Product Life Cycle
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is a product life cycle?
A product life cycle describes the stages a product goes through from when it was first thought of until it finally is removed from the market.
What does a product life cycle represent?
The different stages in the life of a product and the sales that are achieved at each stage.
What are the 5 main stages of a product life cycle?
Introduction
Growth
Maturity
Saturation
Decline
Diagram showing a product life cycle diagram.
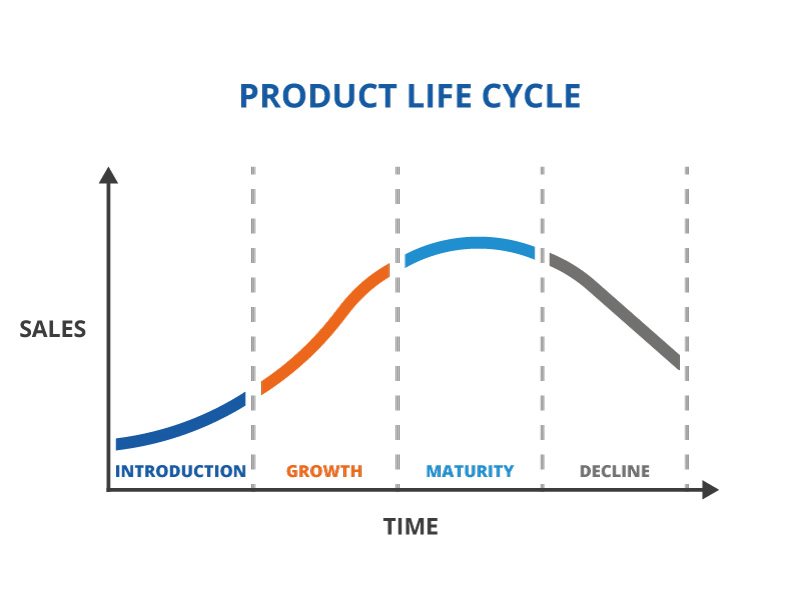
Describe the introduction stage.
The product is new to the market and few potential consumers know of its existence.
Price can be high and sales may be restricted to early adopters (those that must have new technology, gadgets or fashions first).
Profits are often low as development costs have to be repaid and advertising expenditure can often be high.
Describe the growth stage.
The product is becoming more widely known and consumed.
Advertising tries to establish or strengthen the brand and develop an image for the product.
Profits may start to be earned but advertising expenditure is still high. Prices may fall.
Describe the maturity stage.
The product range may be extended.
Competition will likely increase.
Sales are at their peak, profits should be high.
Describe the saturation stage.
Very few new customers are gained, replacement purchases are the trend.
Profits may start to decline.
Describe the decline stage.
Sales fall fast.
Product range may be reduced, with the business
concentrating on core products.
Advertising costs will be reduced.
Profits will fall.
Price is likely to fall.
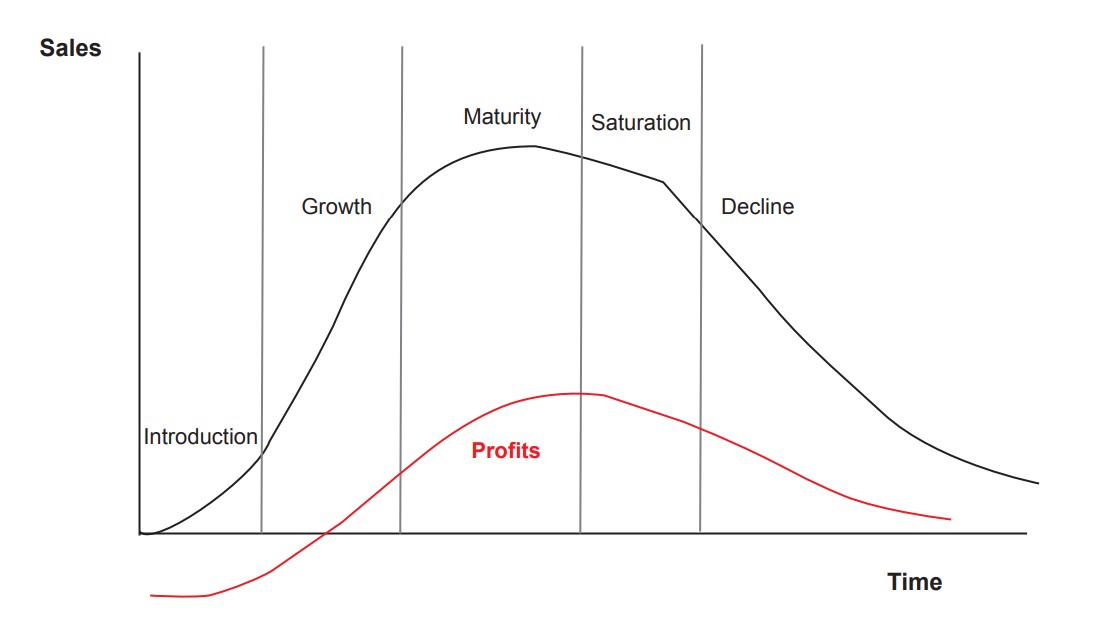
Analyse the graph showing profit plotted against a product life cycle.
Initially losses are made as research and development costs have to be recouped and advertising costs are likely to be high.
As the life cycle moves through growth into maturity, profits are made.
Profits are likely to continue to be made through to the end of the cycle, though at a lower level.
What are extension strategies?
These are methods a business may use in order to prolong / lengthen the life cycle of a product before it goes into decline.
Give some examples of extension strategies.
New packaging
Advertising – try to gain a new audience or remind the current audience.
Price reduction
Updating the product- include new features, flavours etc.
Relaunching the product, aiming at a different segment