asynchronous week 6 women and food breastfeeding
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
summarize why women are disproportionately affected by poverty and at a greater risk for malnutrition over their lifespan
identify WHO breastfeeding recommendations
exclusive breastfeeding up to 6 months and complementary foods with breastfeeding up to 2 years or more
on demand
begin within an hour after birth
bottles and pacifiers should be avoided
explain with examples why breast feeding in accordance with WHO recommendations is the optimal way to feed infants. How are these followed worldwide?
42% of infants are exclusively breastfed for the firsts 6 months worldwide.
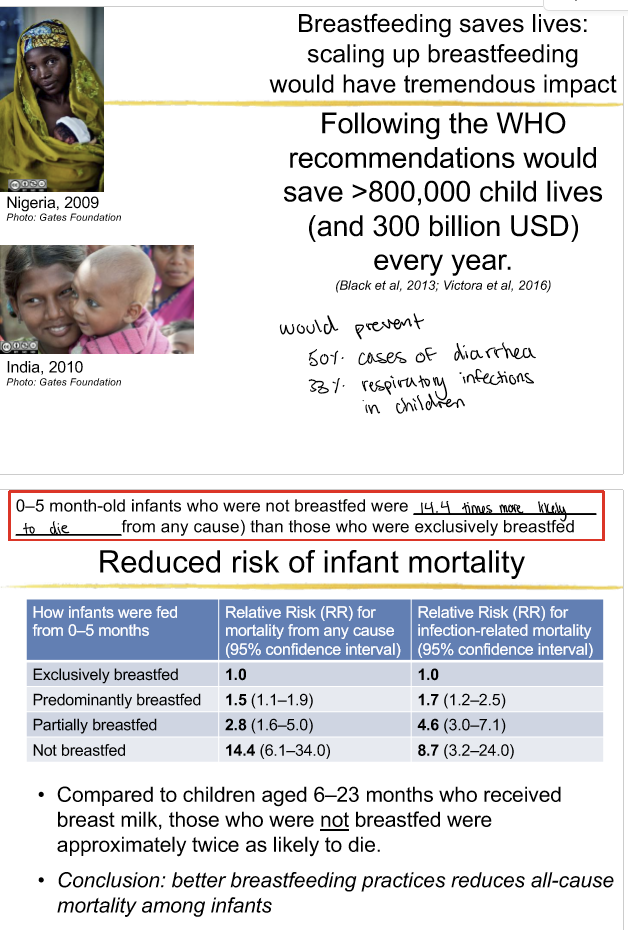
reduced risk of infant mortality, diarrhea and pneumonia are more severe in non breastfed infants
explain why foods need to be introduced to complement breast milk when an infant is 6 months old and nutritional priorities at that time
infant needs more energy and nutrients that can’t be provided only through breastfeeding
iron rich foods are priority
describe breast milk composition and how it varies
contains nutrients and bioactive factors
colostrum (concentrated, very nutritious, mild laxative)
thought to be dirty milk in roadside squatter settlements but it is in fact very healthy containing growth factors and antibodies
foremilk - watery
hindmilk - high fat

all
identify and describe strategies to promote optimal breastfeeding and myths abt breastfeeding in emergencies (natural disaster, famine)
myths: that a mother under stress or suffering from malnutrition cannot nurse
less than 10% to over 60% breastfeeding rates changed since countries experienced large scale humanitarian emergencies
cascade program (people trained to promote and support breastfeeding)
explain how and when infants can become affected with HIV through vertical transmission
when HIV+ woman transmits virus to child during pregnancy, labour, & delivery, or BREASTFEEDING
transmission risk reduced to 1% if ART drug used
summarize and justify breastfeeding recommendations for HIV + mothers
risks of other causes of death are higher than a risk of HIV infection.
if a safe alternative is available use it
commercial infant formula
safe donor breast milk
if not available: breastfeed and ARV
exclusive for 6 months
continue with complementary foods