bulk in the stool and aids in digestion.
Phases of Wound Healing: Inflammatory
Damaged tissue releases cytokines causing blood coagulation and inflammation due to plasma leak in surrounding tissue
Stages of Wound Healing: Proliferative
New tissue formation for wound closure and restoration of skin integrity.
Stages of Wound Healing: Remodeling
Tissue is much weaker than original tissue, and the collagen is reorganized for strength.
Primary healing/First intention
Edges of uninfected wound is stitched together
Secondary healing/Second intention
Wound left open to heal
Delayed primary closure
Wound left open to heal until ready to suture
Skin changes with age
Fat decreases, elasticity reduces, skin becomes thinner and more fragile.
Fall prevention protocol
All falls must be reported regardless if it was assisted or not. First thing to do is ensure the patient is safe and document injuries
Why is it especially important to evaluate a patient who fell without witnesses?
Patients may have trouble recalling the details of the fall or notice any injuries sustained
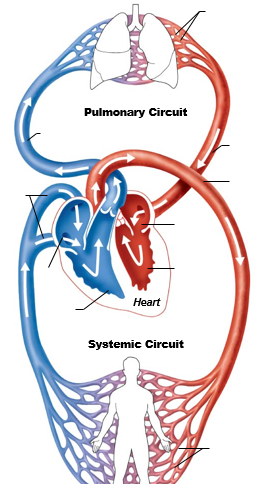
Order of blood flow of pulmonary circuit
RV → PA → Lungs → PV → Trunk
Isotonic solutions
Used to expand the fluid volume of the body, same concentration and osmolality
Hypotonic solutions
Solutions with lower concentration than blood serum, used to hydrate cells and decrease extracellular fluid volume.
Hypertonic solutions
Solutions with higher concentration than blood serum, replace electrolytes
Dextrose
A form of glucose
0.9% Saline
Isotonic
0.45% saline
Hypotonic
5% dextrose in water
Isotonic
10% dextrose in water
Hypertonic
5% dextrose in 0.9% saline
Hyper tonic
5% dextrose in 0.45% saline
Hypertonic
5% dextrose in 0.225% saline
Isotonic
Ringer’s lactate
Isotonic
5% dextrose in Ringer’s lactate
Hypertonic